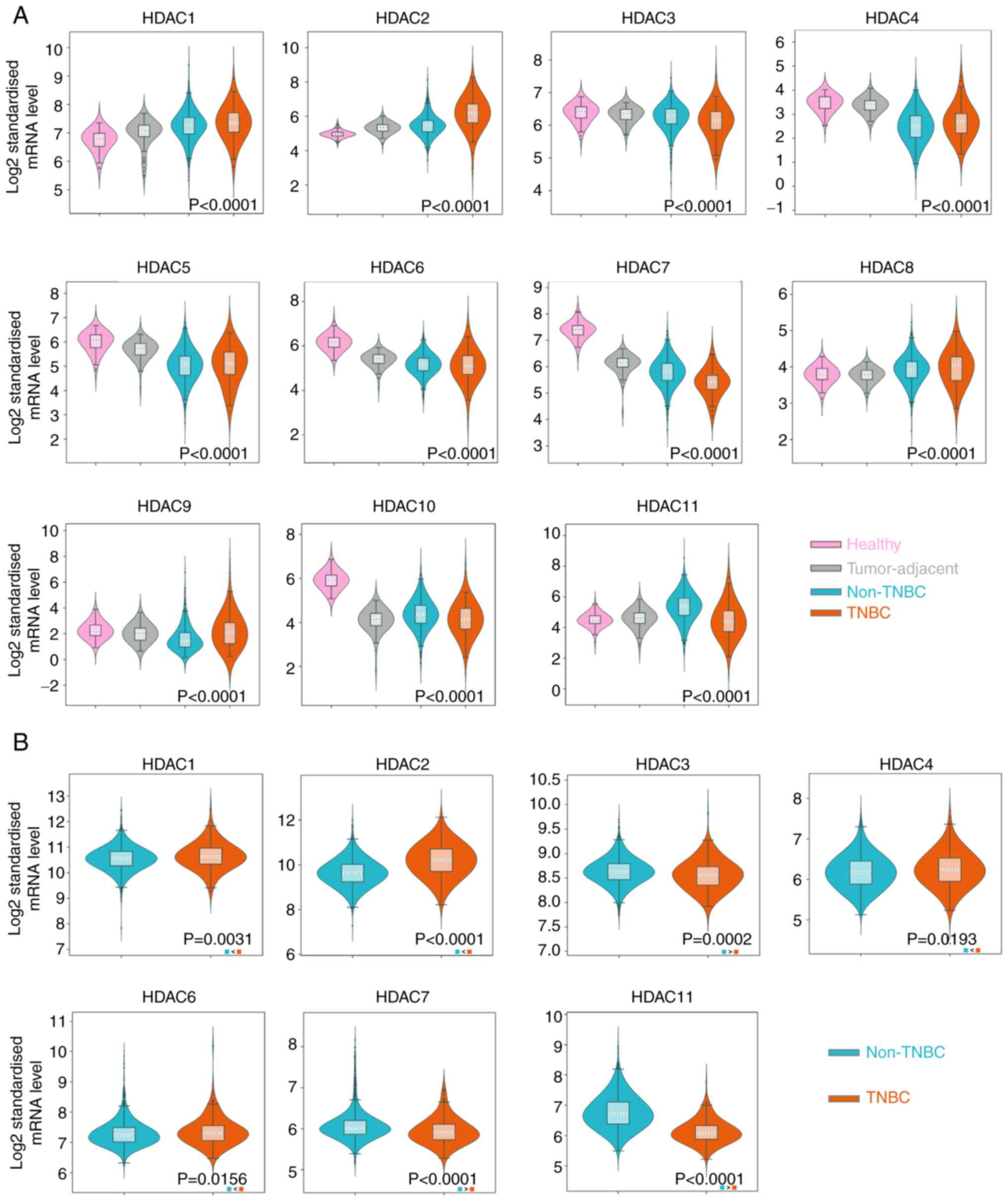
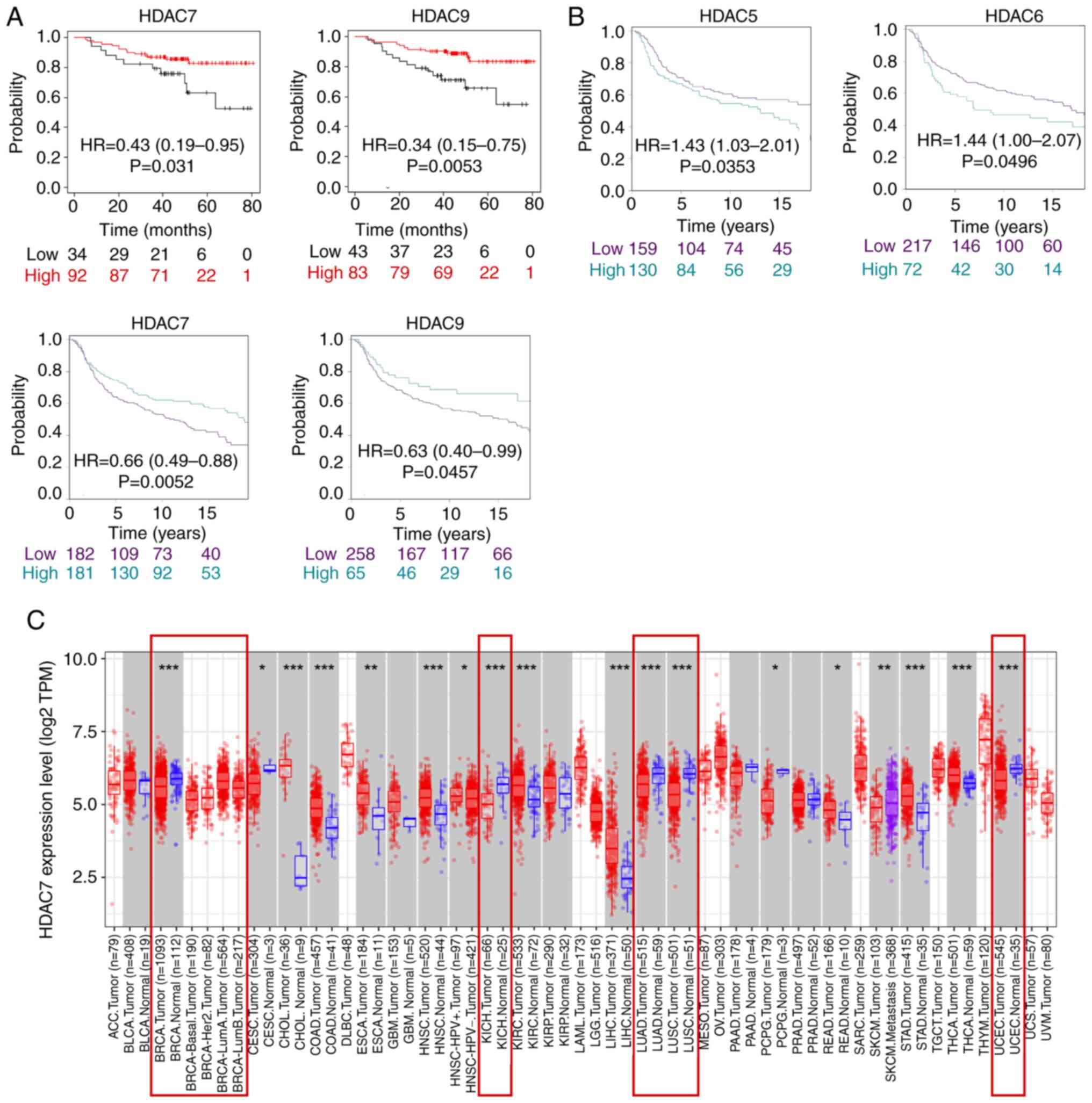
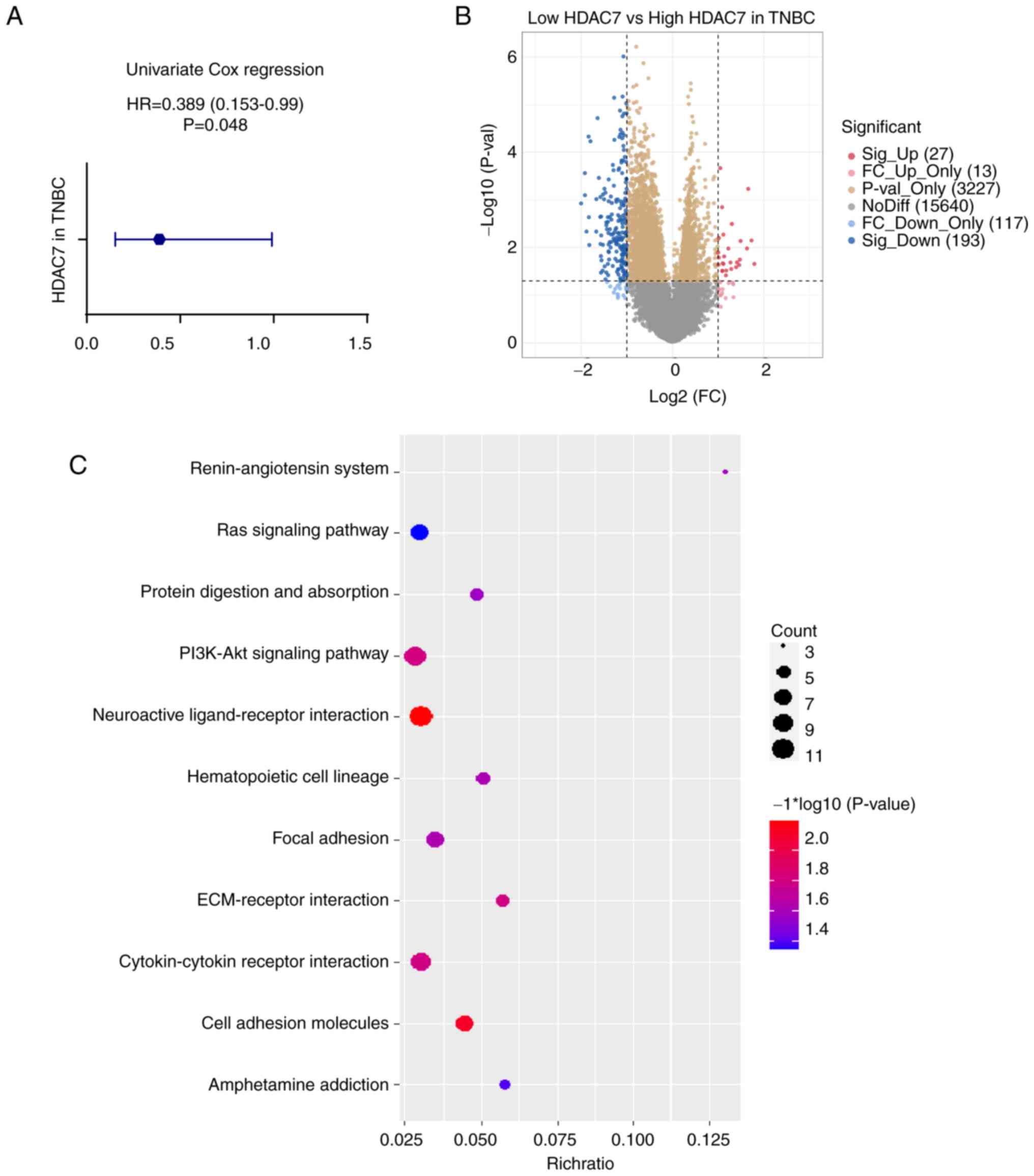
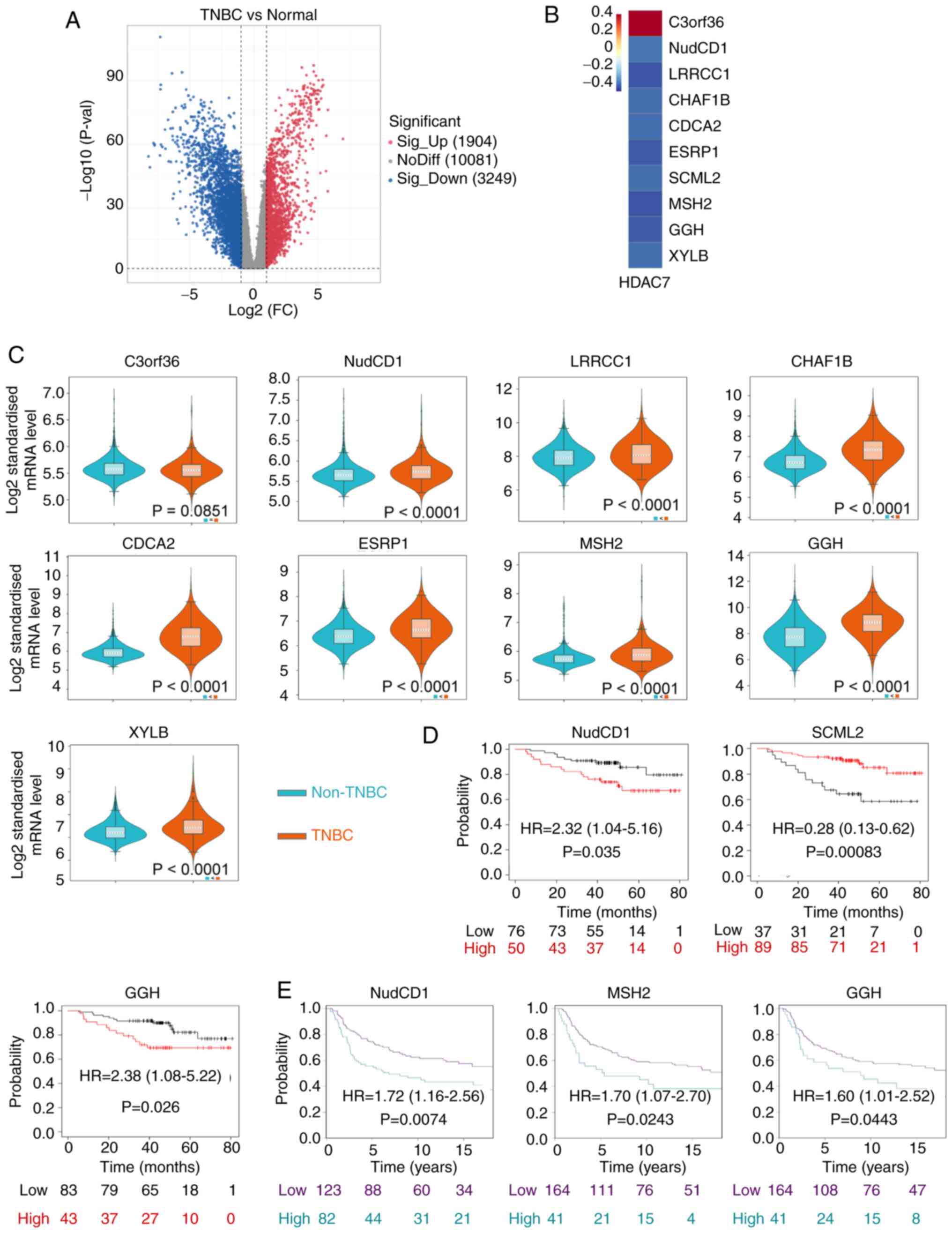
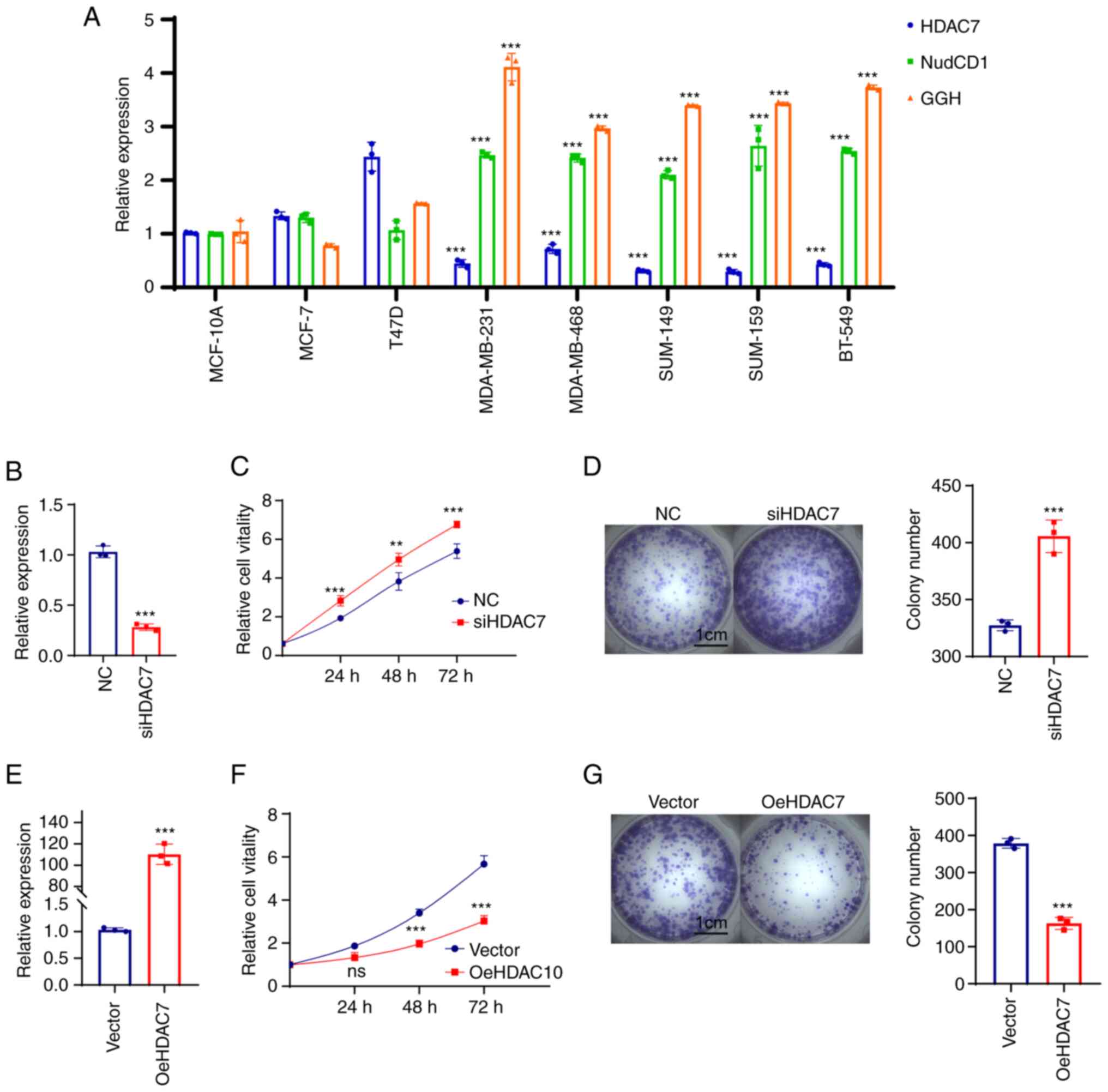
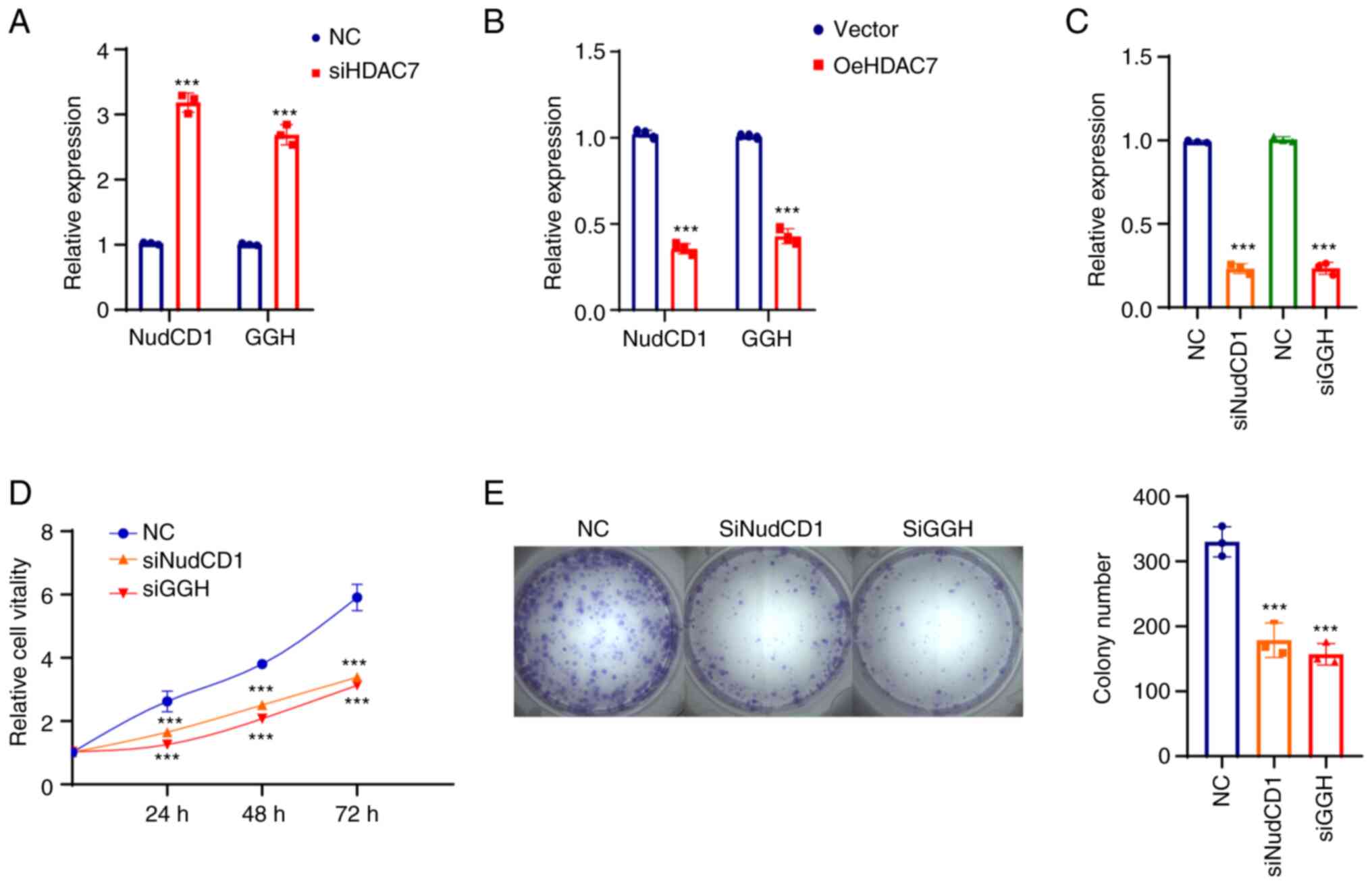
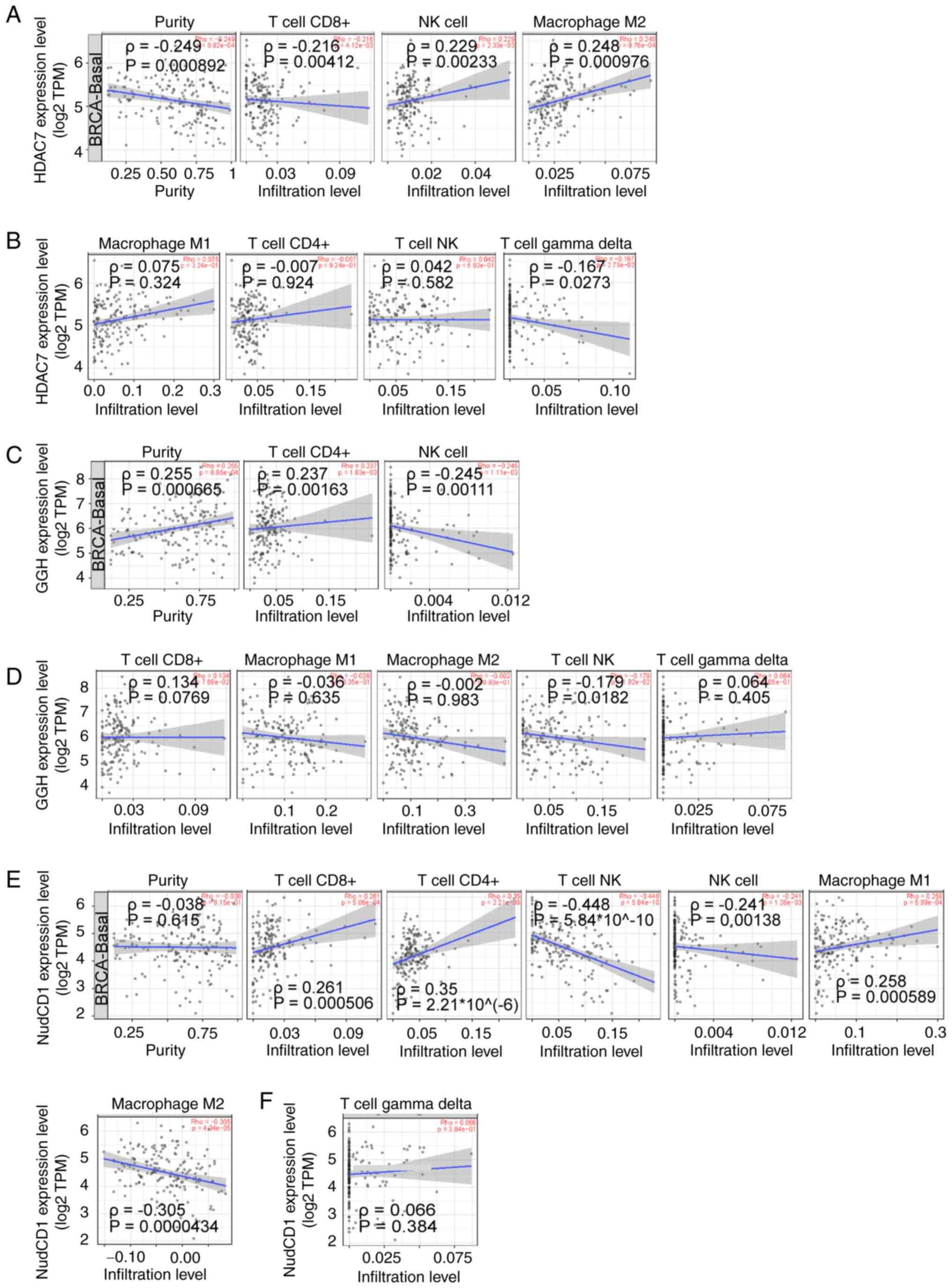
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C
and Curigliano G: Breast cancer. Lancet. 397:1750–1769. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barzaman K, Karami J, Zarei Z,
Hosseinzadeh A, Kazemi MH, Moradi-Kalbolandi S, Safari E and
Farahmand L: Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments.
Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Won KA and Spruck C: Triple-negative
breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (Review).
Int J Oncol. 57:1245–1261. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Portela A and Esteller M: Epigenetic
modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 28:1057–1068.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu Y, Chan YT, Tan HY, Li S, Wang N and
Feng Y: Epigenetic regulation in human cancer: The potential role
of epi-drug in cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 19:792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garcia-Martinez L, Zhang Y, Nakata Y, Chan
HL and Morey L: Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and
resistance. Nat Commun. 12:17862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun L, Zhang H and Gao P: Metabolic
reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer.
Protein Cell. 13:877–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T and Oehme I:
HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett.
277:8–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Falkenberg KJ and Johnstone RW: Histone
deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases
and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:673–691. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ho TCS, Chan AHY and Ganesan A: Thirty
years of HDAC inhibitors: 2020 Insight and hindsight. J Med Chem.
63:12460–12484. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hesham HM, Lasheen DS and Abouzid KAM:
Chimeric HDAC inhibitors: Comprehensive review on the HDAC-based
strategies developed to combat cancer. Med Res Rev. 38:2058–2109.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brancolini C, Gagliano T and Minisini M:
HDACs and the epigenetic plasticity of cancer cells: Target the
complexity. Pharmacol Ther. 238:1081902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH and Samarakoon
SR: Emerging role of histone deacetylase inhibitors as
anti-breast-cancer agents. Drug Discov Today. 24:685–702. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dowling CM, Hollinshead KER, Di Grande A,
Pritchard J, Zhang H, Dillon ET, Haley K, Papadopoulos E, Mehta AK,
Bleach R, et al: Multiple screening approaches reveal HDAC6 as a
novel regulator of glycolytic metabolism in triple-negative breast
cancer. Sci Adv. 7:eabc48972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oba T, Ono M, Matoba H, Uehara T, Hasegawa
Y and Ito KI: HDAC6 inhibition enhances the anti-tumor effect of
eribulin through tubulin acetylation in triple-negative breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 186:37–51. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang ZT, Chen ZJ, Jiang GM, Wu YM, Liu T,
Yi YM, Zeng J, Du J and Wang HS: Histone deacetylase inhibitors
suppress mutant p53 transcription via HDAC8/YY1 signals in triple
negative breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 28:506–515. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu S, Luo Z, Yu PJ, Xie H and He YW:
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) promotes the epithelial
mesenchymal transition of triple negative breast cancer cells via
HDAC8/FOXA1 signals. Biol Chem. 397:75–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Palmieri D, Lockman PR, Thomas FC, Hua E,
Herring J, Hargrave E, Johnson M, Flores N, Qian Y, Vega-Valle E,
et al: Vorinostat inhibits brain metastatic colonization in a model
of triple-negative breast cancer and induces DNA double-strand
breaks. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6148–6157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tate CR, Rhodes LV, Segar HC, Driver JL,
Pounder FN, Burow ME and Collins-Burow BM: Targeting
triple-negative breast cancer cells with the histone deacetylase
inhibitor panobinostat. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rhodes LV, Tate CR, Segar HC, Burks HE,
Phamduy TB, Hoang V, Elliott S, Gilliam D, Pounder FN, Anbalagan M,
et al: Suppression of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by
pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat via inhibition of ZEB family of EMT
master regulators. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 145:593–604. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang K, Liu Z, Yao Y, Qiu Y, Li F, Chen
D, Hamilton DJ, Li Z and Jiang S: Structure-based design of a
selective class I histone deacetylase (HDAC) near-infrared (NIR)
probe for epigenetic regulation detection in triple-negative breast
cancer (TNBC). J Med Chem. 64:4020–4033. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pinkerneil M, Hoffmann MJ, Deenen R,
Köhrer K, Arent T, Schulz WA and Niegisch G: Inhibition of class I
histone deacetylases 1 and 2 promotes urothelial carcinoma cell
death by various mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:299–312. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sulaiman A, McGarry S, Lam KM, El-Sahli S,
Chambers J, Kaczmarek S, Li L, Addison C, Dimitroulakos J, Arnaout
A, et al: Co-inhibition of mTORC1, HDAC and ESR1α retards the
growth of triple-negative breast cancer and suppresses cancer stem
cells. Cell Death Dis. 9:8152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma W, Sun J, Xu J, Luo Z, Diao D, Zhang Z,
Oberly PJ, Minnigh MB, Xie W, Poloyac SM, et al: Sensitizing triple
negative breast cancer to tamoxifen chemotherapy via a
redox-responsive vorinostat-containing polymeric prodrug
nanocarrier. Theranostics. 10:2463–2478. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Torres-Adorno AM, Lee J, Kogawa T,
Ordentlich P, Tripathy D, Lim B and Ueno NT: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor enhances the efficacy of MEK inhibitor through
NOXA-mediated MCL1 degradation in triple-negative and inflammatory
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4780–4792. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Min A, Im SA, Kim DK, Song SH, Kim HJ, Lee
KH, Kim TY, Han SW, Oh DY, Kim TY, et al: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), enhances
anti-tumor effects of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)
inhibitor olaparib in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res. 17:332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang JP and Ling K: EZH2 and histone
deacetylase inhibitors induce apoptosis in triple negative breast
cancer cells by differentially increasing H3 Lys27
acetylation in the BIM gene promoter and enhancers. Oncol Lett.
14:5735–5742. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wiegmans AP, Yap PY, Ward A, Lim YC and
Khanna KK: Differences in expression of key DNA damage repair genes
after epigenetic-induced brcaness dictate synthetic lethality with
PARP1 inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2321–2331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao R, Balusu R, Fiskus W, Mudunuru U,
Venkannagari S, Chauhan L, Smith JE, Hembruff SL, Ha K, Atadja P
and Bhalla KN: Combination of pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor and
autophagy inhibitor exerts superior efficacy against
triple-negative human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
11:973–983. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Garmpis N, Damaskos C, Garmpi A,
Kalampokas E, Kalampokas T, Spartalis E, Daskalopoulou A, Valsami
S, Kontos M, Nonni A, et al: Histone deacetylases as new
therapeutic targets in triple-negative breast cancer: Progress and
promises. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 14:299–313. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang Z, Li W, Hu X, Zhang Q, Sun T, Cui
S, Wang S, Ouyang Q, Yin Y, Geng C, et al: Tucidinostat plus
exemestane for postmenopausal patients with advanced, hormone
receptor-positive breast cancer (ACE): A randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:806–815. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chiu HW, Yeh YL, Wang YC, Huang WJ, Ho SY,
Lin P and Wang YJ: Combination of the novel histone deacetylase
inhibitor YCW1 and radiation induces autophagic cell death through
the downregulation of BNIP3 in triple-negative breast cancer cells
in vitro and in an orthotopic mouse model. Mol Cancer. 15:462016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
da Silva JL, Cardoso Nunes NC, Izetti P,
de Mesquita GG and de Melo AC: Triple negative breast cancer: A
thorough review of biomarkers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
145:1028552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
R Core Team. R, . A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2022, URL. http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
39
|
Kuemmerlen D, Echtermann T, Muentener C
and Sidler X: Agreement of benchmarking high antimicrobial usage
farms based on either animal treatment index or number of national
defined daily doses. Front Vet Sci. 7:6382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li T, Fu J, Zeng Z, Cohen D, Li J, Chen Q,
Li B and Liu XS: TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune
cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 48((W1)): W509–W514. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nolan T, Hands RE and Bustin SA:
Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc.
1:1559–1582. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Keenan TE and Tolaney SM: Role of
immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 18:479–489. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guo K, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Han L, Shao C, Feng
Y, Gao F, Di S, Zhang Z, Zhang J, et al: HDAC7 promotes NSCLC
proliferation and metastasis via stabilization by deubiquitinase
USP10 and activation of β-catenin-FGF18 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 41:912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lei Y, Liu L, Zhang S, Guo S, Li X, Wang
J, Su B, Fang Y, Chen X, Ke H and Tao W: Hdac7 promotes lung
tumorigenesis by inhibiting Stat3 activation. Mol Cancer.
16:1702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu X, Wang M, Wu J, Han Q and Zhang X:
ZNF326 promotes malignant phenotype of glioma by up-regulating
HDAC7 expression and activating Wnt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang H, Wang Y, Dou J, Guo Y, He J, Li L,
Liu X, Chen R, Deng R, Huang J, et al: Acetylation of AGO2 promotes
cancer progression by increasing oncogenic miR-19b biogenesis.
Oncogene. 38:1410–1431. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Azagra A, Meler A, de Barrios O,
Tomás-Daza L, Collazo O, Monterde B, Obiols M, Rovirosa L,
Vila-Casadesús M, Cabrera-Pasadas M, et al: The HDAC7-TET2
epigenetic axis is essential during early B lymphocyte development.
Nucleic Acids Res. 50:8471–8490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Barneda-Zahonero B, Collazo O, Azagra A,
Fernández-Duran I, Serra-Musach J, Islam AB, Vega-Garcia N,
Malatesta R, Camós M, Gómez A, et al: The transcriptional repressor
HDAC7 promotes apoptosis and c-Myc downregulation in particular
types of leukemia and lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16352015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Turtoi A, Mottet D, Matheus N, Dumont B,
Peixoto P, Hennequiere V, Deroanne C, Colige A, De Pauw E,
Bellahcène A and Castronovo V: The angiogenesis suppressor gene
AKAP12 is under the epigenetic control of HDAC7 in endothelial
cells. Angiogenesis. 15:543–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Caslini C, Hong S, Ban YJ, Chen XS and
Ince TA: HDAC7 regulates histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation and
transcriptional activity at super-enhancer-associated genes in
breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 38:6599–6614. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cutano V, Di Giorgio E, Minisini M, Picco
R, Dalla E and Brancolini C: HDAC7-mediated control of tumour
microenvironment maintains proliferative and stemness competence of
human mammary epithelial cells. Mol Oncol. 13:1651–1668. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Witt AE, Lee CW, Lee TI, Azzam DJ, Wang B,
Caslini C, Petrocca F, Grosso J, Jones M, Cohick EB, et al:
Identification of a cancer stem cell-specific function for the
histone deacetylases, HDAC1 and HDAC7, in breast and ovarian
cancer. Oncogene. 36:1707–1720. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Uzelac B, Krivokuca A, Susnjar S,
Milovanovic Z and Supic G: Histone deacetylase 7 gene
overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of triple-negative
breast cancer patients. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 25:227–235.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Han B, Zhang YY, Xu K, Bai Y, Wan LH, Miao
SK, Zhang KX, Zhang HW, Liu Y and Zhou LM: NUDCD1 promotes
metastasis through inducing EMT and inhibiting apoptosis in
colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 8:810–823. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He B, Xia S and Zhang Z: NudCD1 promotes
the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer
cells through the activation of IGF1R-ERK1/2. Pathobiology.
87:244–253. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shubbar E, Helou K, Kovács A, Nemes S,
Hajizadeh S, Enerbäck C and Einbeigi Z: High levels of γ-glutamyl
hydrolase (GGH) are associated with poor prognosis and unfavorable
clinical outcomes in invasive breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:472013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu C, Qi H, Zhang Y, Zhao W and Wu G:
Elevated expression of gamma-glutamyl hydrolase is associated with
poor prognosis and altered immune signature in uterine corpus
endometrial carcinoma. Front Genet. 12:7641942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Maezawa Y, Sakamaki K, Oue N, Kimura Y,
Hashimoto I, Hara K, Kano K, Aoyama T, Hiroshima Y, Yamada T, et
al: High gamma-glutamyl hydrolase and low folylpolyglutamate
synthetase expression as prognostic biomarkers in patients with
locally advanced gastric cancer who were administrated
postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 146:75–86. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Avella Patino DM, Radhakrishnan V,
Suvilesh KN, Manjunath Y, Li G, Kimchi ET, Staveley-O'Carroll KF,
Warren WC, Kaifi JT and Mitchem JB: Epigenetic regulation of cancer
immune cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 83:377–383. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Albertsson PA, Basse PH, Hokland M,
Goldfarb RH, Nagelkerke JF, Nannmark U and Kuppen PJ: NK cells and
the tumour microenvironment: Implications for NK-cell function and
anti-tumour activity. Trends Immunol. 24:603–609. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu SY, Fu T, Jiang YZ and Shao ZM: Natural
killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer. 19:1202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lorenzo-Herrero S, López-Soto A,
Sordo-Bahamonde C, Gonzalez-Rodriguez AP, Vitale M and Gonzalez S:
NK cell-based immunotherapy in cancer metastasis. Cancers (Basel).
11:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bald T, Krummel MF, Smyth MJ and Barry KC:
The NK cell-cancer cycle: Advances and new challenges in NK
cell-based immunotherapies. Nat Immunol. 21:835–847. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|