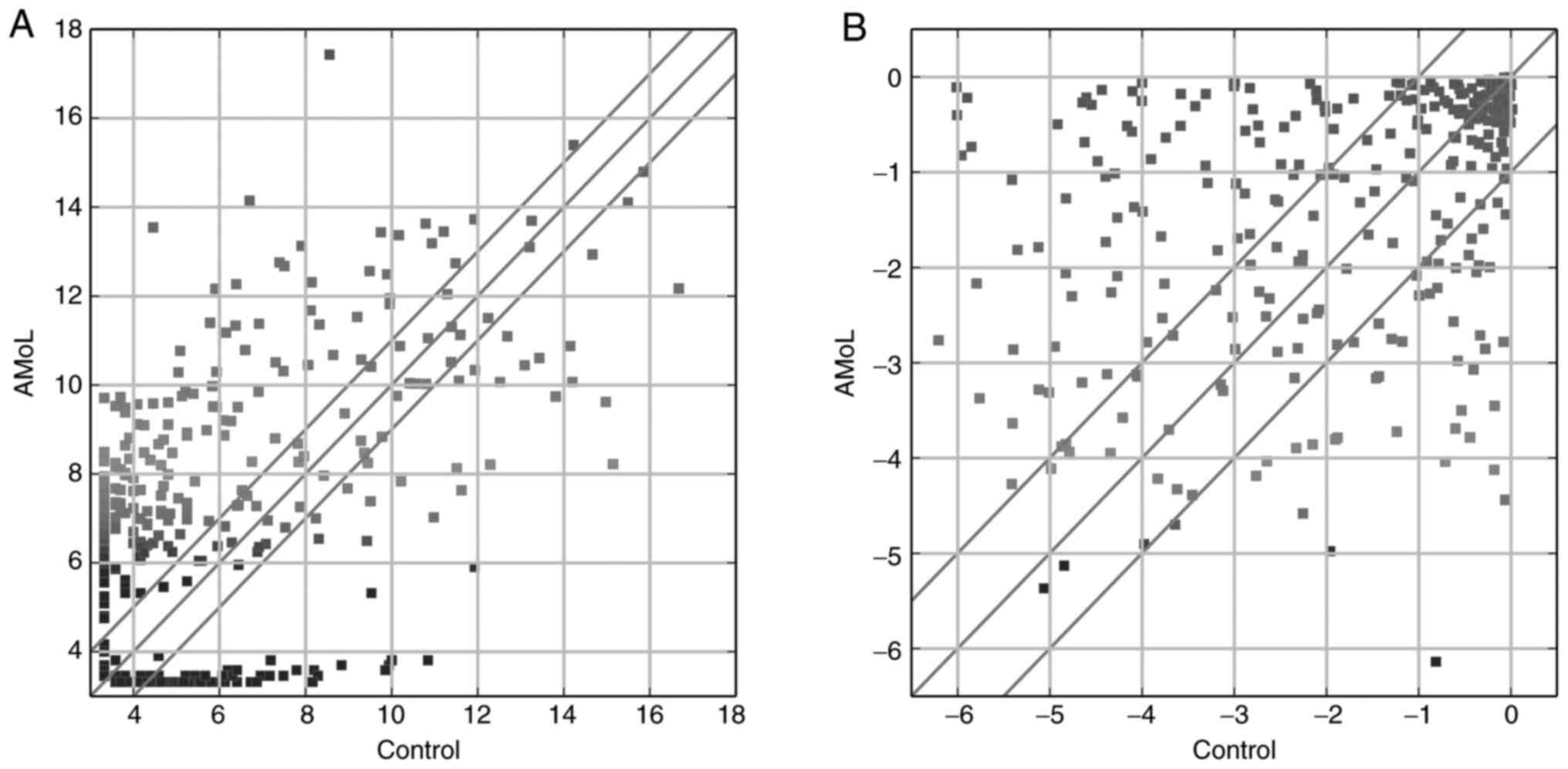
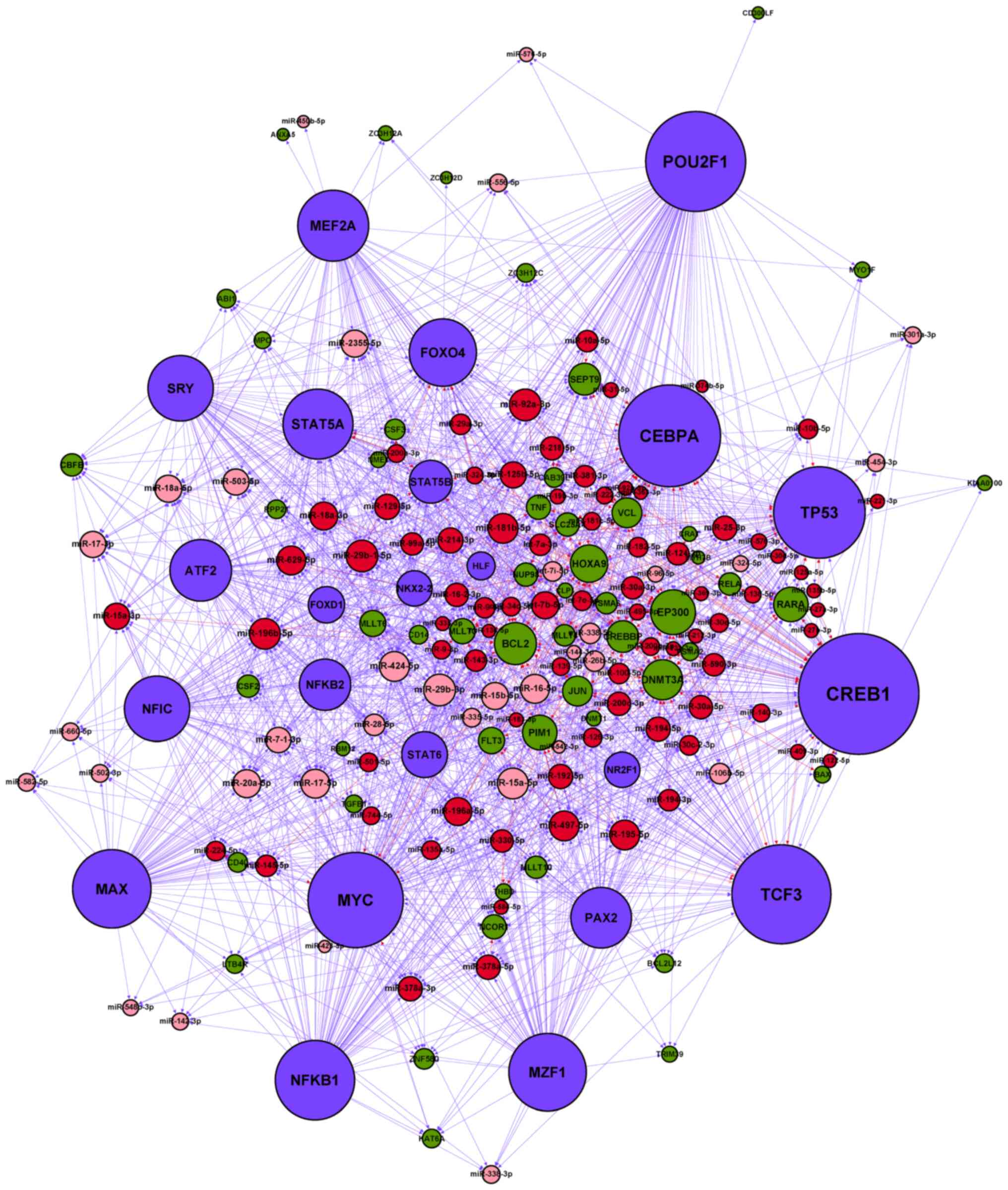
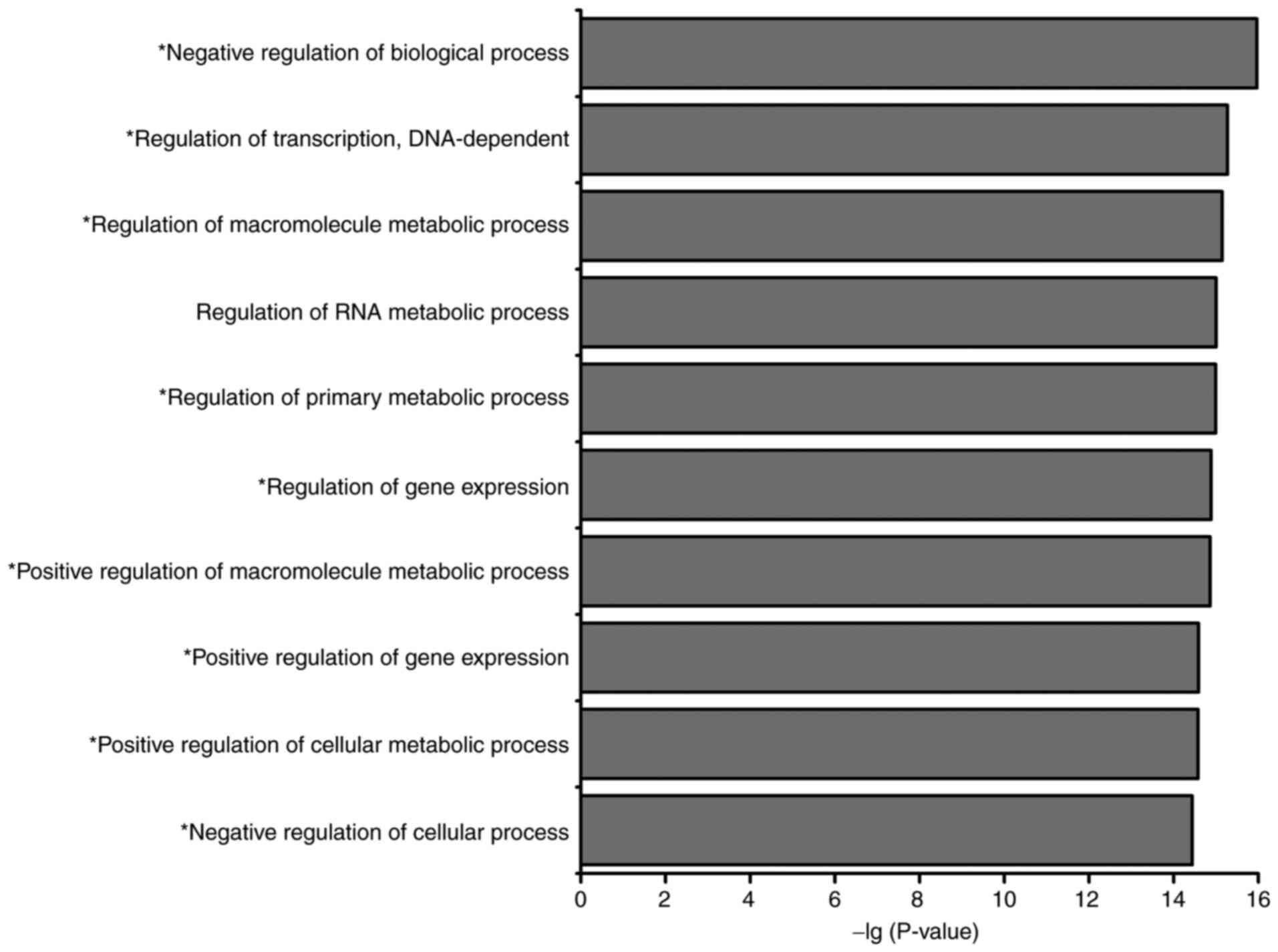
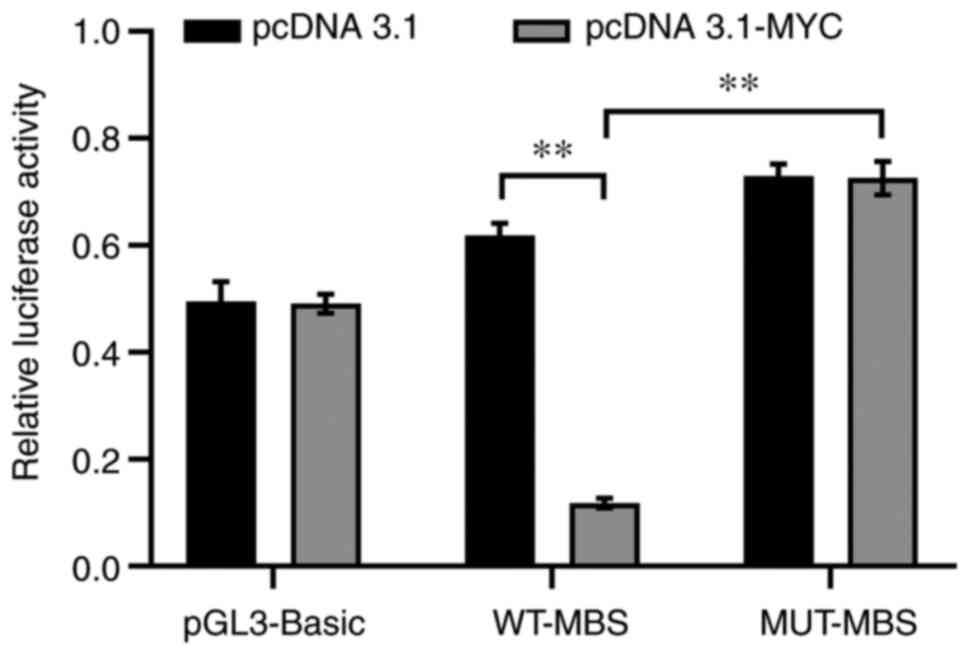
|
1
|
Villeneuve P, Kim DT, Xu W, Brandwein J
and Chang H: The morphological subcategories of acute monocytic
leukemia (M5a and M5b) share similar immunophenotypic and
cytogenetic features and clinical outcomes. Leuk Res. 32:269–273.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y, Ma L, Wang C, Sheng G, Feng L and
Yin C: Autocrine motility factor receptor promotes the
proliferation of human acute monocytic leukemia THP-1 cells. Int J
Mol Med. 36:627–632. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Migliavacca J, Percio S, Valsecchi R,
Ferrero E, Spinelli A, Ponzoni M, Tresoldi C, Pattini L, Bernardi R
and Coltella N: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α regulates a
pro-invasive phenotype in acute monocytic leukemia. Oncotarget.
7:53540–53557. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xing S, Wang B, Gao Y, Li M, Wang T, Sun
Y, Shen Y and Chao H: Cytogenetics and associated mutation profile
in patients with acute monocytic leukemia. Int J Lab Hematol.
41:485–492. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan XJ, Xu J, Gu ZH, Pan CM, Lu G, Shen Y,
Shi JY, Zhu YM, Tang L, Zhang XW, et al: Exome sequencing
identifies somatic mutations of DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT3A
in acute monocytic leukemia. Nat Genet. 43:309–315. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Rooij E and Kauppinen S: Development
of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med. 6:851–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang HM, Kuang S, Xiong X, Gao T, Liu C
and Guo AY: Transcription factor and microRNA co-regulatory loops:
Important regulatory motifs in biological processes and diseases.
Brief Bioinform. 16:45–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hobert O: Gene regulation by transcription
factors and microRNAs. Science. 319:1785–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang W, Mitra R, Lin CC, Wang Q, Cheng F
and Zhao Z: Systematic dissection of dysregulated transcription
factor-miRNA feed-forward loops across tumor types. Brief
Bioinform. 17:996–1008. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Espadinha AS, Prouzet-Mauléon V, Claverol
S, Lagarde V, Bonneu M, Mahon FX and Cardinaud B: A tyrosine
kinase-STAT5-miR21-PDCD4 regulatory axis in chronic and acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 8:76174–76188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wurm AA, Zjablovskaja P, Kardosova M,
Gerloff D, Bräuer-Hartmann D, Katzerke C, Hartmann JU, Benoukraf T,
Fricke S, Hilger N, et al: Disruption of the C/EBPα-miR-182 balance
impairs granulocytic differentiation. Nat Commun. 8:462017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo M, Zhang Q, Xia M, Hu F, Ma Z, Chen Z
and Guo AY: differential co-expression and regulatory network
analysis uncover the relapse factor and mechanism of t cell acute
leukemia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 12:184–194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin XC, Liu XG, Zhang YM, Li N, Yang ZG,
Fu WY, Lan LB, Zhang HT and Dai Y: Integrated analysis of microRNA
and transcription factor reveals important regulators and
regulatory motifs in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int
J Oncol. 50:671–683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sui W, Lin H, Peng W, Huang Y, Chen J,
Zhang Y and Dai Y: Molecular dysfunctions in acute rejection after
renal transplantation revealed by integrated analysis of
transcription factor, microRNA and long noncoding RNA. Genomics.
102:310–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong M, Wang X, Zhao HL, Chen XL, Yuan JH,
Guo JY, Li KQ and Li G: Integrated analysis of transcription
factor, microRNA and LncRNA in an animal model of obliterative
bronchiolitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7050–7058. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin Y, Wu J, Chen H, Mao Y, Liu Y, Mao Q,
Yang K, Zheng X and Xie L: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 is a novel
target in micoRNA-195-mediated cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer
cells. FEBS Lett. 586:442–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rappaport N, Nativ N, Stelzer G, Twik M,
Guan-Golan Y, Stein TI, Bahir I, Belinky F, Morrey CP, Safran M and
Lancet D: MalaCards: An integrated compendium for diseases and
their annotation. Database (Oxford). 2013:bat0182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Felice B, Cattoglio C, Cittaro D, Testa A,
Miccio A, Ferrari G, Luzi L, Recchia A and Mavilio F: Transcription
factor binding sites are genetic determinants of retroviral
integration in the human genome. PLoS One. 4:e45712009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi YJ, Yoon JH, Cha SW and Lee SG:
Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the invasion and migration of THP-1 acute
monocytic leukemia cells via inactivation of the MAPK signaling
pathway. Fitoterapia. 82:911–919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Zhang J, Wang Q, Zhang T, Yang Y,
Yi Y, Gao G, Dong H, Zhu H, Li Y, et al: Bryostatin 5 induces
apoptosis in acute monocytic leukemia cells by activating PUMA and
caspases. Eur J Pharmacol. 718:340–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ash D, Subramanian M, Surolia A and Shaha
C: Nitric oxide is the key mediator of death induced by fisetin in
human acute monocytic leukemia cells. Am J Cancer Res. 5:481–497.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou H, Chen D, Xie H, Xia L, Wang T, Yuan
W and Yan J: Activation of MAPKs in the anti-β2GPI/β2GPI-induced
tissue factor expression through TLR4/IRAKs pathway in THP-1 cells.
Thromb Res. 130:e229–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Zhang T, Wang X, Wei X, Chen Y,
Guo L, Zhang J and Wang C: Curcumin modulates macrophage
polarization through the inhibition of the toll-like receptor 4
expression and its signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:631–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ansa-Addo EA, Lange S, Stratton D,
Antwi-Baffour S, Cestari I, Ramirez MI, McCrossan MV and Inal JM:
Human plasma membrane-derived vesicles halt proliferation and
induce differentiation of THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells. J
Immunol. 185:5236–5246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gong JN, Yu J, Lin HS, Zhang XH, Yin XL,
Xiao Z, Wang F, Wang XS, Su R, Shen C, et al: The role, mechanism
and potentially therapeutic application of microRNA-29 family in
acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Differ. 21:100–112. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang MJ, Cheng YC, Liu CR, Lin S and Liu
HE: A small-molecule c-Myc inhibitor, 10058-F4, induces cell-cycle
arrest, apoptosis, and myeloid differentiation of human acute
myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol. 34:1480–1489. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia B, Tian C, Guo S, Zhang L, Zhao D, Qu
F, Zhao W, Wang Y, Wu X, Da W, et al: c-Myc plays part in drug
resistance mediated by bone marrow stromal cells in acute myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Res. 39:92–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McCormack E, Haaland I, Venås G, Forthun
RB, Huseby S, Gausdal G, Knappskog S, Micklem DR, Lorens JB,
Bruserud O and Gjertsen BT: Synergistic induction of p53 mediated
apoptosis by valproic acid and nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 26:910–917. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morita K, Noura M, Tokushige C, Maeda S,
Kiyose H, Kashiwazaki G, Taniguchi J, Bando T, Yoshida K, Ozaki T,
et al: Autonomous feedback loop of RUNX1-p53-CBFB in acute myeloid
leukemia cells. Sci Rep. 7:166042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fabre C, Carvalho G, Tasdemir E, Braun T,
Adès L, Grosjean J, Boehrer S, Métivier D, Souquère S, Pierron G,
et al: NF-kappaB inhibition sensitizes to starvation-induced cell
death in high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. 26:4071–4083. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rushworth SA, Bowles KM, Raninga P and
MacEwan DJ: NF-kappaB-inhibited acute myeloid leukemia cells are
rescued from apoptosis by heme oxygenase-1 induction. Cancer Res.
70:2973–2983. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho JH, Gelinas R, Wang K, Etheridge A,
Piper MG, Batte K, Dakhallah D, Price J, Bornman D, Zhang S, et al:
Systems biology of interstitial lung diseases: integration of mRNA
and microRNA expression changes. BMC Med Genomics. 4:82011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chatterjee P, Roy D, Bhattacharyya M and
Bandyopadhyay S: Biological networks in Parkinson's disease: an
insight into the epigenetic mechanisms associated with this
disease. BMC Genomics. 18:7212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vaidya A: Can systems biology approach
help in finding more effective treatment for acute myeloid
leukemia? Syst Synth Biol. 8:165–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shalgi R, Lieber D, Oren M and Pilpel Y:
Global and local architecture of the mammalian
microRNA-transcription factor regulatory network. PLoS Comput Biol.
3:e1312007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ye H, Liu X, Lv M, Wu Y, Kuang S, Gong J,
Yuan P, Zhong Z, Li Q, Jia H, et al: MicroRNA and transcription
factor co-regulatory network analysis reveals miR-19 inhibits CYLD
in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:5201–5214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun J, Gong X, Purow B and Zhao Z:
Uncovering MicroRNA and transcription factor mediated regulatory
networks in glioblastoma. PLoS Comput Biol. 8:e10024882012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin Y, Zhang Q, Zhang HM, Liu W, Liu CJ,
Li Q and Guo AY: Transcription factor and miRNA co-regulatory
network reveals shared and specific regulators in the development
of B cell and T cell. Sci Rep. 5:152152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Garzon R, Heaphy CE, Havelange V, Fabbri
M, Volinia S, Tsao T, Zanesi N, Kornblau SM, Marcucci G, Calin GA,
et al: MicroRNA 29b functions in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
114:5331–5341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu H, Wang B, Lin J and Zhao L:
microRNA-29b: An emerging player in human cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:9059–9064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brondfield S, Umesh S, Corella A, Zuber J,
Rappaport AR, Gaillard C, Lowe SW, Goga A and Kogan SC: Direct and
indirect targeting of MYC to treat acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 76:35–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoshida GJ: Emerging roles of Myc in stem
cell biology and novel tumor therapies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:1732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Huang Z, Sheng F and Yin Z: MYC
upregulated LINC00319 promotes human acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
cells growth through stabilizing SIRT6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
509:314–321. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang L, McGraw KL, Sallman DA and List
AF: The role of p53 in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid
leukemia: Molecular aspects and clinical implications. Leuk
Lymphoma. 58:1777–1790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Breccia M and Alimena G: NF-κB as a
potential therapeutic target in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute
myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1157–1176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mott JL, Kurita S, Cazanave SC, Bronk SF,
Werneburg NW and Fernandez-Zapico ME: Transcriptional suppression
of mir-29b-1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J
Cell Biochem. 110:1155–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Perini GF, Ribeiro N, Pinto Neto JV,
Campos LT and Hamerschlak N: BCL-2 as therapeutic target for
hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 11:652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Campos L, Rouault JP, Sabido O, Oriol P,
Roubi N, Vasselon C, Archimbaud E, Magaud JP and Guyotat D: High
expression of bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is
associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood. 81:3091–3096.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pan R, Hogdal LJ, Benito JM, Bucci D, Han
L, Borthakur G, Cortes J, DeAngelo DJ, Debose L, Mu H, et al:
Selective BCL-2 inhibition by ABT-199 causes on-target cell death
in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 4:362–375. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Seipel K, Marques MT, Bozzini MA, Meinken
C, Mueller BU and Pabst T: inactivation of the p53-KLF4-CEBPA axis
in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 22:746–756. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Eyholzer M, Schmid S, Wilkens L, Mueller
BU and Pabst T: The tumour-suppressive miR-29a/b1 cluster is
regulated by CEBPA and blocked in human AML. Br J Cancer.
103:275–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pabst T and Mueller BU: Complexity of
CEBPA dysregulation in human acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:5303–5307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gholami M, Bayat S, Manoochehrabadi S,
Pashaiefar H, Omrani MD, Jalaeikhoo H, Yassaee VR, Ebrahimpour MR,
Behjati F and Mirfakhraie R: Investigation of CEBPA and CEBPA-AS
genes expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Rep Biochem Mol Biol.
7:136–141. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Setten RL, Lightfoot HL, Habib NA and
Rossi JJ: Development of MTL-CEBPA: Small Activating RNA drug for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 19:611–621. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kirstetter P, Schuster MB, Bereshchenko O,
Moore S, Dvinge H, Kurz E, Theilgaard-Mönch K, Månsson R, Pedersen
TA, Pabst T, et al: Modeling of C/EBP alpha mutant acute myeloid
leukemia reveals a common expression signature of committed myeloid
leukemia-initiating cells. Cancer Cell. 13:299–310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|