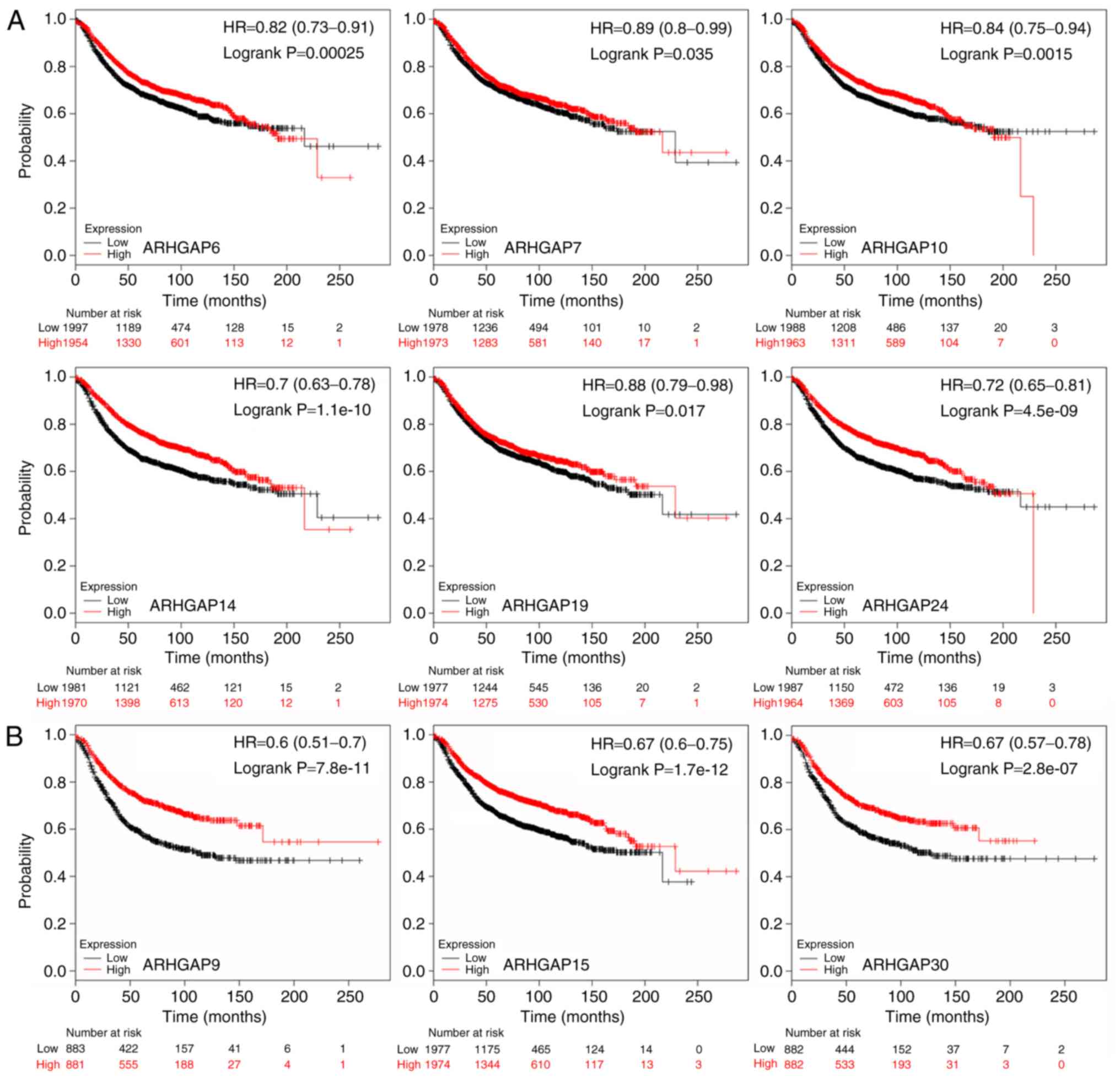
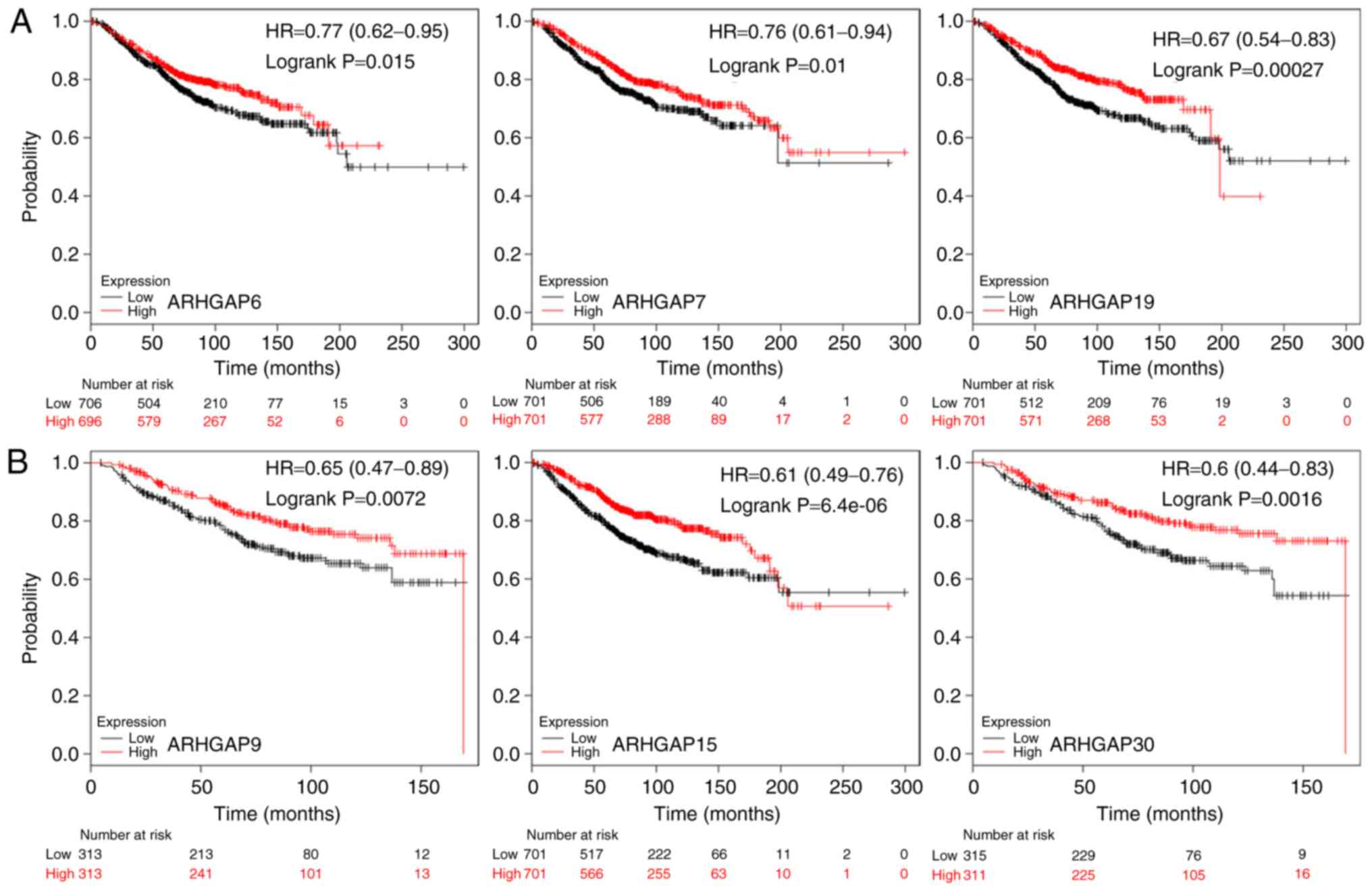
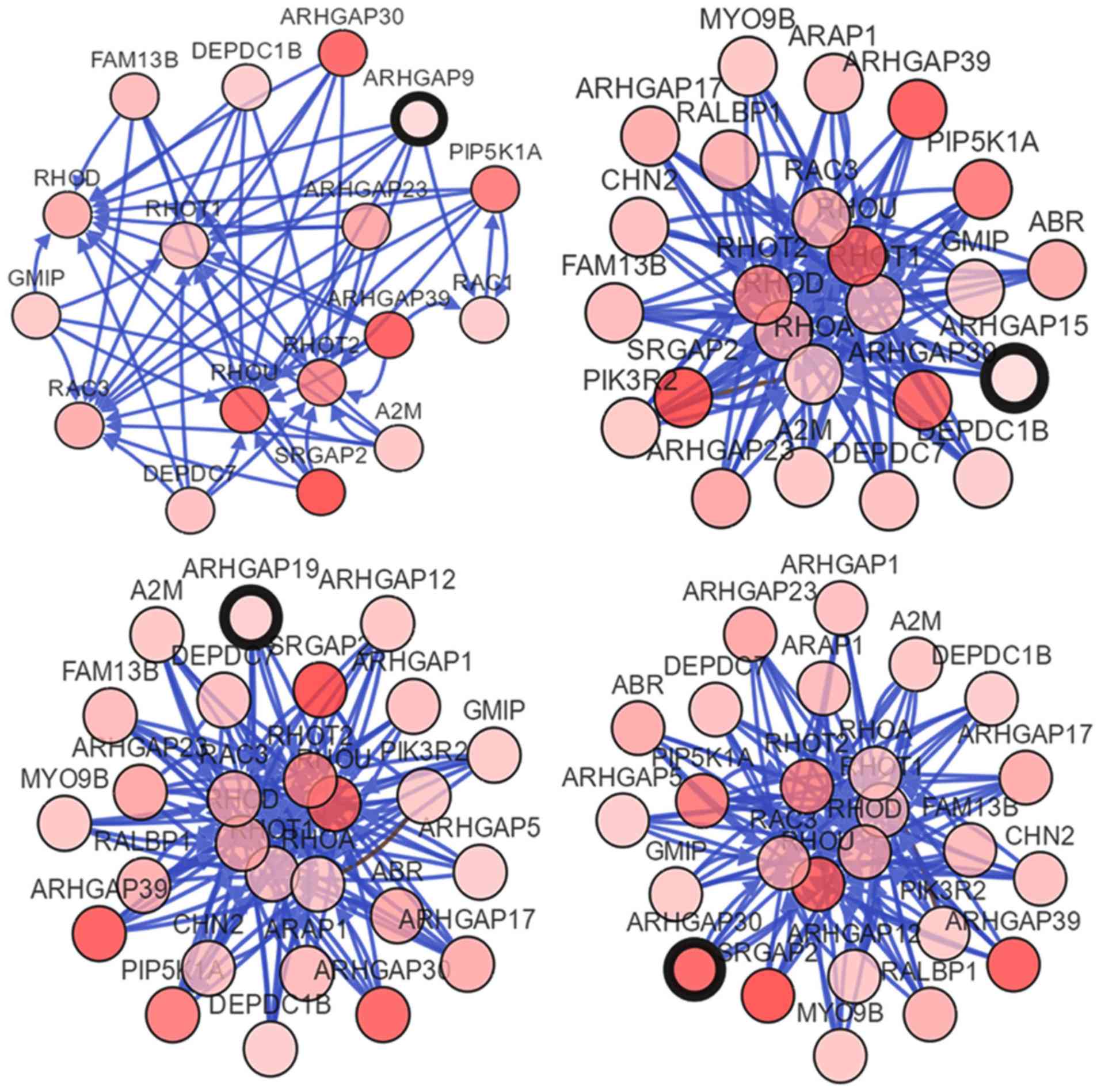
|
1
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vega FM and Ridley AJ: Rho GTPases in
cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett. 582:2093–2101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Etienne-Manneville S and Hall A: Rho
GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gökmen-Polar Y, True JD, Vieth E, Gu Y, Gu
X, Qi GD, Mosley AL and Badve SS: Quantitative phosphoproteomic
analysis identifies novel functional pathways of tumor suppressor
DLC1 in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. PLoS One.
13:e02046582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takagi K, Miki Y, Onodera Y, Ishida T,
Watanabe M, Sasano H and Suzuki T: ARHGAP15 in human breast
carcinoma: A potent tumor suppressor regulated by androgens. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:E8042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aleskandarany MA, Sonbul S, Surridge R,
Mukherjee A, Caldas C, Diez-Rodriguez M, Ashankyty I, Albrahim KI,
Elmouna AM, Aneja R, et al: Rho-GTPase activating-protein 18: A
biomarker associated with good prognosis in invasive breast cancer.
Br J Cancer. 117:1176–1184. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jézéquel P, Frénel JS, Campion L,
Guérin-Charbonnel C, Gouraud W, Ricolleau G and Campone M:
bc-GenExMiner 3.0: New mining module computes breast cancer gene
expression correlation analyses. Database (Oxford).
2013:bas0602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jézéquel P, Campone M, Gouraud W,
Guérin-Charbonnel C, Leux C, Ricolleau G and Campion L:
bc-GenExMiner: An easy-to-use online platform for gene prognostic
analyses in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:765–775.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Le Doussal V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Friedman S,
Hacene K, Spyratos F and Brunet M: Prognostic value of histologic
grade nuclear components of Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR). An
improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of
1262 invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer. 64:1914–1921. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haybittle JL, Blamey RW, Elston CW,
Johnson J, Doyle PJ, Campbell FC, Nicholson RI and Griffiths K: A
prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 45:361–366.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ang BK, Lim CY, Koh SS, Sivakumar N, Taib
S, Lim KB, Ahmed S, Rajagopal G and Ong SH: ArhGAP9, a novel MAP
kinase docking protein, inhibits Erk and p38 activation through WW
domain binding. J Mol Signal. 2:12007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Furukawa Y, Kawasoe T, Daigo Y, Nishiwaki
T, Ishiguro H, Takahashi M, Kitayama J and Nakamura Y: Isolation of
a novel human gene, ARHGAP9, encoding a rho-GTPase activating
protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 284:643–649. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Tang QF, Sun MY, Zhang CY, Zhu
JY, Shen YL, Zhao B, Shao ZY, Zhang LJ and Zhang H: ARHGAP9
suppresses the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells through up-regulating FOXJ2/E-cadherin. Cell Death Dis.
9:9162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang T and Ha M: Silencing ARHGAP9
correlates with the risk of breast cancer and inhibits the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 119:7747–7756. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Radu M, Rawat SJ, Beeser A, Iliuk A, Tao
WA and Chernoff J: ArhGAP15, a Rac-specific GTPase-activating
protein, plays a dual role in inhibiting small GTPase signaling. J
Biol Chem. 288:21117–21125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seoh ML, Ng CH, Yong J, Lim L and Leung T:
ArhGAP15, a novel human RacGAP protein with GTPase binding
property. FEBS Lett. 539:131–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan S, Deng Y, Fu J, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Ru
X and Qin X: Decreased expression of ARHGAP15 promotes the
development of colorectal cancer through PTEN/AKT/FOXO1 axis. Cell
Death Dis. 9:6732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Naji L, Pacholsky D and Aspenström P:
ARHGAP30 is a Wrch-1-interacting protein involved in actin dynamics
and cell adhesion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 409:96–102. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Qian J, Hu Y, Kong X, Chen H, Shi
Q, Jiang L, Wu C, Zou W, Chen Y, et al: ArhGAP30 promotes p53
acetylation and function in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun.
5:47352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
David MD, Petit D and Bertoglio J: The
RhoGAP ARHGAP19 controls cytokinesis and chromosome segregation in
T lymphocytes. J Cell Sci. 127:400–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|