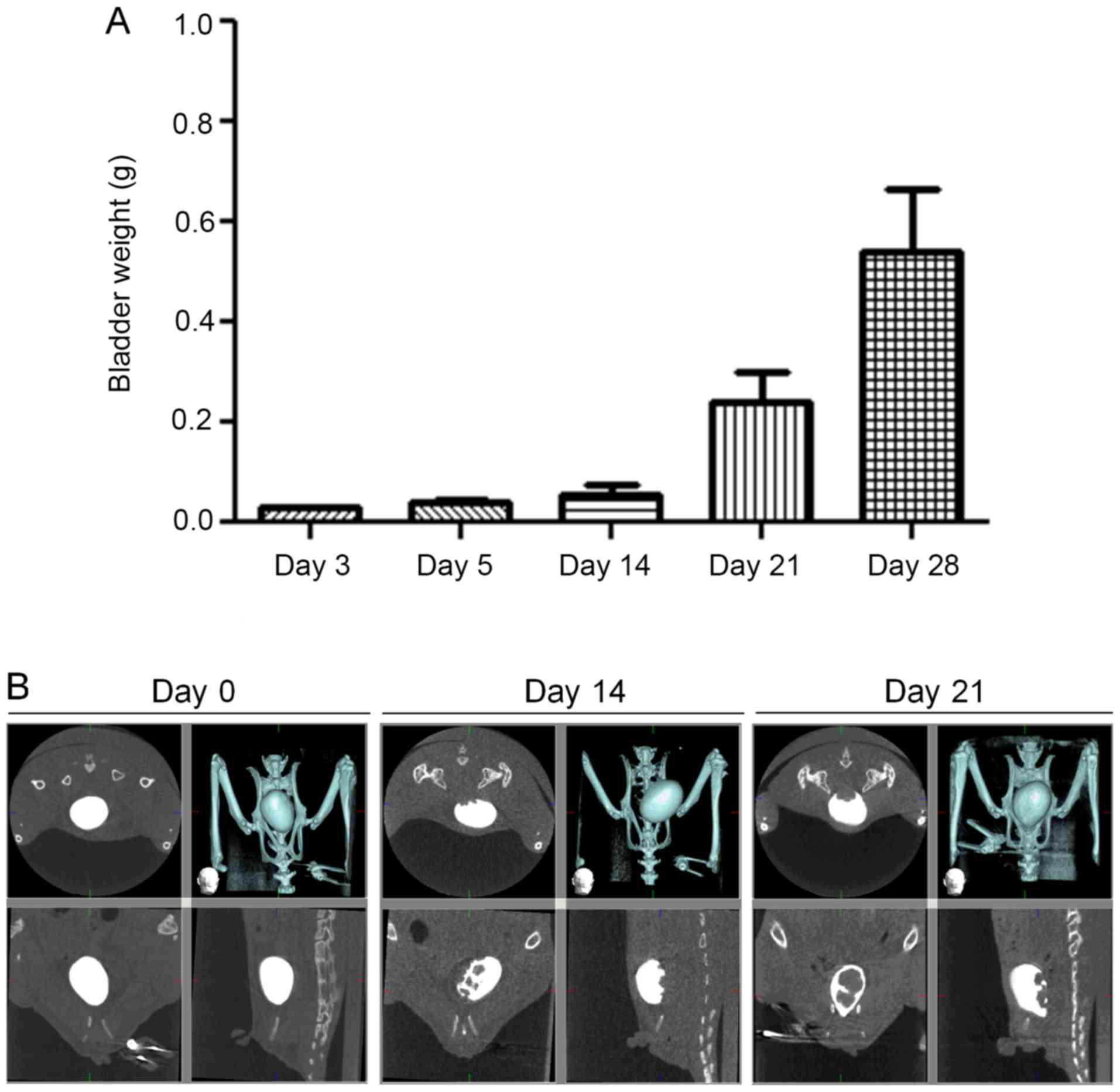
|
1
|
Lynch CF and Cohen MB: Urinary system.
Cancer. 75:316–329. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barocas DA and Clark PE: Bladder cancer.
Curr Opin Oncol. 20:307–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, Algaba F,
Busch C, Cheng L, Kiemeney L, Kriegmair M, Montironi R, Murphy WM,
et al: Bladder cancer: Epidemiology, staging and grading, and
diagnosis. Urology. 66 (Suppl):S4–S34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jacobs BL, Lee CT and Montie JE: Bladder
cancer in 2010: How far have we come? CA Cancer J Clin. 60:244–272.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brawn PN: The origin of invasive carcinoma
of the bladder. Cancer. 50:515–519. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanematsu A, Tsuji Y, Kanba H, Noguchi T,
Kamoto T and Okabe T: The sensitivity and clinical implications of
periodical bladder biopsy following transurethral resection of
superficial bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Hinyokika kiyo.
Acta urologica Japonica (Japanese). 47:1–4. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Koss LG, Nakanishi I and Freed SZ:
Nonpapillary carcinoma in situ and atypical hyperplasia in
cancerous bladders: Further studies of surgically removed bladders
by mapping. Urology. 9:442–455. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koss LG, Tiamson EM and Robbins MA:
Mapping cancerous and precancerous bladder changes. A study of the
urothelium in ten surgically removed bladders. JAMA. 227:281–286.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zincke H, Utz DC and Farrow GM: Review of
mayo clinic experience with carcinoma in situ. Urology. 26
(Suppl):S39–S46. 1985.
|
|
10
|
Kamat AM, Flaig TW, Grossman HB, Konety B,
Lamm D, O'donnell MA, Uchio E, Efstathiou JA and Taylor III JA:
Expert consensus document: Consensus statement on best practice
management regarding the use of intravesical immunotherapy with BCG
for bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 12:225–235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gasión JP and Cruz JF: Improving efficacy
of intravesical chemotherapy. Eur Urol. 50:225–234. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huebner D, Rieger C, Bergmann R, Ullrich
M, Meister S, Toma M, Wiedemuth R, Temme A, Novotny V, Wirth MP, et
al: An orthotopic xenograft model for high-risk non-muscle invasive
bladder cancer in mice: Influence of mouse strain, tumor cell
count, dwell time and bladder pretreatment. BMC Cancer. 17:7902017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Matsumoto R, Tsuda M, Wang L, Maishi N,
Abe T, Kimura T, Tanino M, Nishihara H, Hida K, Ohba Y, et al:
Adaptor protein CRK induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis of bladder cancer cells through HGF/c-Met feedback loop.
Cancer Sci. 106:709–717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van der Horst G, van Asten JJ, Figdor A,
van den Hoogen C, Cheung H, Bevers RF, Pelger RC and van der Pluijm
G: Real-time cancer cell tracking by bioluminescence in a
preclinical model of human bladder cancer growth and metastasis.
Eur Urol. 60:337–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nogawa M, Yuasa T, Kimura S, Tanaka M,
Kuroda J, Sato K, Yokota A, Segawa H, Toda Y, Kageyama S, et al:
Intravesical administration of small interfering RNA targeting
PLK-1 successfully prevents the growth of bladder cancer. J Clin
Invest. 115:978–985. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim CJ, Tambe Y, Mukaisho KI, Sugihara H,
Kageyama S, Kawauchi A and Inoue H: Periostin suppresses in vivo
invasiveness via PDK1/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in a mouse
orthotopic model of bladder cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:4276–4284. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chan E, Patel A, Heston W and Larchian W:
Mouse orthotopic models for bladder cancer research. BJU Int.
104:1286–1291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seager C, Puzio-Kuter AM, Cordon-Cardo C,
McKiernan J and Abate-Shen C: Mouse models of human bladder cancer
as a tool for drug discovery. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 49:142010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Li D, Shao J and Wang X: Animal
models for bladder cancer: The model establishment and evaluation
(Review). Oncol Lett. 9:1515–1519. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kobayashi T, Owczarek TB, McKiernan JM and
Abate-Shen C: Modelling bladder cancer in mice: Opportunities and
challenges. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:42–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Anai S, De Velasco
M, Tanaka M, Tsujikawa K, Ouji Y and Konishi N: A novel human AlkB
homologue, ALKBH8, contributes to human bladder cancer progression.
Cancer Res. 69:3157–3164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou JH, Rosser CJ, Tanaka M, Yang M,
Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Benedict WF: Visualizing superficial
human bladder cancer cell growth in vivo by green fluorescent
protein expression. Cancer Gene Ther. 9:681–686. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
JoVE Science Education Database. Lab
Animal Research. Anesthesia Induction and Maintenance. JoVE;
Cambridge, MA: 2019
|
|
24
|
Kameoka S, Matsumoto K, Kai Y, Yonehara Y,
Arai Y and Honda K: Establishment of temporomandibular joint
puncture technique in rats using in vivo micro-computed tomography
(R_mCT(R)). Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 39:441–445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi R, Yokobori T, Osone K, Tatsuki
H, Takada T, Suto T, Yajima R, Kato T, Fujii T, Tsutsumi S, et al:
Establishment of a novel method to evaluate peritoneal
microdissemination and therapeutic effect using luciferase assay.
Cancer Sci. 107:341–346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Higuchi T, Yokobori T, Naito T, Kakinuma
C, Hagiwara S, Nishiyama M and Asao T: Investigation into
metastatic processes and the therapeutic effects of gemcitabine on
human pancreatic cancer using an orthotopic SUIT2 pancreatic cancer
mouse model. Oncol Lett. 15:3091–3099. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dobek GL and Godbey WT: An orthotopic
model of murine bladder cancer. J Vis Exp. (pii):
25352011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sternberg CN, de Mulder PH, Schornagel JH,
Theodore C, Fossa SD, Van Oosterom AT, Witjes F, Spina M, Van
Groeningen CJ, De Balincourt C, et al: Randomized phase III trial
of high-dose-intensity methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and
cisplatin (MVAC) chemotherapy and recombinant human granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor versus classic MVAC in advanced
urothelial tract tumors: European Organization for Research and
Treatment of Cancer Protocol no. 30924. J Clin Oncol. 19:2638–2646.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghatalia P, Zibelman M, Geynisman DM and
Plimack E: Approved checkpoint inhibitors in bladder cancer: which
drug should be used when? Ther Adv Med Oncol.
10:17588359187883102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT,
Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A,
Lippert CM, et al: Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate,
vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic
bladder cancer: Results of a large, randomized, multinational,
multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 18:3068–3077. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT,
Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Zimmermann A and Arning
M: Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing
gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine,
doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:4602–4608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|