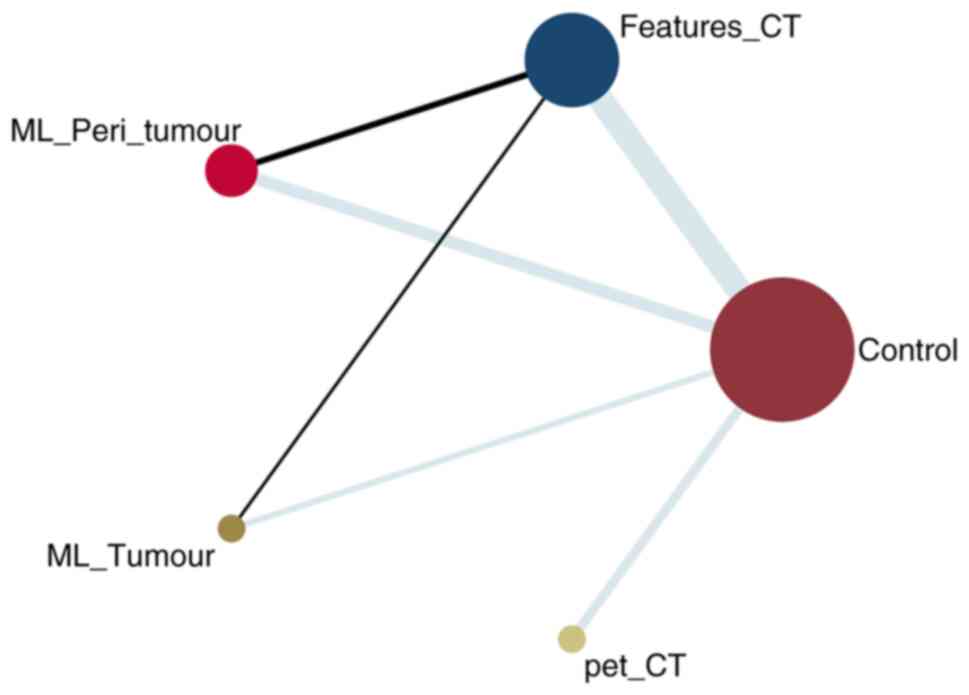
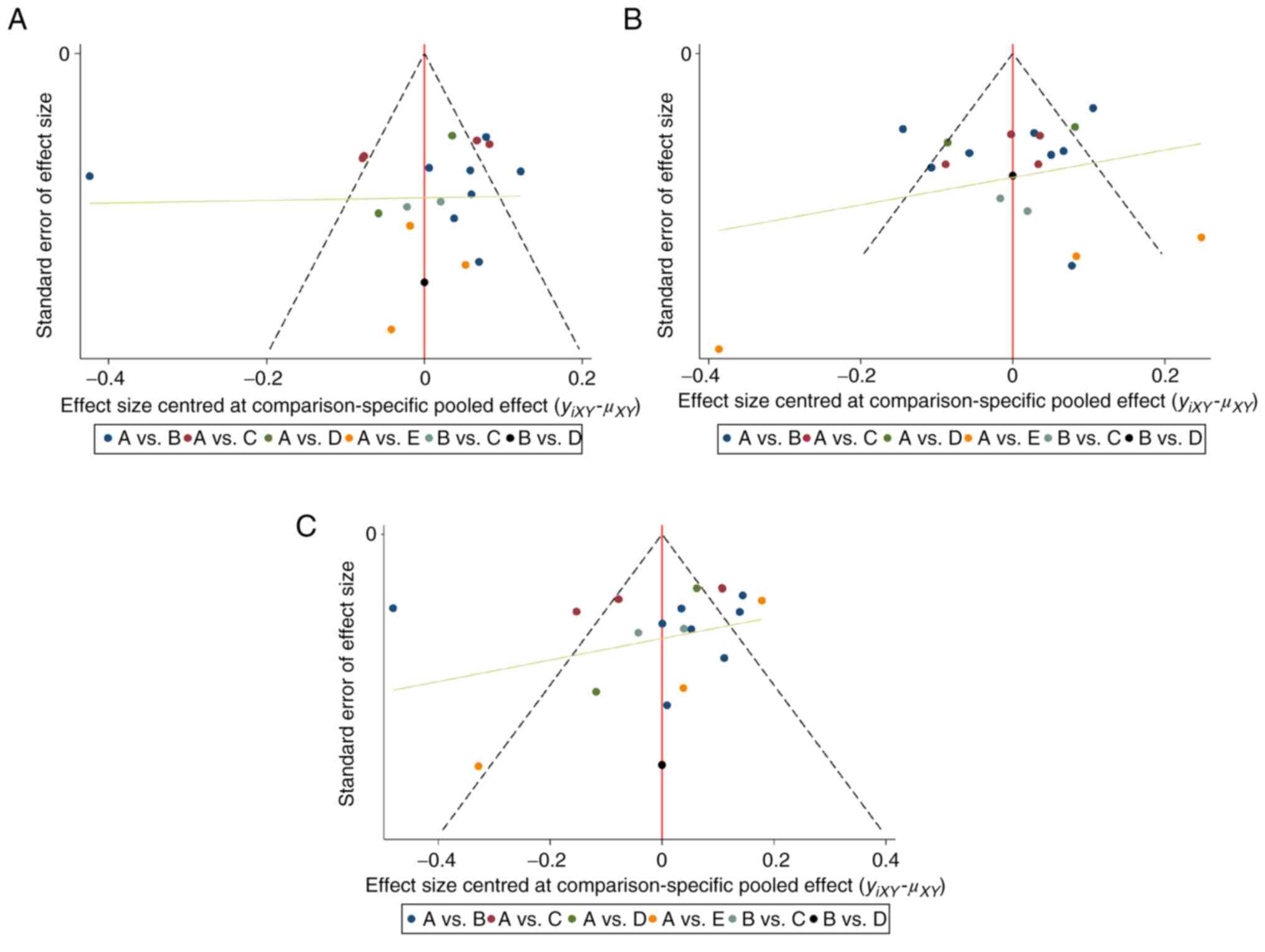
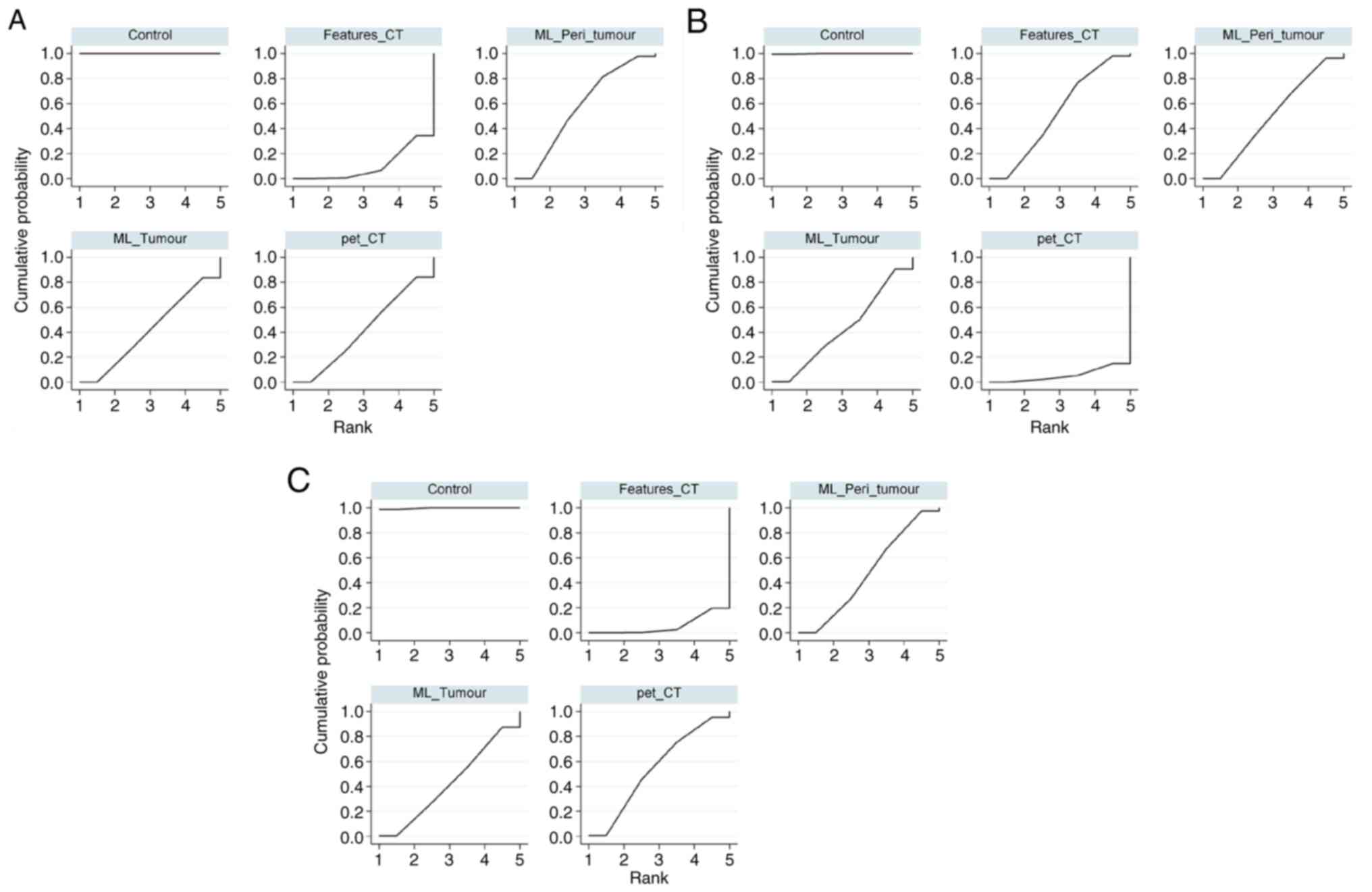
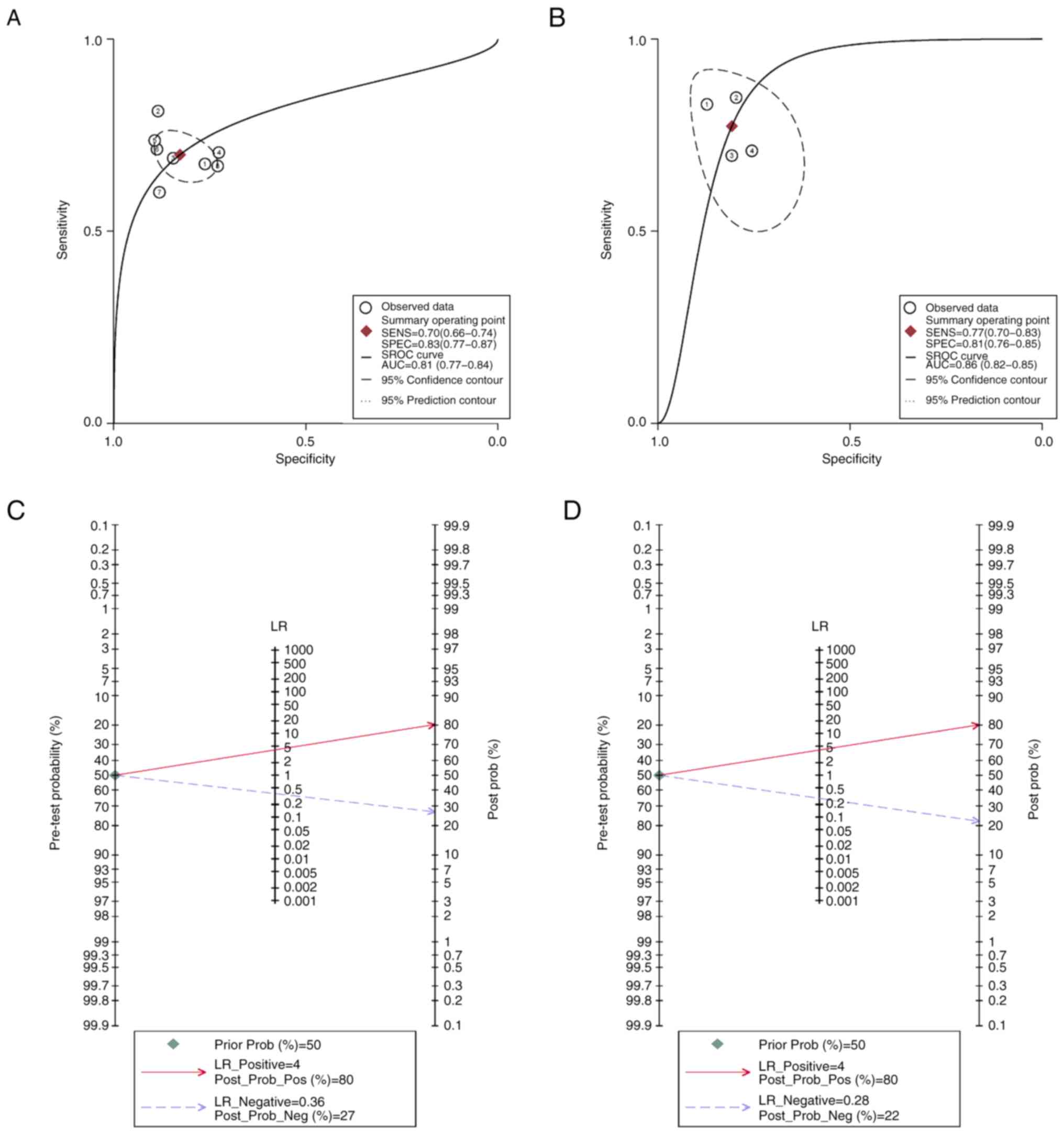
|
1
|
Zhuo Y, Feng M, Yang S, Zhou L, Ge D, Lu
S, Liu L, Shan F and Zhang Z: Radiomics nomograms of tumors and
peritumoral regions for the preoperative prediction of spread
through air spaces in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Oncol.
13:1008202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blaauwgeers H, Flieder D, Warth A, Harms
A, Monkhorst K, Witte B and Thunnissen E: A prospective study of
loose tissue fragments in non-small cell lung cancer resection
specimens: An alternative view to ‘spread through air spaces’. Am J
Surg Pathol. 41:1226–1230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
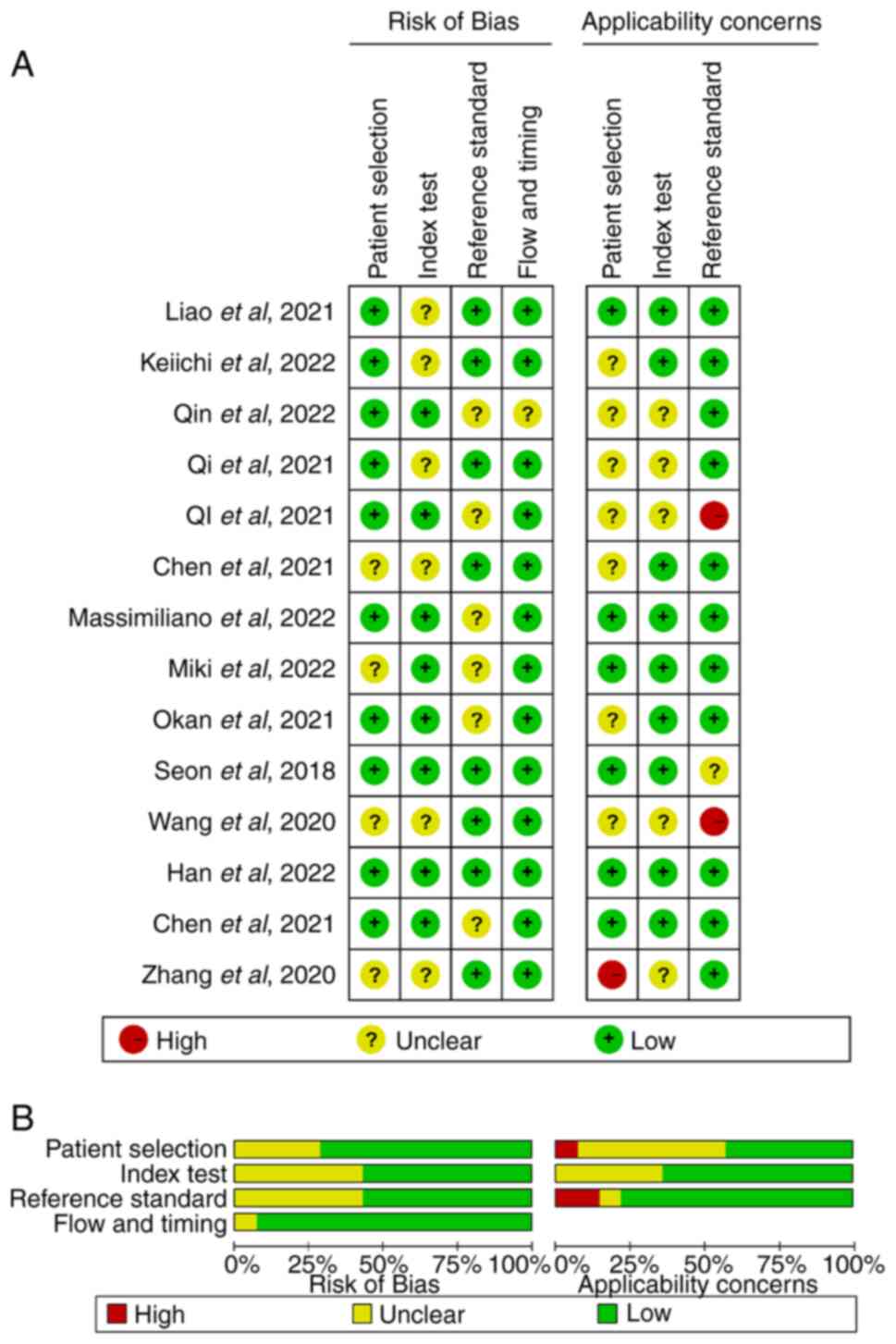
3
|
Kadota K, Nitadori JI, Sima CS, Ujiie H,
Rizk NP, Jones DR, Adusumilli PS and Travis WD: Tumor spread
through air spaces is an important pattern of invasion and impacts
the frequency and location of recurrences after limited resection
for small stage I lung adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 10:806–814.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG,
Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E,
Flieder DB, et al: The 2015 world health organization
classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and
radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1243–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liao G, Huang L, Wu S, Zhang P, Xie D, Yao
L, Zhang Z, Yao S, Shanshan L, Wang S, et al: Preoperative CT-based
peritumoral and tumoral radiomic features prediction for tumor
spread through air spaces in clinical stage I lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung Cancer. 163:87–95. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Terada Y, Takahashi T, Morita S,
Kashiwabara K, Nagayama K, Nitadori JI, Anraku M, Sato M,
Shinozaki-Ushiku A and Nakajima J: Spread through air spaces is an
independent predictor of recurrence in stage III (N2) lung
adenocarcinoma. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 29:442–448. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Niu Y, Han X, Zeng Y, Nanding A, Bai Q,
Guo S, Hou Y, Yu Y, Zhang Q and Li X: The significance of spread
through air spaces in the prognostic assessment model of stage I
lung adenocarcinoma and the exploration of its invasion mechanism.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:7125–7138. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eguchi T, Kameda K, Lu S, Bott MJ, Tan KS,
Montecalvo J, Chang JC, Rekhtman N, Jones DR, Travis WD and
Adusumilli PS: Lobectomy is associated with better outcomes than
sublobar resection in spread through air spaces (STAS)-positive T1
lung adenocarcinoma: A propensity score-matched analysis. J Thorac
Oncol. 14:87–98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ji GW, Zhang YD, Zhang H, Zhu FP, Wang K,
Xia YX, Zhang YD, Jiang WJ, Li XC and Wang XH: Biliary tract cancer
at CT: A radiomics-based model to predict lymph node metastasis and
survival outcomes. Radiology. 290:90–98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Autorino R, Gui B, Panza G, Boldrini L,
Cusumano D, Russo L, Nardangeli A, Persiani S, Campitelli M,
Ferrandina G, et al: Radiomics-based prediction of two-year
clinical outcome in locally advanced cervical cancer patients
undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Radiol Med. 127:498–506.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cong H, Peng W, Tian Z, Vallières M,
Chuanpei X, Aijun Z and Benxin Z: FDG-PET/CT radiomics models for
the early prediction of locoregional recurrence in head and neck
cancer. Curr Med Imaging. 17:374–383. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang C, Luo Y, Yuan J, You S, Chen Z, Wu
M, Wang G and Gong J: CT-based radiomics and machine learning to
predict spread through air space in lung adenocarcinoma. Eur
Radiol. 30:4050–4057. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li C, Jiang C, Gong J, Wu X, Luo Y and Sun
G: A CT-based logistic regression model to predict spread through
air space in lung adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg.
10:1984–1993. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu A, Sun X, Xu J, Xuan Y, Zhao Y, Qiu T,
Hou F, Qin Y, Wang Y, Lu T, et al: Relevance and prognostic ability
of Twist, Slug and tumor spread through air spaces in lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 9:1986–1998. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Y, Jiang C, Kang W, Gong J, Luo D,
You S, Cheng Z, Luo Y and Wu K: Development and validation of a
CT-based nomogram to predict spread through air space (STAS) in
peripheral stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Radiol. 40:586–594.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nishimori M, Iwasa H, Miyatake K, Nitta N,
Nakaji K, Matsumoto T, Yamanishi T, Yoshimatsu R, Iguchi M, Tamura
M and Yamagami T: 18F FDG-PET/CT analysis of spread through air
spaces (STAS) in clinical stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Nucl
Med. 36:897–903. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M,
Hamel C, Moran J, Moher D, Tugwell P, Welch V, Kristjansson E and
Henry DA: AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic
reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of
healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 358:j40082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J,
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA: Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions version 6.4 (updated August
2023). Cochrane; 2023
|
|
19
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM; QUADAS-2 group, : QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang SR, Li QL, Tian F, Li J, Li WX, Chen
M, Sang T, Cao CL and Shi LN: Diagnostic value of multiple
diagnostic methods for lymph node metastases of papillary thyroid
carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
12:9906032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kutob L and Schneider F: Lung cancer
staging. Surg Pathol Clin. 13:57–71. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heinecke A, Tallarita M and De Iorio M:
Bayesian splines versus fractional polynomials in network
meta-analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 20:2612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani
A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, Ioannidis JP, Straus S, Thorlund K, Jansen
JP, et al: The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of
systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health
care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med.
162:777–784. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kapor S, Rankovic MJ, Khazaei Y, Crispin
A, Schüler I, Krause F, Lussi A, Neuhaus K, Eggmann F, Michou S, et
al: Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic methods for
occlusal surface caries. Clin Oral Investig. 25:4801–4815. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bassi M, Russomando A, Vannucci J,
Ciardiello A, Dolciami M, Ricci P, Pernazza A, D'Amati G,
Terracciano CM, Faccini R, et al: Role of radiomics in predicting
lung cancer spread through air spaces in a heterogeneous dataset.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 11:560–571. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qi L, Li X, He L, Cheng G, Cai Y, Xue K
and Li M: Comparison of diagnostic performance of spread through
airspaces of lung adenocarcinoma based on morphological analysis
and perinodular and intranodular radiomic features on chest CT
images. Front Oncol. 11:6544132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen LW, Lin MW, Hsieh MS, Yang SM, Wang
HJ, Chen YC, Chen HY, Hu YH, Lee CE, Chen JS, et al: Radiomic
values from high-grade subtypes to predict spread through air
spaces in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 114:999–1006. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim SK, Kim TJ, Chung MJ, Kim TS, Lee KS,
Zo JI and Shim YM: Lung Adenocarcinoma: CT features associated with
spread through air spaces. Radiology. 289:831–840. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin L, Sun Y, Zhu R, Hu B and Wu J:
Clinicopathological and CT features of tumor spread through air
space in invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:9591132022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi L, Xue K, Cai Y, Lu J, Li X and Li M:
Predictors of CT morphologic features to identify spread through
air spaces preoperatively in small-sized lung adenocarcinoma. Front
Oncol. 10:5484302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Feng H, Xiao F, Shao W,
Liang C, Sun H, Gu X and Liu D: Predictive value of radiological
features on spread through air space in stage cIA lung
adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Dis. 12:6494–6504. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han X, Fan J, Zheng Y, Ding C, Zhang X,
Zhang K, Wang N, Jia X, Li Y, Liu J, et al: The value of CT-based
radiomics for predicting spread through air spaces in stage IA lung
adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:7573892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takehana K, Sakamoto R, Fujimoto K, Matsuo
Y, Nakajima N, Yoshizawa A, Menju T, Nakamura M, Yamada R, Mizowaki
T and Nakamoto Y: Peritumoral radiomics features on preoperative
thin-slice CT images can predict the spread through air spaces of
lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 12:103232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang XY, Zhao YF, Yang L, Liu Y, Yang YK
and Wu N: Correlation analysis between metabolic tumor burden
measured by positron emission tomography/computed tomography and
the 2015 World Health Organization classification of lung
adenocarcinoma, with a risk prediction model of tumor spread
through air spaces. Transl Cancer Res. 9:6412–6422. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Falay O, Selçukbiricik F, Tanju S, Erus S,
Kapdağli M, Cesur E, Yavuz Ö, Bulutay P, Firat P, Mandel NM and
Dilege Ş: The prediction of spread through air spaces with
preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT in cases with primary lung
adenocarcinoma, its effect on the decision for an adjuvant
treatment and its prognostic role. Nucl Med Commun. 42:922–927.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang S, Shou H, Wen H, Wang X, Wang H, Lu
C, Gu J, Xu F, Zhu Q, Wang L and Ge D: An individual nomogram can
reliably predict tumor spread through air spaces in non-small-cell
lung cancer. BMC Pulm Med. 22:2092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Toki MI, Harrington K and Syrigos KN: The
role of spread through air spaces (STAS) in lung adenocarcinoma
prognosis and therapeutic decision making. Lung Cancer.
146:127–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun F, Huang Y, Yang X, Zhan C, Xi J, Lin
Z, Shi Y, Jiang W and Wang Q: Solid component ratio influences
prognosis of GGO-featured IA stage invasive lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Imagin. 20:872020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bai S, Wang Z, Sun Z and Liu Z: Study on
the relationship between lung cancer stromal cells and air cavity
diffusion based on an image acquisition system. Contrast Media Mol
Imaging. 2022:24921242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Reyhan M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhou J,
Zhang Y, Yue NJ and Nie K: The impact of phantom design and
material-dependence on repeatability and reproducibility of
CT-based radiomics features. Med Phys. 49:1648–1659. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steyerberg EW, Vickers AJ, Cook NR, Gerds
T, Gonen M, Obuchowski N, Pencina MJ and Kattan MW: Assessing the
performance of prediction models: A framework for traditional and
novel measures. Epidemiology. 21:128–138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, McShane LM,
Cavenagh MM and Altman DG: Reporting recommendations for tumor
marker prognostic studies (REMARK): An abridged explanation and
elaboration. J Natl Cancer Inst. 110:803–811. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, Gordon
AC, Komorowski M, Harvey H, Topol EJ, Ioannidis JPA, Collins GS and
Maruthappu M: Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic
review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning
studies. BMJ. 368:m6892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Christodoulou E, Ma J, Collins GS,
Steyerberg EW, Verbakel JY and Van Calster B: A systematic review
shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logistic
regression for clinical prediction models. J Clin Epidemiol.
110:12–22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|