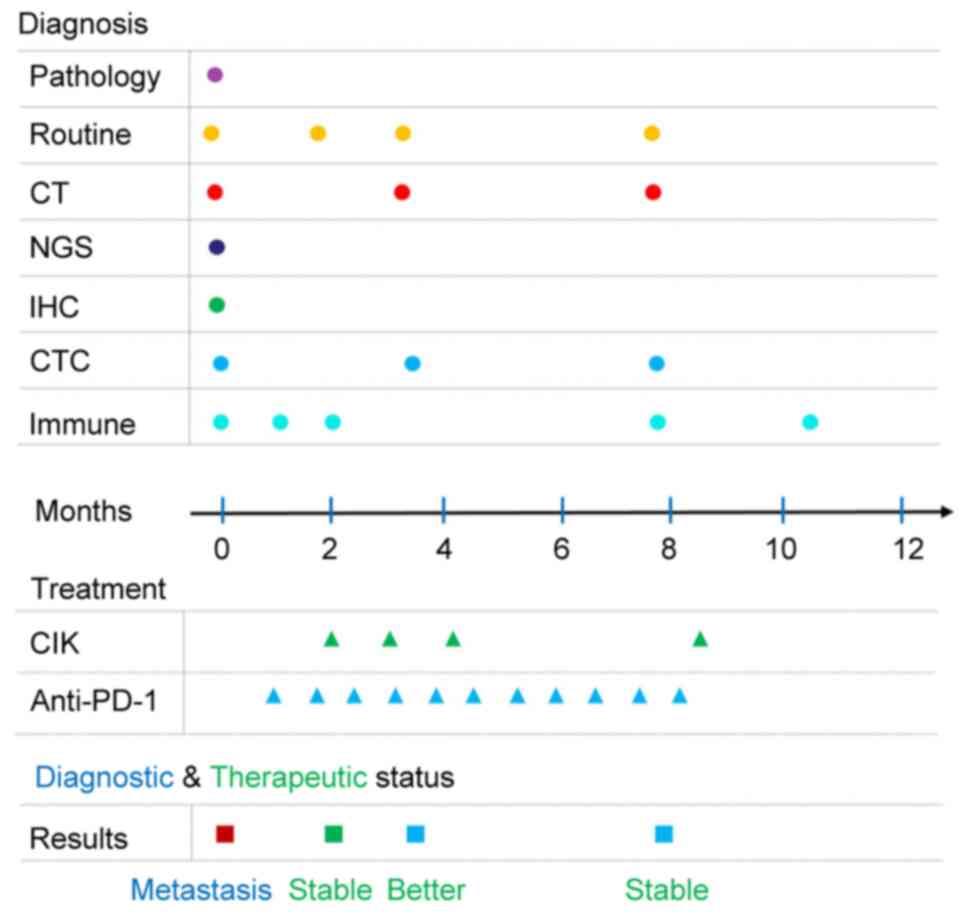
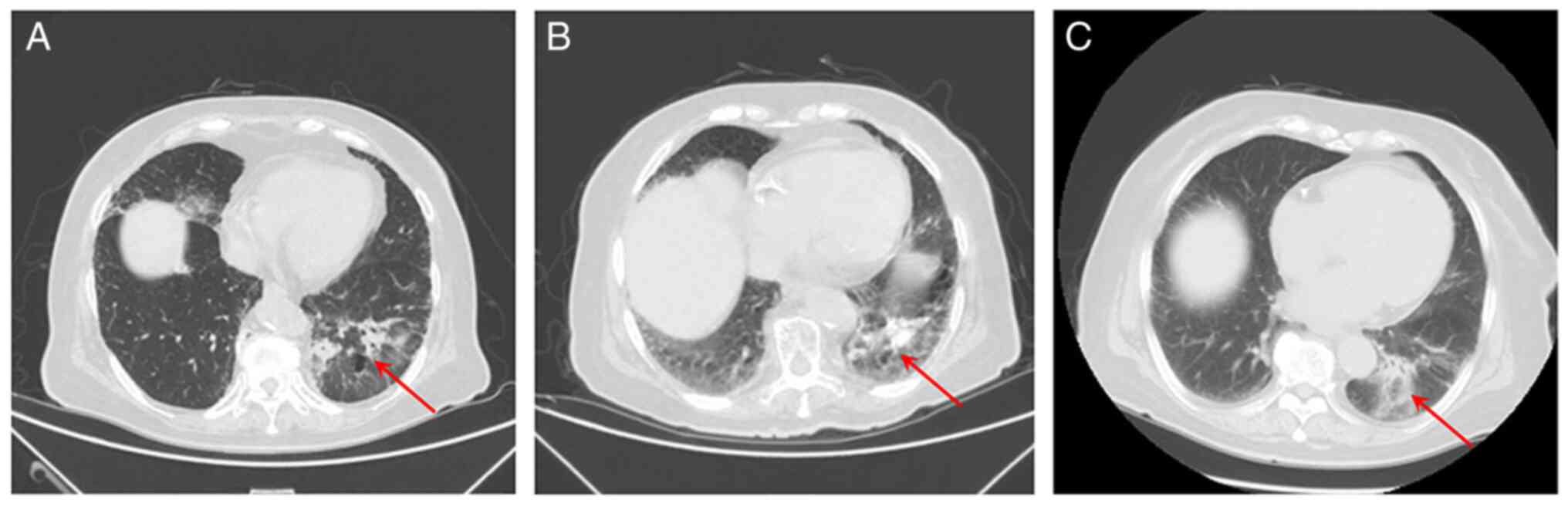
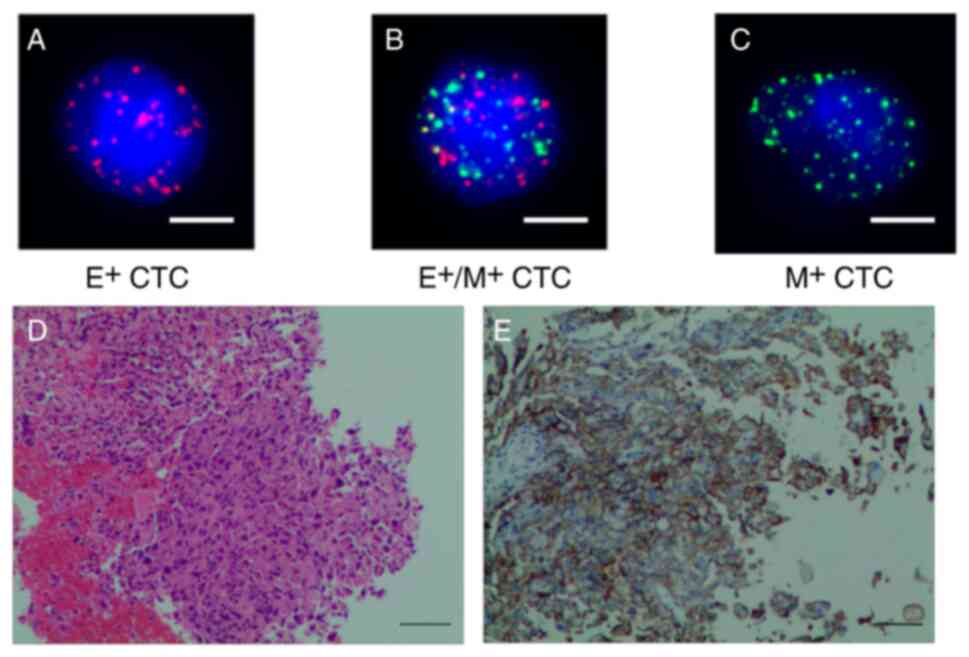
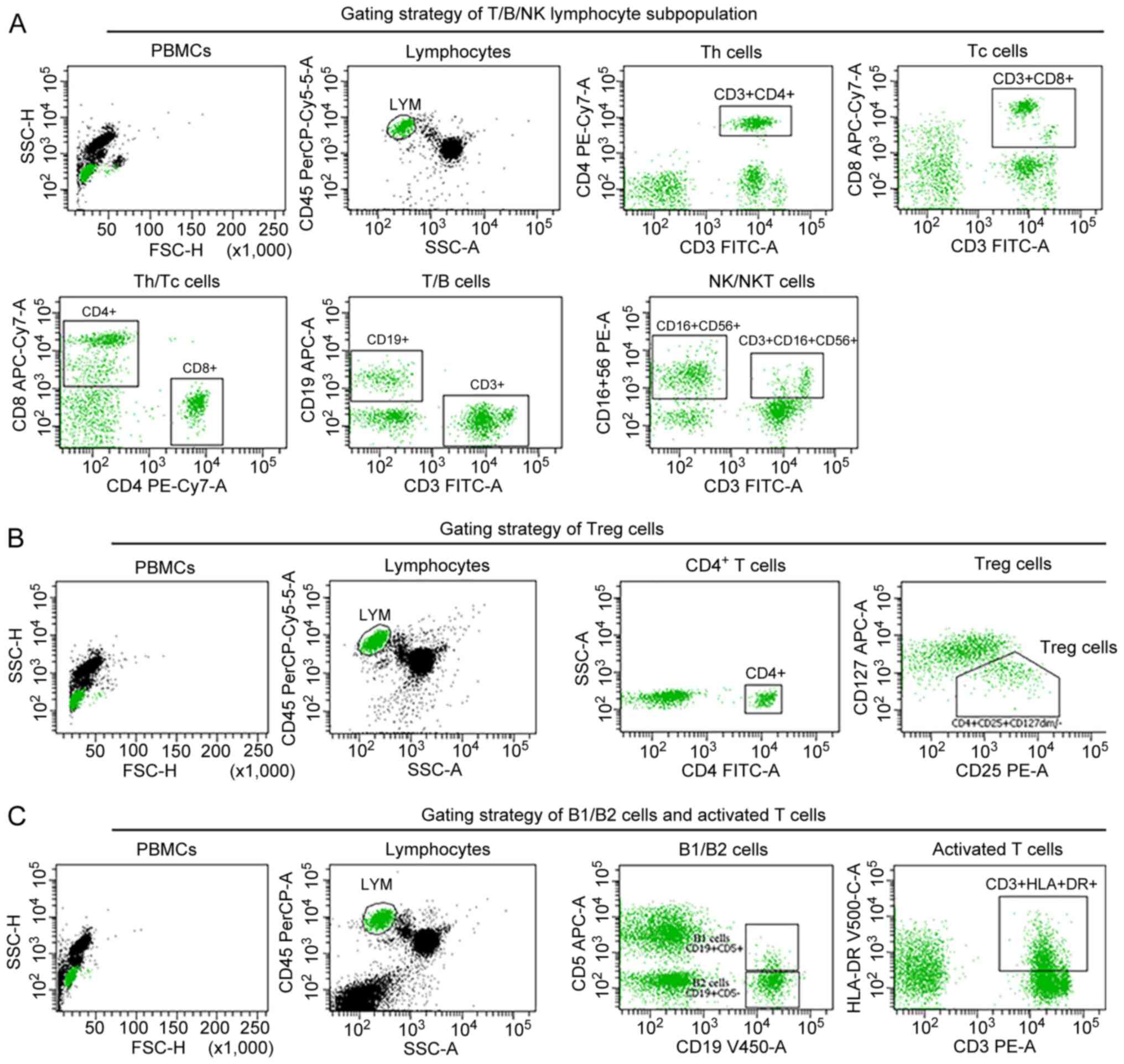
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A and Bray F: Cancer statistics for the
year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. 149:778–789. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sosa E, D'Souza G, Akhtar A, Sur M, Love
K, Duffels J, Raz DJ, Kim JY, Sun V and Erhunmwunsee L: Racial and
socioeconomic disparities in lung cancer screening in the United
States: A systematic review. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:299–314. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khanna P, Blais N, Gaudreau PO and
Corrales-Rodriguez L: Immunotherapy comes of age in lung cancer.
Clin Lung Cancer. 18:13–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spagnuolo A and Gridelli C: The role of
immunotherapy in the first-line treatment of elderly advanced
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:23192023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xia L, Liu Y and Wang Y: PD-1/PD-L1
blockade therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Current
status and future directions. Oncologist. 24 (Suppl 1):S31–S41.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Momotow J, Bühnen I, Trautmann-Grill K,
Kobbe G, Hahn D, Schroers R, Heinrich B, Gaska T, Forstbauer H,
Schmidt B, et al: Outcomes of anti-programmed death 1 treatment for
relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: A German Hodgkin Study Group
multicentre real-world analysis. Br J Haematol. 198:401–404. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan D, Hu AY, Antonia SJ and Li CY: A Gene
mutation signature predicting immunotherapy benefits in patients
with NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 16:419–427. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hoffner B, Leighl NB and Davies M:
Toxicity management with combination chemotherapy and programmed
death 1/programmed death ligand 1 inhibitor therapy in advanced
lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 85:1019792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H and Wu
K: Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current
advances and future directions. Mol Cancer. 21:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang K, Sun B, Luo N, Guo H, Hu J and
Peng J: Programmed death receptor 1 (PD1) knockout and human
telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) transduction can enhance
persistence and antitumor efficacy of cytokine-induced killer cells
against hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:4573–4582.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dehno MN, Li Y, Weiher H and Schmidt-Wolf
IGH: Increase in efficacy of checkpoint inhibition by
cytokine-induced-killer cells as a combination immunotherapy for
renal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:30782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Chen Y, Feng F, Chen C, Zeng H,
Wen S, Xu X, He J and Li J: Programmed cell death
protein-1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade enhances the antitumor
efficacy of adoptive cell therapy against non-small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Dis. 10:6711–6721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Poh SL and Linn YC: Immune checkpoint
inhibitors enhance cytotoxicity of cytokine-induced killer cells
against human myeloid leukaemic blasts. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
65:525–536. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu LW, Yang MY, Zhou M, Li JJ, Liu B and
Pan YY: Improvement of cytotoxicity of autologous CIKs from
patients with breast cancer to MCF-7 cells by suppressed PD-1
expression. Cancer Biomark. 20:609–615. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han Y, Mu D, Liu T, Zhang H, Zhang J, Li
S, Wang R, Du W, Hui Z, Zhang X and Ren X: Autologous
cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells enhance the clinical response
to PD-1 blocking antibodies in patients with advanced non-small
cell lung cancer: A preliminary study. Thorac Cancer. 12:145–152.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Liu X, Till B, Sun M, Li X and Gao
Q: Combination of cytokine-induced killer cells and programmed cell
death-1 blockade works synergistically to enhance therapeutic
efficacy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung
cancer. Front Immunol. 9:15132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao L, Han L, Zhang Y, Li T, Yang Y, Li
W, Shang Y, Lin H and Gao Q: Combination of PD-1 blockade and
RetroNectin®-activated cytokine-induced killer in
preheavily treated non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective
study. Immunotherapy. 10:1315–1323. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pievani A, Borleri G, Pende D, Moretta L,
Rambaldi A, Golay J and Introna M: Dual-functional capability of
CD3+CD56+ CIK cells, a T-cell subset that acquires NK function and
retains TCR-mediated specific cytotoxicity. Blood. 118:3301–3310.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mata-Molanes JJ, Sureda González M,
Valenzuela Jiménez B, Martínez Navarro EM and Brugarolas Masllorens
A: Cancer immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells. Target
Oncol. 12:289–299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Huang H, Han L, Li T, Wang Z and
Gao Q: Advanced renal-cell carcinoma pseudoprogression after
combined immunotherapy: Case report and literature review. Front
Oncol. 11:6404472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L, Li T, Song Y, Yang Y, Ma B, Zhang
Y, Shang Y, Xu B, Guo J, Qin P, et al: High complete response rate
in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving
autologous cytokine-induced killer cell therapy plus
anti-programmed death-1 agent: A single-center study. Front
Immunol. 12:7792482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharma A and Schmidt-Wolf IGH: 30 Years of
CIK cell therapy: Recapitulating the key breakthroughs and future
perspective. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:3882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao S, Li N, Gao S, Xue Q, Ying J, Wang S,
Tao X, Zhao J, Mao Y, Wang B, et al: Neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor
(Sintilimab) in NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 15:816–826. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Guo W, Zhou B, Wang S, Li N, Qiu
B, Lv F, Zhao L, Li J, Shao K, et al: Three-year follow-up of
neoadjuvant programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitor (Sintilimab)
in NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 17:909–920. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Helling M and Venulet J: Drug recording
and classification by the WHO research centre for international
monitoring of adverse reactions to drugs. Methods Inf Med.
13:169–178. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vaseq R, Sharma A, Li Y and Schmidt-Wolf
IGH: Revising the landscape of cytokine-induced killer cell therapy
in lung cancer: Focus on immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:56262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Feng Y, Feng G, Lu X, Qian W, Ye J,
Manrique CA, Ma C and Lu Y; written on behalf of the AME Lung
Cancer Collaborative Group, : Exploratory analysis of introducing
next-generation sequencing-based method to treatment-naive lung
cancer patients. J Thorac Dis. 10:5904–5912. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsoulos N, Papadopoulou E, Metaxa-Mariatou
V, Tsaousis G, Efstathiadou C, Tounta G, Skapeti K, Bourkoula J,
Zarogoulidis P, Pentheroudakis GE, et al: Molecular profiling of
502 patient cohort with NSCLC using a 27 somatic gene panel. J Clin
Oncol. 35:e231932017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xing Y, Qin F, Zhai Y, Yang J, Yan Y, Li
D, Zhang H, Hu R, Xu X, Cao X, et al: Association of clinical
features of colorectal cancer with circulating tumor cells and
systemic inflammatory markers. Dis Markers. 2022:51055992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xing Y, Zhang X, Qin F, Yang J, Ai L, Wang
Q and Zhai Y: The clinical significance of circulating tumor cells
and T lymphocyte subtypes in pancreatic cancer patients.
Bioengineered. 13:2130–2138. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang X, Jiang L, Jin Y, Li P, Hou Y, Yun
J, Wu C, Sun W, Fan X, Kuang D, et al: PD-L1 expression in chinese
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A
multi-center retrospective observational study. J Cancer.
24:7390–7398. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Poondla N, Sheykhhasan M, Akbari M, Samadi
P, Kalhor N and Manoochehri H: The promise of CAR T-cell therapy
for the treatment of cancer stem cells: A short review. Curr Stem
Cell Res Ther. 17:400–406. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tang Q, Zuo W, Wan C, Xiong S, Xu C, Yuan
C, Sun Q, Zhou L and Li X: Comprehensive genomic profiling of upper
tract urothelial carcinoma and urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
identifies distinct molecular characterizations with potential
implications for targeted therapy & immunotherapy. Front
Immunol. 13:10977302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Weber J: Immune checkpoint proteins: A new
therapeutic paradigm for cancer-preclinical background: CTLA-4 and
PD-1 blockade. Semin Oncol. 37:430–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS,
Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, Teng SL, et
al: MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in
metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 515:558–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku
IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu
V, et al: PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive
immune resistance. Nature. 515:568–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|