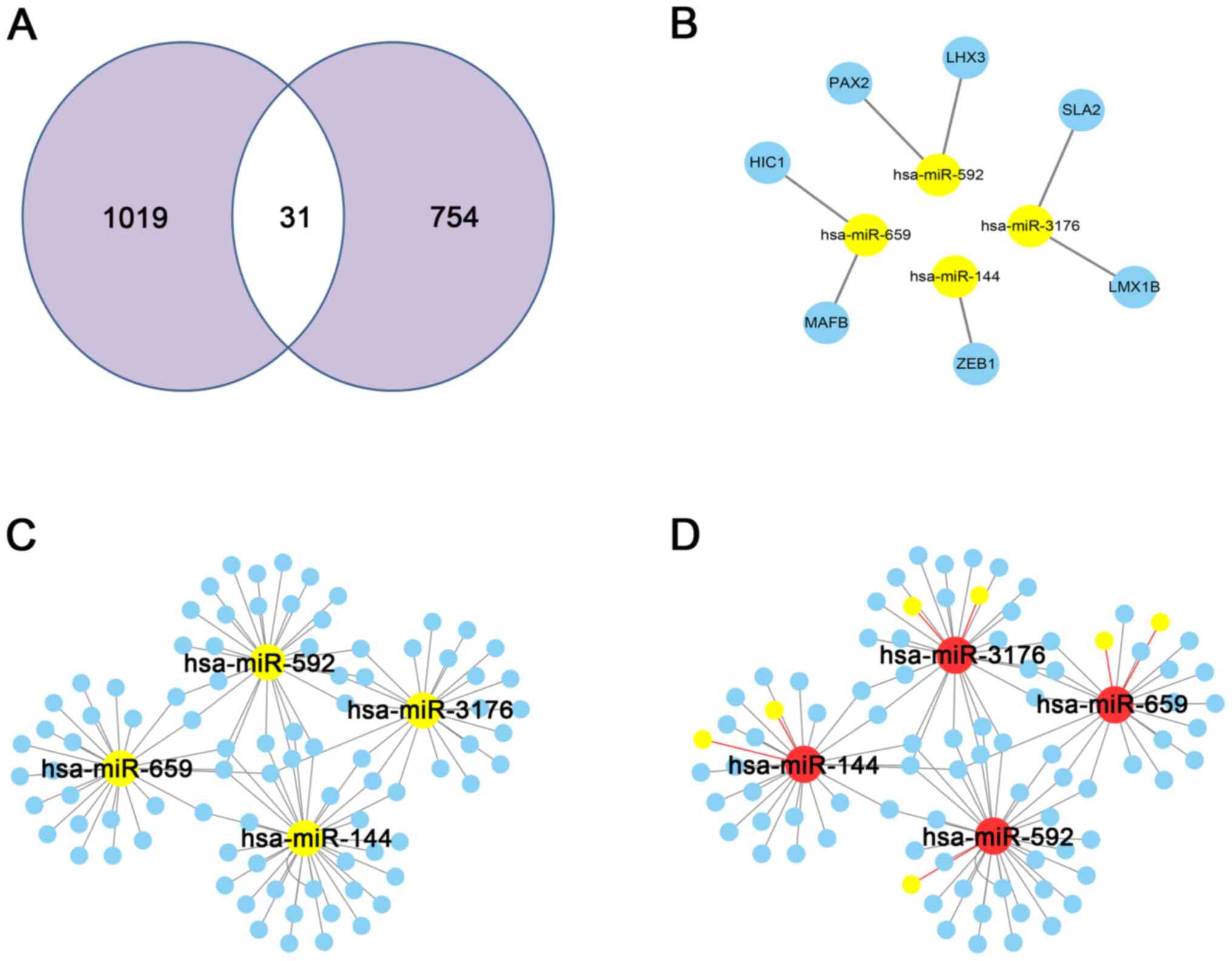
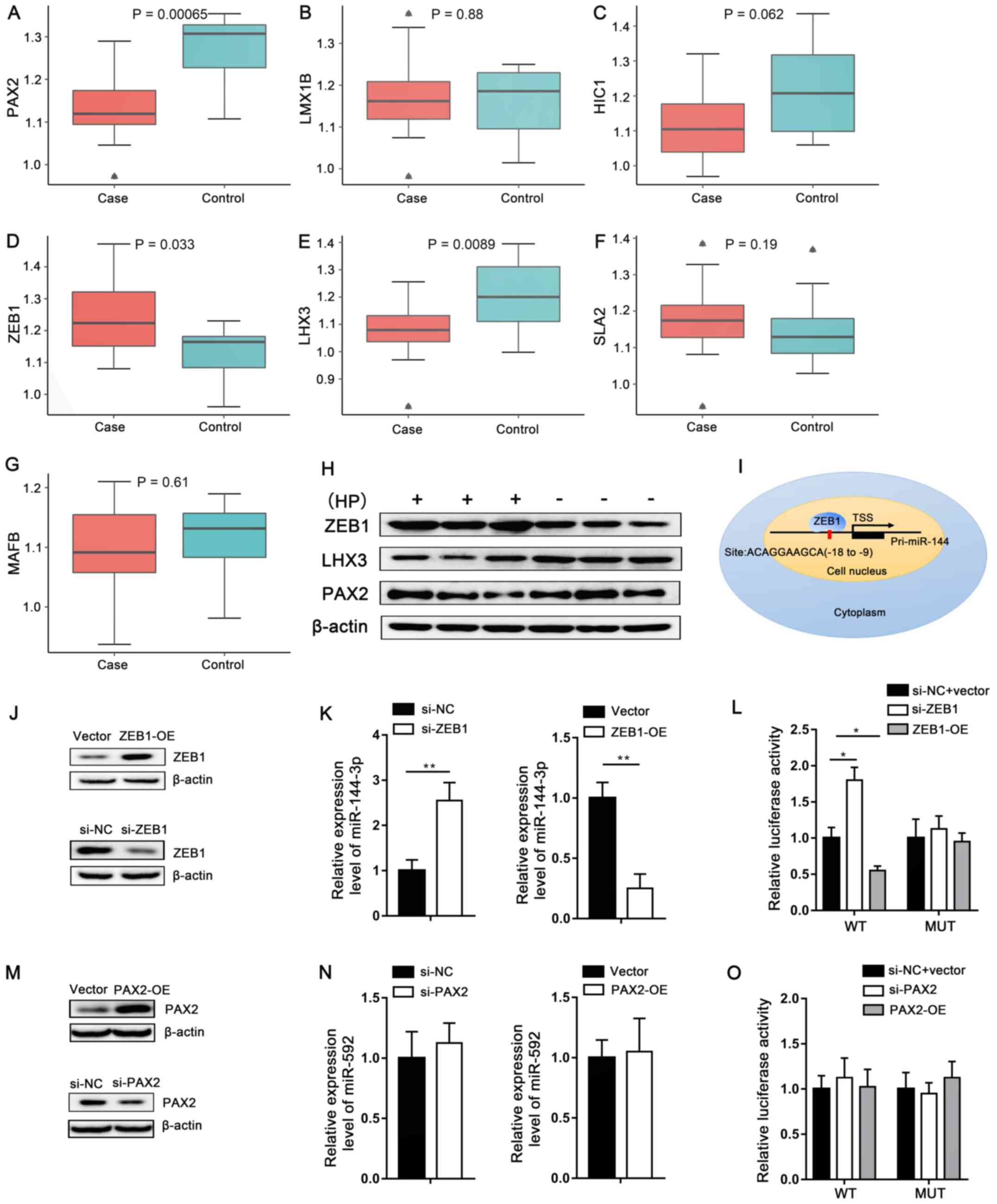
|
1
|
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP,
Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N and Sibley RK: Helicobacter
pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
325:1127–1131. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sepulveda AR: Helicobacter, inflammation,
and gastric cancer. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 1:9–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo LL, Song CH, Wang P, Dai LP, Zhang JY
and Wang KJ: Competing endogenous RNA networks and gastric cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 21:11680–11687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh R and Mo YY: Role of microRNAs in
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:201–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song S and Ajani JA: The role of microRNAs
in cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:109–118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA and
Baltimore D: Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:111–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Huang WY, Huang HY,
Chen W, Weng SL and Huang HD: A systematic review of microRNA
expression profiling studies in human gastric cancer. Cancer Med.
3:878–888. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Link A and Kupcinskas J: MicroRNAs as
non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer: Current
insights and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol.
24:3313–3329. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu L, Qu W and Zhong Z: Down-regulation
of miR-503 expression predicate advanced mythological features and
poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:5609–5613. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Latchman DS: Transcription factors: An
overview. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 29:1305–1312. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hughes TR: Introduction to ‘a handbook of
transcription factors’. Subcell Biochem. 52:1–6. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lichti J, Gallus C and Glasmacher E:
Immune responses-transcriptional and post-transcriptional networks
pass the baton. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:1–4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sussenbach JS, Rodenburg RJ, Scheper W and
Holthuizen P: Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation
of the human IGF-II gene expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 343:63–71.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lefkofsky HB, Veloso A and Ljungman M:
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of nucleotide
excision repair genes in human cells. Mutat Res. 776:9–15. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang HM, Kuang S, Xiong X, Gao T, Liu C
and Guo AY: Transcription factor and microRNA co-regulatory loops:
Important regulatory motifs in biological processes and diseases.
Brief Bioinform. 16:45–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen D, Lu T, Tan J, Zhao K, Li Y, Zhao W,
Li H, Wang Q, Wang Y and Wei L: Identification of a transcription
factor-microRNA network in esophageal adenocarcinoma through
bioinformatics analysis and validation through qRT-PCR. Cancer
Manag Res. 11:3315–3326. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Colaprico A, Silva TC, Olsen C, Garofano
L, Cava C, Garolini D, Sabedot TS, Malta TM, Pagnotta SM,
Castiglioni I, et al: TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for
integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:e712016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dweep H, Gretz N and Sticht C: MiRWalk
database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1182:289–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khan A, Fornes O, Stigliani A, Gheorghe M,
Castro-Mondragon JA, van der Lee R, Bessy A, Chèneby J, Kulkarni
SR, Tan G, et al: JASPAR 2018: Update of the open-access database
of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework.
Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D260–D266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schistosomes, liver flukes and
Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7-14 June 1994. IARC Monogr
Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 61:1–241. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Martel C, Ferlay J, Franceschi S,
Vignat J, Bray F, Forman D and Plummer M: Global burden of cancers
attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic
analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:607–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu H, Liu Y, Cheng P, Wang C, Liu Y, Zhou
W, Xu Y and Ji G: CircRNA_0000392 promotes colorectal cancer
progression through the miR-193a-5p/PIK3R3/AKT axis. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 39:2832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khan K, Javed Z, Sadia H, Sharifi-Rad J,
Cho WC and Luparello C: Quercetin and MicroRNA interplay in
apoptosis regulation in ovarian cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
27:2328–2336. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carvalho GB, Costa LE, Lage DP, Ramos FF,
Santos TTO, Ribeiro PAF, Dias DS, Salles BCS, Lima MP, Carvalho LM,
et al: High-through identification of T cell-specific phage-exposed
mimotopes using PBMCs from tegumentary leishmaniasis patients and
their use as vaccine candidates against Leishmania amazonensis
infection. Parasitology. 146:322–332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Steinlechner M and Parson W: Automation
and high through-put for a DNA database laboratory: Development of
a laboratory information management system. Croat Med J.
42:252–255. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Castranio EL, Mounier A, Wolfe CM, Nam KN,
Fitz NF, Letronne F, Schug J, Koldamova R and Lefterov I: Gene
co-expression networks identify Trem2 and Tyrobp as major hubs in
human APOE expressing mice following traumatic brain injury.
Neurobiol Dis. 105:1–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aldinucci D and Casagrande N: Inhibition
of the CCL5/CCR5 Axis against the progression of gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:14772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bo C, Zhang H, Cao Y, Lu X, Zhang C, Li S,
Kong X, Zhang X, Bai M, Tian K, et al: Construction of a
TF-miRNA-gene feed-forward loop network predicts biomarkers and
potential drugs for myasthenia gravis. Sci Rep. 11:24162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong Z, Wang Q, Hong C, Liu M, Qiu P, Lin
R, Lin X, Chen F, Li Q, Liu L, et al: Identification of seven cell
cycle-related genes with unfavorable prognosis and construction of
their TF-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in breast cancer. J Cancer.
12:740–753. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bertonha FB, Bando SY, Ferreira LR,
Chaccur P, Vinhas C, Zerbini MC, Carneiro-Sampaio MM and
Moreira-Filho CA: Age-related transcriptional modules and
TF-miRNA-mRNA interactions in neonatal and infant human thymus.
PLoS One. 15:e02275472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang XF, Liu JY, Li JL, Wang FZ and Sun
BL: ZEB1 causes the production of
hsa-microRNA-99b/let-7e/microRNA-125a cluster and promotes invasion
of liver cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:1468–1475.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cao J, Han X, Qi X, Jin X and Li X: TUG1
promotes osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by upregulating EZH2 expression
via miR-144-3p. Int J Oncol. 51:1115–1123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guan H, Liang W, Xie Z, Li H, Liu J, Liu
L, Xiu L and Li Y: Down-regulation of miR-144 promotes thyroid
cancer cell invasion by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Endocrine.
48:566–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pan Y, Zhang J, Fu H and Shen L: MiR-144
functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer through inhibiting
ZEB1/2-mediated epithelial mesenchymal transition process. Onco
Targets Ther. 9:6247–6255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang G, An H and Fang X: MicroRNA-144
regulates proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of cells in
malignant solitary pulmonary nodule via zinc finger E-box-binding
homeobox 1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5960–5967. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pan HL, Wen ZS, Huang YC, Cheng X, Wang
GZ, Zhou YC, Wang ZY, Guo YQ, Cao Y and Zhou GB: Down-regulation of
microRNA-144 in air pollution-related lung cancer. Sci Rep.
5:143312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao ZY, Liu H and Zhang Z: MiR-144-3p
increases radiosensibility of gastric cancer cells by targeting
inhibition of ZEB1. Clin Transl Oncol. 23:491–500. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wittekind C: The development of the TNM
classification of gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 65:399–403. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|