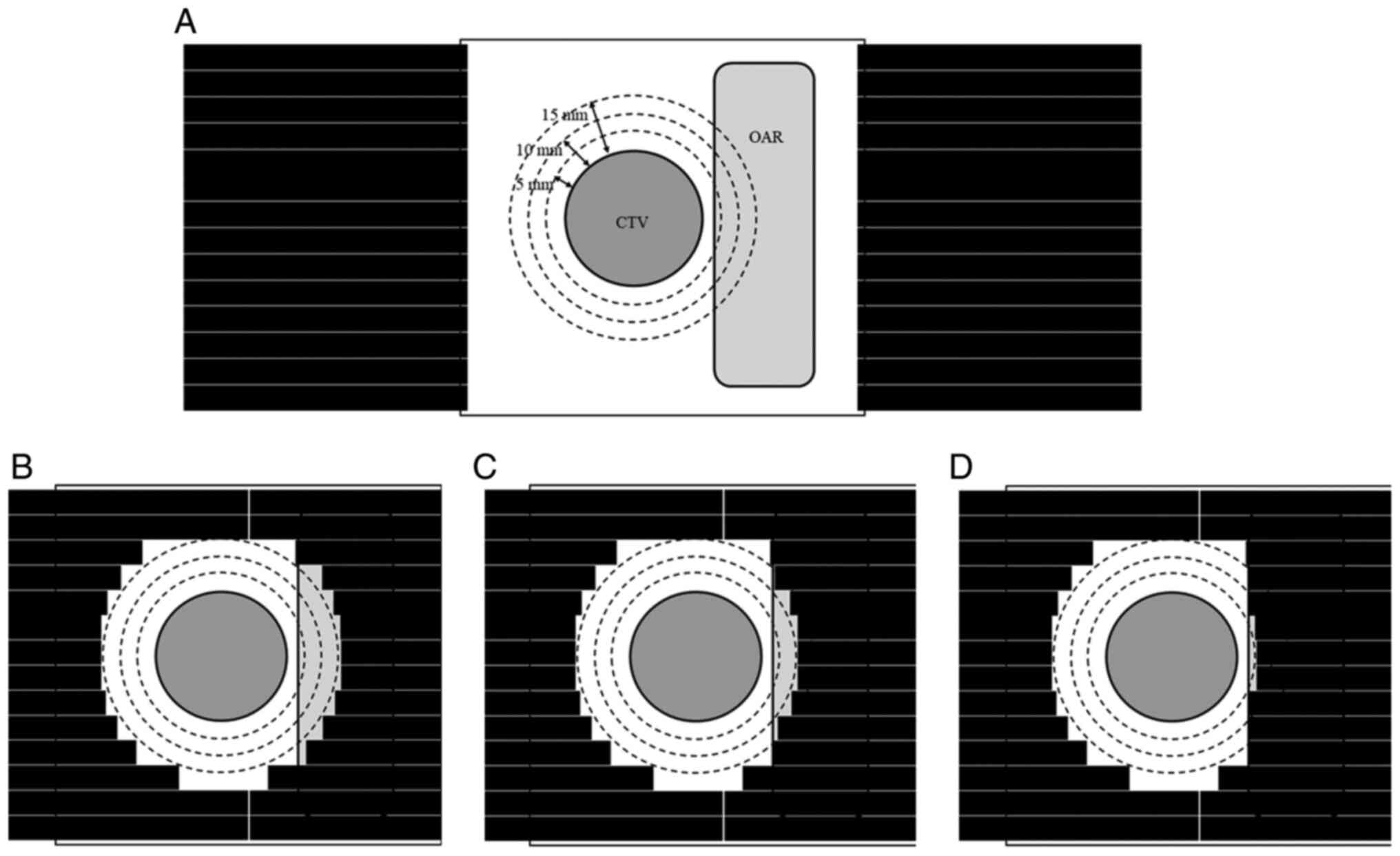
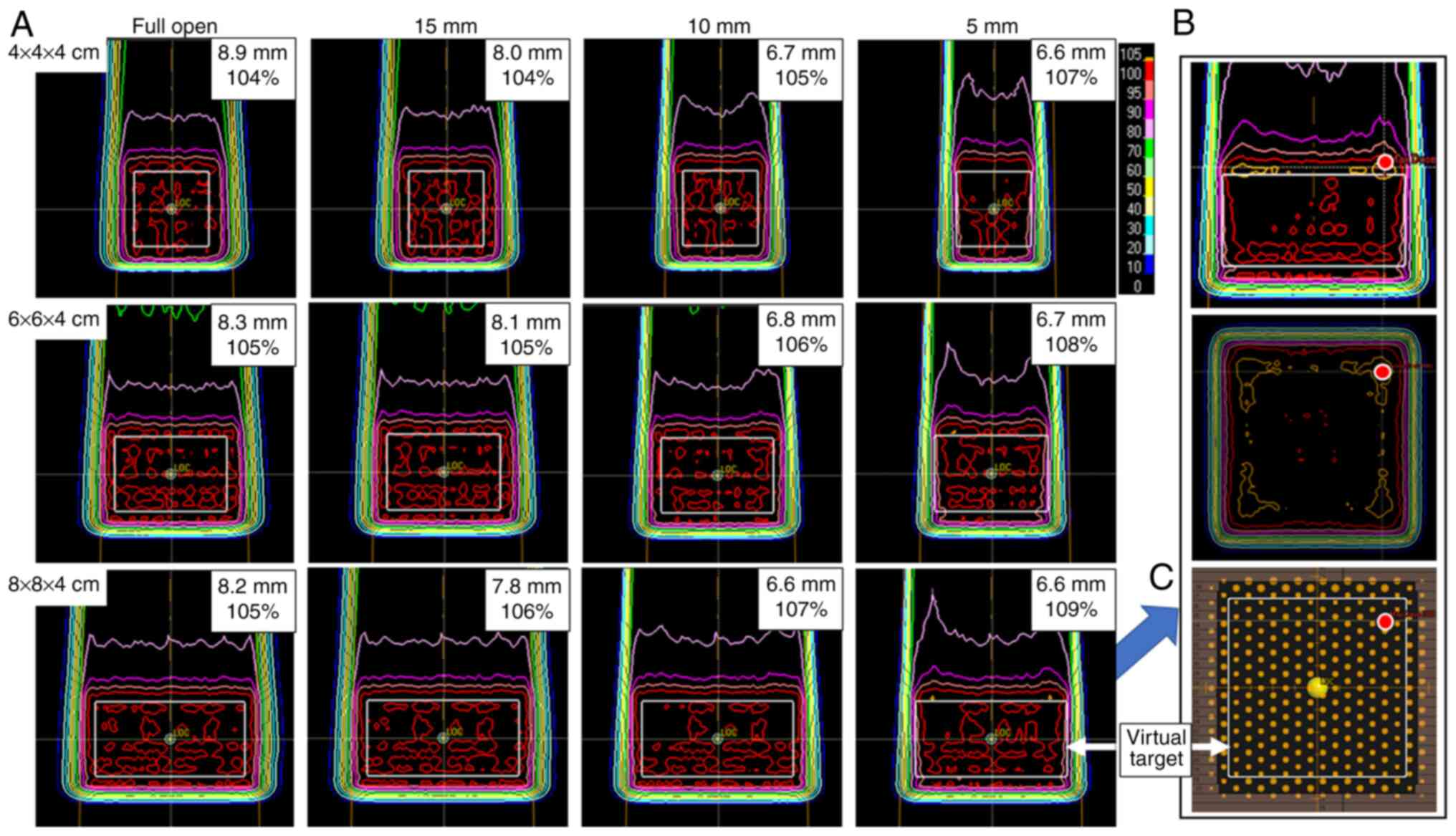
|
1
|
Lawrence JH, Tobias CA, Born JL, Linfoot
JA, Kling RP and Gottschalk A: Alpha and proton heavy particles and
the bragg peak in therapy. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc.
75:111–116. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bortfeld T and Schlegel W: An analytical
approximation of depth-dose distributions for therapeutic proton
beams. Phys Med Biol. 41:1331–1339. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Foote RL, Stafford SL, Petersen IA, Pulido
JS, Clarke MJ, Schild SE, Garces YI, Olivier KR, Miller RC, Haddock
MG, et al: The clinical case for proton beam therapy. Radiat Oncol.
7:1742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holliday EB and Frank SJ: Proton radiation
therapy for head and neck cancer: A review of the clinical
experience to date. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 89:292–302. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Royce TJ and Efstathiou JA: Proton therapy
for prostate cancer: A review of the rationale, evidence, and
current state. Urol Oncol. 37:628–636. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Haas-Kogan D, Indelicato D, Paganetti H,
Esiashvili N, Mahajan A, Yock T, Flampouri S, MacDonald S, Fouladi
M, Stephen K, et al: National cancer institute workshop on proton
therapy for children: Considerations regarding brainstem injury.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 101:152–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klein J and Dawson LA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma radiation therapy: Review of evidence and future
opportunities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 87:22–32. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chuong MD, Hallemeier CL, Jabbour SK, Yu
J, Badiyan S, Merrell KW, Mishra MV, Li H, Verma V and Lin SH:
Improving outcomes for esophageal cancer using proton beam therapy.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 95:488–497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lomax A: Intensity modulation methods for
proton radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 44:185–205. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hyer DE, Hill PM, Wang D, Smith BR and
Flynn RT: A dynamic collimation system for penumbra reduction in
spot-scanning proton therapy: Proof of concept. Med Phys.
41:0917012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DeLaney TF: Proton therapy in the clinic.
Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 43:465–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bert C and Durante M: Motion in
radiotherapy: Particle therapy. Phys Med Biol. 56:R113–R144. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schippers JM and Lomax AJ: Emerging
technologies in proton therapy. Acta Oncol. 50:838–850. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Engelsman M, Schwarz M and Dong L: Physics
controversies in proton therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 23:88–96.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van de Water S, Kraan AC, Breedveld S,
Schillemans W, Teguh DN, Kooy HM, Madden TM, Heijmen BJ and
Hoogeman MS: Improved efficiency of multi-criteria IMPT treatment
planning using iterative resampling of randomly placed pencil
beams. Phys Med Biol. 58:6969–6983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van de Water S, Safai S, Schippers JM,
Weber DC and Lomax AJ: Towards FLASH proton therapy: The impact of
treatment planning and machine characteristics on achievable dose
rates. Acta Oncol. 58:1463–1469. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rosas S, Belosi FM, Bizzocchi N, Böhlen T,
Zepter S, Morach P, Lomax AJ, Weber DC and Hrbacek J: Benchmarking
a commercial proton therapy solution: The Paul Scherrer Institut
experience. Br J Radiol. 93:201909202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meier G, Leiser D, Besson R, Mayor A,
Safai S, Weber DC and Lomax AJ: Contour scanning for penumbra
improvement in pencil beam scanned proton therapy. Phys Med Biol.
62:2398–2416. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bues M, Newhauser WD, Titt U and Smith AR:
Therapeutic step and shoot proton beam spot-scanning with a
multi-leaf collimator: A Monte Carlo study. Radiat Prot Dosimetry.
115:164–169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sugiyama S, Katsui K, Tominaga Y, Waki T,
Katayama N, Matsuzaki H, Kariya S, Kuroda M, Nishizaki K and
Kanazawa S: Dose distribution of intensity-modulated proton therapy
with and without a multi-leaf collimator for the treatment of
maxillary sinus cancer: A comparative effectiveness study. Radiat
Oncol. 14:2092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dowdell SJ, Clasie B, Depauw N, Metcalfe
P, Rosenfeld AB, Kooy HM, Flanz JB and Paganetti H: Monte Carlo
study of the potential reduction in out-of-field dose using a
patient-specific aperture in pencil beam scanning proton therapy.
Phys Med Biol. 57:2829–2842. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang D, Smith BR, Gelover E, Flynn RT and
Hyer DE: A method to select aperture margin in collimated spot
scanning proton therapy. Phys Med Biol. 60:N109–N119. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yasui K, Toshito T, Omachi C, Hayashi K,
Tanaka K, Asai K, Shimomura A, Muramatsu R and Hayashi N:
Evaluation of dosimetric advantages of using patient-specific
aperture system with intensity-modulated proton therapy for the
shallow depth tumor. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 19:132–137. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smith B, Gelover E, Moignier A, Wang D,
Flynn RT, Lin L, Kirk M, Solberg T and Hyer DE: Technical Note: A
treatment plan comparison between dynamic collimation and a fixed
aperture during spot scanning proton therapy for brain treatment.
Med Phys. 43:46932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moignier A, Gelover E, Wang D, Smith B,
Flynn R, Kirk M, Lin L, Solberg T, Lin A and Hyer D: Theoretical
benefits of dynamic collimation in pencil beam scanning proton
therapy for brain tumors: Dosimetric and radiobiological metrics.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 95:171–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Winterhalter C, Meier G, Oxley D, Weber
DC, Lomax AJ and Safai S: Contour scanning, multi-leaf collimation
and the combination thereof for proton pencil beam scanning. Phys
Med Biol. 64:0150022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Smith BR, Hyer DE, Hill PM and Culberson
WS: Secondary neutron dose from a dynamic collimation system during
intracranial pencil beam scanning proton therapy: A monte carlo
investigation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 103:241–250. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kimstrand P, Traneus E, Ahnesjo A and
Tilly N: Parametrization and application of scatter kernels for
modelling scanned proton beam collimator scatter dose. Phys Med
Biol. 53:3405–3429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saini J, Traneus E, Maes D, Regmi R, Bowen
SR, Bloch C and Wong T: Advanced Proton Beam Dosimetry Part I:
Review and performance evaluation of dose calculation algorithms.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 7:171–179. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maes D, Saini J, Zeng J, Rengan R, Wong T
and Bowen SR: Advanced proton beam dosimetry part II: Monte Carlo
vs. Pencil beam-based planning for lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 7:114–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gill P, Murray W and Saunders M: Software
for large-scale nonlinear programming. User's guide for SNOPT
Version. 7:1–116. 2008.
|
|
32
|
Hyer DE, Hill PM, Wang D, Smith BR and
Flynn RT: Effects of spot size and spot spacing on lateral penumbra
reduction when using a dynamic collimation system for spot scanning
proton therapy. Phys Med Biol. 59:N187–N196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moteabbed M, Yock TI, Depauw N, Madden TM,
Kooy HM and Paganetti H: Impact of spot size and beam-shaping
devices on the treatment plan quality for pencil beam scanning
proton therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 95:190–198. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|