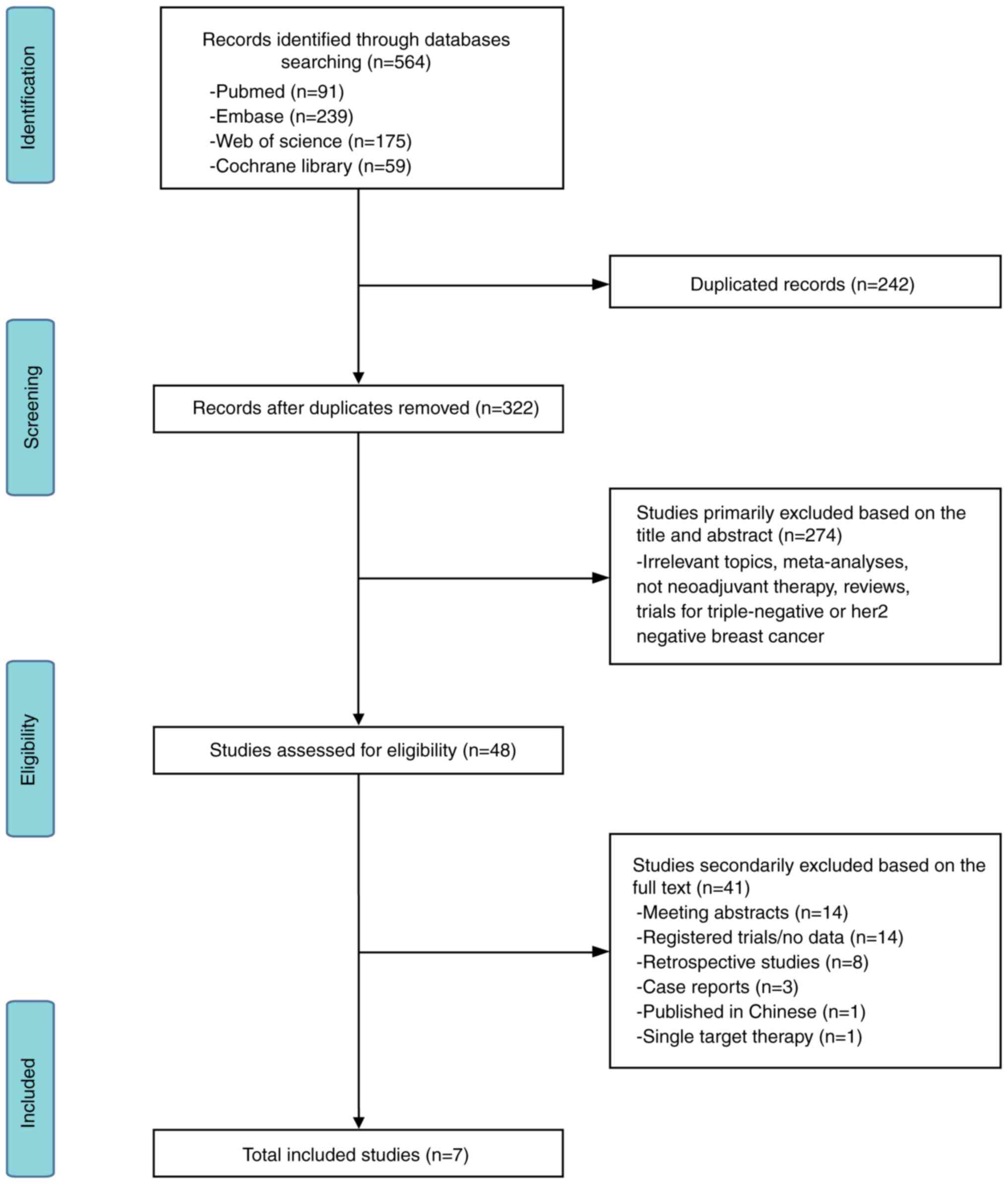
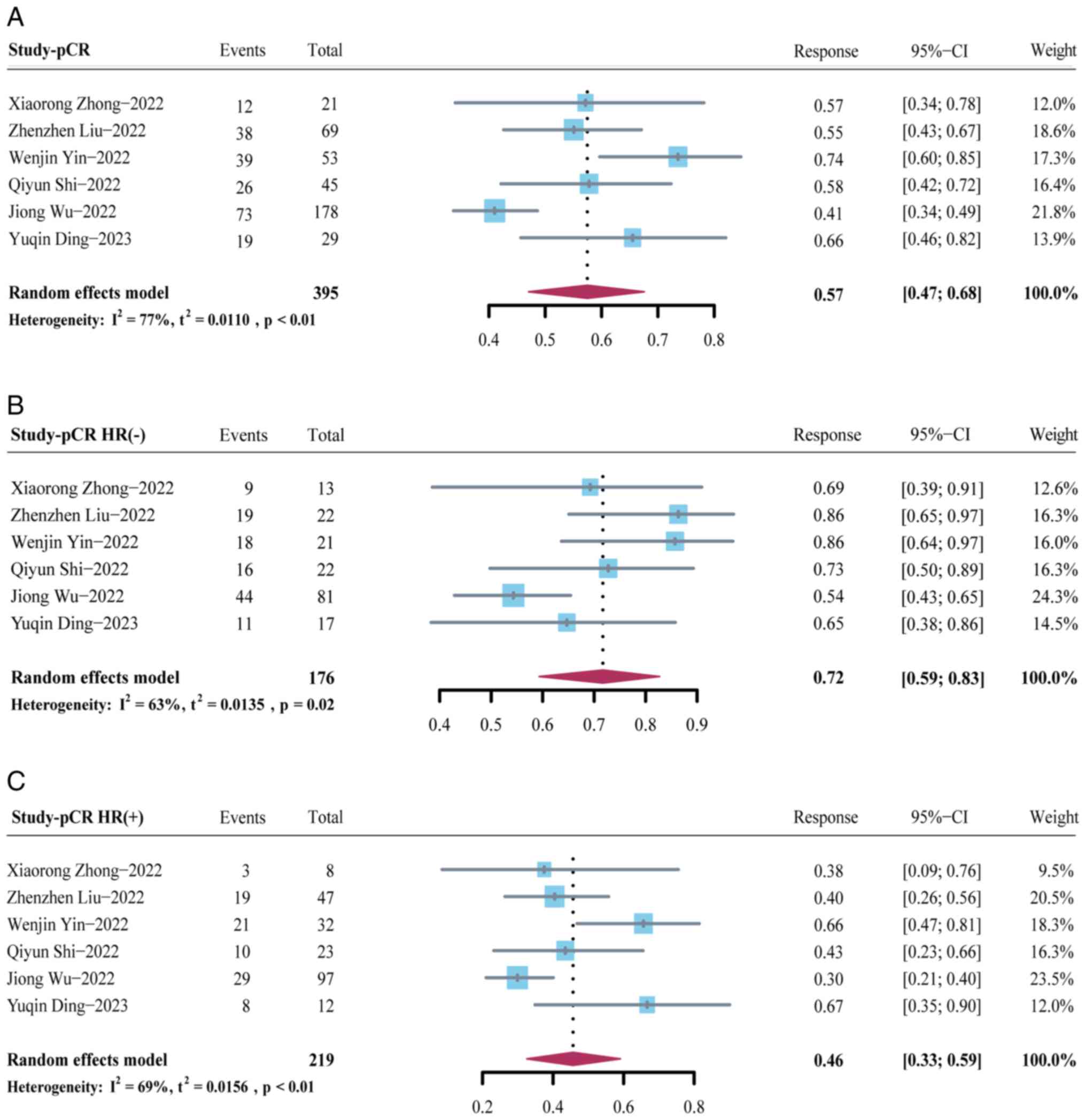
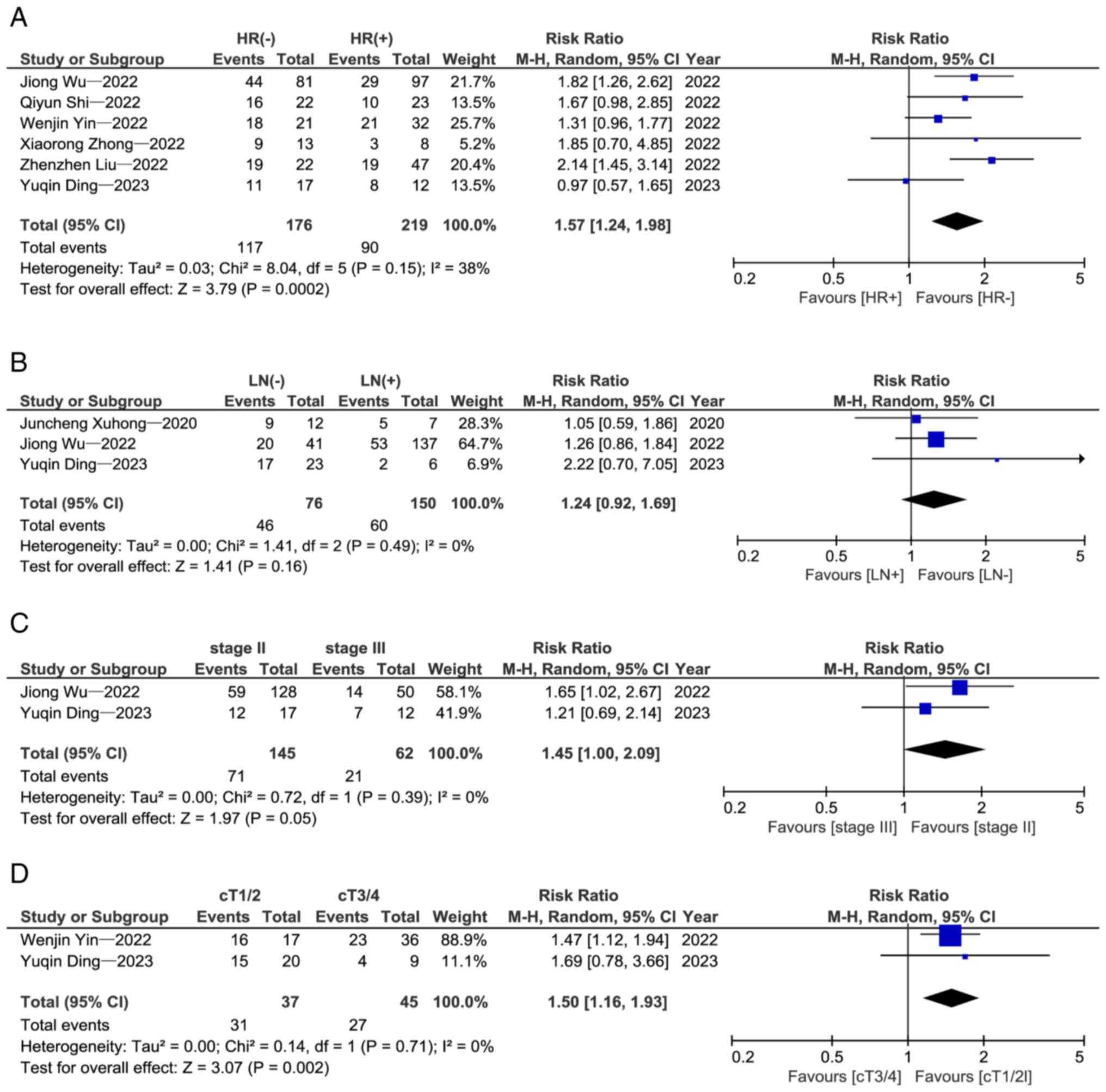
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loibl S and Gianni L: HER2-positive breast
cancer. Lancet. 389:2415–2429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh JC, Jhaveri K and Esteva FJ:
HER2-positive advanced breast cancer: Optimizing patient outcomes
and opportunities for drug development. Br J Cancer. 111:1888–1898.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J and Xu B: Targeted therapeutic
options and future perspectives for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 4:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C
and Curigliano G: Breast cancer. Lancet. 397:1750–1769. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Korde LA, Somerfield MR, Carey LA, Crews
JR, Denduluri N, Hwang ES, Khan SA, Loibl S, Morris EA, Perez A, et
al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted
therapy for breast cancer: ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol.
39:1485–1505. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Spring LM, Fell G, Arfe A, Sharma C,
Greenup R, Reynolds KL, Smith BL, Alexander B, Moy B, Isakoff SJ,
et al: Pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
and impact on breast cancer recurrence and survival: A
comprehensive meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 26:2838–2848. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Yang C, Wan H, Zhang G, Feng J and
Zhang L, Chen X, Zhong D, Lou L, Tao W and Zhang L: Discovery and
development of pyrotinib: A novel irreversible EGFR/HER2 dual
tyrosine kinase inhibitor with favorable safety profiles for the
treatment of breast cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci. 110:51–61. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma F, Ouyang Q, Li W, Jiang Z, Tong Z, Liu
Y, Li H, Yu S, Feng J, Wang S, et al: Pyrotinib or lapatinib
combined with capecitabine in HER2-positive metastatic breast
cancer with prior taxanes, anthracyclines, and/or trastuzumab: A
randomized, phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 37:2610–2619. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin S, Chi Y, Du Y, Wang J, Shan C, Yi W,
Shang M, Man X, Tan Q and Li H: Efficacy and safety of
pyrotinib-containing regimen in the patients with HER2-positive
metastatic breast cancer: A multicenter real-world study. Cancer
Med. 12:2333–2344. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan M, Bian L, Hu X, Zhang Q, Ouyang Q,
Feng J, Yin Y, Sun T, Tong Z, Wang X, et al: Pyrotinib plus
capecitabine for human epidermal factor receptor 2-positive
metastatic breast cancer after trastuzumab and taxanes (PHENIX): A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Transl
Breast Cancer Res. 1:132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yan M, Ouyang Q, Sun T, Niu L, Yang J, Li
L, Song Y, Hao C, Chen Z, Orlandi A, et al: Pyrotinib plus
capecitabine for patients with human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases (PERMEATE):
A multicentre, single-arm, two-cohort, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol.
23:353–361. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu B, Yan M, Ma F, Hu X, Feng J, Ouyang Q,
Tong Z, Li H, Zhang Q, Sun T, et al: Pyrotinib plus capecitabine
versus lapatinib plus capecitabine for the treatment of
HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (PHOEBE): A multicentre,
open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
22:351–360. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan Y, Liu X, Cai Y and Li W: Pyrotinib
versus lapatinib therapy for HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer
patients after first-line treatment failure: A meta-analysis and
systematic review. PLoS One. 18:e02797752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blair HA: Pyrotinib: First global
approval. Drugs. 78:1751–1755. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski
F, Panis Y and Chipponi J: Methodological index for non-randomized
studies (minors): Development and validation of a new instrument.
ANZ J Surg. 73:712–716. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong X, He P, Chen J, Yan X, Wei B, Zhang
Z, Bu H, Li J, Tian T, Lv Q, et al: Neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus
trastuzumab and nab-paclitaxel for HER2-positive early or locally
advanced breast cancer: An exploratory phase II trial. Gland Surg.
11:216–225. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin W, Wang Y, Wu Z, Ye Y, Zhou L, Xu S,
Lin Y, Du Y, Yan T, Yang F, et al: Neoadjuvant trastuzumab and
pyrotinib for locally advanced HER2-positive breast cancer
(NeoATP): Primary analysis of a phase II study. Clin Cancer Res.
28:3677–3685. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Z, Wang C, Chen X, Zhu J, Sun X, Xia
Q, Lu Z, Qiao J, Zhou Y, Wang H, et al: Pathological response and
predictive role of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in HER2-positive
early breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus
trastuzumab and chemotherapy (Panphila): A multicentre phase 2
trial. Eur J Cancer. 165:157–168. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xuhong J, Qi X, Tang P, Fan L, Chen L,
Zhang F, Tan X, Yan W, Zhong L, He C, et al: Neoadjuvant pyrotinib
plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for stage I–III HER2-positive
breast cancer: A phase II clinical trial. Oncologist.
25:e1909–e1920. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ding Y, Mo W, Xie X, Wang O, He X, Zhao S,
Gu X, Liang C, Qin C, Ding K, et al: Neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus
trastuzumab, docetaxel, and carboplatin in early or locally
advanced human epidermal receptor 2-positive breast cancer in
China: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
phase 2 trial. Oncol Res Treat. 46:303–311. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Jiang Z, Liu Z, Yang B, Yang H, Tang
J, Wang K, Liu Y, Wang H, Fu P, et al: Neoadjuvant pyrotinib,
trastuzumab, and docetaxel for HER2-positive breast cancer
(PHEDRA): A double-blind, randomized phase 3 trial. BMC Med.
20:4982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi Q, Xuhong J, Luo T, Ge J, Liu F, Lan
Y, Chen Q, Tang P, Fan L, Chen L, et al: PIK3CA mutations are
associated with pathologic complete response rate to neoadjuvant
pyrotinib and trastuzumab plus chemotherapy for HER2-positive
breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 128:121–129. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guarneri V, Griguolo G, Miglietta F, Conte
PF, Dieci MV and Girardi F: Survival after neoadjuvant therapy with
trastuzumab-lapatinib and chemotherapy in patients with
HER2-positive early breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized
trials. ESMO Open. 7:1004332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Yu Y, Lin Y, Kang S, Lv X, Liu Y,
Lin J, Wang J and Song C: P079-Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant
therapy for HER2-positive early breast cancer: A network
meta-analysis. Breast. 56 (Suppl 1):S49–S50. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, Roman L,
Tseng LM, Liu MC, Lluch A, Staroslawska E, de la Haba-Rodriguez J,
Im SA, et al: Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and
trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early
HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): A randomised multicentre,
open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:25–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shao Z, Pang D, Yang H, Li W, Wang S, Cui
S, Liao N, Wang Y, Wang C, Chang YC, et al: Efficacy, safety, and
tolerability of pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel for patients
with early or locally advanced ERBB2-positive breast cancer in
Asia: The PEONY phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol.
6:e1936922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hurvitz SA, Martin M, Symmans WF, Jung KH,
Huang CS, Thompson AM, Harbeck N, Valero V, Stroyakovskiy D,
Wildiers H, et al: Neoadjuvant trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and
chemotherapy versus trastuzumab emtansine plus pertuzumab in
patients with HER2-positive breast cancer (KRISTINE): A randomised,
open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:115–126.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schneeweiss A, Chia S, Hickish T, Harvey
V, Eniu A, Hegg R, Tausch C, Seo JH, Tsai YF, Ratnayake J, et al:
Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab in combination with standard
neoadjuvant anthracycline-containing and anthracycline-free
chemotherapy regimens in patients with HER2-positive early breast
cancer: A randomized phase II cardiac safety study (TRYPHAENA). Ann
Oncol. 24:2278–2284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Van Sebille YZA, Gibson RJ, Wardill HR and
Bowen JM: ErbB small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)
induced diarrhoea: Chloride secretion as a mechanistic hypothesis.
Cancer Treat Rev. 41:646–652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yusta B, Holland D, Koehler JA, Maziarz M,
Estall JL, Higgins R and Drucker DJ: ErbB signaling is required for
the proliferative actions of GLP-2 in the murine gut.
Gastroenterology. 137:986–996. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tian C, Wang M, Liu H, Liu J, Xu M and Ma
L: Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus
docetaxel/liposomal doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide for HER2-positive
breast cancer. Ir J Med Sci. 192:1041–1049. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mao X, Lv P, Gong Y, Wu X, Tang P, Wang S,
Zhang D, You W, Wang O, Zhou J, et al: Pyrotinib-containing
neoadjuvant therapy in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: A
multicenter retrospective analysis. Front Oncol. 12:8555122022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Q, Wang Y, Zhu M, Gu Y and Tang Y:
Clinical observation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with pyrotinib
plus trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer: A cohort study.
Gland Surg. 10:3389–3402. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yao DS, Wang W, Chang JY, Zhang Y, Zhang
HW, Xu JX and Cai HF: Neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus nab-paclitaxel,
doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide for HER2-positive locally
advanced breast cancer: A retrospective case-series study. Gland
Surg. 10:3362–3368. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Califano R, Tariq N, Compton S, Fitzgerald
DA, Harwood CA, Lal R, Lester J, McPhelim J, Mulatero C,
Subramanian S, et al: Expert consensus on the management of adverse
events from EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the UK. Drugs.
75:1335–1348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Swain SM, Shastry M and Hamilton E:
Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer: Advances and future
directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 22:101–126. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roy V and Perez EA: Beyond trastuzumab:
Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in HER-2-positive breast
cancer. Oncologist. 14:1061–1069. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim JW, Lim AR, You JY, Lee JH, Song SE,
Lee NK, Jung SP, Cho KR, Kim CY and Park KH: PIK3CA mutation is
associated with poor response to HER2-targeted therapy in breast
cancer patients. Cancer Res Treat. 55:531–541. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Loibl S, Majewski I, Guarneri V,
Nekljudova V, Holmes E, Bria E, Denkert C, Schem C, Sotiriou C, Loi
S, et al: PIK3CA mutations are associated with reduced pathological
complete response rates in primary HER2-positive breast cancer:
Pooled analysis of 967 patients from five prospective trials
investigating lapatinib and trastuzumab. Ann Oncol. 27:1519–1525.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A,
Paepke S, Lehmann A, Rezai M, Zahm DM, Sinn P, Khandan F, Eidtmann
H, et al: PIK3CA mutations are associated with lower rates of
pathologic complete response to anti-human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2 (her2) therapy in primary HER2-overexpressing breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 32:3212–3220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ma F, Li Q, Chen S, Zhu W, Fan Y, Wang J,
Luo Y, Xing P, Lan B, Li M, et al: Phase I study and biomarker
analysis of pyrotinib, a novel irreversible pan-erbb receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
35:3105–3112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu W, Yang J, Zhang Z, Xu D and Li N:
Pyrotinib for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res. 12:247–256. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|