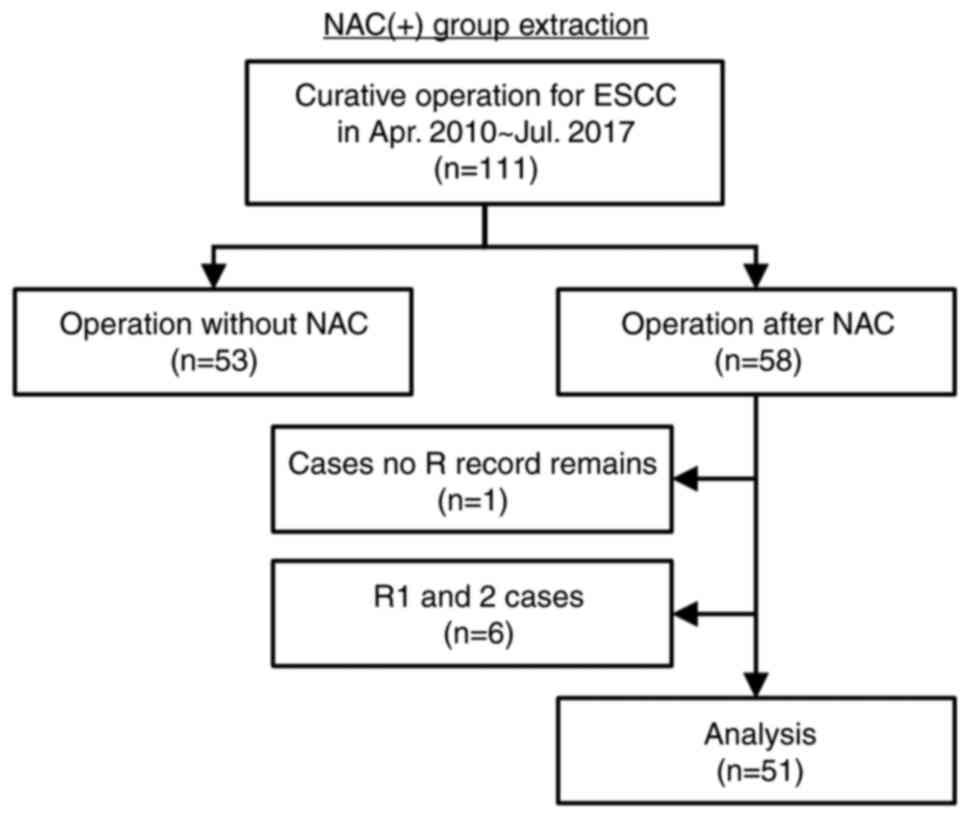
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Watanabe M, Tachimori Y, Oyama T, Toh Y,
Matsubara H, Ueno M, Kono K, Uno T, Ishihara R, Muro K, et al:
Comprehensive registry of esophageal cancer in Japan, 2013.
Esophagus. 18:1–24. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blackham AU, Yue B, Almhanna K, Saeed N,
Fontaine JP, Hoffe S, Shridhar R, Frakes J, Coppola D and Pimiento
JM: The prognostic value of residual nodal disease following
neoadjuvant chemoradiation for esophageal cancer in patients with
complete primary tumor response. J Surg Oncol. 112:597–602. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kamarajah SK, Navidi M, Wahed S, Immanuel
A, Hayes N, Griffin SM and Phillips AW: Significance of neoadjuvant
downstaging in carcinoma of esophagus and gastroesophageal
junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 27:3182–3192. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bollschweiler E, Hölscher AH, Metzger R,
Besch S, Mönig SP, Baldus SE and Drebber U: Prognostic significance
of a new grading system of lymph node morphology after neoadjuvant
radiochemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg.
92:2020–2027. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berger AC, Farma J, Scott WJ, Freedman G,
Weiner L, Cheng JD, Wang H and Goldberg M: Complete response to
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal carcinoma is associated
with significantly improved survival. J Clin Oncol. 23:4330–4337.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsuyama J, Doki Y, Yasuda T, Miyata H,
Fujiwara Y, Takiguchi S, Yamasaki M, Makari Y, Matsuura N, Mano M
and Monden M: The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on lymph node
micrometastases in squamous cell carcinomas of the thoracic
esophagus. Surgery. 141:570–580. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hiraki Y, Kimura Y, Imano M, Kato H, Iwama
M, Shiraishi O, Yasuda A, Shinkai M, Makino T, Motoori M, et al:
Controlling lymph node micrometastases by neoadjuvant chemotherapy
affects the prognosis in advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Surg Today. 51:118–126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa
S, Shimizu H, Nakamura T, Yabusaki H, Aoyama N, Kurita A, et al: A
randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with
cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for
localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic
esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 19:68–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mariette C, Dahan L, Mornex F, Maillard E,
Thomas PA, Meunier B, Boige V, Pezet D, Robb WB, Le Brun-Ly V, et
al: Surgery alone versus chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for
stage I and II esophageal cancer: Final analysis of randomized
controlled phase III trial FFCD 9901. J Clin Oncol. 32:2416–2422.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kitagawa Y, Uno T, Oyama T, Kato K, Kato
H, Kawakubo H, Kawamura O, Kusano M, Kuwano H, Takeuchi H, et al:
Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan
esophageal society: Part 1. Esophagus. 16:1–24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kitagawa Y, Uno T, Oyama T, Kato K, Kato
H, Kawakubo H, Kawamura O, Kusano M, Kuwano H, Takeuchi H, et al:
Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan
esophageal society: Part 2. Esophagus. 16:25–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamasaki M, Yasuda T, Yano M, Hirao M,
Kobayashi K, Fujitani K, Tamura S, Kimura Y, Miyata H, Motoori M,
et al: Multicenter randomized phase II study of cisplatin and
fluorouracil plus docetaxel (DCF) compared with cisplatin and
fluorouracil plus Adriamycin (ACF) as preoperative chemotherapy for
resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (OGSG1003). Ann
Oncol. 28:116–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsu PK, Chien LI, Wang LC and Chou TY;
Taipei Veterans General Hospital Esophageal Cancer Panel, :
Lymphovascular invasion and extracapsular invasion are risk factors
for distant recurrence after preoperative chemoradiotherapy and
oesophagectomy in patients with oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 51:1188–1194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tu CC, Hsu PK, Chien LI, Liu WC, Huang CS,
Hsieh CC, Hsu HS and Wu YC: Prognostic histological factors in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after preoperative
chemoradiation followed by surgery. BMC Cancer. 17:622017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lagarde SM, Phillips AW, Navidi M, Disep
B, Immanuel A and Griffin SM: The presence of lymphovascular and
perineural infiltration after neoadjuvant therapy and
oesophagectomy identifies patients at high risk for recurrence. Br
J Cancer. 113:1427–1433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee PC, Mirza FM, Port JL, Stiles BM, Paul
S, Christos P and Altorki NK: Predictors of recurrence and
disease-free survival in patients with completely resected
esophageal carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 141:1196–1206.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang N, Jia Y, Wang J, Wang X, Bao C, Song
Q, Tan B and Cheng Y: Prognostic significance of lymph node ratio
in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:2335–2341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moon DH, Jeon JH, Yang HC, Kim YI, Lee JY,
Kim MS, Lee JM and Lee GK: Intramural metastasis as a risk factor
for recurrence in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 106:249–256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khan M, Urooj N, Syed AA, Khattak S, Kazmi
A, Ashraf MI and Batool S: Prognostic factors for recurrence in
esophageal cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy and
surgery: A single-institution analysis. Cureus.
12:e81082020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang CH, Hwang Y, Lee HJ, Park IK and Kim
YT: Risk factors for local recurrence and optimal length of
esophagectomy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 102:1074–1080. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Japan Esophageal Society: Japanese
classification of esophageal cancer, 11th edition: Part I.
Esophagus. 14:1–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Japan Esophageal Society: Japanese
classification of esophageal cancer, 11th edition: Part II and III.
Esophagus. 14:37–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brierley J, Gospodarowicz MD and Wittekind
CT: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 8th Edition. Wiley;
Oxford: pp. 57–62. 2017
|
|
25
|
Markar SR, Gronnier C, Duhamel A, Pasquer
A, Théreaux J, Chalret du Rieu M, Lefevre JH, Turner K, Luc G and
Mariette C; FREGAT Working Group-FRENCH-AFC, . Significance of
microscopically incomplete resection margin after esophagectomy for
esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 263:712–718. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hulshoff JB, Faiz Z, Karrenbeld A,
Kats-Ugurlu G, Burgerhof JG, Smit JK and Plukker JT: Prognostic
value of the circumferential resection margin in esophageal cancer
patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 22
(Suppl 3):S1301–S1309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gilbert S, Martel AB, Seely AJ, Maziak DE,
Shamji FM, Sundaresan SR and Villeneuve PJ: Prognostic significance
of a positive radial margin after esophageal cancer resection. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 149:548–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schlick CJR, Khorfan R, Odell DD, Merkow
RP and Bentrem DJ: Margin positivity in resectable esophageal
cancer: Are there modifiable risk factors? Ann Surg Oncol.
27:1496–1507. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshida N, Baba Y, Shigaki H, Harada K,
Iwatsuki M, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y, Kurashige J, Kosumi K, Tokunaga
R, et al: Risk factors of early recurrence within 6 months after
esophagectomy following neoadjuvant chemotherapy for resectable
advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol.
21:1071–1078. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang H, Chen X, Wang S, Fan J and Lu L:
Poorer prognosis associated with simultaneous lymphatic and
vascular invasion in patients with squamous carcinoma of the
thoracic oesophagus. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 52:378–384. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Inomata M, Shiroshita H, Uchida H, Bandoh
T, Akira S, Yamaguchi S, Kurokawa Y, Seki Y, Eguchi S, Wada N, et
al: Current status of endoscopic surgery in Japan: The 14th
national survey of endoscopic surgery by the Japan society for
endoscopic surgery. Asian J Endosc Surg. 13:7–18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Udagawa H: Past, present, and future of
three-field lymphadenectomy for thoracic esophageal cancer. Ann
Gastroenterol Surg. 4:324–330. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsuda S, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo H and
Kitagawa Y: Three-field lymph node dissection in esophageal cancer
surgery. J Thorac Dis. 9 (Suppl 8):S731–S740. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shang QX, Chen LQ, Hu WP, Deng HY, Yuan Y
and Cai J: Three-field lymph node dissection in treating the
esophageal cancer. J Thorac Dis. 8:E1136–E1149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye T, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Chen H:
Three-field or two-field resection for thoracic esophageal cancer:
A meta-analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 96:1933–1941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ma GW, Situ DR, Ma QL, Long H, Zhang LJ,
Lin P and Rong TH: Three-field vs two-field lymph node dissection
for esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol.
20:18022–18030. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Altorki N, Kent M, Ferrara C and Port J:
Three-field lymph node dissection for squamous cell and
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg. 236:177–183. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lerut T, Nafteux P, Moons J, Coosemans W,
Decker G, De Leyn P, Van Raemdonck D and Ectors N: Three-field
lymphadenectomy for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal
junction in 174 R0 resections: Impact on staging, disease-free
survival, and outcome: A plea for adaptation of TNM classification
in upper-half esophageal carcinoma. Ann Surg. 240:962–974. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Reynolds JV, Muldoon C, Hollywood D, Ravi
N, Rowley S, O'Byrne K, Kennedy J and Murphy TJ: Long-term outcomes
following neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann
Surg. 245:707–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mariette C, Piessen G, Briez N and
Triboulet JP: The number of metastatic lymph nodes and the ratio
between metastatic and examined lymph nodes are independent
prognostic factors in esophageal cancer regardless of neoadjuvant
chemoradiation or lymphadenectomy extent. Ann Surg. 247:365–371.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koen Talsma A, Shapiro J, Looman CW, van
Hagen P, Steyerberg EW, van der Gaast A, van Berge Henegouwen MI,
Wijnhoven BP, van Lanschot JJ; CROSS Study Group, ; et al: Lymph
node retrieval during esophagectomy with and without neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy: Prognostic and therapeutic impact on survival.
Ann Surg. 260:786–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chirieac LR, Swisher SG, Ajani JA, Komaki
RR, Correa AM, Morris JS, Roth JA, Rashid A, Hamilton SR and Wu TT:
Posttherapy pathologic stage predicts survival in patients with
esophageal carcinoma receiving preoperative chemoradiation. Cancer.
103:1347–1355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schneider PM, Baldus SE, Metzger R, Kocher
M, Bongartz R, Bollschweiler E, Schaefer H, Thiele J, Dienes HP,
Mueller RP and Hoelscher AH: Histomorphologic tumor regression and
lymph node metastases determine prognosis following neoadjuvant
radiochemotherapy for esophageal cancer: Implications for response
classification. Ann Surg. 242:684–692. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miyata H, Tanaka K, Makino T, Yamasaki M,
Miyazaki Y, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Morii
E, et al: The impact of pathological tumor regression and nodal
status on survival and systemic disease in patients undergoing
neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Ann Surg Oncol. 25:2409–2417. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mohammed RA, Martin SG, Gill MS, Green AR,
Paish EC and Ellis IO: Improved methods of detection of
lymphovascular invasion demonstrate that it is the predominant
method of vascular invasion in breast cancer and has important
clinical consequences. Am J Surg Pathol. 31:1825–1833. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu J, Li H, Zhou P, Cai T, Tang Z, Wang
Y, Cui Y, Sun Y and Wang X: Reevaluation of lymphovascular invasion
in gastric cancer using endothelial markers D2-40 and EVG: Enhanced
detection, better predictor of lymph node metastasis and biological
aggressiveness. J Surg Oncol. 123:1736–1741. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|