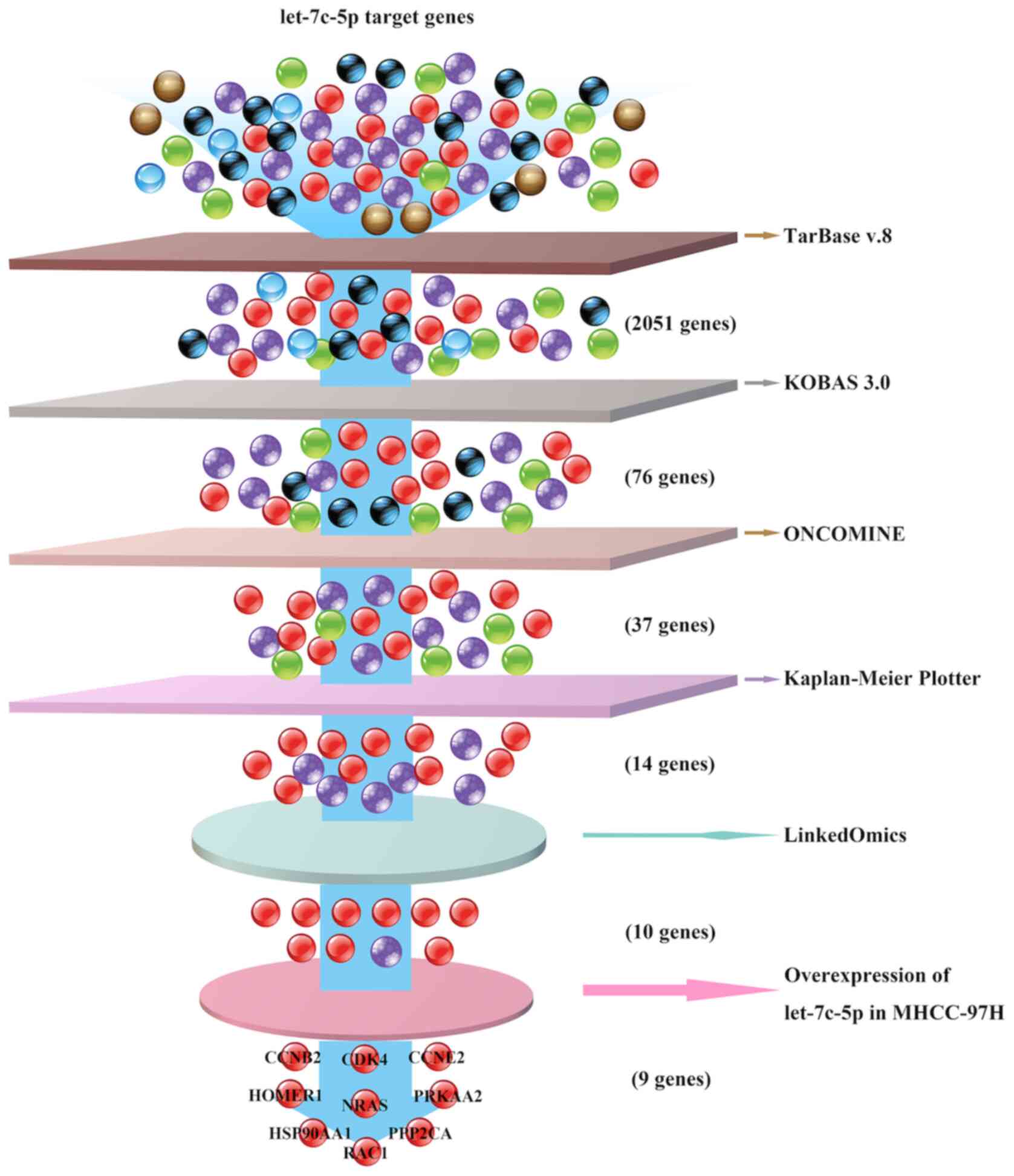
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim NG, Nguyen PP, Dang H, Kumari R,
Garcia G, Esquivel CO and Nguyen MH: Temporal trends in disease
presentation and survival of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma: A real-world experience from 1998 to 2015. Cancer.
124:2588–2598. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inui M, Martello G and Piccolo S: MicroRNA
control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:252–263.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ryan BM, Robles AI and Harris CC: Genetic
variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:389–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang S and He X: The role of microRNAs in
liver cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 104:235–240. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gailhouste L and Ochiya T: Cancer-related
microRNAs and their role as tumor suppressors and oncogenes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 28:437–451.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li D, Zhang J and Li J: Role of miRNA
sponges in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 500:10–19.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Lu L, Luo Z, Li W, Lu Y, Tang Q
and Pu J: miR-383 inhibits cell growth and promotes cell apoptosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting IL-17 via STAT3 signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 120:1095512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu X, Wu L, Yao J, Jiang H, Wang Q, Yang
Z and Wu F: MicroRNA let-7c inhibits cell proliferation and induces
cell cycle arrest by targeting CDC25A in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01242662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, Kodama T,
Miyagi T, Hosui A, Tatsumi T, Ishida H, Noda T, Nagano H, et al:
The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and
potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 52:698–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo H, German P, Bai S, Barnes S, Guo W,
Qi X, Lou H, Liang J, Jonasch E, Mills GB and Ding Z: The PI3K/AKT
Pathway and renal cell carcinoma. J Genet Genomics. 42:343–353.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Faes S and Dormond O: PI3K and AKT:
Unfaithful partners in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21138–21152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Q, Lui VW and Yeo W: Targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol.
7:1149–1167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou YQ, Yao Y, Bao YL, Song ZB, Yang C,
Gao XL, Zhang WJ, Sun LG, Yu CL, Huang YX, et al: Juglanthraquinone
C induces intracellular ROS increase and apoptosis by activating
the Akt/Foxo signal pathway in HCC cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:49416232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Q, Yu WN, Chen X, Peng XD, Jeon SM,
Birnbaum MJ, Guzman G and Hay N: Spontaneous hepatocellular
carcinoma after the combined deletion of Akt isoforms. Cancer Cell.
29:523–535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deng M, Bragelmann J, Schultze JL and
Perner S: Web-TCGA: An online platform for integrated analysis of
molecular cancer data sets. BMC Bioinformatics. 17:722016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma Z, Liu T, Huang W, Liu H, Zhang HM, Li
Q, Chen Z and Guo AY: MicroRNA regulatory pathway analysis
identifies miR-142-5p as a negative regulator of TGF-β pathway via
targeting SMAD3. Oncotarget. 7:71504–71513. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wong NW, Chen Y, Chen S and Wang X:
OncomiR: An online resource for exploring pan-cancer microRNA
dysregulation. Bioinformatics. 34:713–715. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karagkouni D, Paraskevopoulou MD,
Chatzopoulos S, Vlachos IS, Tastsoglou S, Kanellos I, Papadimitriou
D, Kavakiotis I, Maniou S, Skoufos G, et al: DIANA-TarBase v8: A
decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA-gene
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D239–D245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ai C and Kong L: CGPS: A machine
learning-based approach integrating multiple gene set analysis
tools for better prioritization of biologically relevant pathways.
J Genet Genomics. 45:489–504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xie C, Mao X, Huang J, Ding Y, Wu J, Dong
S, Kong L, Gao G, Li CY and Wei L: KOBAS 2.0: A web server for
annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:W316–W322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu J, Mao X, Cai T, Luo J and Wei L: KOBAS
server: A web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway
identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:W720–W724. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
von Eschenbach AC and Buetow K: Cancer
informatics vision: CaBIG. Cancer Inform. 2:22–24. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Menyhárt O, Nagy Á and Győrffy B:
Determining consistent prognostic biomarkers of overall survival
and vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. R Soc Open Sci.
5:1810062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nagy A, Lanczky A, Menyhart O and Gyorffy
B: Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma
using expression data of independent datasets. Sci Rep. 8:92272018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J and Zhang B:
LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer
types. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D956–D963. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
The Gene Ontology C: The Gene Ontology
Resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Reimand J, Kull M, Peterson H, Hansen J
and Vilo J: g:Profiler-a web-based toolset for functional profiling
of gene lists from large-scale experiments. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:W193–W200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Raudvere U, Kolberg L, Kuzmin I, Arak T,
Adler P, Peterson H and Vilo J: g:Profiler: A web server for
functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019
update). Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W191–W198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O,
Zuberi K, Badrawi R, Chao P, Franz M, Grouios C, Kazi F, Lopes CT,
et al: The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network
integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:W214–W220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Max F, Rodriguez H, Lopes C, Zuberi K,
Montojo J, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA update 2018. Nuclc
Acids Res. 46:W60–W64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43((Database Issue)): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Song Y, Wang F, Huang Q, Cao Y, Zhao Y and
Yang C: MicroRNAs contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma. Mini Rev
Med Chem. 15:459–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Han Y, Liu Y, Fu X, Zhang Q, Huang H,
Zhang C, Li W and Zhang J: miR-9 inhibits the metastatic ability of
hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting beta galactoside
alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1. J Physiol Biochem. 74:491–501. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang Y, Tai Q, Zhang J, Kang J, Gao F,
Zhong F, Cai L, Fang F and Gao Y: MiRNA-206 inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis
by modulating cMET expression. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
51:243–253. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhu XM, Wu LJ, Xu J, Yang R and Wu FS:
Let-7c microRNA expression and clinical significance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 39:2323–2329. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jilek JL, Zhang QY, Tu MJ, Ho PY, Duan Z,
Qiu JX and Yu AM: Bioengineered Let-7c inhibits orthotopic
hepatocellular carcinoma and improves overall survival with minimal
immunogenicity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 14:498–508. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo H, Hao E, Tan D, Wei W, Xie J, Feng X,
Du Z, Huang C, Bai G, Hou Y, et al: Apoptosis effect of
Aegiceras corniculatum on human colorectal cancer via
activation of FoxO signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol.
134:1108612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Farhan M, Wang H, Gaur U, Little PJ, Xu J
and Zheng W: FOXO signaling pathways as therapeutic targets in
cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 13:815–827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nam HJ and van Deursen JM: Cyclin B2 and
p53 control proper timing of centrosome separation. Nat Cell Biol.
16:538–549. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Q, Sun S, Zhu C, Zheng Y, Cai Q,
Liang X, Xie H and Zhou J: Prediction and analysis of weighted
genes in hepatocellular carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis.
Mol Med Rep. 19:2479–2488. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lauper N, Beck AR, Cariou S, Richman L,
Hofmann K, Reith W, Slingerland JM and Amati B: Cyclin E2: A novel
CDK2 partner in the late G1 and S phases of the mammalian cell
cycle. Oncogene. 17:2637–2643. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hwang HC and Clurman BE: Cyclin E in
normal and neoplastic cell cycles. Oncogene. 24:2776–2786. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Caldon CE and Musgrove EA: Distinct and
redundant functions of cyclin E1 and cyclin E2 in development and
cancer. Cell Div. 5:22010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sherr CJ, Beach D and Shapiro GI:
Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov.
6:353–367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xiang X, You XM and Li LQ: Expression of
HSP90AA1/HSPA8 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with
depression. Onco Targets Ther. 11:3013–3023. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Piredda ML, Gaur G, Catalano G, Divona M,
Banella C, Travaglini S, Puzzangara MC, Voso MT, Lo-Coco F and
Noguera NI: PML/RARA inhibits expression of HSP90 and its target
AKT. Br J Haematol. 184:937–948. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hou C, Li Y, Liu H, Dang M, Qin G, Zhang N
and Chen R: Profiling the interactome of protein kinase C zeta by
proteomics and bioinformatics. Proteome Sci. 16:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fox MM, Phoenix KN, Kopsiaftis SG and
Claffey KP: AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 2 isoform
suppression in primary breast cancer alters AMPK growth control and
apoptotic signaling. Genes Cancer. 4:3–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Vila IK, Yao Y, Kim G, Xia W, Kim H, Kim
SJ, Park MK, Hwang JP, González-Billalabeitia E, Hung MC, et al: A
UBE2O-AMPKα2 axis that promotes tumor initiation and progression
offers opportunities for therapy. Cancer Cell. 31:208–224. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jardin I, Albarran L, Bermejo N, Salido GM
and Rosado JA: Homers regulate calcium entry and aggregation in
human platelets: A role for Homers in the association between STIM1
and Orai1. Biochem J. 445:29–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Moccia F, Zuccolo E, Poletto V, Turin I,
Guerra G, Pedrazzoli P, Rosti V, Porta C and Montagna D: Targeting
stim and orai proteins as an alternative approach in anticancer
therapy. Curr Med Chem. 23:3450–3480. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR and
Albert S: Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1177–1195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dietrich P, Gaza A, Wormser L, Fritz V,
Hellerbrand C and Bosserhoff AK: Neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene
homolog (NRAS) is a novel prognostic marker and contributes to
sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia.
21:257–268. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xiang RF, Stack D, Huston SM, Li SS,
Ogbomo H, Kyei SK and Mody CH: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin
substrate (Rac) and Src Family Kinases (SFK) Are proximal and
essential for phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K) activation in
natural Killer (NK) Cell-mediated Direct Cytotoxicity against
cryptococcus neoformans. J Biol Chem. 291:6912–6922. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen L, Chan TH, Yuan YF, Hu L, Huang J,
Ma S, Wang J, Dong SS, Tang KH, Xie D, et al: CHD1L promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis in mice and is
associated with these processes in human patients. J Clin Invest.
120:1178–1191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhao P, Zhang W, Wang SJ, Yu XL, Tang J,
Huang W, Li Y, Cui HY, Guo YS, Tavernier J, et al: HAb18G/CD147
promotes cell motility by regulating annexin II-activated RhoA and
Rac1 signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatology. 54:2012–2024. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ran RZ, Chen J, Cui LJ, Lin XL, Fan MM,
Cong ZZ, Zhang H, Tan WF, Zhang GQ and Zhang YJ: miR-194 inhibits
liver cancer stem cell expansion by regulating RAC1 pathway. Exp
Cell Res. 378:66–75. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|