|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang X, Yuan T, Liang M, Du M, Xia S,
Dittmar R, Wang D, See W, Costello BA, Quevedo F, et al: Exosomal
miR-1290 and miR-375 as prognostic markers in castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 67:33–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kar S, Sengupta D, Deb M, Pradhan N and
Patra SK: SOX2 function and Hedgehog signaling pathway are
co-conspirators in promoting androgen independent prostate cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:253–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parnes HL, House MG and Tangrea JA:
Prostate cancer prevention: Strategies for agent development. Curr
Opin Oncol. 25:242–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun X, Yang Z, Zhang Y, He J, Wang F, Su
P, Han J, Song Z and Fei Y: Prognostic implications of tissue and
serum levels of microRNA-128 in human prostate cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:8394–8401. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
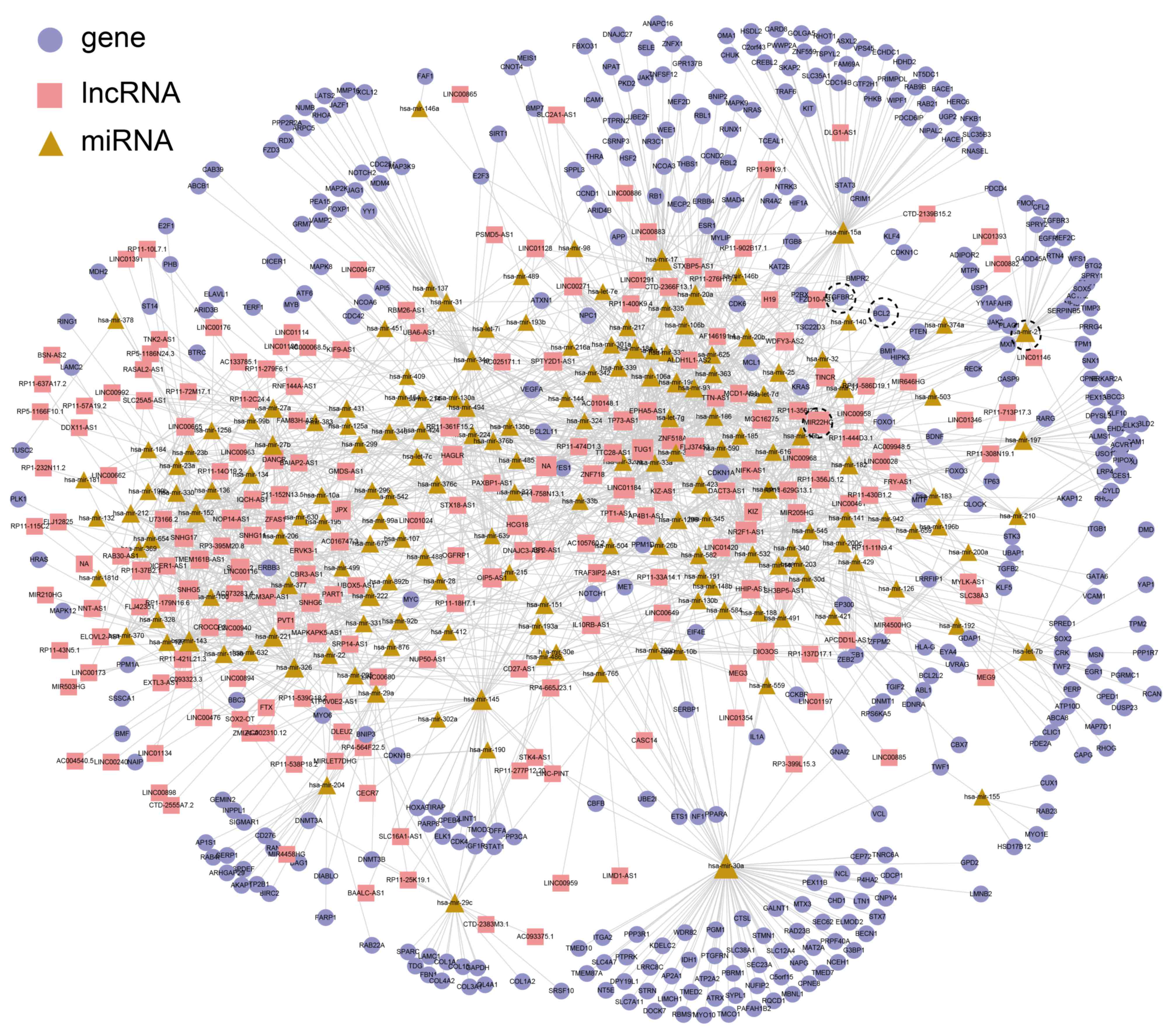
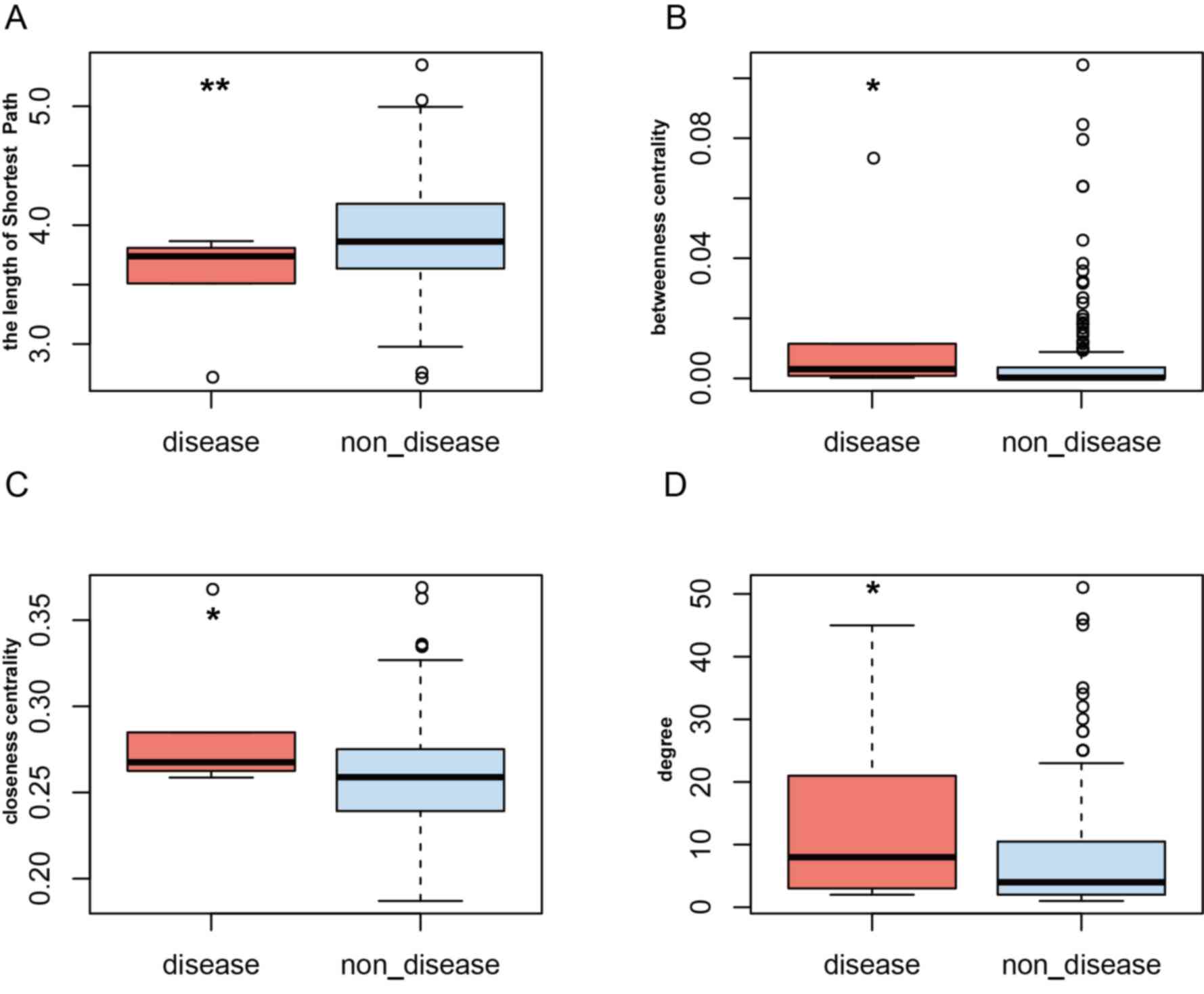
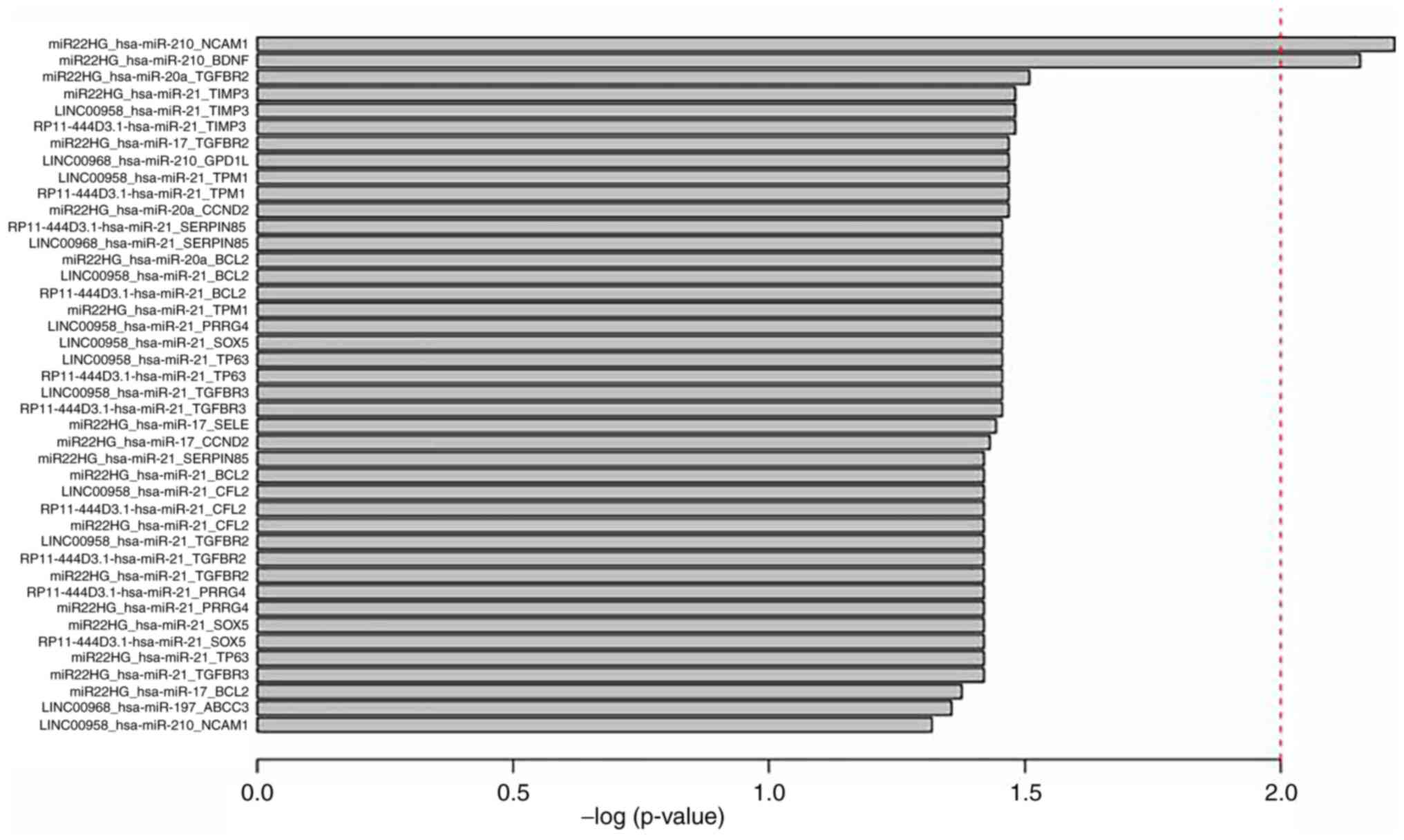
6
|
Das DK, Osborne JR, Lin HY, Park JY and
Ogunwobi OO: miR-1207-3p is a novel prognostic biomarker of
prostate cancer. Transl Oncol. 9:236–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ling CQ, Wang LN, Wang Y, Zhang YH, Yin
ZF, Wang M and Ling C: The roles of traditional Chinese medicine in
gene therapy. J Integr Med. 12:67–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perkel JM: Visiting ‘noncodarnia’.
Biotechniques. 54:301, 303–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu K, Yao H, Wen Y, Zhao H, Zhou N, Lei S
and Xiong L: Functional role of a long non-coding RNA
LIFR-AS1/miR-29a/TNFAIP3 axis in colorectal cancer resistance to
pohotodynamictherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:2871–2880. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavac M and Glavac D:
Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers.
2017:72439682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Groskopf J, Aubin SM, Deras IL, Blase A,
Bodrug S, Clark C, Brentano S, Mathis J, Pham J, Meyer T, et al:
APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: Development of a method to aid in
the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Chem. 52:1089–1095. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 34:9–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li SQ, Li F, Xiao Y, Wang CM, Tuo L, Hu J,
Yang XB, Wang JS, Shi WH, Li X and Cao XF: Comparison of long
noncoding RNAs, microRNAs and messenger RNAs involved in initiation
and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
10:652–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thum T and Condorelli G: Long noncoding
RNAs and microRNAs in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Circ Res.
116:751–762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tay Y, Karreth FA and Pandolfi PP:
Aberrant ceRNA activity drives lung cancer. Cell Res. 24:259–260.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu Y, Xiao X and Yang S: LncRNA MALAT1
acts as an oncogene in multiple myeloma through sponging miR-509-5p
to modulate FOXP1 expression. Oncotarget. 8:101984–101993. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tripathi V, Shen Z, Chakraborty A, Giri S,
Freier SM, Wu X, Zhang Y, Gorospe M, Prasanth SG, Lal A and
Prasanth KV: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 controls cell cycle
progression by regulating the expression of oncogenic transcription
factor B-MYB. PLoS Genet. 9:e10033682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang R, Guo Y, Ma Z, Ma G, Xue Q, Li F
and Liu L: Long non-coding RNA PTENP1 functions as a ceRNA to
modulate PTEN level by decoying miR-106b and miR-93 in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:26079–26089. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Samir N, Matboli M, El-Tayeb H, El-Tawdi
A, Hassan MK, Waly A, El-Akkad HAE, Ramadan MG, Al-Belkini TN,
El-Khamisy S and El-Asmar F: Competing endogenous RNA network
crosstalk reveals novel molecular markers in colorectal cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 8:6869–6881. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
An Y, Furber K and Ji S: Pseudogenes
regulate parental gene expression via ceRNA network. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:185–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu H, Wu R, Chen M, Li D, Dai J, Zhang Y,
Gao K, Yu J, Hu G, Guo Y, et al: Comprehensive analysis of
differentially expressed profiles of lncRNAs and construction of
miR-133b mediated ceRNA network in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:21095–21105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Giza DE, Vasilescu C and Calin GA:
MicroRNAs and ceRNAs: Therapeutic implications of RNA networks.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:1285–1293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell.
163:1011–1025. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue D, Lu H, Xu HY, Zhou CX and He XZ:
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 enhances the docetaxel resistance of
prostate cancer cells via miR-145-5p-mediated regulation of AKAP12.
J Cell Mol Med. 22:3223–3237. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Z, Dai J and Shen H: Systematic
analysis reveals long noncoding RNAs regulating neighboring
transcription factors in human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Basis Dis. 9:2785–2792. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin
YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, et al: miRTarBase
2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target
interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D239–D247. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL,
Maniou S, Karathanou K and Kalfakakou D: DIANA-TarBase v7.0:
Indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:
mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 43((Database Issue)):
D153–D159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42((Database Issue)): D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Reczko M, Maragkakis M, Dalamagas TM and Hatzigeorgiou
AG: DIANA-LncBase: Experimentally verified and computationally
predicted microRNA targets on long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41((Database Issue)): D239–D245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, Qiu C, Liu M, Chen
X, Zhang Q, Yan G and Cui Q: LncRNADisease: A database for
long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res.
41((Database Issue)): D983–D986. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rich JT, Neely JG, Paniello RC, Voelker
CC, Nussenbaum B and Wang EW: A practical guide to understanding
Kaplan-Meier curves. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 143:331–336. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Du Z, Sun T, Hacisuleyman E, Fei T, Wang
X, Brown M, Rinn JL, Lee MG, Chen Y, Kantoff PW and Liu XS:
Integrative analyses reveal a long noncoding RNA-mediated sponge
regulatory network in prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 7:109822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Karreth FA and Pandolfi PP: ceRNA
cross-talk in cancer: When ce-bling rivalries go awry. Cancer
Discov. 3:1113–1121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen WJ, Tang RX, He RQ, Li DY, Liang L,
Zeng JH, Hu XH, Ma J, Li SK and Chen G: Clinical roles of the
aberrantly expressed lncRNAs in lung squamous cell carcinoma: A
study based on RNA-sequencing and microarray data mining.
Oncotarget. 8:61282–61304. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li DS, Ainiwaer JL, Sheyhiding I, Zhang Z
and Zhang LW: Identification of key long non-coding RNAs as
competing endogenous RNAs for miRNA-mRNA in lung adenocarcinoma.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2285–2295. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Seitz AK, Christensen LL, Christensen E,
Faarkrog K, Ostenfeld MS, Hedegaard J, Nordentoft I, Nielsen MM,
Palmfeldt J, Thomson M, et al: Profiling of long non-coding RNAs
identifies LINC00958 and LINC01296 as candidate oncogenes in
bladder cancer. Sci Rep. 7:3952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang Y, Guo JX and Shao ZQ: miR-21 targets
and inhibits tumor suppressor gene PTEN to promote prostate cancer
cell proliferation and invasion: An experimental study. Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 10:87–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shen SJ, Zhang YH, Gu XX, Jiang SJ and Xu
LJ: Yangfei Kongliu Formula, a compound Chinese herbal medicine,
combined with cisplatin, inhibits growth of lung cancer cells
through transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway. J Integr
Med. 15:242–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brattain MG, Markowitz SD and Willson JK:
The type II transforming growth factor-beta receptor as a
tumor-suppressor gene. Curr Opin Oncol. 8:49–53. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chowdhury S, Ammanamanchi S and Howell GM:
Epigenetic targeting of transforming growth factor β receptor II
and implications for cancer therapy. Mo Cell Pharmacol. 1:57–70.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bonci D and De Maria R: miR-15/miR-16
loss, miR-21 upregulation, or deregulation of their target genes
predicts poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients. Mol Cell
Oncol. 3:e11097442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guan Y, Wu Y, Liu Y, Ni J and Nong S:
Association of microRNA-21 expression with clinicopathological
characteristics and the risk of progression in advanced prostate
cancer patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy. Prostate.
76:986–993. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mishra S, Deng JJ, Gowda PS, Rao MK, Lin
CL, Chen CL, Huang T and Sun LZ: Androgen receptor and microRNA-21
axis downregulates transforming growth factor beta receptor II
(TGFBR2) expression in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 33:4097–4106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|