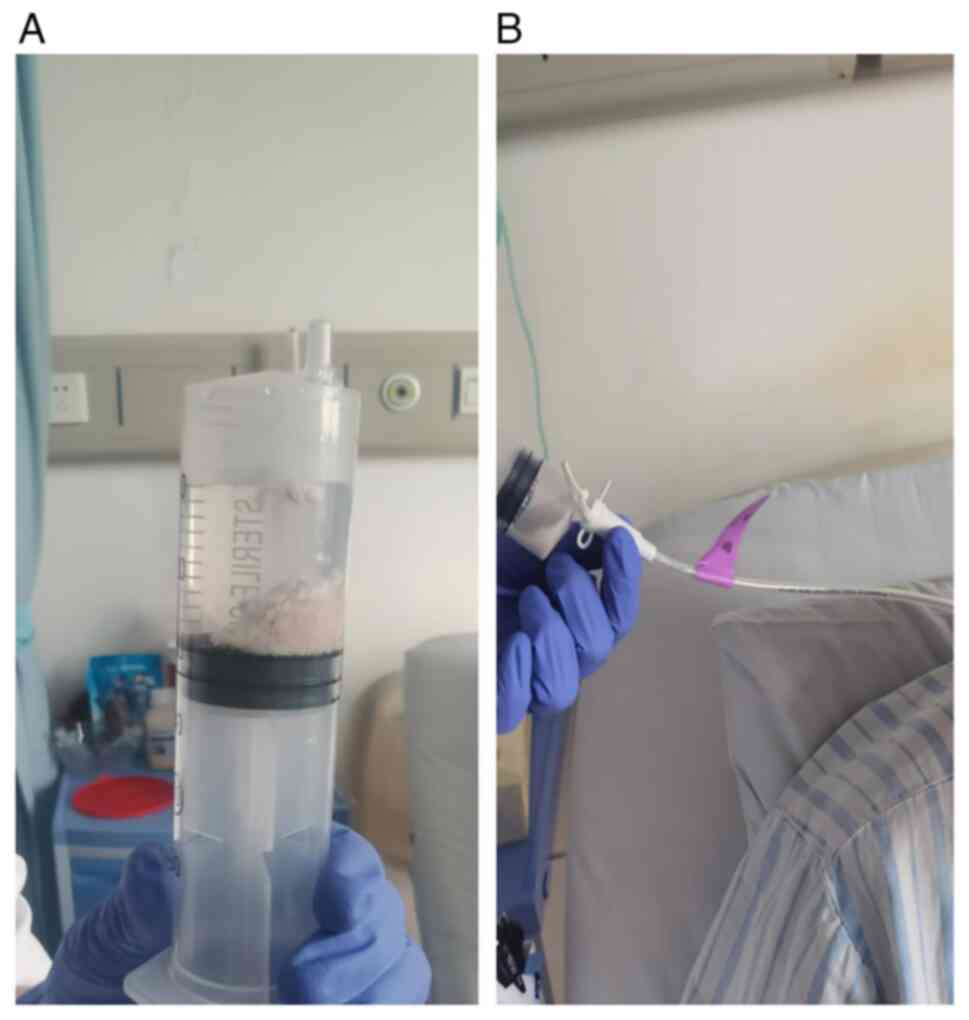
|
1
|
Horn L, Whisenant JG, Wakelee H, Reckamp
KL, Qiao H, Leal TA, Du L, Hernandez J, Huang V, Blumenschein GR,
et al: Monitoring therapeutic response and resistance: Analysis of
circulating tumor DNA in patients with ALK+ lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 14:1901–1911. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Solomon BJ, Besse B, Bauer TM, Felip E,
Soo RA, Camidge DR, Chiari R, Bearz A, Lin CC, Gadgeel SM, et al:
Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung
cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol.
19:1654–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bauer TM, Shaw AT, Johnson ML, Navarro A,
Gainor JF, Thurm H, Pithavala YK, Abbattista A, Peltz G and Felip
E: Brain penetration of lorlatinib: Cumulative incidences of CNS
and non-CNS progression with lorlatinib in patients with previously
treated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Target Oncol.
15:55–65. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
US FDA, . FDA approves lorlatinib for
metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-lorlatinib-metastatic-alk-positive-nsclcSeptember
29–2023
|
|
5
|
US FDA, . Crizotinib prescribing
information. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/202570s016lbl.pdfSeptember
29–2023
|
|
6
|
US FDA, . Alectinib prescribing
information. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdfSeptember
29–2023
|
|
7
|
US FDA, . Lorlatinib prescribing
information. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdfSeptember
29–2023
|
|
8
|
Chubachi S, Yasuda H, Irie H, Fukunaga K,
Naoki K, Soejima K and Betsuyaku T: A case of non-small cell lung
cancer with possible ‘disease flare’ on nivolumab treatment. Case
Rep Oncol Med. 2016:10756412016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kazemi NY, Langstraat C and John Weroha S:
Non-gestational choriocarcinoma with hyperprogression on
pembrolizumab: A case report and review of the literature. Gynecol
Oncol Rep. 39:1009232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Champiat S, Dercle L, Ammari S, Massard C,
Hollebecque A, Postel-Vinay S, Chaput N, Eggermont A, Marabelle A,
Soria JC and Ferté C: Hyperprogressive disease is a new pattern of
progression in cancer patients treated by anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:1920–1928. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kato S, Goodman A, Walavalkar V,
Barkauskas DA, Sharabi A and Kurzrock R: Hyperprogressors after
immunotherapy: Analysis of genomic alterations associated with
accelerated growth rate. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4242–4250. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, Bai L, Liu X, Liu Y, Li S, Liu J,
Zhang S, Yang C, Ren X and Cheng Y: Factors related to rapid
progression of non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese patients
treated using single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment.
Thorac Cancer. 11:1170–1179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Azam F, Latif MF, Farooq A, Tirmazy SH,
AlShahrani S, Bashir S and Bukhari N: Performance status assessment
by using ECOG (eastern cooperative oncology group) score for cancer
patients by oncology healthcare professionals. Case Rep Oncol.
12:728–736. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagasaka M, Ge Y, Sukari A, Kukreja G and
Ou SI: A user's guide to lorlatinib. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
151:1029692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zou HY, Li Q, Engstrom LD, West M,
Appleman V, Wong KA, McTigue M, Deng YL, Liu W, Brooun A, et al:
PF-06463922 is a potent and selective next-generation ROS1/ALK
inhibitor capable of blocking crizotinib-resistant ROS1 mutations.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:3493349–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Solomon BJ, Bauer TM, Ignatius Ou SH, Liu
G, Hayashi H, Bearz A, Penkov K, Wu YL, Arrieta O, Jassem J, et al:
Post hoc analysis of lorlatinib intracranial efficacy and safety in
patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer from
the phase III CROWN study. J Clin Oncol. 40:3593–3602. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaw AT, Bauer TM, de Marinis F, Felip E,
Goto Y, Liu G, Mazieres J, Kim DW, Mok T, Polli A, et al:
First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 383:2018–2029. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson TW, Richardson PF, Bailey S,
Brooun A, Burke BJ, Collins MR, Cui JJ, Deal JG, Deng YL, Dinh D,
et al: Discovery of
(10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
(PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma
kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain
exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant
mutations. J Med Chem. 57:4720–4744. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hibma JE, O'Gorman M, Nepal S, Pawlak S,
Ginman K and Pithavala YK: Evaluation of the absolute oral
bioavailability of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase/c-ROS oncogene 1
kinase inhibitor lorlatinib in healthy participants. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 89:71–81. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frelaut M, Le Tourneau C and Borcoman E:
Hyperprogression under Immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20:26742019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferrara R, Caramella C, Texier M, Audigier
Valette C, Tessonnier L, Mezquita L, Lahmar J, Mazieres J, Zalcman
G, Brosseau S, et al: Hyperprogressive disease (HPD) is frequent in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts) treated with anti
PD1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (IO). Ann Oncol. 28 (Suppl
5):v464–v465. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Peters S, Gettinger S, Johnson ML, Jänne
PA, Garassino MC, Christoph D, Toh CK, Rizvi NA, Chaft JE,
Carcereny Costa E, et al: Phase II trial of atezolizumab as
first-line or subsequent therapy for patients with programmed
death-ligand 1-selected advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
(BIRCH). J Clin Oncol. 35:2781–2789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu SY, Dong ZY, Wu SP, Xie Z, Yan LX, Li
YF, Yan HH, Su J, Yang JJ, Zhou Q, et al: Clinical relevance of
PD-L1 expression and CD8+ T cells infiltration in patients with
EGFR-mutated and ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
125:86–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang YK, Reck M, Nghiem P, Feng Y, Plautz
G, Kim HR, Owonikoko TK, Boku N, Chen LT, Lei M, et al: Assessment
of hyperprogression versus the natural course of disease
development with nivolumab with or without ipilimumab versus
placebo in phase III, randomized, controlled trials. J Immunother
Cancer. 10:e0042732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Longo V, Catino A, Montrone M, Pizzutilo
P, Ugenti I, Lacalamita R, Del Bene G, Pesola F, Marech I and
Galetta D: Esophageal stricture caused by ALK-positive NSCLC
esophageal metastasis resolved after a few days of lorlatinib
therapy without stent placement. JTO Clin Res Rep.
1:1000442020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sasaki K, Yokota Y, Isojima T, Fujii M,
Hasui K, Chen Y, Saito K, Takahata T, Kindaichi S and Sato A:
Enteral lorlatinib after alectinib as a treatment option in
anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer with
triple problems: Carcinomatous meningitis, poor performance status,
and dysphagia-a case report. Respirol Case Rep. 9:e007962021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|