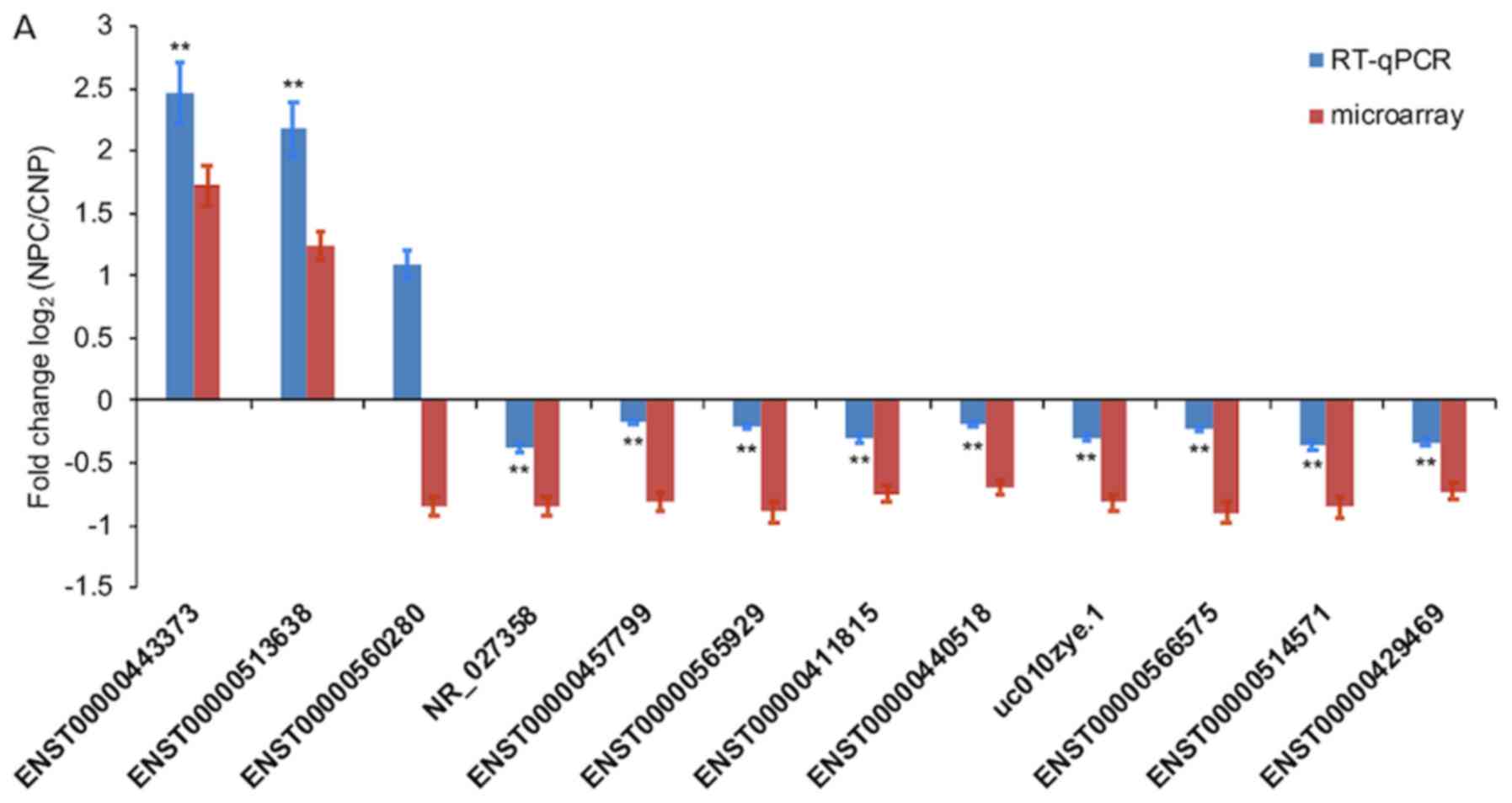
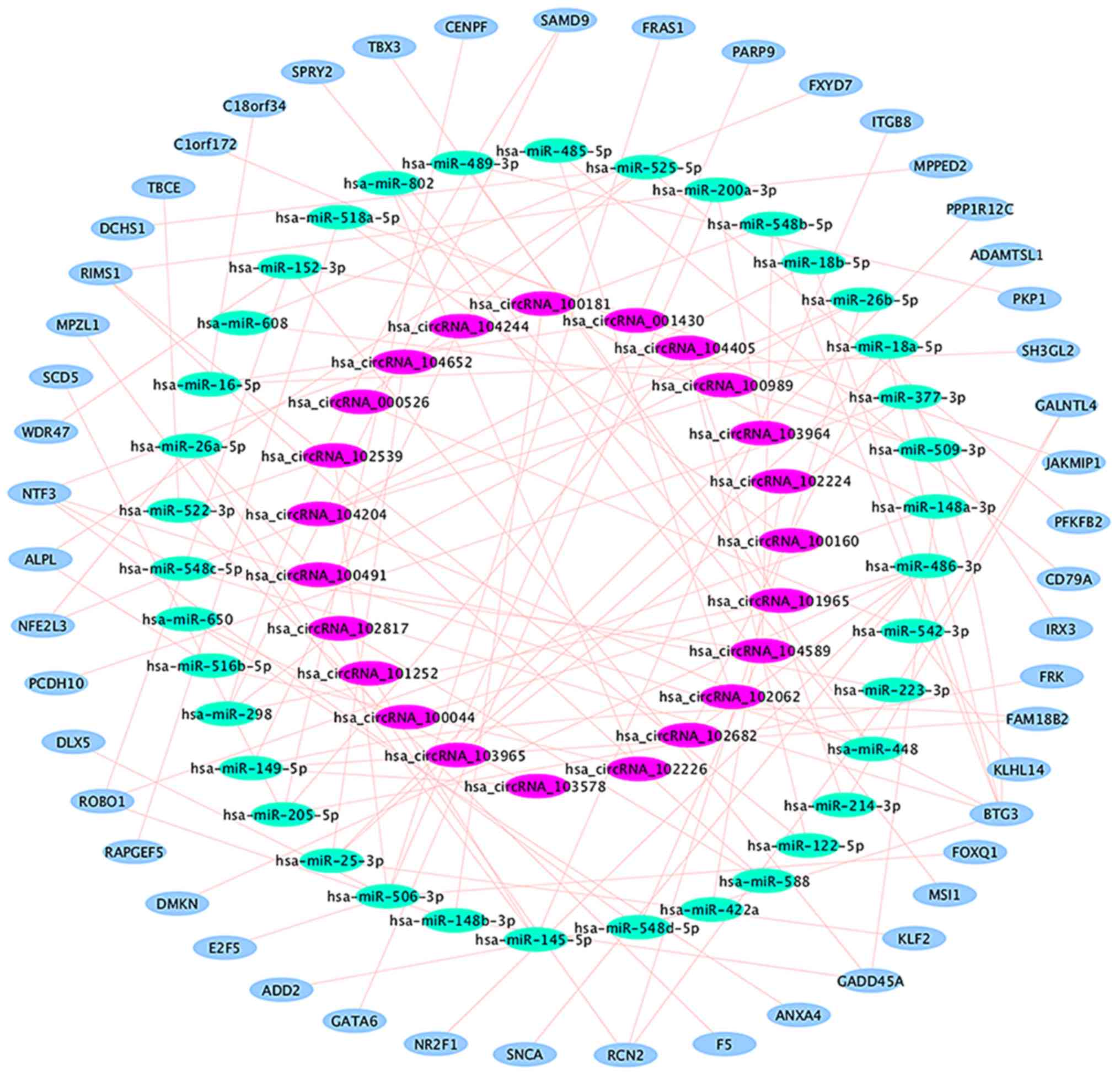
|
1
|
Tsang CM, Lui VWY, Bruce JP, Pugh TJ and
Lo KW: Translational genomics of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. Sep 12–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun
Y and Ma J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 394:64–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wilusz JE and Sharp PA: A circuitous route
to noncoding RNA. Science. 340:440–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu J and Hann SS: Functions and roles of
long-non-coding RNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 45:1191–1204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS and Slack FJ:
Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:5–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li LJ, Leng RX, Fan YG, Pan HF and Ye DQ:
Translation of noncoding RNAs: Focus on lncRNAs, pri-miRNAs, and
circRNAs. Exp Cell Res. 361:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang QQ and Deng YF: Long non-coding RNAs
as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in head and neck
cancers. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:1286–1292. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anfossi S, Fu X, Nagvekar R and Calin GA:
MicroRNAs, regulatory messengers inside and outside cancer cells.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1056:87–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zang J, Lu D and Xu A: The interaction of
circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA
maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 98:87–97. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gong Z, Yang Q, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Li X, Zu
X, Deng H, Chen P, Liao Q, Xiang B, et al: An integrative
transcriptomic analysis reveals p53 regulated miRNA, mRNA, and
lncRNA networks in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:3683–3695. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma DD, Yuan LL and Lin LQ: lncRNA HOTAIR
contributes to the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via
up-regulating FASN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:5143–5152.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang ZZ, Cao HC, Huang DL, Chen XF, Wan J
and Zhang W: MicroRNA-200c plays an oncogenic role in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting PTEN. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177036552017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shuai M, Hong J, Huang D, Zhang X and Tian
Y: Upregulation of circRNA_0000285 serves as a prognostic biomarker
for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is involved in radiosensitivity.
Oncol Lett. 16:6495–6501. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paul P, Deka H, Malakar AK, Halder B and
Chakraborty S: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Understanding its
molecular biology at a fine scale. Eur J Cancer Prev. 27:33–41.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nicolas FE: Role of ncRNAs in development,
diagnosis and treatment of human cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug
Discov. 12:128–135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT and
Kjems J: Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in
the field. Oncogene. 37:555–565. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du WW, Zhang C, Yang W, Yong T, Awan FM
and Yang BB: Identifying and characterizing circRNA-protein
interaction. Theranostics. 7:4183–4191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu M, Zhu K, Qian X and Li W:
Identification of miRNA/mRNA-negative regulation pairs in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 22:2215–2234. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Liu J, Fu X and Yang A:
Identification of key genes and pathways in tongue squamous cell
carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Med Sci Monit.
23:5924–5932. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lim SY, Yuzhalin AE, Gordon-Weeks AN and
Muschel RJ: Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 signaling axis in cancer
metastasis. Oncotarget. 7:28697–28710. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang ZQ, Zang WD, Chen R, Ye BW, Wang XW,
Yi SH, Chen W, He F and Ye G: Gene expression profile and
enrichment pathways in different stages of bladder cancer. Genet
Mol Res. 12:1479–1489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okai I, Wang L, Gong L, Arko-Boham B, Hao
L, Zhou X, Qi X, Hu J and Shao S: Overexpression of JAKMIP1
associates with Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation and promotes
cancer cell proliferation in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother.
67:228–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu X, Zhao Y, Wei L, Zhu B, Song D, Wang
J, Yu L and Wu J: CCDC178 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis through modulation of anoikis. Oncogene. 36:4047–4059.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alajez NM, Lenarduzzi M, Ito E, Hui AB,
Shi W, Bruce J, Yue S, Huang SH, Xu W, Waldron J, et al: MiR-218
suppresses nasopharyngeal cancer progression through downregulation
of survivin and the SLIT2-ROBO1 pathway. Cancer Res. 71:2381–2391.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ying J, Li H, Seng TJ, Langford C,
Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Putti T, Murray P, Chan AT and Tao Q:
Functional epigenetics identifies a protocadherin PCDH10 as a
candidate tumor suppressor for nasopharyngeal, esophageal and
multiple other carcinomas with frequent methylation. Oncogene.
25:1070–1080. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cao JY, Liu L, Chen SP, Zhang X, Mi YJ,
Liu ZG, Li MZ, Zhang H, Qian CN, Shao JY, et al: Prognostic
significance and therapeutic implications of centromere protein F
expression in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
9:2372010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|