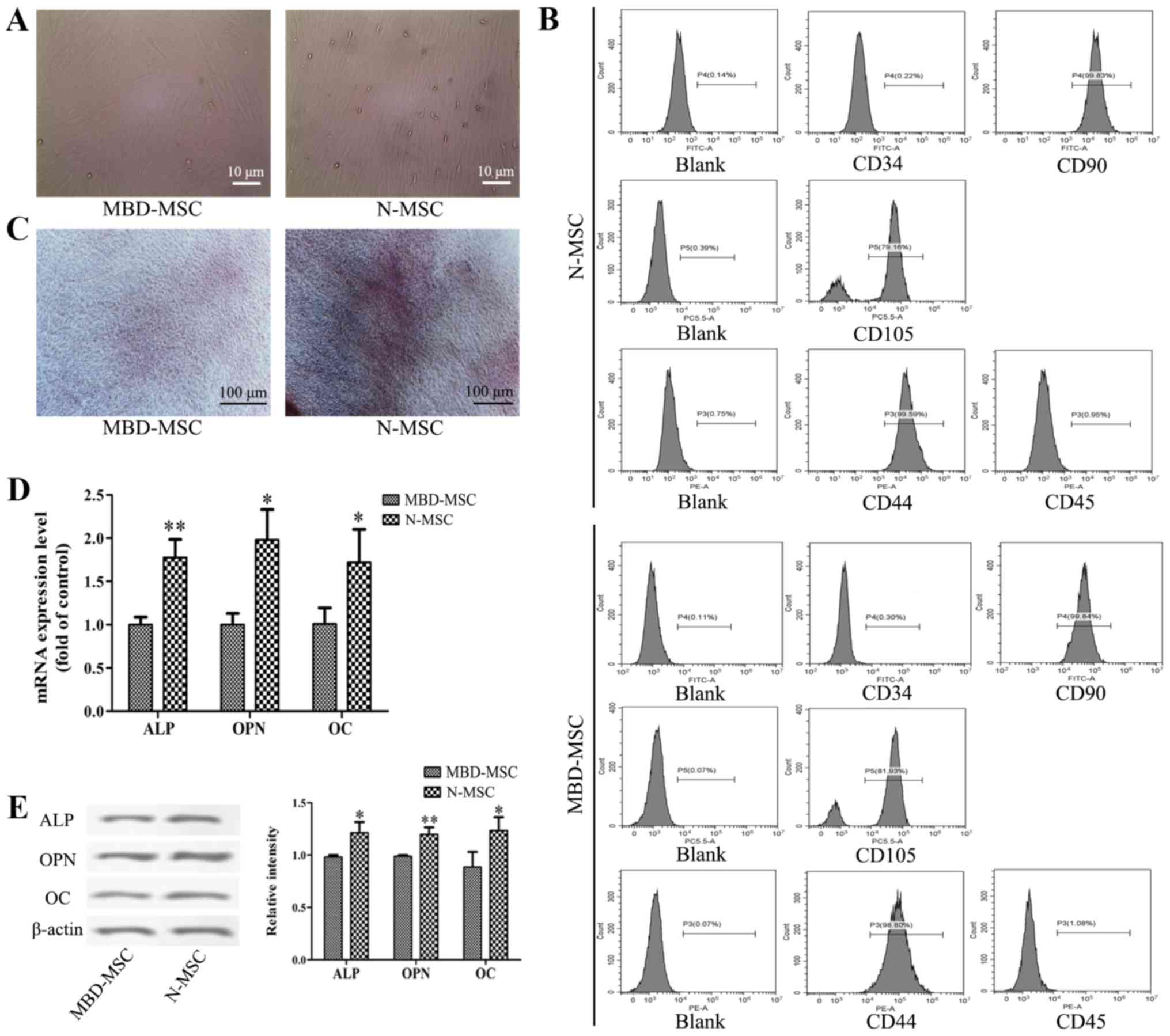
|
1
|
Kyle RA and Rajkumar SV: Criteria for
diagnosis, staging, risk stratification and response assessment of
multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 23:3–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Anderson KC: Progress and paradigms in
multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5419–5427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yaccoby S: Advances in the understanding
of myeloma bone disease and tumour growth. Br J Haematol.
149:311–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heider U, Hofbauer LC, Zavrski I, Kaiser
M, Jakob C and Sezer O: Novel aspects of osteoclast activation and
osteoblast inhibition in myeloma bone disease. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 338:687–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li H, Li T, Fan J, Li T, Fan L, Wang S,
Weng X, Han Q and Zhao RC: miR-216a rescues dexamethasone
suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation
and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 22:1935–1945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raje N and Roodman GD: Advances in the
biology and treatment of bone disease in multiple myeloma. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1278–1286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gregory RI and Shiekhattar R: MicroRNA
biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 65:3509–3512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv H, Sun Y and Zhang Y: miR-133 is
involved in estrogen Deficiency-Induced osteoporosis through
modulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Med Sci Monit. 21:1527–1534. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Q, Liu W, Sinha KM, Yasuda H and de
Crombrugghe B: Identification and characterization of microRNAs
controlled by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix.
PLoS One. 8:e581042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vimalraj S and Selvamurugan N: MicroRNAs:
Synthesis, gene regulation and osteoblast differentiation. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 15:7–18. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou M, Li M and Yu X: Regulation of
microRNA in osteoblast differentiation and its clinical
significance. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 26:755–759.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Berenson JR: Myeloma bone disease. Best
Pract Res Clin Haematol. 18:653–672. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diao Y, Ma Q, Cui F and Zhong Y: Human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: Osteogenesis in vivo as seed
cells for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A.
91:123–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rodan GA and Martin TJ: Therapeutic
approaches to bone diseases. Science. 289:1508–1514. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ell B and Kang Y: MicroRNAs as regulators
of bone homeostasis and bone metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 3:5492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu R, Li H, Liu W, Yang L, Tan YF and Luo
XH: Targeting miRNAs in osteoblast differentiation and bone
formation. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1109–1120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inose H, Ochi H, Kimura A, Fujita K, Xu R,
Sato S, Iwasaki M, Sunamura S, Takeuchi Y, Fukumoto S, et al: A
microRNA regulatory mechanism of osteoblast differentiation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:20794–20799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng YB, Li X, Li ZY, Zhao J, Yuan XB, Ren
Y, Cui ZD, Liu YD and Yang XJ: microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/β-catenin
pathway. J Orthop Res. 33:957–964. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Arfat Y, Basra MAR, Shahzad M, Majeed K,
Mahmood N and Munir H: miR-208a-3p Suppresses osteoblast
differentiation and inhibits bone formation by targeting ACVR1. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 11:323–336. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Gao Y, Cai L, Li F, Lou Y, Xu N,
Kang Y and Yang H: MicroRNA-221 is involved in the regulation of
osteoporosis through regulates RUNX2 protein expression and
osteoblast differentiation. Am J Transl Res. 9:126–135.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Derynck R, Zhang Y and Feng XH: Smads:
Transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell. 95:737–740.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hackinger S, Trajanoska K, Styrkarsdottir
U, Zengini E, Steinberg J, Ritchie GRS, Hatzikotoulas K, Gilly A,
Evangelou E, Kemp JP, et al: Evaluation of shared genetic aetiology
between osteoarthritis and bone mineral density identifies SMAD3 as
a novel osteoarthritis risk locus. Hum Mol Genet. 26:3850–3858.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu Z, Greenblatt MB, Yan G, Feng H, Sun J,
Lotinun S, Brady N, Baron R, Glimcher LH and Zou W: SMURF2
regulates bone homeostasis by disrupting SMAD3 interaction with
vitamin D receptor in osteoblasts. Nat Commun. 8:145702017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu Q, Tu ML, Li CJ, Zhang L, Jiang TJ, Liu
T and Luo XH: GDF11 inhibits bone formation by activating Smad2/3
in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Calcif Tissue Int.
99:500–509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Borton AJ, Frederick JP, Datto MB, Wang XF
and Weinstein RS: The loss of Smad3 results in a lower rate of bone
formation and osteopenia through dysregulation of osteoblast
differentiation and apoptosis. J Bone Miner Res. 16:1754–1764.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang X, Chen L, Xu X, Li C, Huang C and
Deng CX: TGF-beta/Smad3 signals repress chondrocyte hypertrophic
differentiation and are required for maintaining articular
cartilage. J Cell Biol. 153:35–46. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luo G, Xu B and Huang Y: Icariside II
promotes the osteogenic differentiation of canine bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 signaling
pathways. Am J Transl Res. 9:2077–2087. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tong Y, Feng W, Wu Y, Lv H, Jia Y and
Jiang D: Mechano-growth factor accelerates the proliferation and
osteogenic differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells through
the PI3K/AKT pathway. BMC Biochem. 16:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gu YX, Du J, Si MS, Mo JJ, Qiao SC and Lai
HC: The roles of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in regulating MC3T3-E1
preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation on SLA and SLActive
titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 101:748–754. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang S, Chen X, Hu Y, Wu J, Cao Q, Chen S
and Gao Y: All-trans retinoic acid modulates Wnt3A-induced
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activating
the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signalling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
422:243–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
You L, Gu W, Chen L, Pan L, Chen J and
Peng Y: miR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed
osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7249–7261.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|