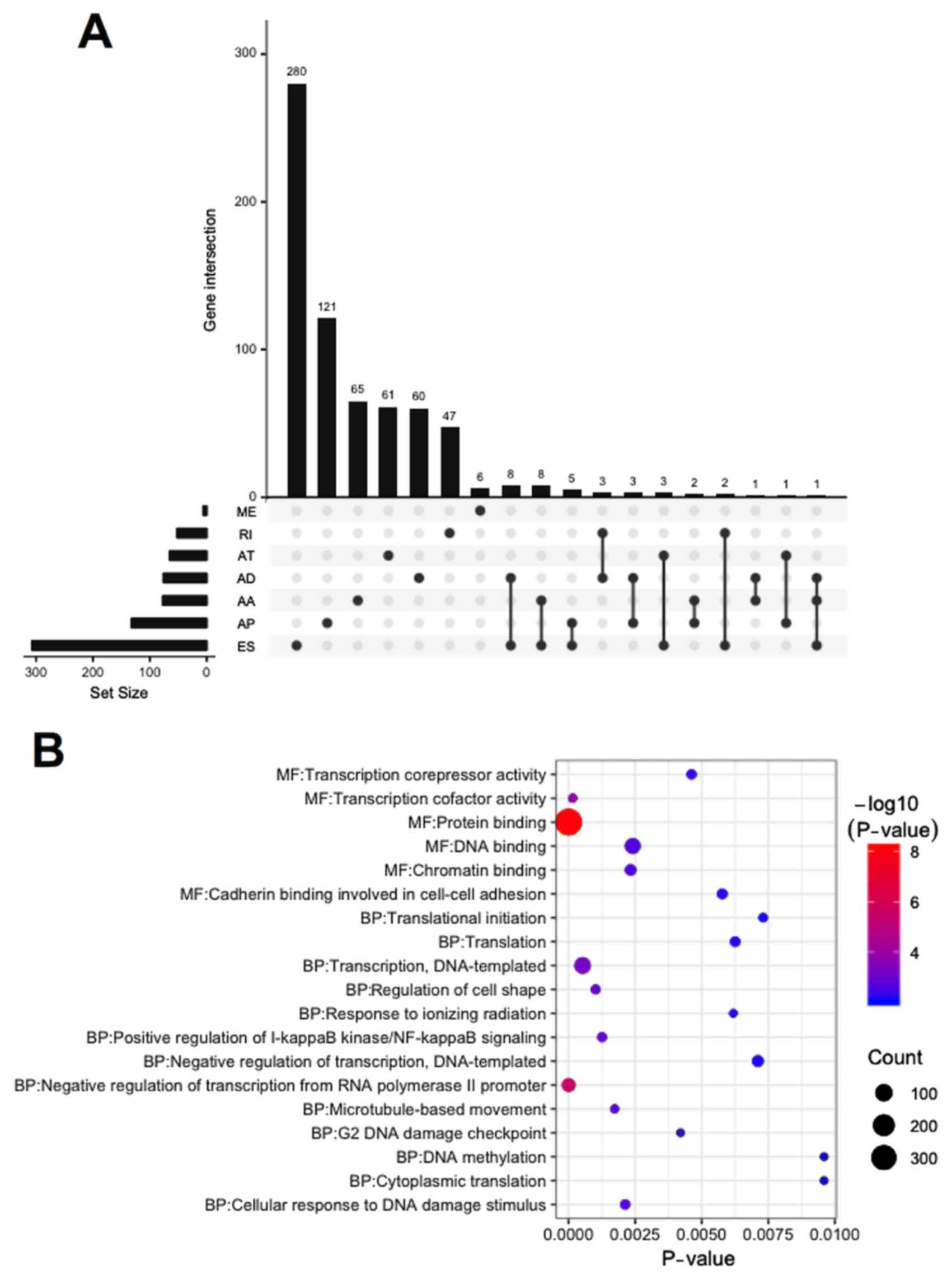
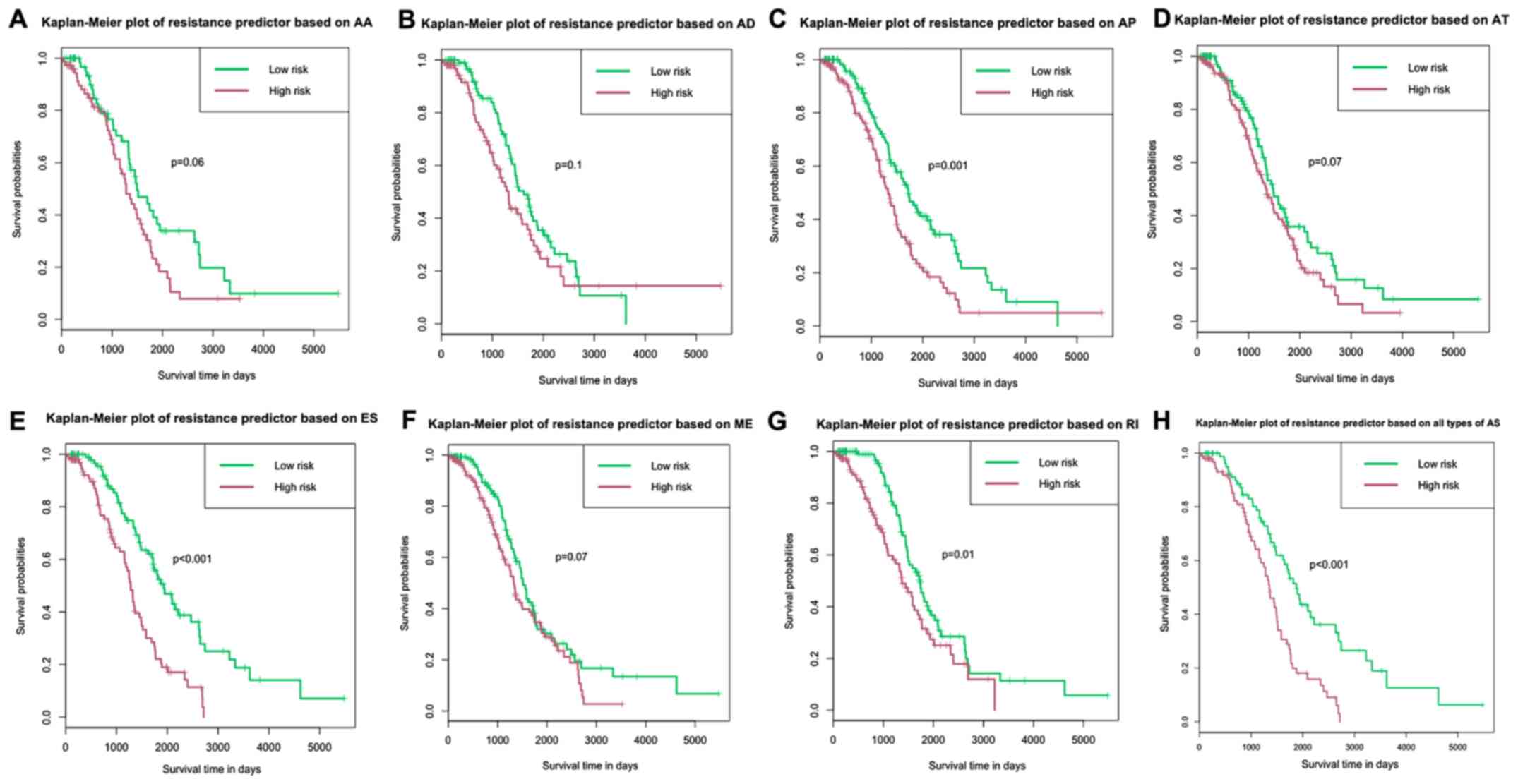
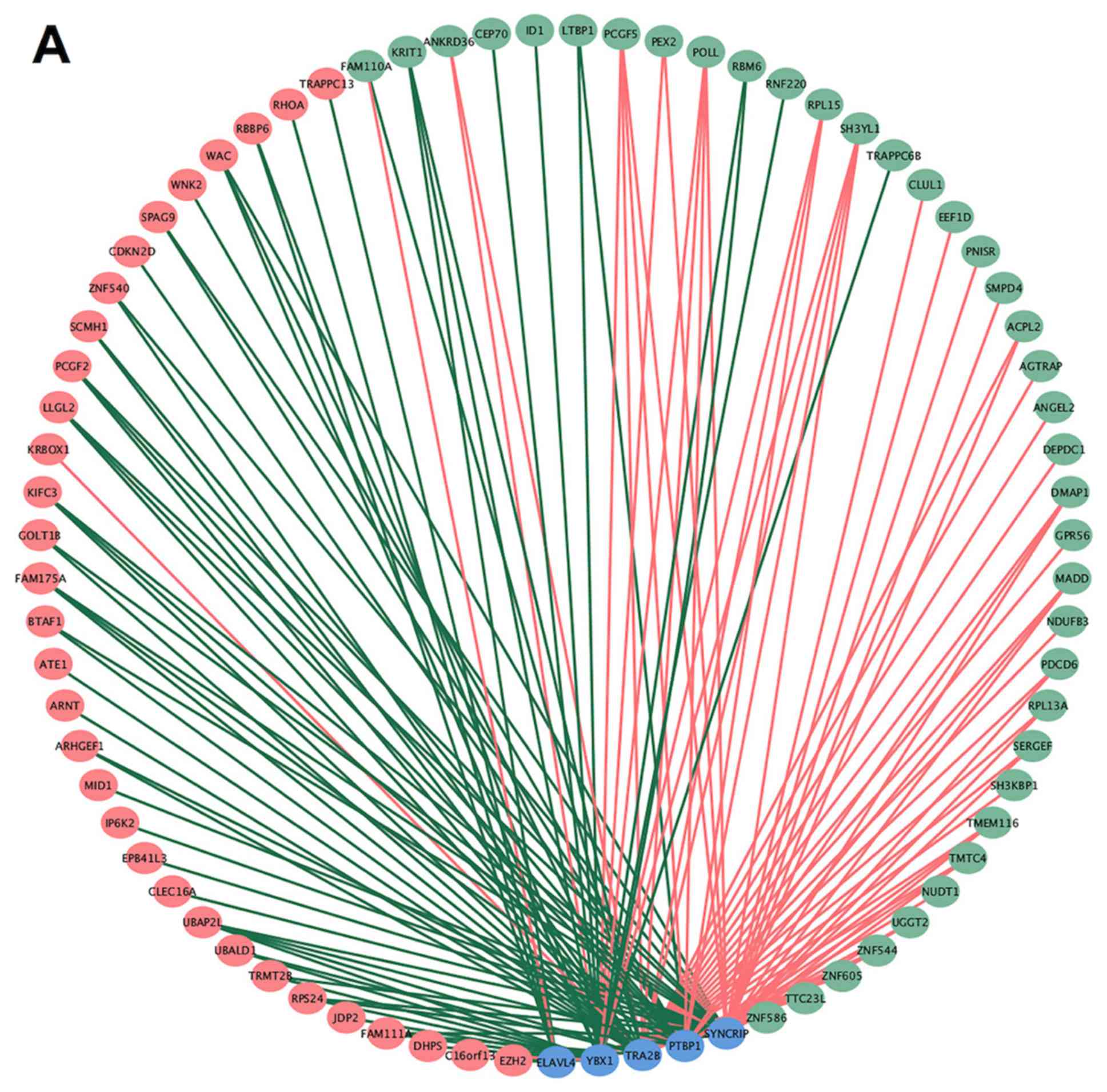
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jessmon P, Boulanger T, Zhou W and
Patwardhan P: Epidemiology and treatment patterns of epithelial
ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:427–437. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bowtell DD, Böhm S, Ahmed AA, Aspuria PJ,
Bast RC, Beral V, Berek JS, Birrer MJ, Blagden S, Bookman MA, et
al: Rethinking ovarian cancer II: Reducing mortality from
high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:668–679. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ryner L, Guan Y, Firestein R, Xiao Y, Choi
Y, Rabe C, Lu S, Fuentes E, Huw LY, Lackner MR, et al: Upregulation
of Periostin and reactive Stroma is associated with primary
chemoresistance and predicts clinical outcomes in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2941–2951. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muñoz-Galván S, Felipe-Abrio B,
García-Carrasco M, Domínguez-Piñol J, Suarez-Martinez E,
Verdugo-Sivianes EM, Espinosa-Sánchez A, Navas LE, Otero-Albiol D,
Marin JJ, et al: New markers for human ovarian cancer that link
platinum resistance to the cancer stem cell phenotype and define
new therapeutic combinations and diagnostic tools. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:2342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Zyl B, Tang D and Bowden NA:
Biomarkers of platinum resistance in ovarian cancer: What can we
use to improve treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 25:R303–R318. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shu T, Li Y, Wu X, Li B and Liu Z:
Down-regulation of HECTD3 by HER2 inhibition makes serous ovarian
cancer cells sensitive to platinum treatment. Cancer Lett.
411:65–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bai L, Wang A, Zhang Y, Xu X and Zhang X:
Knockdown of MALAT1 enhances chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer
cells to cisplatin through inhibiting the Notch1 signaling pathway.
Exp Cell Res. 366:161–171. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai H, Cao D, Yang J, Li M, Zhang Z and
Shen K: Genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity of epithelial ovarian
cancer and the clinical implications for molecular targeted
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 20:581–593. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Konecny GE, Winterhoff B and Wang C:
Gene-expression signatures in ovarian cancer: Promise and
challenges for patient stratification. Gynecol Oncol. 141:379–385.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chon HS and Lancaster JM: Microarray-based
gene expression studies in ovarian cancer. Cancer Control. 18:8–15.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Salton M and Misteli T: Small molecule
modulators of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med.
22:28–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Narayanan SP, Singh S and Shukla S: A saga
of cancer epigenetics: Linking epigenetics to alternative splicing.
Biochem J. 474:885–896. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nilsen TW and Graveley BR: Expansion of
the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature.
463:457–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakka K, Ghigna C, Gabellini D and
Dilworth FJ: Diversification of the muscle proteome through
alternative splicing. Skelet Muscle. 8:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang SH, Elemento O, Zhang J, Zhuang ZW,
Simons M and Hla T: ELAVL1 regulates alternative splicing of eIF4E
transporter to promote postnatal angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:18309–18314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Nie H, Ma X and Xu Z:
Alternative splicing of inner-ear-expressed genes. Front Med.
10:250–257. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin L, Park JW, Ramachandran S, Zhang Y,
Tseng YT, Shen S, Waldvogel HJ, Curtis MA, Faull RL, Troncoso JC,
et al: Transcriptome sequencing reveals aberrant alternative
splicing in Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 25:3454–3466.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Urbanski LM, Leclair N and Anczuków O:
Alternative-splicing defects in cancer: Splicing regulators and
their downstream targets, guiding the way to novel cancer
therapeutics. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 9:e14762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martinez-Montiel N, Rosas-Murrieta NH,
Anaya Ruiz M, Monjaraz-Guzman E and Martinez-Contreras R:
Alternative splicing as a target for cancer treatment. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(pii): E5452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dvinge H, Kim E, Abdel-Wahab O and Bradley
RK: RNA splicing factors as oncoproteins and tumour suppressors.
Nat Rev Cancer. 16:413–430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sveen A, Kilpinen S, Ruusulehto A, Lothe
RA and Skotheim RI: Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer; Expression
changes and driver mutations of splicing factor genes. Oncogene.
35:2413–2427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen S, Wang Y, Wang C, Wu YN and Xing Y:
SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation. Nat Commun.
7:115482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song J, Liu YD, Su J, Yuan D, Sun F and
Zhu J: Systematic analysis of alternative splicing signature
unveils prognostic predictor for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.
J Cell Physiol. 234:22753–22764. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu GQ, Zhou YJ, Qiu LX, Wang B, Yang Y,
Liao WT, Luo YH, Shi YH, Zhou J, Fan J and Dai Z: Prognostic
alternative mRNA splicing signature in hepatocellular carcinoma: A
study based on large-scale sequencing data. Carcinogenesis. May
17–2019.doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz073 (Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu J, Chen Z and Yong L: Systematic
profiling of alternative splicing signature reveals prognostic
predictor for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 148:368–374. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ryan M, Wong WC, Brown R, Akbani R, Su X,
Broom B, Melott J and Weinstein J: TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of
alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:D1018–D1022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Berger AC, Korkut A, Kanchi RS, Hegde AM,
Lenoir W, Liu W, Liu Y, Fan H, Shen H, Ravikumar V, et al: A
Comprehensive Pan-cancer molecular study of gynecologic and breast
cancers. Cancer Cell. 33:690–705.e9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Piva F, Giulietti M, Burini AB and
Principato G: SpliceAid 2: A database of human splicing factors
expression data and RNA target motifs. Hum Mutat. 33:81–85. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Akaike H: Information theory and an
extension of the maximum likelihood principle. 2nd Int. Sympo. on
Information Theor, 1972. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-0919-5_38
|
|
33
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goebel G, Berger R, Strasak AM, Egle D,
Müller-Holzner E, Schmidt S, Rainer J, Presul E, Parson W, Lang S,
et al: Elevated mRNA expression of CHAC1 splicing variants is
associated with poor outcome for breast and ovarian cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 106:189–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bhattacharya R, Mitra T, Ray Chaudhuri S
and Roy SS: Mesenchymal splice isoform of CD44 (CD44s) promotes
EMT/invasion and imparts stem-like properties to ovarian cancer
cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:3373–3383. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Upheber S, Karle A, Miller J, Schlaugk S,
Gross E and Reuning U: Alternative splicing of KAI1 abrogates its
tumor-suppressive effects on integrin αvβ3-mediated ovarian cancer
biology. Cell Signal. 27:652–662. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Markman M: Antineoplastic agents in the
management of ovarian cancer: Current status and emerging
therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:515–519. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
He X, Ee PL, Coon JS and Beck WT:
Alternative splicing of the multidrug resistance protein 1/ATP
binding cassette transporter subfamily gene in ovarian cancer
creates functional splice variants and is associated with increased
expression of the splicing factors PTB and SRp20. Clin Cancer Res.
10:4652–4660. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun Y, Li T, Ma K, Tian Z, Zhu Y, Chen F
and Hu G: The impacts of ERCC1 gene exon VIII alternative splicing
on cisplatin-resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Invest.
27:891–897. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao H, Sun Q, Li L, Zhou J, Zhang C, Hu
T, Zhou X, Zhang L, Wang B, Li B, et al: High expression levels of
AGGF1 and MFAP4 predict primary platinum-based chemoresistance and
are associated with adverse prognosis in patients with serous
ovarian cancer. J Cancer. 10:397–407. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu R, Zeng Y, Zhou CF, Wang Y, Li X, Liu
ZQ, Chen XP, Zhang W and Zhou HH: Long noncoding RNA expression
signature to predict platinum-based chemotherapeutic sensitivity of
ovarian cancer patients. Sci Rep. 7:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Matte I, Garde-Granger P, Bessette P and
Piché A: Serum CA125 and ascites leptin level ratio predicts
baseline clinical resistance to first-line platinum-based treatment
and poor prognosis in patients with high grade serous ovarian
cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 9:160–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|