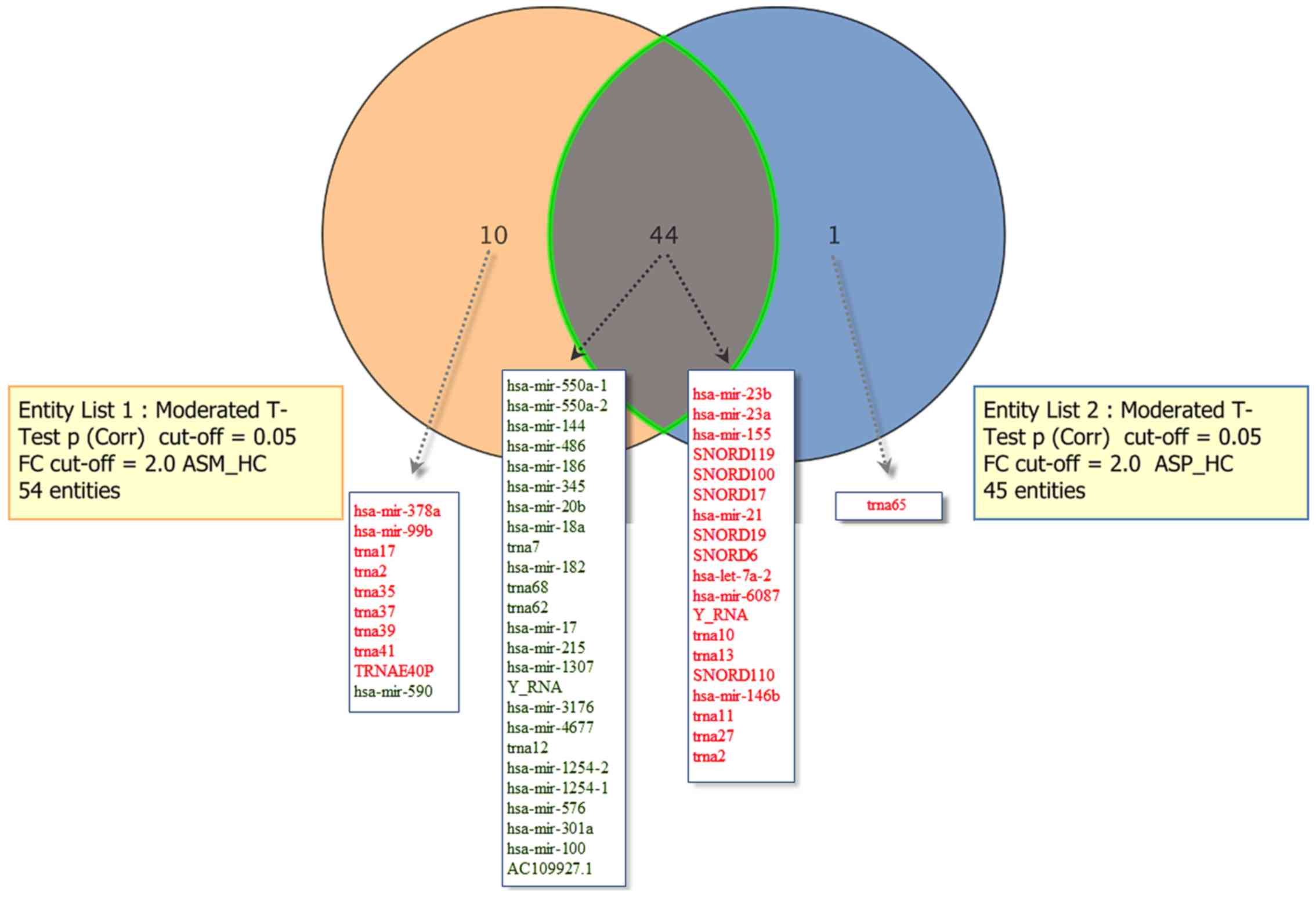
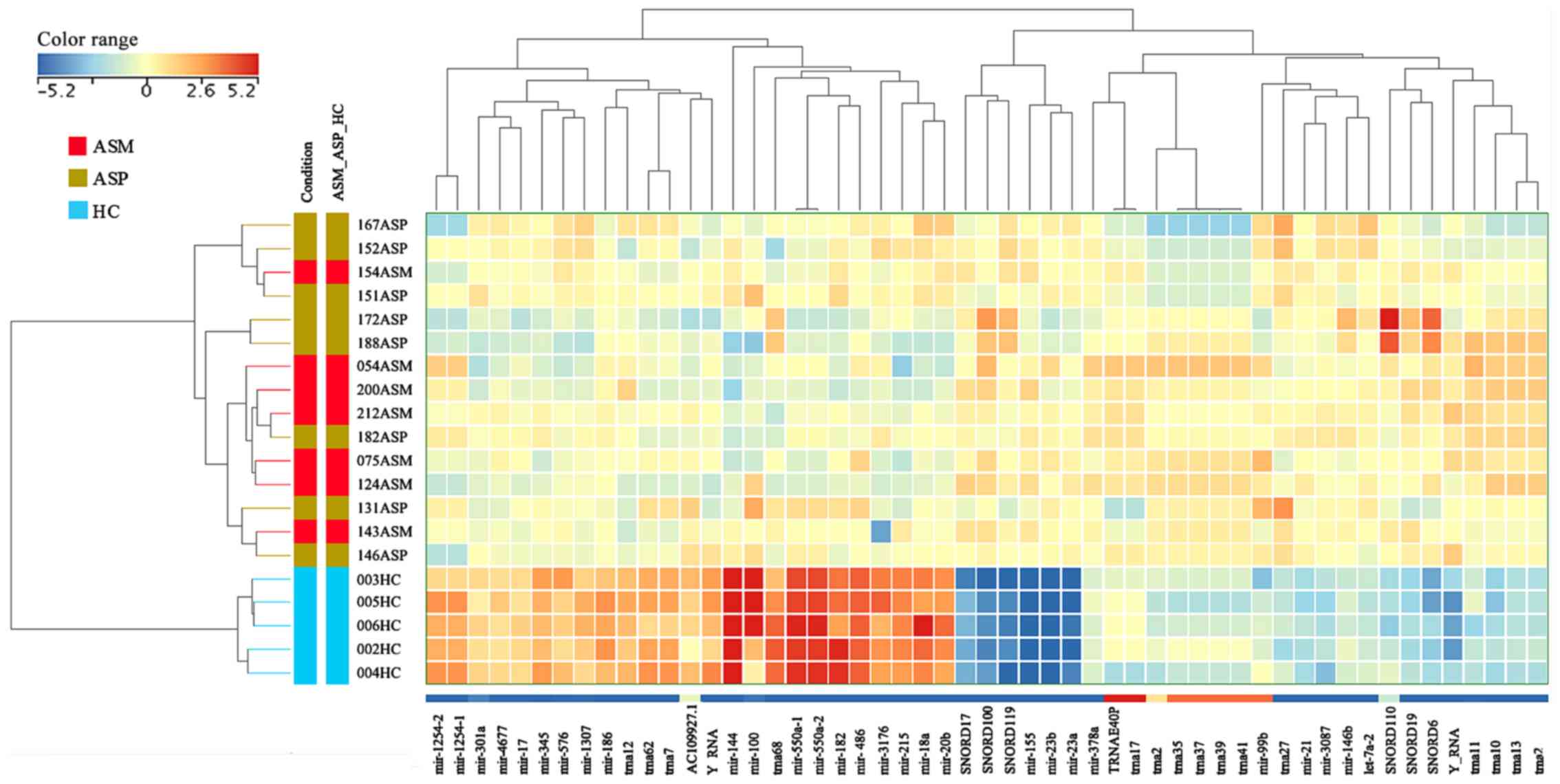
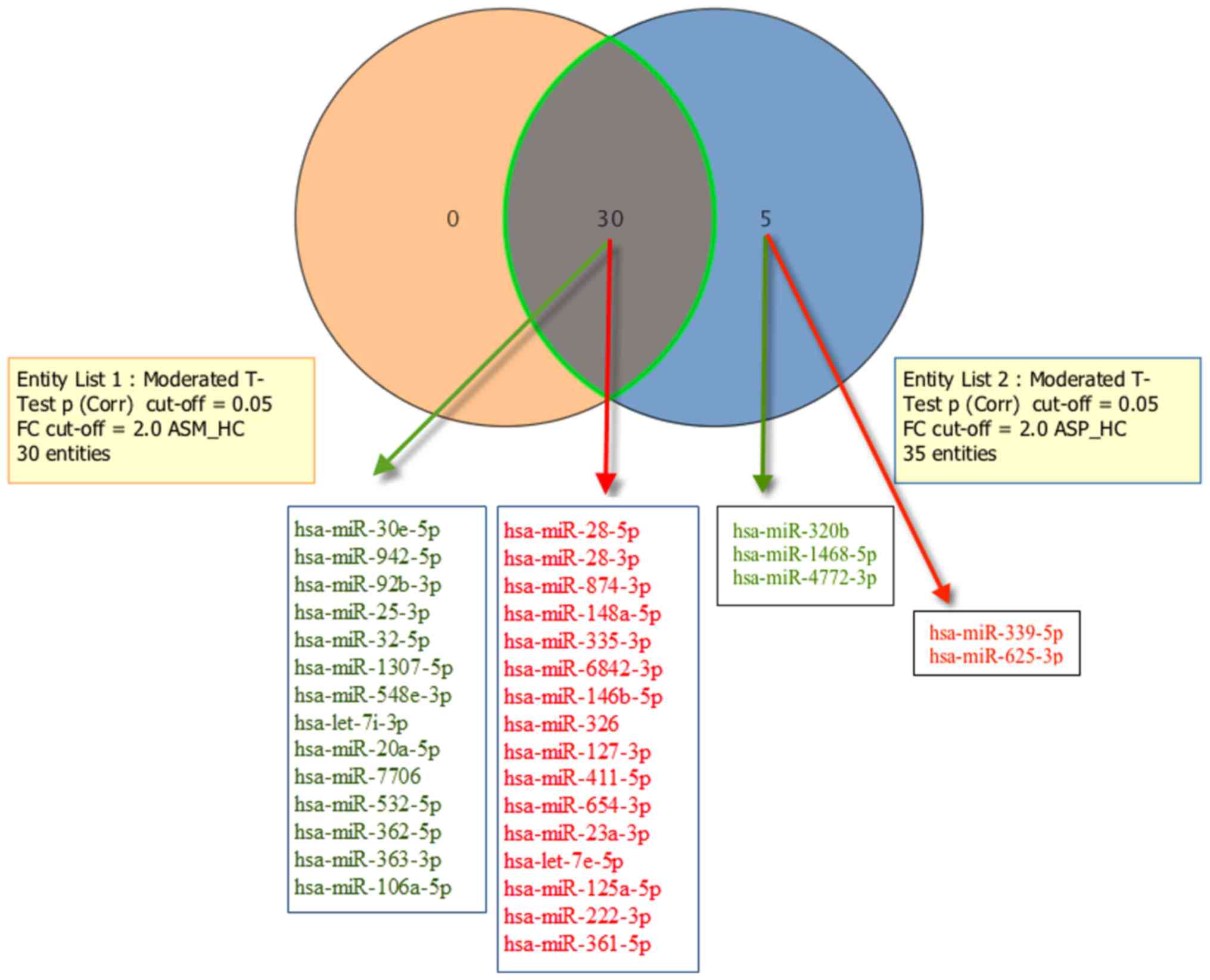
|
1
|
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn
PA, Minna JD and Gallo RC: Detection and isolation of type C
retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a
patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
77:7415–7419. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gessain A and Cassar O: Epidemiological
aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front
Microbiol. 3:3882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsuoka M: Human T-cell leukemia virus
type I and adult T-cell leukemia. Oncogene. 22:5131–5140. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verdonck K, Gonzalez E, Van Dooren S,
Vandamme AM, Vanham G and Gotuzzo E: Human T-lymphotropic virus 1:
Recent knowledge about an ancient infection. Lancet Infect Dis.
7:266–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Franchini G, Ambinder RF and Barry M:
Viral disease in hematology. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 409–423. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murphy EL, Hanchard B, Figueroa JP, Gibbs
WN, Lofters WS, Campbell M, Goedert JJ and Blattner WA: Modelling
the risk of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in persons infected with
human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Int J Cancer. 43:250–253. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamaguchi K and Watanabe T: Human T
lymphotropic virus type-I and adult T-cell leukemia in Japan. Int J
Hematol. 76 (Suppl 2):240–245. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsuoka M and Jeang KT: Human T-cell
leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular
transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:270–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Higuchi M and Fujii M: Distinct functions
of HTLV-1 Tax1 from HTLV-2 Tax2 contribute key roles to viral
pathogenesis. Retrovirology. 6:1172009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshida M, Seiki M, Yamaguchi K and
Takatsuki K: Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia
provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests
causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:2534–2537. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takeda S, Maeda M, Morikawa S, Taniguchi
Y, Yasunaga J, Nosaka K, Tanaka Y and Matsuoka M: Genetic and
epigenetic inactivation of tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells.
Int J Cancer. 109:559–567. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mesnard JM, Barbeau B and Devaux C: HBZ, a
new important player in the mystery of adult T-cell leukemia.
Blood. 108:3979–3982. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagata Y, Kontani K, Enami T, Kataoka K,
Ishii R, Totoki Y, Kataoka TR, Hirata M, Aoki K, Nakano K, et al:
Variegated RHOA mutations in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood.
127:596–604. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Etoh K, Yamaguchi K, Tokudome S, Watanabe
T, Okayama A, Stuver N, Mueller N, Takatsuki K and Matsuoka M:
Rapid quantification of HTLV–I provirus load: Detection of
monoclonal proliferation of HTLV–I-infected cells among blood
donors. Int J Cancer. 81:859–864. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohshima K, Mukai Y, Shiraki H, Suzumiya J,
Tashiro K and Kikuchi M: Clonal integration and expression of human
T-cell lymphotropic virus type I in carriers detected by polymerase
chain reaction and inverse PCR. Am J Hematol. 54:306–312. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Furukawa Y, Fujisawa J, Osame M, Toita M,
Sonoda S, Kubota R, Ijichi S and Yoshida M: Frequent clonal
proliferation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
(HTLV-1)-infected T cells in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy
(HAM-TSP). Blood. 80:1012–1016. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ikeda S, Momita S, Kinoshita K, Kamihira
S, Moriuchi Y, Tsukasaki K, Ito M, Kanda T, Moriuchi R, Nakamura T,
et al: Clinical course of human T-lymphotropic virus type I
carriers with molecularly detectable monoclonal proliferation of T
lymphocytes: Defining a low- and high-risk population. Blood.
82:2017–2024. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carvalho EM and Da Fonseca Porto A:
Epidemiological and clinical interaction between HTLV-1 and
Strongyloides stercoralis. Parasite Immunol. 26:487–497. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS,
Urban AE, Zhu X, Rinn JL, Tongprasit W, Samanta M, Weissman S, et
al: Global identification of human transcribed sequences with
genome tiling arrays. Science. 306:2242–2246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Lassmann T,
Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F, Xue C, et
al: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature. 489:101–108.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higuchi C, Nakatsuka A, Eguchi J,
Teshigawara S, Kanzaki M, Katayama A, Yamaguchi S, Takahashi N,
Murakami K, Ogawa D, et al: Identification of circulating miR-101,
miR-375 and miR-802 as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes. Metabolism.
64:489–497. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Qi X,
Richardson JA, Hill J and Olson EN: Control of stress-dependent
cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science.
316:575–579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang WC, Chin TM, Yang H, Nga ME, Lunny
DP, Lim EK, Sun LL, Pang YH, Leow YN, Malusay SR, et al:
Tumour-initiating cell-specific miR-1246 and miR-1290 expression
converge to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat
Commun. 7:117022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Farazi TA, Juranek SA and Tuschl T: The
growing catalog of small RNAs and their association with distinct
Argonaute/Piwi family members. Development. 135:1201–1214. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mattick JS and Makunin IV: Non-coding RNA.
Hum Mol Genet 15 (Spec No 1). R17–R29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ambros V, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Burge CB,
Carrington JC, Chen X, Dreyfuss G, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S,
Marshall M, et al: A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA.
9:277–279. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Bateman A, Marshall M,
Khanna A and Eddy SR: Rfam: An RNA family database. Nucleic Acids
Res. 31:439–441. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Wu B, Xu J and Liu C: Genome-wide
identification and characterization of long intergenic non-coding
RNAs in Ganoderma lucidum. PLoS One. 9:e994422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell
RB and Cohen SM: Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated
microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the
proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 113:25–36. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wienholds E, Koudijs MJ, van Eeden FJ,
Cuppen E and Plasterk RH: The microRNA-producing enzyme Dicer1 is
essential for zebrafish development. Nat Genet. 35:217–218. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M and Hay BA: The
Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required
for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol. 13:790–795. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bandiera S, Hatem E, Lyonnet S and
Henrion-Caude A: microRNAs in diseases: From candidate to modifier
genes. Clin Genet. 77:306–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bueno MJ and Malumbres M: MicroRNAs and
the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812:592–601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pichler K, Schneider G and Grassmann R:
MicroRNA miR-146a and further oncogenesis-related cellular
microRNAs are dysregulated in HTLV-1-transformed T lymphocytes.
Retrovirology. 5:1002008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yeung ML, Yasunaga J, Bennasser Y, Dusetti
N, Harris D, Ahmad N, Matsuoka M and Jeang KT: Roles for microRNAs,
miR-93 and miR-130b, and tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1
tumor suppressor in cell growth dysregulation by human T-cell
lymphotrophic virus 1. Cancer Res. 68:8976–8985. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ruggero K, Corradin A, Zanovello P,
Amadori A, Bronte V, Ciminale V and D'Agostino DM: Role of
microRNAs in HTLV-1 infection and transformation. Mol Aspects Med.
31:367–382. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bellon M, Lepelletier Y, Hermine O and
Nicot C: Deregulation of microRNA involved in hematopoiesis and the
immune response in HTLV–I adult T-cell leukemia. Blood.
113:4914–4917. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ruggero K, Guffanti A, Corradin A, Sharma
VK, De Bellis G, Corti G, Grassi A, Zanovello P, Bronte V, Ciminale
V and D'Agostino DM: Small noncoding RNAs in cells transformed by
human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: A role for a tRNA fragment as a
primer for reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 88:3612–3622. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Heneine W, Khabbaz RF, Lal RB and Kaplan
JE: Sensitive and specific polymerase chain reaction assays for
diagnosis of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV–I) and
HTLV–II infections in HTLV–I/II-seropositive individuals. J Clin
Microbiol. 30:1605–1607. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pessoa R, Watanabe JT, Nukui Y, Pereira J,
Casseb J, de Oliveira AC, Segurado AC and Sanabani SS: Molecular
characterization of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 full and
partial genomes by Illumina massively parallel sequencing
technology. PLoS One. 9:e933742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shadrach B and Warshawsky I: A comparison
of multiplex and monoplex T-cell receptor gamma PCR. Diagn Mol
Pathol. 13:127–134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Clissa PB, Pessoa R, Ferraz KF, de Souza
DR and Sanabani SS: Data on global expression of non-coding RNome
in mice gastrocnemius muscle exposed to jararhagin, snake venom
metalloproteinase. Data Brief. 9:685–688. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Langenberger D, Bermudez-Santana CI,
Stadler PF and Hoffmann S: Identification and classification of
small RNAs in transcriptome sequence data. Pac Symp Biocomput.
80–87. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hansen KD, Irizarry RA and Wu Z: Removing
technical variability in RNA-seq data using conditional quantile
normalization. Biostatistics. 13:204–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mestdagh P, Hartmann N, Baeriswyl L,
Andreasen D, Bernard N, Chen C, Cheo D, D'Andrade P, DeMayo M,
Dennis L, et al: Evaluation of quantitative miRNA expression
platforms in the microRNA quality control (miRQC) study. Nat
Methods. 11:809–815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Motameny S, Wolters S, Nürnberg P and
Schumacher B: Next Generation Sequencing of miRNAs-Strategies,
Resources and Methods. Genes (Basel). 1:70–84. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dias S, Hemmings S, Muller C, Louw J and
Pheiffer C: MicroRNA expression varies according to glucose
tolerance, measurement platform, and biological source. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:10801572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Leshkowitz D, Horn-Saban S, Parmet Y and
Feldmesser E: Differences in microRNA detection levels are
technology and sequence dependent. RNA. 19:527–538. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tsukasaki K, Tsushima H, Yamamura M, Hata
T, Murata K, Maeda T, Atogami S, Sohda H, Momita S, Ideda S, et al:
Integration patterns of HTLV–I provirus in relation to the clinical
course of ATL: Frequent clonal change at crisis from indolent
disease. Blood. 89:948–956. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wattel E, Vartanian JP, Pannetier C and
Wain-Hobson S: Clonal expansion of human T-cell leukemia virus type
I-infected cells in asymptomatic and symptomatic carriers without
malignancy. J Virol. 69:2863–2868. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Moles R and Nicot C: The Emerging Role of
miRNAs in HTLV-1 Infection and ATLL Pathogenesis. Viruses.
7:4047–4074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Van Duyne R, Guendel I, Klase Z, Narayanan
A, Coley W, Jaworski E, Roman J, Popratiloff A, Mahieux R,
Kehn-Hall K and Kashanchi F: Localization and sub-cellular
shuttling of HTLV-1 tax with the miRNA machinery. PLoS One.
7:e406622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Abe M, Suzuki H, Nishitsuji H, Shida H and
Takaku H: Interaction of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I Rex
protein with Dicer suppresses RNAi silencing. FEBS Lett.
584:4313–4318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yamagishi M, Nakano K, Miyake A, Yamochi
T, Kagami Y, Tsutsumi A, Matsuda Y, Sato-Otsubo A, Muto S,
Utsunomiya A, et al: Polycomb-mediated loss of miR-31 activates
NIK-dependent NF-kappaB pathway in adult T cell leukemia and other
cancers. Cancer Cell. 21:121–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cameron JE, Fewell C, Yin Q, McBride J,
Wang X, Lin Z and Flemington EK: Epstein-Barr virus growth/latency
III program alters cellular microRNA expression. Virology.
382:257–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cobb BS, Hertweck A, Smith J, O'Connor E,
Graf D, Cook T, Smale ST, Sakaguchi S, Livesey FJ, Fisher AG and
Merkenschlager M: A role for Dicer in immune regulation. J Exp Med.
203:2519–2527. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tomita M, Tanaka Y and Mori N: MicroRNA
miR-146a is induced by HTLV-1 tax and increases the growth of
HTLV-1-infected T-cells. Int J Cancer. 130:2300–2309. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Deng J, He M, Chen L, Chen C, Zheng J and
Cai Z: The loss of miR-26a-mediated post-transcriptional regulation
of cyclin E2 in pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and decreased
patient survival. PLoS One. 8:e764502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Deng M, Tang HL, Lu XH, Liu MY, Lu XM, Gu
YX, Liu JF and He ZM: miR-26a suppresses tumor growth and
metastasis by targeting FGF9 in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
8:e726622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lin Y, Chen H, Hu Z, Mao Y, Xu X, Zhu Y,
Xu X, Wu J, Li S, Mao Q, et al: miR-26a inhibits proliferation and
motility in bladder cancer by targeting HMGA1. FEBS Lett.
587:2467–2473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sander S, Bullinger L, Klapproth K,
Fiedler K, Kestler HA, Barth TF, Möller P, Stilgenbauer S, Pollack
JR and Wirth T: MYC stimulates EZH2 expression by repression of its
negative regulator miR-26a. Blood. 112:4202–4212. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang B, Liu XX, He JR, Zhou CX, Guo M, He
M, Li MF, Chen GQ and Zhao Q: Pathologically decreased miR-26a
antagonizes apoptosis and facilitates carcinogenesis by targeting
MTDH and EZH2 in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:2–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mavrakis KJ, Van Der Meulen J, Wolfe AL,
Liu X, Mets E, Taghon T, Khan AA, Setty M, Rondou P, Vandenberghe
P, et al: A cooperative microRNA-tumor suppressor gene network in
acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Nat Genet. 43:673–678.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Batchu RB, Gruzdyn OV, Qazi AM, Kaur J,
Mahmud EM, Weaver DW and Gruber SA: Enhanced phosphorylation of p53
by microRNA-26a leading to growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer.
Surgery. 158:981–987. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang J, Han C and Wu T: MicroRNA-26a
promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth by activating β-catenin.
Gastroenterology. 143:246–256.e8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Salvatori B, Iosue I, Mangiavacchi A,
Loddo G, Padula F, Chiaretti S, Peragine N, Bozzoni I, Fazi F and
Fatica A: The microRNA-26a target E2F7 sustains cell proliferation
and inhibits monocytic differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia
cells. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Luzi E, Marini F, Sala SC, Tognarini I,
Galli G and Brandi ML: Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose
tissue-derived stem cells is modulated by the miR-26a targeting of
the SMAD1 transcription factor. J Bone Miner Res. 23:287–295. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chai ZT, Kong J, Zhu XD, Zhang YY, Lu L,
Zhou JM, Wang LR, Zhang KZ, Zhang QB, Ao JY, et al: MicroRNA-26a
inhibits angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGFA through the
PIK3C2α/Akt/HIF-1α pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e779572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Qian X, Zhao P, Li W, Shi ZM, Wang L, Xu
Q, Wang M, Liu N, Liu LZ and Jiang BH: MicroRNA-26a promotes tumor
growth and angiogenesis in glioma by directly targeting prohibitin.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 19:804–812. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M,
Felli N, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Cimmino A, Zupo S, Dono M, et al:
MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic
lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11755–11760.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fukuda RI, Tsuchiya K, Suzuki K, Itoh K,
Fujita J, Utsunomiya A and Tsuji T: HTLV–I Tax regulates the
cellular proliferation through the down-regulation of
PIP3-phosphatase expressions via the NF-κB pathway. Int J Biochem
Mol Biol. 3:95–104. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu L, Wang S, Chen R, Wu Y, Zhang B,
Huang S, Zhang J, Xiao F, Wang M and Liang Y: Myc induced
miR-144/451 contributes to the acquired imatinib resistance in
chronic myelogenous leukemia cell K562. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
425:368–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Whitman SP, Maharry K, Radmacher MD,
Becker H, Mrózek K, Margeson D, Holland KB, Wu YZ, Schwind S,
Metzeler KH, et al: FLT3 internal tandem duplication associates
with adverse outcome and gene- and microRNA-expression signatures
in patients 60 years of age or older with primary cytogenetically
normal acute myeloid leukemia: A Cancer and Leukemia Group B study.
Blood. 116:3622–3626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bai XT and Nicot C: miR-28-3p is a
cellular restriction factor that inhibits human T cell leukemia
virus, type 1 (HTLV-1) replication and virus infection. J Biol
Chem. 290:5381–5390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen L, Han L, Wei J, Zhang K, Shi Z, Duan
R, Li S, Zhou X, Pu P, Zhang J and Kang C: SNORD76, a box C/D
snoRNA, acts as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma. Sci Rep.
5:85882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Koduru SV, Tiwari AK, Leberfinger A,
Hazard SW, Kawasawa YI, Mahajan M and Ravnic DJ: A Comprehensive
NGS data analysis of differentially regulated miRNAs, piRNAs,
lncRNAs and sn/snoRNAs in triple negative breast cancer. J Cancer.
8:578–596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|