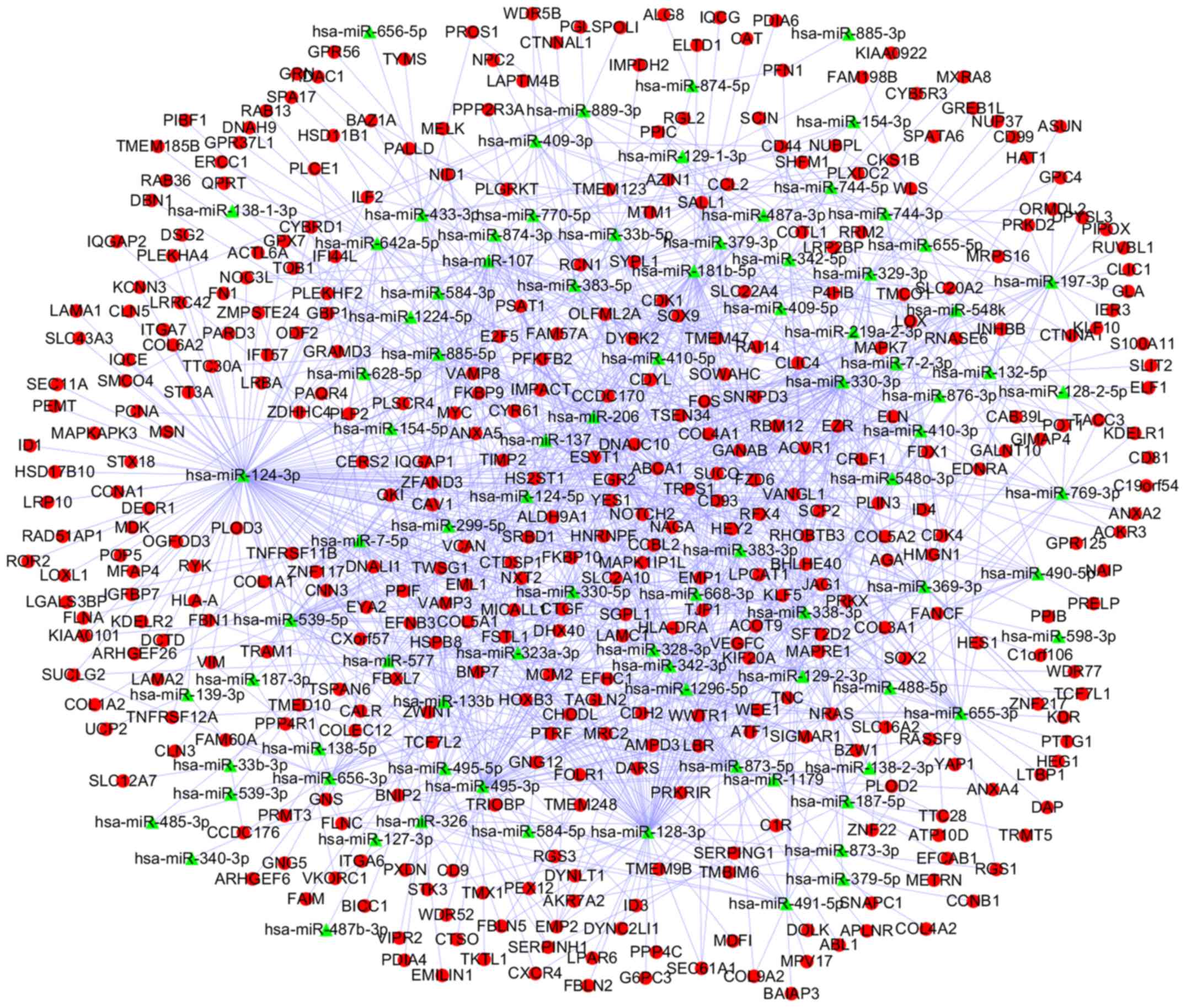
|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, de Blank PM,
Finlay JL, Gurney JG, McKean-Cowdin R, Stearns DS, Wolff JE, Liu M,
Wolinsky Y, et al: American brain tumor association adolescent and
young adult primary brain and central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the united states in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 18 (Suppl
1):i1–i50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kilday JP, Rahman R, Dyer S, Ridley L,
Lowe J, Coyle B and Grundy R: Pediatric ependymoma: Biological
perspectives. Mol Cancer Res. 7:765–786. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li AM, Dunham C, Tabori U, Carret AS,
McNeely PD, Johnston D, Lafay-Cousin L, Wilson B, Eisenstat DD,
Jabado N, et al: EZH2 expression is a prognostic factor in
childhood intracranial ependymoma: A Canadian Pediatric Brain Tumor
Consortium study. Cancer. 121:1499–1507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 world health organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vera-Bolanos E, Aldape K, Yuan Y, Wu J,
Wani K, Necesito-Reyes MJ, Colman H, Dhall G, Lieberman FS,
Metellus P, et al: Clinical course and progression-free survival of
adult intracranial and spinal ependymoma patients. Neuro Oncol.
17:440–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang B, Pan X and Anderson TA: MicroRNA:
A new player in stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 209:266–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Margolin-Miller Y, Yanichkin N, Shichrur
K, Toledano H, Ohali A, Tzaridis T, Michowitz S, Fichman-Horn S,
Feinmesser M, Pfister SM, et al: Prognostic relevance of miR-124-3p
and its target TP53INP1 in pediatric ependymoma. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 56:639–650. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang ML, Hsieh TH, Liu YR, Chen YW, Lee
YY, Chang FC, Lin SC, Huang MC, Donald Ming-Tak H, Wong TT, et al:
Significance of cyclin D1 overexpression in progression and
radio-resistance of pediatric ependymomas. Oncotarget. 9:2527–2542.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Statistical Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
11
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kanehisa M: The KEGG database. Novartis
Found Symp. 247:91–103, 119-128, 244–152. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fabregat A, Sidiropoulos K, Garapati P,
Gillespie M, Hausmann K, Haw R, Jassal B, Jupe S, Korninger F,
McKay S, et al: The Reactome pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:D481–487. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Janky R, Verfaillie A, Imrichova H, Van de
Sande B, Standaert L, Christiaens V, Hulselmans G, Herten K, Naval
Sanchez M, Potier D, et al: iRegulon: From a gene list to a gene
regulatory network using large motif and track collections. PLoS
Comput Biol. 10:e10037312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maragkakis M, Vergoulis T, Alexiou P,
Reczko M, Plomaritou K, Gousis M, Kourtis K, Koziris N, Dalamagas T
and Hatzigeorgiou AG: Hatzigeorgiou DIANA-microT Web server upgrade
supports Fly and Worm miRNA target prediction and bibliographic
miRNA to disease association. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:W145–W158.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Vlachos IS, Vergoulis T, Reczko M, Filippidis C,
Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-microT web server v5.0:
Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W169–W173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D53. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsang JS, Ebert MS and van Oudenaarden A:
Genome-wide dissection of microRNA functions and cotargeting
networks using gene set signatures. Mol Cell. 38:140–153. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vejnar CE, Blum M and Zdobnov EM: miRmap
web: Comprehensive microRNA target prediction online. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:W165–W168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsu PW, Huang HD, Hsu SD, Lin LZ, Tsou AP,
Tseng CP, Stadler PF, Washietl S and Hofacker IL: miRNAMap: Genomic
maps of microRNA genes and their target genes in mammalian genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D135–D139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam
WL, Thomson AM, Lim B and Rigoutsos I: A pattern-based method for
the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their
corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 126:1203–1217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Krüger J and Rehmsmeier M: RNAhybrid:
microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34:W451–W454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW,
Grimson A and Bartel DP: Weak seed-pairing stability and high
target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other
microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1139–1146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Wu C, Chen N, Gu H, Yen A, Cao L,
Wang E and Wang L: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted
therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 7:33440–33450.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dimitrova V and Arcaro A: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in medulloblastoma. Curr Mol Med.
15:82–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Verstegen MJ, Leenstra DT, Ijlst-Keizers H
and Bosch DA: Proliferation- and apoptosis-related proteins in
intracranial ependymomas: An immunohistochemical analysis. J
Neurooncol. 56:21–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gupta RK, Sharma MC, Suri V, Kakkar A,
Singh M and Sarkar C: Study of chromosome 9q gain, Notch pathway
regulators and Tenascin-C in ependymomas. J Neurooncol.
116:267–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Faria C, Miguens J, Antunes JL, Salgado D,
Nunes S, Barroso C, Martins Mdo C, Nunes VM and Roque L: Pediatric
brain tumors: Genetics and clinical outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr.
5:263–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen X, Zhang FH, Chen QE, Wang YY, Wang
YL, He JC and Zhou J: The clinical significance of CDK1 expression
in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal.
20:e7–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen H, Huang Q, Zhai DZ, Dong J, Wang AD
and Lan Q: CDK1 expression and effects of CDK1 silencing on the
malignant phenotype of glioma cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
29:484–488. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brown DV, Daniel PM, D'Abaco GM, Gogos A,
Ng W, Morokoff AP and Mantamadiotis T: Coexpression analysis of
CD133 and CD44 identifies proneural and mesenchymal subtypes of
glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget. 6:6267–6280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang J, Hou Z, Wang C, Wang H and Zhang H:
Gene expression profiles reveal key genes for early diagnosis and
treatment of adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. Cancer Gene Ther.
25:227–239. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhong S, Wu B, Dong X, Han Y, Jiang S,
Zhang Y, Bai Y, Luo SX, Chen Y, Zhang H and Zhao G: Identification
of driver genes and key pathways of glioblastoma shows JNJ-7706621
as a novel antiglioblastoma drug. World Neurosurg. 109:e329–e342.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, Li S, Xu L, Li X, Li
Y, Li Z, Ng SS, Sung JJ, et al: miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal
cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage
II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 34:4142–4152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pu Y, Zhao F, Wang H, Cai W, Gao J, Li Y
and Cai S: MiR-34a-5p promotes the multi-drug resistance of
osteosarcoma by targeting the CD117 gene. Oncotarget.
7:28420–28434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Li Z, Hu
Y, Shang X and Liu Y: MiR-449a exerts tumor-suppressive functions
in human glioblastoma by targeting Myc-associated zinc-finger
protein. Mol Oncol. 9:640–656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhi F, Zhou G, Shao N, Xia X, Shi Y, Wang
Q, Zhang Y, Wang R, Xue L, Wang S, et al: miR-106a-5p inhibits the
proliferation and migration of astrocytoma cells and promotes
apoptosis by targeting FASTK. PLoS One. 8:e723902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhi F, Chen X, Wang S, Xia X, Shi Y, Guan
W, Shao N, Qu H, Yang C, Zhang Y, et al: The use of hsa-miR-21,
hsa-miR-181b and hsa-miR-106a as prognostic indicators of
astrocytoma. Eur J Cancer. 46:1640–1649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mao G, Ren P, Wang G, Yan F and Zhang Y:
MicroRNA-128-3p protects mouse against cerebral ischemia through
reducing p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. J Mol
Neurosci. 61:152–158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang R, Liu C, Niu Y, Jing Y, Zhang H,
Wang J, Yang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY and Li D: MicroRNA-128-3p
regulates mitomycin C-induced DNA damage response in lung cancer
cells through repressing SPTAN1. Oncotarget. 8:58098–58107.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mets E, Van Peer G, Van der Meulen J,
Boice M, Taghon T, Goossens S, Mestdagh P, Benoit Y, De Moerloose
B, Van Roy N, et al: MicroRNA-128-3p is a novel oncomiR targeting
PHF6 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica.
99:1326–1333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang CY, Huang XP, Zhu JY, Chen ZG, Li
XJ, Zhang XH, Huang S, He JB, Lian F, Zhao YN, et al: miR-128-3p
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by regulating
PIK3R1 and is correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Oncol
Rep. 33:2889–2898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Meng H, Wang K, Chen X, Guan X, Hu L,
Xiong G, Li J and Bai Y: MicroRNA-330-3p functions as an oncogene
in human esophageal cancer by targeting programmed cell death 4. Am
J Cancer Res. 5:1062–1075. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pantaleo MA, Ravegnini G, Astolfi A,
Simeon V, Nannini M, Saponara M, Urbini M, Gatto L, Indio V,
Sammarini G, et al: Integrating miRNA and gene expression profiling
analysis revealed regulatory networks in gastrointestinal stromal
tumors. Epigenomics. 8:1347–1366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|