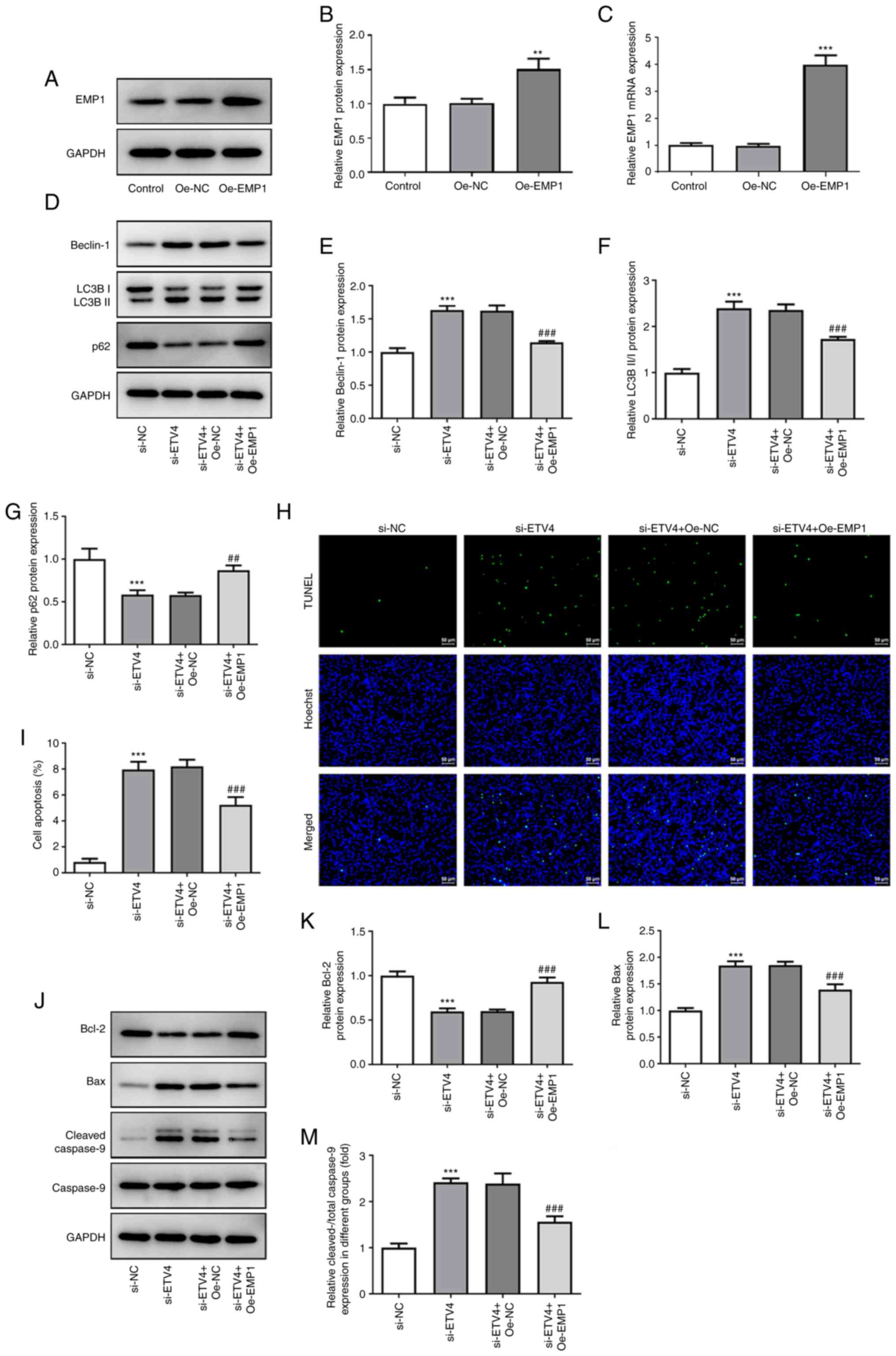
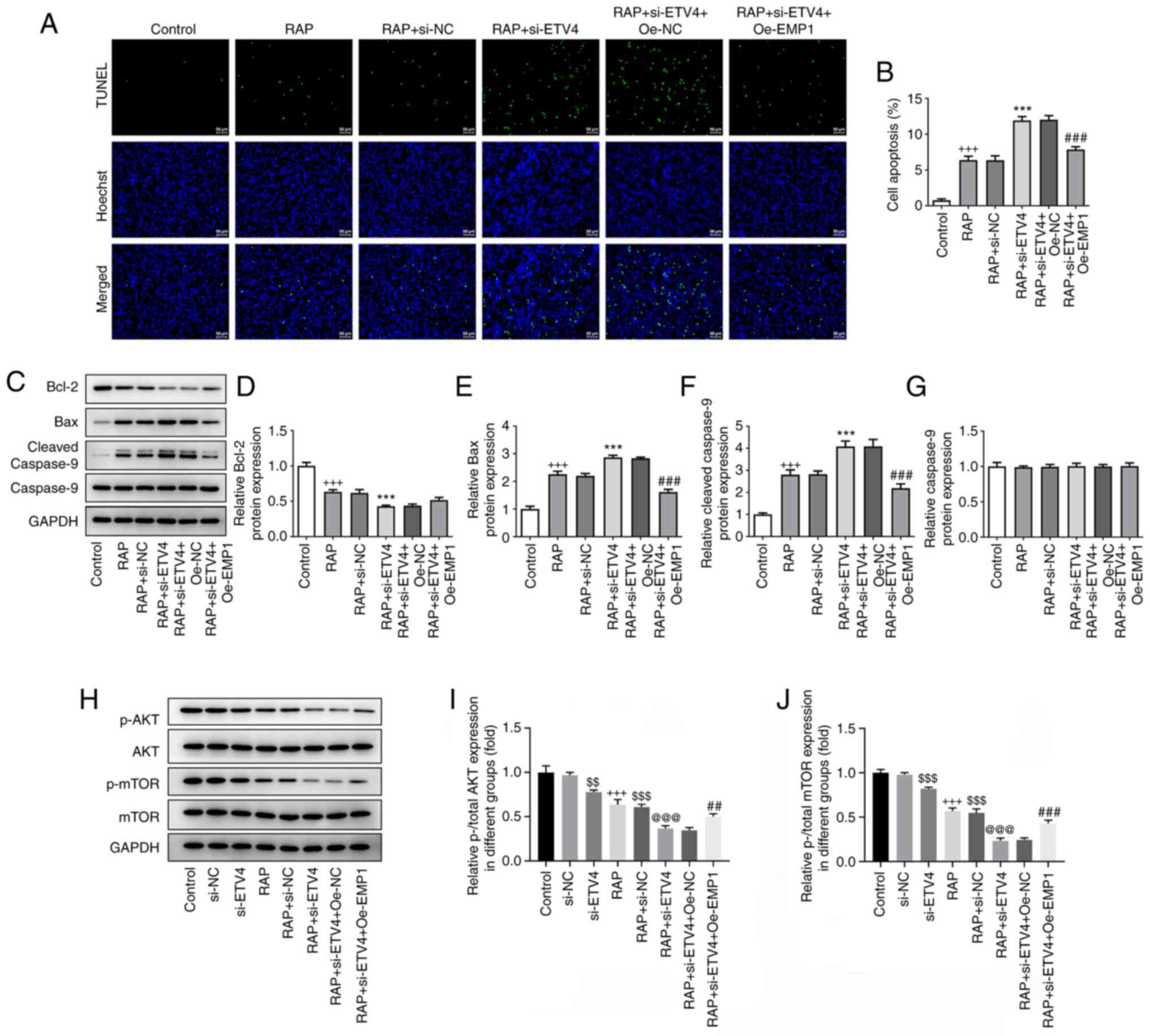
|
1
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gimple RC, Bhargava S, Dixit D and Rich
JN: Glioblastoma stem cells: Lessons from the tumor hierarchy in a
lethal cancer. Genes Dev. 33:591–609. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hambardzumyan D, Squatrito M, Carbajal E
and Holland EC: Glioma formation, cancer stem cells, and akt
signaling. Stem cell Rev. 4:203–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jawhari S, Ratinaud MH and Verdier M:
Glioblastoma, hypoxia and autophagy: A survival-prone
‘ménage-à-trois’. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leng Y, Chen Z, Ding H, Zhao X, Qin L and
Pan Y: Overexpression of microRNA-29b inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis of colorectal
cancer through the ETV4/ERK/EGFR axis. Cancer Cell Int. 21:172021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu L, Hu H, Zheng LS, Wang MY, Mei Y, Peng
LX, Qiang YY, Li CZ, Meng DF, Wang MD, et al: ETV4 is a theranostic
target in clear cell renal cell carcinoma that promotes metastasis
by activating the pro-metastatic gene FOSL1 in a PI3K-AKT dependent
manner. Cancer Lett. 482:74–89. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Ding X, Liu B, Li M, Chang Y, Shen
H, Xie SM, Xing L and Li Y: ETV4 overexpression promotes
progression of non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating PXN and
MMP1 transcriptionally. Mol Carcinog. 59:73–86. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Li X, Wu H, Wang H, Yao L, Deng Z
and Zhou Y: EMP1 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and
stemness in gliomas through PI3K-AKT signaling and CD44. J Cell
Biochem. 120:17142–17150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miao L, Jiang Z, Wang J, Yang N, Qi Q,
Zhou W, Feng Z, Li W, Zhang Q, Huang B, et al: Epithelial membrane
protein 1 promotes glioblastoma progression through the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 42:605–614.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiapaer S, Furuta T, Tanaka S, Kitabayashi
T and Nakada M: Potential strategies overcoming the temozolomide
resistance for glioblastoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 58:405–421.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee JE, Yoon SS and Moon EY:
Curcumin-induced autophagy augments its antitumor effect against
A172 human glioblastoma cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 27:484–491.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE and
Kruchko C: CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central
nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009.
Neuro Oncol. 14 (Suppl 5):v1–v49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grossman SA, Ye X, Piantadosi S, Desideri
S, Nabors LB, Rosenfeld M, Fisher J and NABTT CNS Consortium:
Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with
radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United
States. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2443–2449. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cosi I, Pellecchia A, De Lorenzo E, Torre
E, Sica M, Nesi G, Notaro R and De Angioletti M: ETV4 promotes late
development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and cell
proliferation through direct and p53-mediated downregulation of
p21. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rodriguez AC, Vahrenkamp JM, Berrett KC,
Clark KA, Guillen KP, Scherer SD, Yang CH, Welm BE, Janát-Amsbury
MM, Graves BJ and Gertz J: ETV4 is necessary for estrogen signaling
and growth in endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Res. 80:1234–1245.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu ST, Sun BH, Ge JN, Shi JL, Zhu MS, Wei
ZG, Li TT, Zhang ZC, Chen WS and Lei ST: CRLF1-MYH9 interaction
regulates proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma through the ERK/ETV4 axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
11:5352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Padul V, Epari S, Moiyadi A, Shetty P and
Shirsat NV: ETV/Pea3 family transcription factor-encoding genes are
overexpressed in CIC-mutant oligodendrogliomas. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 54:725–733. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang J, Wei Y, Shen J, Liu D, Chen X,
Zhou J, Zong H, Yun X, Kong X, Zhang S, et al: Functional
interaction of E1AF and Sp1 in glioma invasion. Mol Cell Biol.
27:8770–8782. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azad MB, Chen Y, Henson ES, Cizeau J,
McMillan-Ward E, Israels SJ and Gibson SB: Hypoxia induces
autophagic cell death in apoptosis-competent cells through a
mechanism involving BNIP3. Autophagy. 4:195–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang Y, Liu J, Hong W, Fei X and Liu R:
Arctigenin inhibits glioblastoma proliferation through the AKT/mTOR
pathway and induces autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2020:35426132020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|