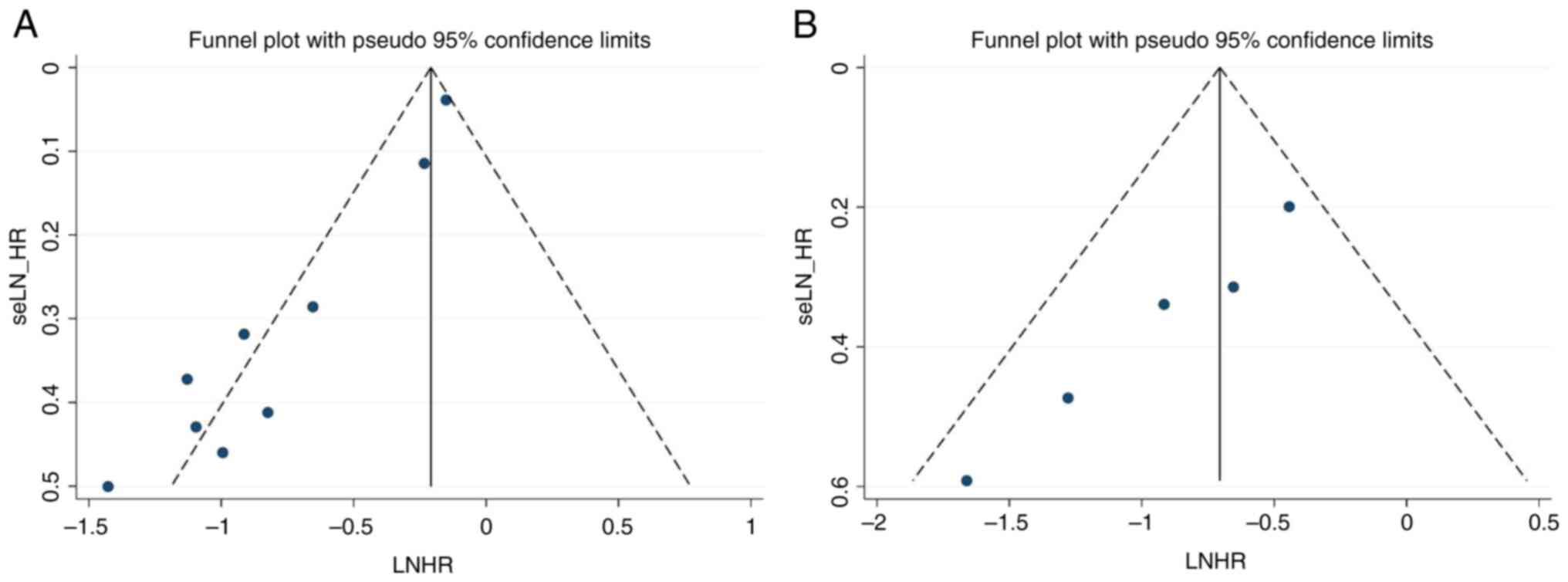
|
1
|
Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU and Polyak K:
Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast
cancer: Improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov.
9:176–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Diana A, Carlino F, Franzese E,
Oikonomidou O, Criscitiello C, De Vita F, Ciardiello F and Orditura
M: Early triple negative breast cancer: Conventional treatment and
emerging therapeutic landscapes. Cancers (Basel). 12:8192020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Won KA and Spruck C: Triple-negative
breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (Review).
Int J Oncol. 57:1245–1261. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gupta GK, Collier AL, Lee D, Hoefer RA,
Zheleva V, Siewertsz van Reesema LL, Tang-Tan AM, Guye ML, Chang
DZ, Winston JS, et al: Perspectives on triple-negative breast
cancer: Current treatment strategies, unmet needs, and potential
targets for future therapies. Cancers (Basel). 12:23922020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, Im YH, Lee ES,
Yokota I, Kuroi K, Im SA, Park BW, Kim SB, et al: Adjuvant
capecitabine for breast cancer after preoperative chemotherapy. N
Engl J Med. 376:2147–2159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K,
Costantino JP, Wolmark N, Bonnefoi H, Cameron D, Gianni L,
Valagussa P, et al: Pathological complete response and long-term
clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis.
Lancet. 384:164–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Isakoff SJ: Triple-negative breast cancer:
Role of specific chemotherapy agents. Cancer J. 16:53–61. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Symmans WF, Wei C, Gould R, Yu X, Zhang Y,
Liu M, Walls A, Bousamra A, Ramineni M, Sinn B, et al: Long-Term
prognostic risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy associated with
residual cancer burden and breast cancer subtype. J Clin Oncol.
35:1049–1060. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Criollo A, Ortiz C, Lidereau R, Mariette C, Chaput N, Mira JP,
Delaloge S, et al: The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates
the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol
Rev. 220:47–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zitvogel L and Kroemer G: The immune
response against dying tumor cells: Avoid disaster, achieve cure.
Cell Death Differ. 15:1–2. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
García-Teijido P, Cabal ML, Fernández IP
and Pérez YF: Tumor-Infiltrating lymphocytes in triple negative
breast cancer: The future of immune targeting. Clin Med Insights
Oncol. 10 (Suppl 1):S31–S39. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ravelli A, Roviello G, Cretella D,
Cavazzoni A, Biondi A, Cappelletti MR, Zanotti L, Ferrero G, Ungari
M, Zanconati F, et al: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and breast
cancer: Beyond the prognostic and predictive utility. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176950232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dieci MV, Radosevic-Robin N, Fineberg S,
van den Eynden G, Ternes N, Penault-Llorca F, Pruneri G, D'Alfonso
TM, Demaria S, Castaneda C, et al: Update on tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer, including recommendations to
assess TILs in residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy and in
carcinoma in situ: A report of the International Immuno-Oncology
Biomarker Working Group on breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 52((Pt
2)): 16–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao G, Wang Z, Qu X and Zhang Z:
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with
triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 20:1792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Demaria S, Volm MD, Shapiro RL, Yee HT,
Oratz R, Formenti SC, Muggia F and Symmans WF: Development of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer after neoadjuvant
paclitaxel chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3025–3030.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J,
Welch V, Losos M and Tugwell P: The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)
for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomised Studies in
Meta-Analyses. Symposium on Systematic Reviews: Beyond the Basics.
2014.
|
|
18
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials revisited. Contemp Clin Trials. 45((Pt A)):
139–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luen SJ, Salgado R, Dieci MV, Vingiani A,
Curigliano G, Gould RE, Castaneda C, D'Alfonso T, Sanchez J, Cheng
E, et al: Prognostic implications of residual disease
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and residual cancer burden in
triple-negative breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 30:236–242. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park JH, Ahn JH and Kim SB: How shall we
treat early triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): From the current
standard to upcoming immuno-molecular strategies. ESMO Open. 3
(Suppl 1):e0003572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Andre F, Dieci MV, Dubsky P, Sotiriou C,
Curigliano G, Denkert C and Loi S: Molecular pathways: Involvement
of immune pathways in the therapeutic response and outcome in
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:28–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ladoire S, Mignot G, Dabakuyo S, Arnould
L, Apetoh L, Rébé C, Coudert B, Martin F, Bizollon MH, Vanoli A, et
al: In situ immune response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
breast cancer predicts survival. J Pathol. 224:389–400. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee H, Lee M, Seo JH, Gong G and Lee HJ:
Changes in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy and clinical significance in triple negative breast
cancer. Anticancer Res. 40:1883–1890. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani
S, Lederer B, Heppner BI, Weber KE, Budczies J, Huober J, Klauschen
F, Furlanetto J, et al: Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and
prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis
of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol.
19:40–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pruneri G, Gray KP, Vingiani A, Viale G,
Curigliano G, Criscitiello C, Láng I, Ruhstaller T, Gianni L,
Goldhirsch A, et al: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are a
powerful prognostic marker in patients with triple-negative breast
cancer enrolled in the IBCSG phase III randomized clinical trial
22–00. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 158:323–331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pruneri G, Vingiani A, Bagnardi V,
Rotmensz N, De Rose A, Palazzo A, Colleoni AM, Goldhirsch A and
Viale G: Clinical validity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
analysis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
27:249–256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dieci MV, Criscitiello C, Goubar A, Viale
G, Conte P, Guarneri V, Ficarra G, Mathieu MC, Delaloge S,
Curigliano G and Andre F: Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes on residual disease after primary chemotherapy for
triple-negative breast cancer: A retrospective multicenter study.
Ann Oncol. 25:611–618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lejeune M, Reverté L, Sauras E, Gallardo
N, Bosch R, Roso A, Petit A, Peg V, Riu F, García-Fontgivell J, et
al: Prognostic implications of the residual tumor microenvironment
after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer
patients without pathological complete response. Cancers (Basel).
15:5972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Zong B, Yu Y, Wang Y, Tang Z, Chen
R, Huang M and Liu S: Ki67 index changes and tumor-infiltrating
lymphocyte levels impact the prognosis of triple-negative breast
cancer patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 11:6686102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghajar CM: On leukocytes in mammary
development and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:a0132762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
da Silva JL, de Albuquerque LZ, Rodrigues
FR, de Mesquita GG, Fernandes PV, Thuler LCS and de Melo AC:
Prognostic influence of residual tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
subtype after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast
cancer. Front Oncol. 11:6367162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pinard C, Debled M, Ben Rejeb H, Velasco
V, Tunon de Lara C, Hoppe S, Richard E, Brouste V, Bonnefoi H and
MacGrogan G: Residual cancer burden index and tumor-infiltrating
lymphocyte subtypes in triple-negative breast cancer after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 179:11–23. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gu-Trantien C, Loi S, Garaud S, Equeter C,
Libin M, de Wind A, Ravoet M, Le Buanec H, Sibille C,
Manfouo-Foutsop G, et al: CD4+ follicular helper T cell
infiltration predicts breast cancer survival. J Clin Invest.
123:2873–2892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin KR, Pang DM, Jin YB, Hu Q, Pan YM, Cui
JH, Chen XP, Lin YX, Mao XF, Duan HB and Luo W: Circulating
CD8+ T-cell repertoires reveal the biological
characteristics of tumors and clinical responses to chemotherapy in
breast cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:1743–1752.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsumoto H, Thike AA, Li H, Yeong J, Koo
SL, Dent RA, Tan PH and Iqbal J: Increased CD4 and CD8-positive T
cell infiltrate signifies good prognosis in a subset of
triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
156:237–247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miyashita M, Sasano H, Tamaki K, Hirakawa
H, Takahashi Y, Nakagawa S, Watanabe G, Tada H, Suzuki A, Ohuchi N
and Ishida T: Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating CD8+
and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in residual tumors and alterations in these
parameters after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast
cancer: A retrospective multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res.
17:1242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sheri A, Smith IE, Johnston SR, A'Hern R,
Nerurkar A, Jones RL, Hills M, Detre S, Pinder SE, Symmans WF and
Dowsett M: Residual proliferative cancer burden to predict
long-term outcome following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol.
26:75–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Asano Y, Kashiwagi S, Goto W, Takada K,
Takahashi K, Hatano T, Noda S, Takashima T, Onoda N, Tomita S, et
al: Prediction of survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
breast cancer by evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and
residual cancer burden. BMC Cancer. 17:8882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cortes J, Cescon DW, Rugo HS, Nowecki Z,
Im SA, Yusof MM, Gallardo C, Lipatov O, Barrios CH, Holgado E, et
al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus
chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable
or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): A
randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical
trial. Lancet. 396:1817–1828. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Loi S, Adams S, Schmid P, Cortés J, Cescon
DW, Winer EP, Toppmeyer DL, Rugo HS, De Laurentiis M, Nanda R, et
al: Relationship between tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) levels
and response to pembrolizumab (pembro) in metastatic
triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC): Results from KEYNOTE-086.
Ann Oncol. 28:V6082017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Schmid P, Salgado R, Park YH,
Muñoz-Couselo E, Kim SB, Sohn J, Im SA, Foukakis T, Kuemmel S, Dent
R, et al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment
of high-risk, early-stage triple-negative breast cancer: Results
from the phase 1b open-label, multicohort KEYNOTE-173 study. Ann
Oncol. 31:569–581. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ellis PM, Vella ET and Ung YC: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for patients with advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer: A systematic review. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:444–459.e1.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kluger HM, Zito CR, Turcu G, Baine MK,
Zhang H, Adeniran A, Sznol M, Rimm DL, Kluger Y, Chen L, et al:
PD-L1 studies across tumor types, its differential expression and
predictive value in patients treated with immune checkpoint
inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4270–4279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Blackley EF and Loi S: Targeting immune
pathways in breast cancer: Review of the prognostic utility of TILs
in early stage triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Breast. 48
(Suppl 1):S44–S48. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|