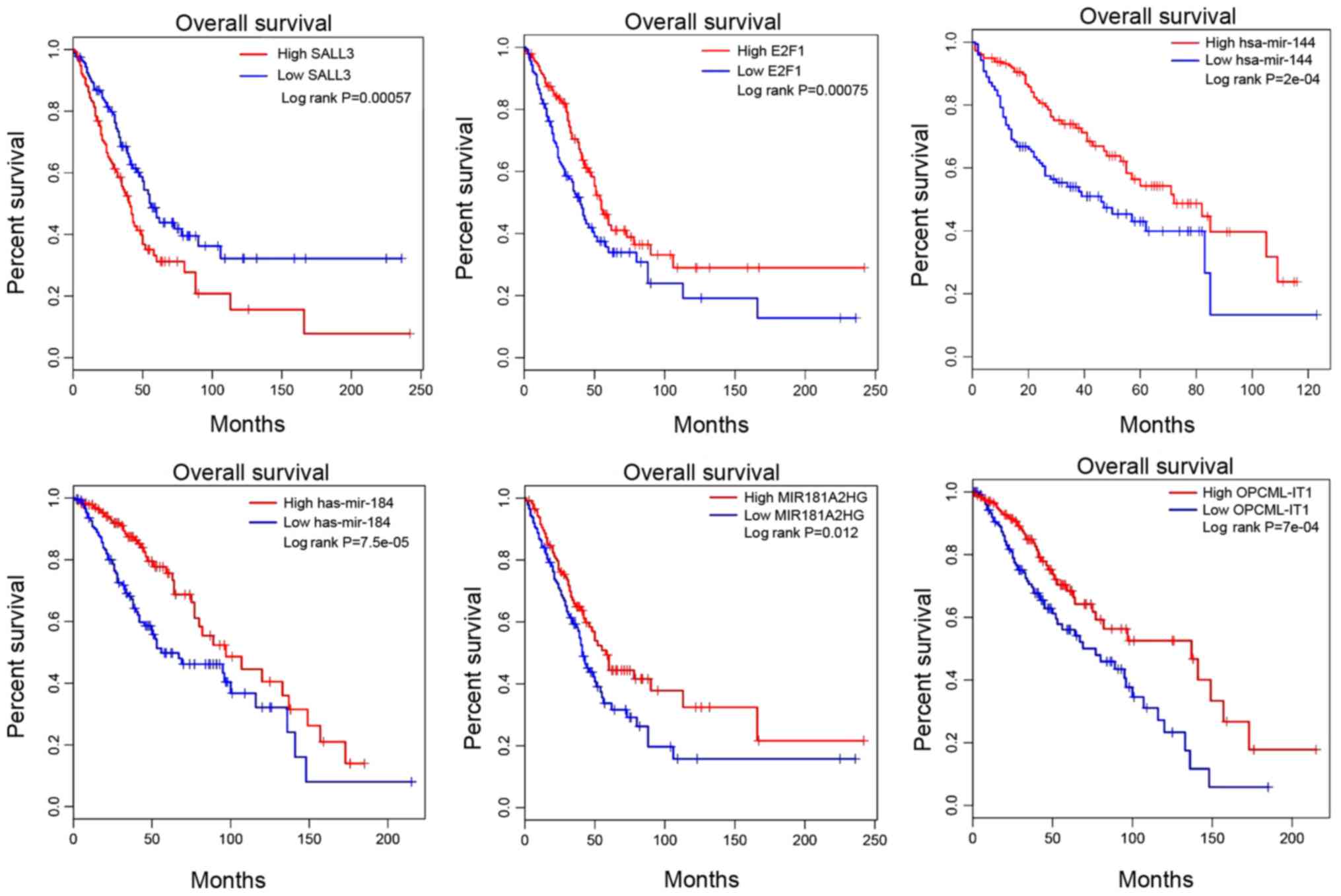
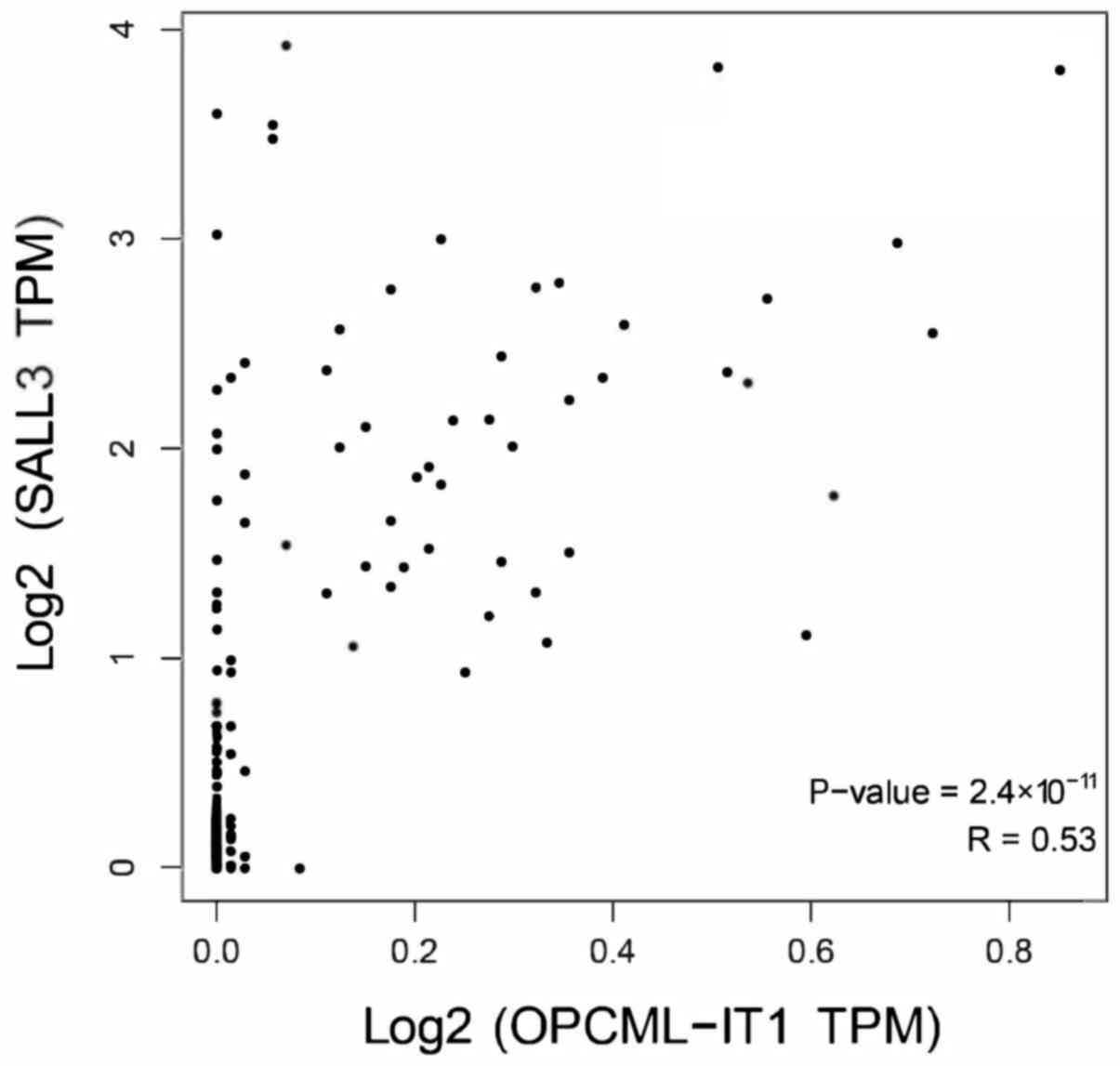
|
1
|
Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G,
Marzioni M, Andersen JB, Invernizzi P, Lind GE, Folseraas T, Forbes
SJ, Fouassier L, et al: Expert consensus document:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives
consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of
Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:261–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, DeMatteo RP, Gonen M,
Burke EC, Bodniewicz BS J, Youssef BA M, Klimstra D and Blumgart
LH: Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar
cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 234:507–519. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maithel SK, Gamblin TC, Kamel I,
Corona-Villalobos CP, Thomas M and Pawlik TM: Multidisciplinary
approaches to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer.
119:3929–3942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baltimore D: Our genome unveiled. Nature.
409:814–816. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gong Z, Zhang S, Zeng Z, Wu H, Yang Q,
Xiong F, Shi L, Yang J, Zhang W, Zhou Y, et al: LOC401317, a
p53-regulated long non-coding RNA, inhibits cell proliferation and
induces apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2.
PLoS One. 9:e1106742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang W, Huang C, Gong Z, Zhao Y, Tang K,
Li X, Fan S, Shi L, Li X, Zhang P, et al: Expression of LINC00312,
a long intergenic non-coding RNA, is negatively correlated with
tumor size but positively correlated with lymph node metastasis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Mol Histol. 44:545–554. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jeyapalan Z, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Fang L,
He C and Yang BB: Expression of CD44 3′-untranslated region
regulates endogenous microRNA functions in tumorigenesis and
angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3026–3041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B,
Haveman WJ and Pandolfi PP: A coding-independent function of gene
and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature.
465:1033–1038. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu Q, Yin J, Zeng A, Jin X, Zhang Z, Yan W
and You Y: H19 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate
EMT by sponging miR-130a-3p in glioma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
50:233–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao G, Fu Y, Su Z and Wu R: How long
non-coding RNAs and microRNAs mediate the endogenous RNA network of
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A comprehensive analysis.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:332–341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB,
Yin DD, Kong R, Xia R, Lu KH, Li JH, et al: Lnc RNA HOTAIR
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression
by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song X, Cao G, Jing L, Lin S, Wang X,
Zhang J, Wang M, Liu W and Lv C: Analysing the relationship between
lncRNA and protein-coding gene and the role of lncRNA as ceRNA in
pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 18:991–1003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu G, Yao W, Gumireddy K, Li A, Wang J,
Xiao W, Chen K, Xiao H, Li H, Tang K, et al: Pseudogene PTENP1
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to suppress clear-cell
renal cell carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:3086–3097.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xi X, Chu Y, Liu N, Wang Q, Yin Z, Lu Y
and Chen Y: Joint bioinformatics analysis of underlying potiential
functions of has-let-7b-5p and core genes in human glioma. J Transl
Med. 17:1292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ivliev AE, t Hoen PA and Sergeeva MG:
Coexpression network analysis identifies transcriptional modules
related to proastrocytic differentiation and sprouty signaling in
glioma. Cancer Res. 24:10060–10070. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: Eigengene
networks for studying the relationships between co-expression
modules. BMC Syst Biol. 1:542007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang B and Horvath S: A general framework
for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet
Mol Biol. 4:Article17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsu SD, Tseng YT, Shrestha S, Lin YL,
Khaleel A, Chou CH, Chu CF, Huang HY, Lin CM, Ho SY, et al:
miRTarBase update 2014: An information resource for experimentally
validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res.
42((Database Issue)): D78–D85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeggari A, Marks DS and Larsson E:
miRcode: A map of putative microRNA target sites in the long
non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics. 28:2062–2063. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li P, Dong M and Wang Z: Downregulation of
TSPAN13 by miR-369-3p inhibits cell proliferation in papillary
thyroid cancer (PTC). Bosn J Basic Med Sci. Aug 2–2018.doi:
10.17305/bjbms.2018.2865 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luo L, Xia L, Zha B, Zuo C, Deng D, Chen
M, Hu L, He Y, Dai F, Wu J, et al: miR-335-5p targeting ICAM-1
inhibits invasion and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:983–990. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia E, Bhandari A, Shen Y, Zhou X and Wang
O: lncRNA LINC00673 induces proliferation, metastasis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in thyroid carcinoma via
Kruppel-like factor 2. Int J Oncol. 53:1927–1938. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuan N, Zhang G, Bie F, Ma M, Ma Y, Jiang
X, Wang Y and Hao X: Integrative analysis of lncRNAs and miRNAs
with coding RNAs associated with ceRNA crosstalk network in triple
negative breast cancer. OncoTargets Therapy. 10:5883–5897. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang C, Yuan N, Wu L, Wang X, Dai J, Song
P, Li F, Xu C and Zhao X: An integrated analysis for long noncoding
RNAs and microRNAs with the mediated competing endogenous RNA
network in papillary renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Therapy.
10:4037–4050. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li F, Huang C, Li Q and Wu X: Construction
and comprehensive analysis for dysregulated long non-coding RNA
(lncRNA)-associated competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in
gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 24:37–49. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wan M, Zhang FM, Li ZL, Kang PC, Jiang PM,
Wang YM, Wang ZD, Zhong XY, Li CL, Wang H, et al: Identifying
survival-associated ceRNA clusters in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 36:1542–1550. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu S, Kong D, Chen Q, Ping Y and Pang D:
Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol
cancer. 16:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brouwers B, Fumagalli D, Brohee S, Hatse
S, Govaere O, Floris G, Van den Eynde K, Bareche Y, Schöffski P,
Smeets A, et al: The footprint of the ageing stroma in older
patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 19:782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang C, Song JJ, Lee J and Kim MY:
Epigenetics: An emerging player in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6433–6447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr Biol.
24:R762–R776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang R, Chen Y, Tang C, Li H, Wang B, Yan
Q, Hu J and Zou S: MicroRNA-144 suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell
proliferation and invasion through targeting platelet activating
factor acetylhydrolase isoform 1b. BMC Cancer. 14:9172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Phua YW, Nguyen A, Roden DL, Elsworth B,
Deng N, Nikolic I, Yang J, Mcfarland A, Russell R, Kaplan W, et al:
MicroRNA profiling of the pubertal mouse mammary gland identifies
miR-184 as a candidate breast tumour suppressor gene. Breast Cancer
Res. 17:832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu GG, Li WH, He WG, Jiang N, Zhang GX,
Chen W, Yang HF, Liu QL, Huang YN, Zhang L, et al: Mir-184
post-transcriptionally regulates SOX7 expression and promotes cell
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e887962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Misawa K, Mochizuki D, Imai A, Misawa Y,
Endo S, Mima M, Kawasaki H, Carey TE and Kanazawa T: Epigenetic
silencing of SALL3 is an independent predictor of poor survival in
head and neck cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 9:642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin M, Liu Y, Ding X, Ke Q, Shi J, Ma Z,
Gu H, Wang H, Zhang C, Yang C, et al: E2F1 transactivates IQGAP3
and promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through IQGAP3-mediated PKC-alpha activation. Am J Cancer Res.
9:285–299. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ren Z, Kang W, Wang L, Sun B, Ma J, Zheng
C, Sun J, Tian Z, Yang X and Xiao W: E2F1 renders prostate cancer
cell resistant to ICAM-1 mediated antitumor immunity by NF-κB
modulation. Mol Cancer. 13:842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang S, Wu B, Sun H, Ji F, Sun T, Zhao Y
and Zhou D: Interrupted E2F1-miR-34c-SCF negative feedback loop by
hyper-methylation promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation.
Biosci Rep. 36:e002932016. View Article : Google Scholar
|