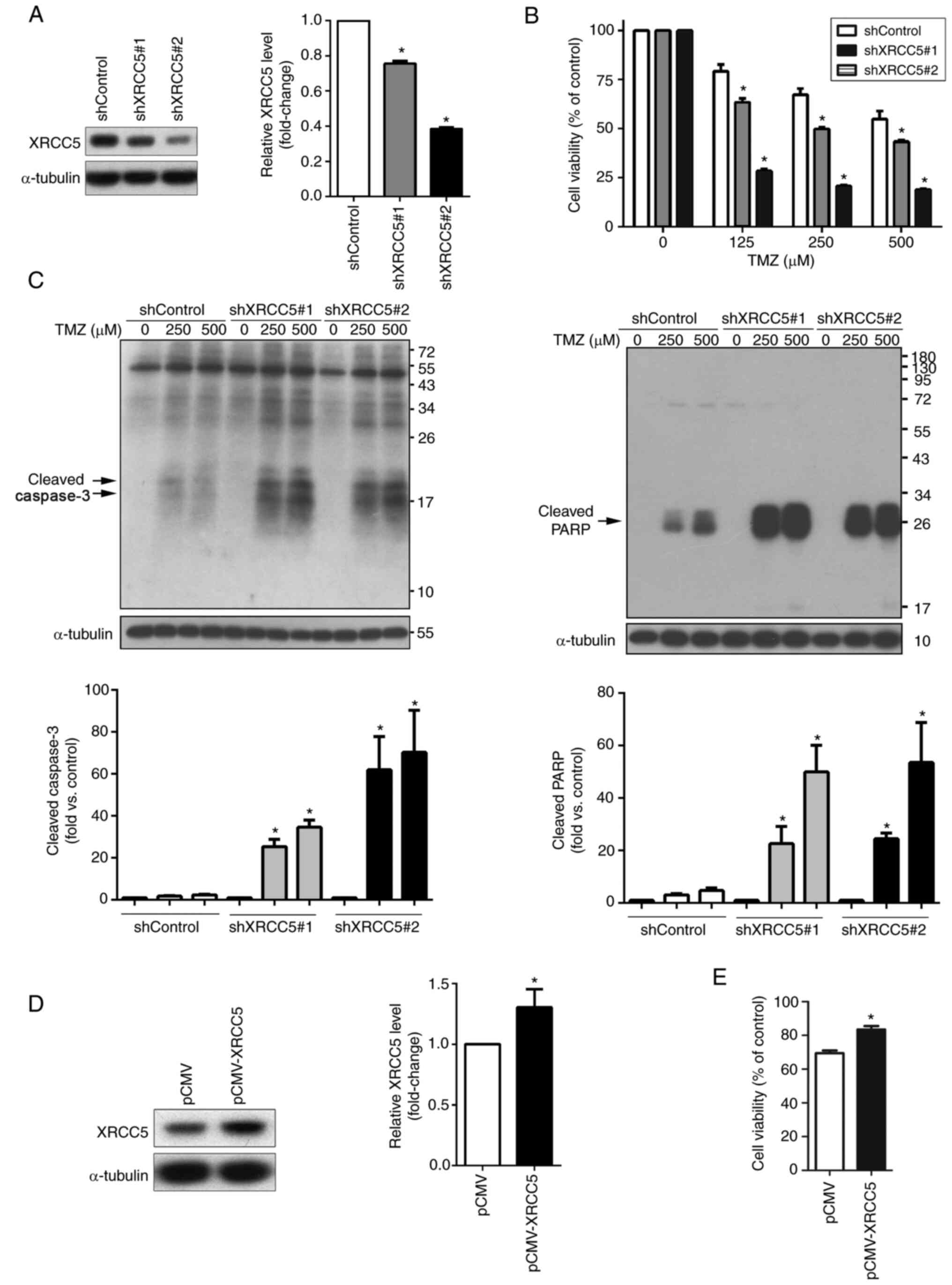
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Gittleman H, Patil N,
Waite K, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS Statistical
Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro Oncol. 21 (Suppl
5):v1–v100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, Fredericks
R, Fink K, Prados MD, Brada M, Spence A, Hohl RJ, Shapiro W, et al:
A phase II study of temozolomide vs. procarbazine in patients with
glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer. 83:588–593.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hottinger AF, Ben Aissa A, Espeli V,
Squiban D, Dunkel N, Vargas MI, Hundsberger T, Mach N, Schaller K,
Weber DC, et al: Phase I study of sorafenib combined with radiation
therapy and temozolomide as first-line treatment of high-grade
glioma. Br J Cancer. 110:2655–2661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fu D, Calvo JA and Samson LD: Balancing
repair and tolerance of DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:104–120. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF and Bradshaw TD:
Temozolomide: Mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 5:102–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quiros S, Roos WP and Kaina B: Processing
of O6-methylguanine into DNA double-strand breaks requires two
rounds of replication whereas apoptosis is also induced in
subsequent cell cycles. Cell Cycle. 9:168–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bocangel DB, Finkelstein S, Schold SC,
Bhakat KK, Mitra S and Kokkinakis DM: Multifaceted resistance of
gliomas to temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2725–2734.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan CH, Liu WL, Cao H, Wen C, Chen L and
Jiang G: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase as a promising
target for the treatment of temozolomide-resistant gliomas. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e8762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Happold C, Roth P, Wick W, Schmidt N,
Florea AM, Silginer M, Reifenberger G and Weller M: Distinct
molecular mechanisms of acquired resistance to temozolomide in
glioblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 122:444–455. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roos WP, Frohnapfel L, Quiros S, Ringel F
and Kaina B: XRCC3 contributes to temozolomide resistance of
glioblastoma cells by promoting DNA double-strand break repair.
Cancer Lett. 424:119–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang B, Fu X, Hao J, Sun J, Li Z, Li H and
Xu H: PAXX Participates in Base Excision Repair via Interacting
with Pol β and Contributes to TMZ Resistance in Glioma Cells. J Mol
Neurosci. 66:214–221. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gil Del Alcazar CR, Todorova PK, Habib AA,
Mukherjee B and Burma S: Augmented HR repair mediates acquired
temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Res.
14:928–940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hata N, Mizoguchi M, Kuga D, Hatae R,
Akagi Y, Sangatsuda Y, Amemiya T, Michiwaki Y, Fujioka Y, Takigawa
K, et al: First-line bevacizumab contributes to survival
improvement in glioblastoma patients complementary to temozolomide.
J Neurooncol. 146:451–458. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caplen NJ, Parrish S, Imani F, Fire A and
Morgan RA: Specific inhibition of gene expression by small
double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:9742–9747. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Agrawal N, Dasaradhi PV, Mohmmed A,
Malhotra P, Bhatnagar RK and Mukherjee SK: RNA interference:
Biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
67:657–685. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salm F, Cwiek P, Ghosal A, Lucia
Buccarello A, Largey F, Wotzkow C, Höland K, Styp-Rekowska B,
Djonov V, Zlobec I, et al: RNA interference screening identifies a
novel role for autocrine fibroblast growth factor signaling in
neuroblastoma chemoresistance. Oncogene. 32:3944–3953. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding Y, Huang D, Zhang Z, Smith J, Petillo
D, Looyenga BD, Feenstra K, Mackeigan JP, Furge KA and The BT:
Combined gene expression profiling and RNAi screening in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma identify PLK1 and other therapeutic kinase
targets. Cancer Res. 71:5225–5234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pannunzio NR, Watanabe G and Lieber MR:
Nonhomologous DNA end-joining for repair of DNA double-strand
breaks. J Biol Chem. 293:10512–10523. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meek K, Dang V and Lees-Miller SP: DNA-PK:
The means to justify the ends? Adv Immunol. 99:33–58. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lieber MR: The mechanism of double-strand
DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Annu
Rev Biochem. 79:181–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang IY, Youn CK, Kim HB, Kim MH, Cho HJ,
Yoon Y, Lee YS, Chung MH and You HJ: Oncogenic H-Ras up-regulates
expression of Ku80 to protect cells from gamma-ray irradiation in
NIH3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 65:6811–6819. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang HW, Kim SY, Yi SL, Son SH, Song DY,
Moon SY, Kim JH, Choi EK, Ahn SD, Shin SS, et al: Expression of
Ku80 correlates with sensitivities to radiation in cancer cell
lines of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 42:979–986. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Q, Li P, Xu M, Yin J, Su Z, Li W and
Zhang J: Ku80 is highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma and
promotes cisplatin resistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:992012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shang B, Jia Y, Chen G and Wang Z: Ku80
correlates with neoadjuvant chemotherapy resistance in human lung
adenocarcinoma, but reduces cisplatin/pemetrexed-induced apoptosis
in A549 cells. Respir Res. 18:562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhuang L, Liu F, Peng P, Xiong H, Qiu H,
Fu X, Xiao Z and Huang X: Effect of Ku80 on the radiosensitization
of cisplatin in the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa. Oncol Lett.
15:147–154. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsieh MJ, Huang C, Lin CC, Tang CH, Lin
CY, Lee IN, Huang HC and Chen JC: Basic fibroblast growth factor
promotes doxorubicin resistance in chondrosarcoma cells by
affecting XRCC5 expression. Mol Carcinog. 59:293–303. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan Y, Li J, Wei W, Fang H, Duan Y, Li N,
Zhang Y, Yu J and Wang J: Ku80 gene knockdown by the CRISPR/Cas9
technique affects the biological functions of human thyroid
carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 42:2486–2498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torcivia-Rodriguez J, Dingerdissen H,
Chang TC and Mazumder R: A primer for access to repositories of
cancer-related genomic big data. Methods Mol Biol. 1878:1–37. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saha SK, Islam SMR, Kwak KS, Rahman MS and
Cho SG: PROM1 and PROM2 expression differentially modulates
clinical prognosis of cancer: A multiomics analysis. Cancer Gene
Ther. 27:147–167. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang C, Chen E, Peng K, Wang H, Cheng X,
Wang Y, Yu S, Yu Y, Cui Y and Liu T: Mining the role of
angiopoietin-like protein family in gastric cancer and seeking
potential therapeutic targets by integrative bioinformatics
analysis. Cancer Med. 9:4850–4863. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Osuka S and Van Meir EG: Overcoming
therapeutic resistance in glioblastoma: The way forward. J Clin
Invest. 127:415–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shergalis A, Bankhead A III, Luesakul U,
Muangsin N and Neamati N: Current challenges and opportunities in
treating glioblastoma. Pharmacol Rev. 70:412–445. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gusev Y, Bhuvaneshwar K, Song L, Zenklusen
JC, Fine H and Madhavan S: The REMBRANDT study, a large collection
of genomic data from brain cancer patients. Sci Data. 5:1801582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen JC, Lee IN, Huang C, Wu YP, Chung CY,
Lee MH, Lin MH and Yang JT: Valproic acid-induced amphiregulin
secretion confers resistance to temozolomide treatment in human
glioma cells. BMC Cancer. 19:7562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chapman JR, Taylor MR and Boulton SJ:
Playing the end game: DNA double-strand break repair pathway
choice. Mol Cell. 47:497–510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kaina B and Christmann M: DNA repair in
personalized brain cancer therapy with temozolomide and
nitrosoureas. DNA Repair (Amst). 78:128–141. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Quiros S, Roos WP and Kaina B: Rad51 and
BRCA2-New molecular targets for sensitizing glioma cells to
alkylating anticancer drugs. PLoS One. 6:e271832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ding J, Wu S, Zhang C, Garyali A,
Martinez-Ledesma E, Gao F, Pokkulandra A, Li X, Bristow C, Carugo
A, et al: BRCA1 identified as a modulator of temozolomide
resistance in P53 wild-type GBM using a high-throughput shRNA-based
synthetic lethality screening. Am J Cancer Res. 9:2428–2441.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chai KM, Wang CY, Liaw HJ, Fang KM, Yang
CS and Tzeng SF: Downregulation of BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex
subunit 3 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide. Oncotarget.
5:10901–10915. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kondo N, Takahashi A, Mori E, Noda T,
Zdzienicka MZ, Thompson LH, Helleday T, Suzuki M, Kinashi Y,
Masunaga S, et al: FANCD1/BRCA2 plays predominant role in the
repair of DNA damage induced by ACNU or TMZ. PLoS One.
6:e196592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang T, Chai J and Chi L: Induction Of
XLF And 53BP1 expression is associated with temozolomide resistance
in glioblastoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 12:10139–10151. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zeng A, Wei Z, Yan W, Yin J, Huang X, Zhou
X, Li R, Shen F, Wu W, Wang X and You Y: Exosomal transfer of
miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in
drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 436:10–21. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Roos WP, Batista LF, Naumann SC, Wick W,
Weller M, Menck CF and Kaina B: Apoptosis in malignant glioma cells
triggered by the temozolomide-induced DNA lesion O6-methylguanine.
Oncogene. 26:186–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kondo N, Takahashi A, Mori E, Ohnishi K,
McKinnon PJ, Sakaki T, Nakase H and Ohnishi T: DNA ligase IV as a
new molecular target for temozolomide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
387:656–660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Meek K, Gupta S, Ramsden DA and
Lees-Miller SP: The DNA-dependent protein kinase: The director at
the end. Immunol Rev. 200:132–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou C, Tang H, Yu J, Zhuang D and Zhang
H: Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the
non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in patient with glioma.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:9463–9467. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He X, Zhu X, Li L, Zhang J, Wu R, Zhang Y,
Kang L, Yuan D and Jin T: The relationship between polymorphisms of
XRCC5 genes with astrocytoma prognosis in the Han Chinese
population. Oncotarget. 7:85283–85290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|