|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu KY, Wang LT, Hsu SH and Wang SN:
Homeobox genes and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
11(pii): E6212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xue F, Liu Y, Chu H, Wen Y, Yan L, Tang Q,
Xiao E, Zhang D and Zhang H: eIF5A2 is an alternative pathway for
cell proliferation in cetuximab-treated epithelial hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 8:4670–4681. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xue F, Liu Y, Zhang H, Wen Y, Yan L, Tang
Q, Xiao E and Zhang D: Let-7a enhances the sensitivity of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cetuximab by regulating STAT3
expression. Onco Targets Ther. 9:7253–7261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Banini BA and Sanyal AJ: The use of cell
free DNA in the diagnosis of HCC. Hepatoma Res. 5(pii):
342019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amicone L and Marchetti A:
Microenvironment and tumor cells: Two targets for new molecular
therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 3:242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Waller LP, Deshpande V and Pyrsopoulos N:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Hepatol.
7:2648–2663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mordente A, Meucci E, Martorana GE and
Silvestrini A: Cancer biomarkers discovery and validation: State of
the art, problems and future perspectives. Adv Exp Med Biol.
867:9–26. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cetin B, Gumusay O, Cengiz M and Ozet A:
Advances of molecular targeted therapy in gastric cancer. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 47:125–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deng M, Brägelmann J, Schultze JL and
Perner S: Web-TCGA: An online platform for integrated analysis of
molecular cancer data sets. BMC Bioinformatics. 17:722016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zuliani-Alvarez L and Midwood KS:
Fibrinogen-related proteins in tissue repair: How a unique domain
with a common structure controls diverse aspects of wound healing.
Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:273–285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomsen T, Schlosser A, Holmskov U and
Sorensen GL: Ficolins and FIBCD1: Soluble and membrane bound
pattern recognition molecules with acetyl group selectivity. Mol
Immunol. 48:369–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schlosser A, Thomsen T, Moeller JB,
Nielsen O, Tornoe I, Mollenhauer J, Moestrup SK and Holmskov U:
Characterization of FIBCD1 as an acetyl group-binding receptor that
binds chitin. J Immunol. 183:3800–3809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shrive AK, Moeller JB, Burns I, Paterson
JM, Shaw AJ, Schlosser A, Sorensen GL, Greenhough TJ and Holmskov
U: Crystal structure of the tetrameric fibrinogen-like recognition
domain of fibrinogen C domain containing 1 (FIBCD1) protein. J Biol
Chem. 289:2880–2887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Doolittle RF, McNamara K and Lin K:
Correlating structure and function during the evolution of
fibrinogen-related domains. Protein Sci. 21:1808–1823. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rossi V, Bally I, Thielens NM, Esser AF
and Arlaud GJ: Baculovirus-mediated expression of truncated modular
fragments from the catalytic region of human complement serine
protease C1s. Evidence for the involvement of both complement
control protein modules in the recognition of the C4 protein
substrate. J Biol Chem. 273:1232–1239. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peschl P, Ramberger M, Höftberger R,
Jöhrer K, Baumann M, Rostásy K and Reindl M: Methodological
challenges in protein microarray and immunohistochemistry for the
discovery of novel autoantibodies in paediatric acute disseminated
encephalomyelitis. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E6792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
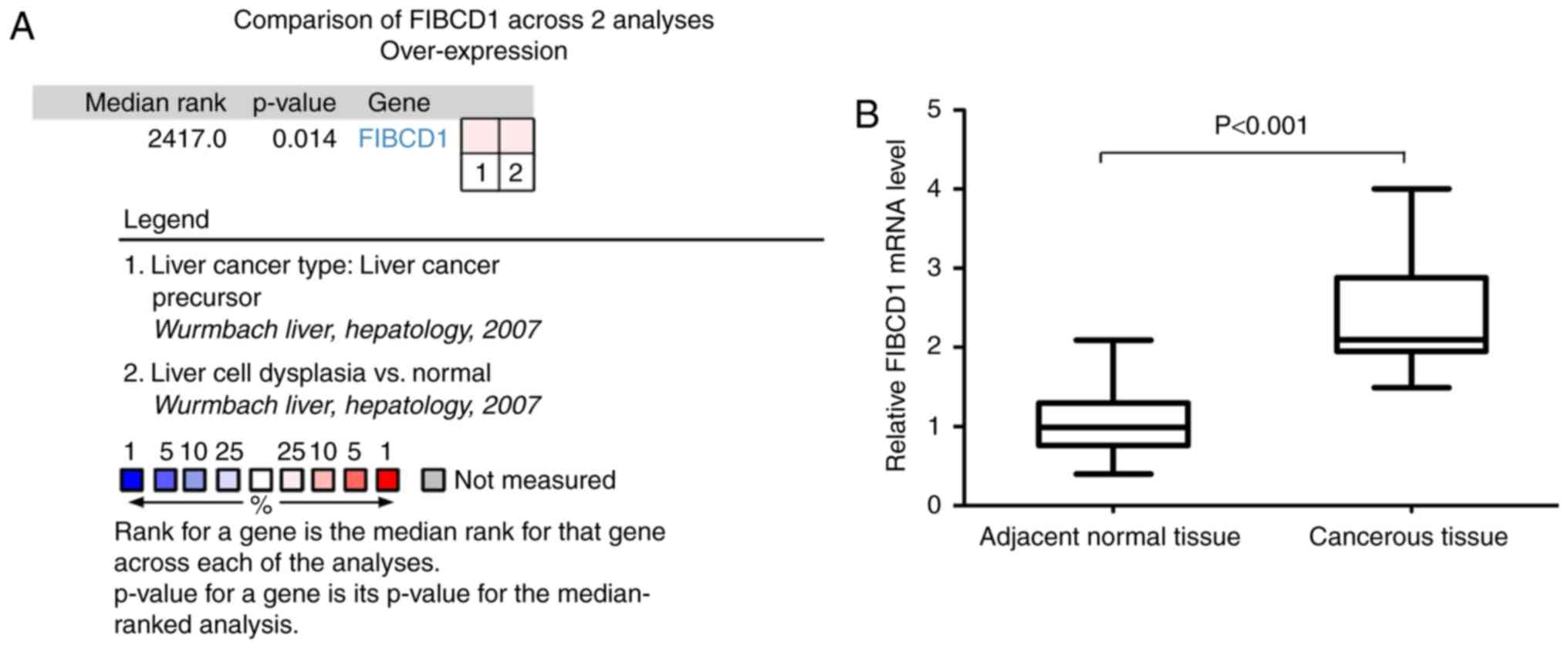
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao T, Pan W, Sun X and Shen H: Increased
expression of TET3 predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with
ovarian cancer-a bioinformatics integrative analysis. J Ovarian
Res. 12:1012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W,
Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Fiel I, Thung S, Mazzaferro V, Bruix J, et
al: Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 45:938–947. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Terentiev AA and Moldogazieva NT:
Alpha-fetoprotein: A renaissance. Tumour Biol. 34:2075–2091. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sauzay C, Petit A, Bourgeois AM, Barbare
JC, Chauffert B, Galmiche A and Houessinon A: Alpha-foetoprotein
(AFP): A multi-purpose marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Chim Acta. 463:39–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abdel-Rahman O: Assessment of the
discriminating value of the 8th AJCC stage grouping for
hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 20:41–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
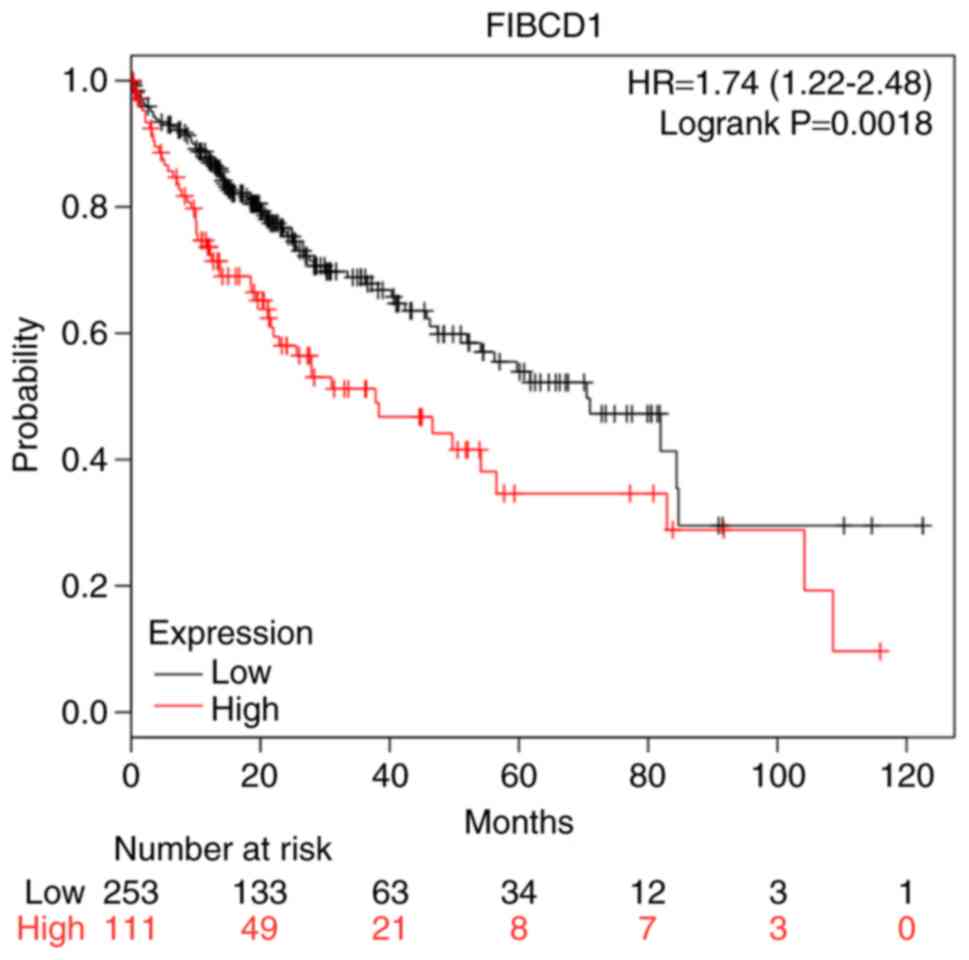
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M and Rimm DL:
X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and
outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7252–7259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parikh ND, Fu S, Rao H, Yang M, Li Y,
Powell C, Wu E, Lin A, Xing B, Wei L and Lok ASF: Risk assessment
of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in China
and the USA. Dig Dis Sci. 62:3243–3253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanda M, Sugimoto H and Kodera Y: Genetic
and epigenetic aspects of initiation and progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10584–10597.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu J and Gao DZ: Distinction immune genes
of hepatitis-induced heptatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics.
28:3191–3194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Finn RS: Advanced HCC: Emerging molecular
therapies. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 58:25–34. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marquardt JU, Galle PR and Teufel A:
Molecular diagnosis and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC):
An emerging field for advanced technologies. J Hepatol. 56:267–275.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang K, Fan Y, Chen G, Wang Z, Kong D and
Zhang P: MEK-ERK inhibition potentiates WAY-600-induced anti-cancer
efficiency in preclinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) models.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:330–337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhong CQ, Zhang XP, Ma N, Zhang EB, Li JJ,
Jiang YB, Gao YZ, Yuan YM, Lan SQ, Xie D and Cheng SQ: FABP4
suppresses proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells and predicts a poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Med. 7:2629–2640. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thomsen T, Moeller JB, Schlosser A,
Sorensen GL, Moestrup SK, Palaniyar N, Wallis R, Mollenhauer J and
Holmskov U: The recognition unit of FIBCD1 organizes into a
noncovalently linked tetrameric structure and uses a hydrophobic
funnel (S1) for acetyl group recognition. J Biol Chem.
285:1229–1238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
von Huth S, Moeller JB, Schlosser A,
Marcussen N, Nielsen O, Nielsen V, Sorensen GL and Holmskov U:
Immunohistochemical localization of fibrinogen C domain containing
1 on epithelial and mucosal surfaces in human tissues. J Histochem
Cytochem. 66:85–97. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bueter CL, Specht CA and Levitz SM: Innate
sensing of chitin and chitosan. PLoS Pathog. 9:e10030802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurita K: Chitin and chitosan: Functional
biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar Biotechnol (NY).
8:203–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Elieh Ali Komi D, Sharma L and Dela Cruz
CS: Chitin and its effects on inflammatory and immune responses.
Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 54:213–223. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tong PL, Roediger B, Kolesnikoff N, Biro
M, Tay SS, Jain R, Shaw LE, Grimbaldeston MA and Weninger W: The
skin immune atlas: three-dimensional analysis of cutaneous
leukocyte subsets by multiphoton microscopy. J Invest Dermatol.
135:84–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abdel-Rahman SM: Genetic predictors of
susceptibility to dermatophytoses. Mycopathologia. 182:67–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang C, Zhu J, Zhou P, Zhu H, Wang W, Jin
Q and Li P: Overexpression of FIBCD1 is predictive of poor
prognosis in gastric cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 149:474–483. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garlatti V, Belloy N, Martin L, Lacroix M,
Matsushita M, Endo Y, Fujita T, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Arlaud GJ,
Thielens NM and Gaboriaud C: Structural insights into the innate
immune recognition specificities of L- and H-ficolins. EMBO J.
26:623–633. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, He Y, Luo N, Patel SJ, Han Y, Gao
R, Modak M, Carotta S, Haslinger C, Kind D, et al: Landscape and
dynamics of single immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell.
179:829–845 e20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang Y, Liu X, Liu G, Wang X, Hu R and
Liang X: PIG11 over-expression predicts good prognosis and induces
HepG2 cell apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-dependent
mitochondrial pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:435–442. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Tan J, Ou S, Chen J and Chen L:
MicroRNA-101-3p suppresses proliferation and migration in
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the HGF/c-Met pathway. Invest
New Drugs. Mar 30–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ma C, Xu T, Sun X, Zhang S, Liu S, Fan S,
Lei C, Tang F, Zhai C, Li C, et al: Network pharmacology and
bioinformatics approach reveals the therapeutic mechanism of action
of baicalein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2019:75183742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang Z, Zhuang L, Szatmary P, Wen L, Sun
H, Lu Y, Xu Q and Chen X: Upregulation of heat shock proteins
(HSPA12A, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5 and HSPA6) in tumour tissues is
associated with poor outcomes from HBV-related early-stage
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 12:256–263. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|