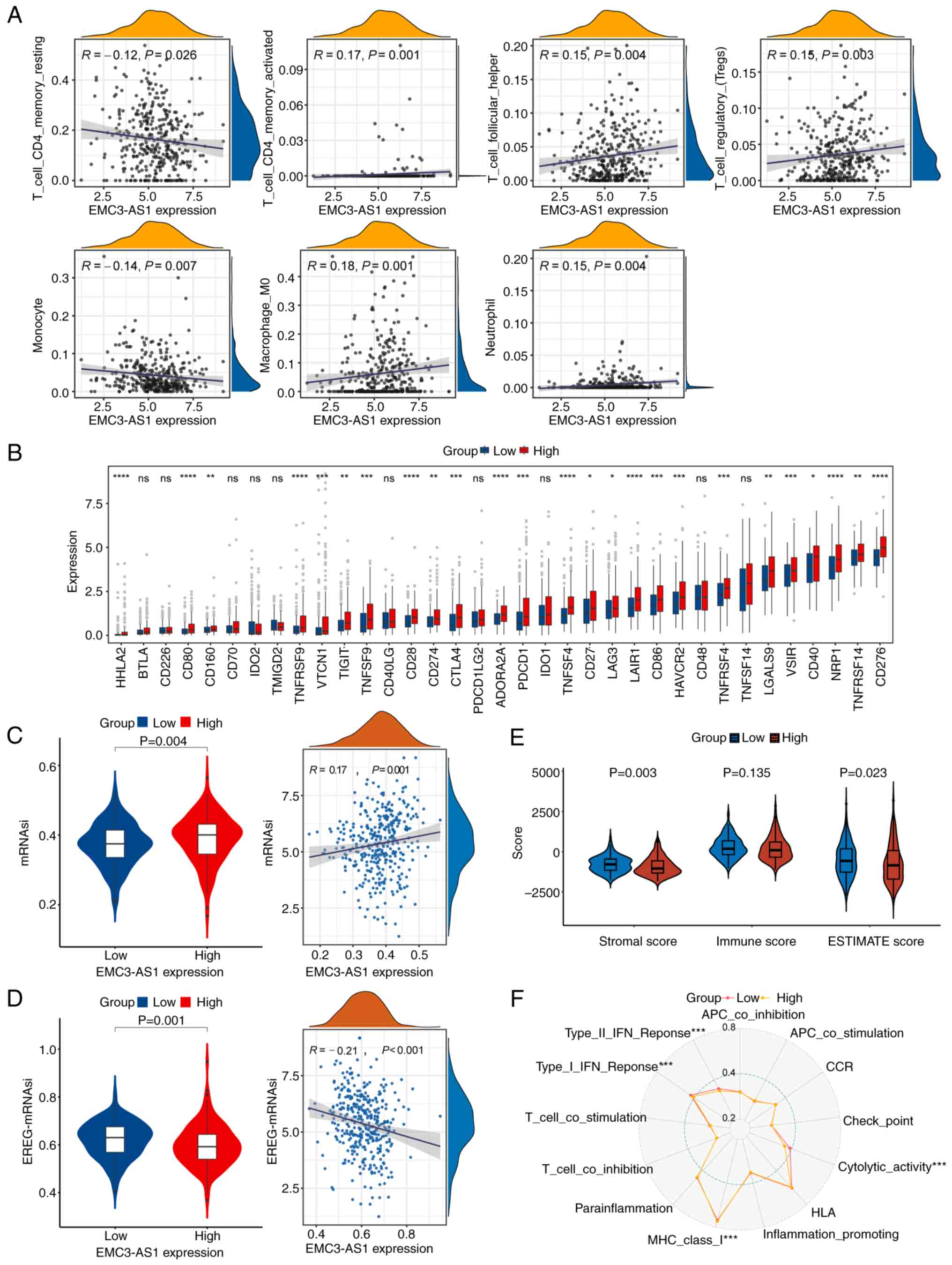
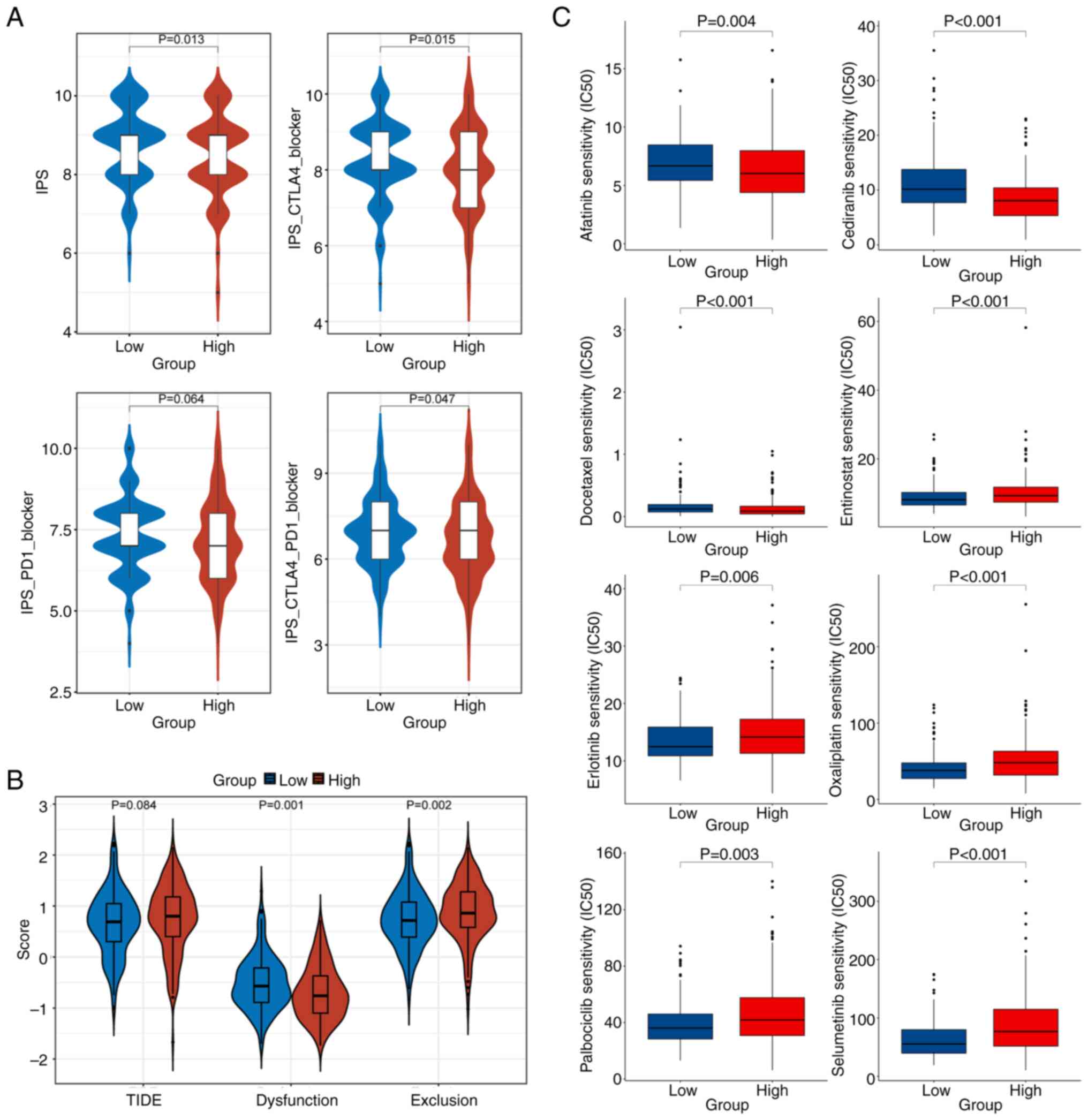
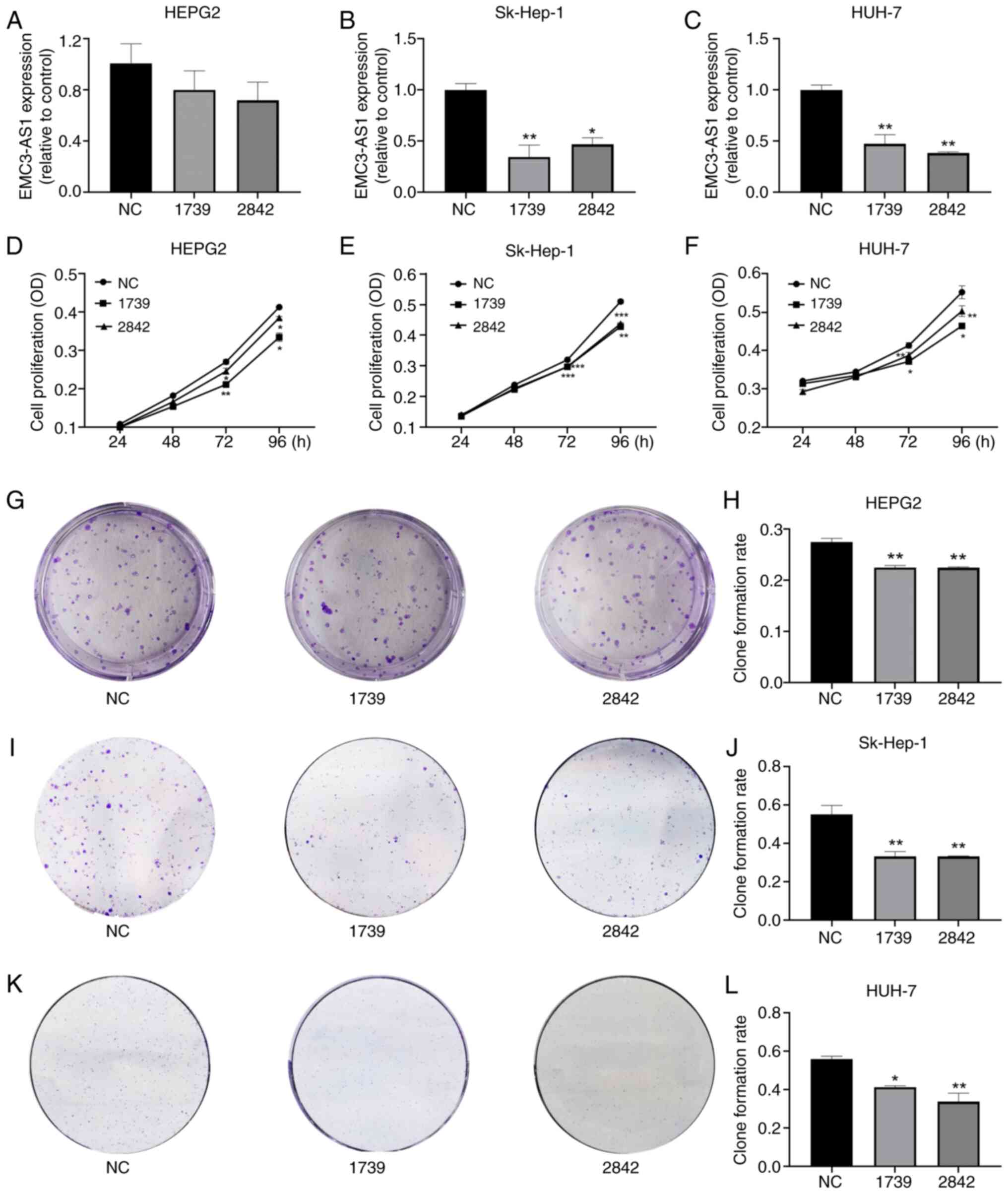
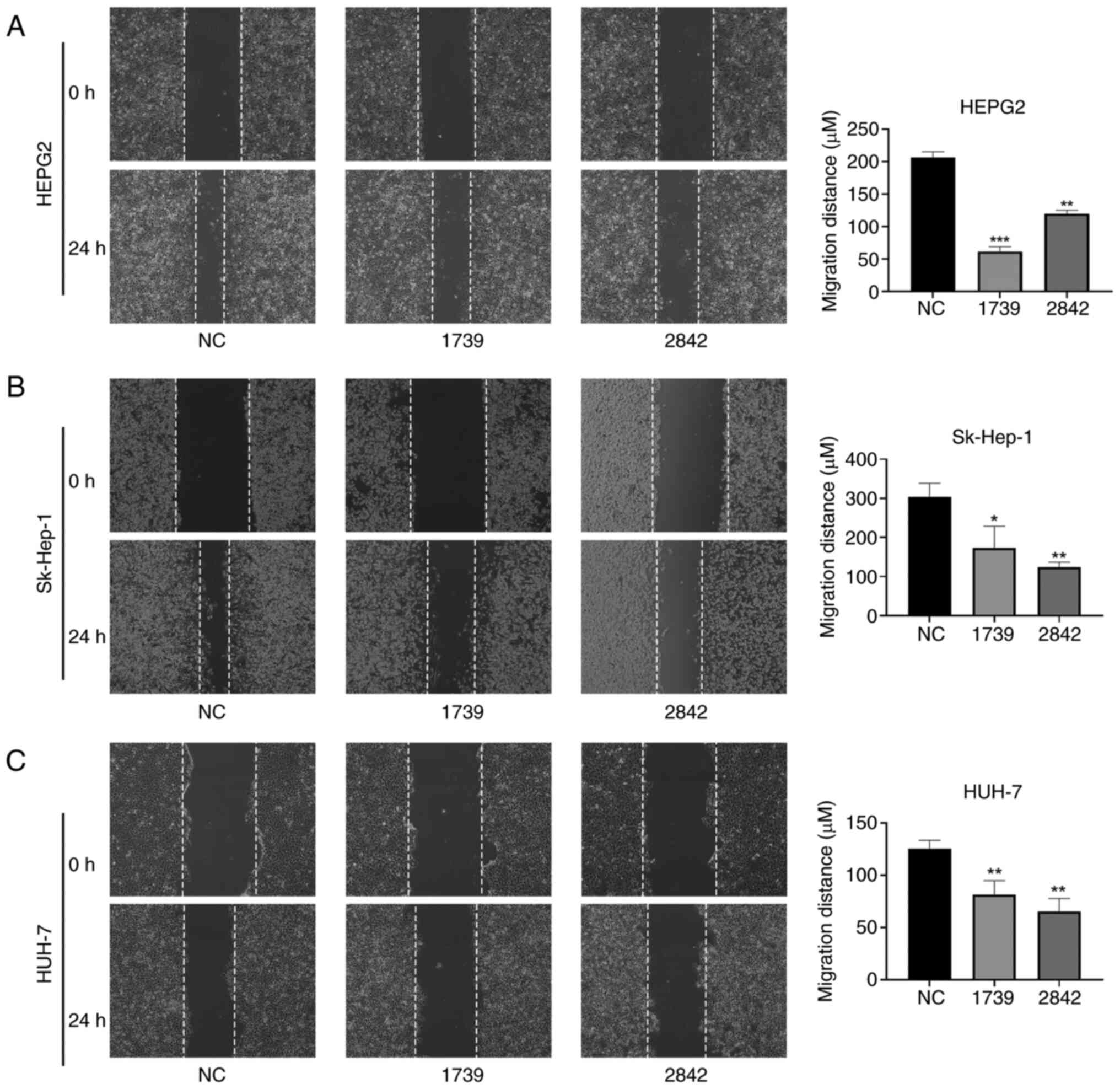
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, Paradis
V, Rugge M, Schirmacher P, Washington KM, Carneiro F and Cree IA;
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, : The 2019 WHO
classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology.
76:182–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang W, Hu B, Han J, Wang Z, Ma G, Ye H,
Yuan J, Cao J, Zhang Z, Shi J, et al: Surgery after conversion
therapy with PD-1 Inhibitors plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors are
effective and safe for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot
study of ten patients. Front Oncol. 11:7479502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caley DP, Pink RC, Trujillano D and Carter
DRF: Long noncoding RNAs, chromatin, and development.
ScientificWorldJournal. 10:90–102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang MC, Ni JJ, Cui WY, Wang BY and Zhuo
W: Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic
opportunities. Am J Cancer Res. 9:1354–1366. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Z, Zhou JK, Peng Y, He W and Huang
C: The role of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Cancer. 19:772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Liu X, Lin C, Jia X, Zhu H, Song J
and Zhang Y: Noncoding RNAs regulate alternative splicing in
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malakoti F, Targhazeh N, Karimzadeh H,
Mohammadi E, Asadi M, Asemi Z and Alemi F: Multiple function of
lncRNA MALAT1 in cancer occurrence and progression. Chem Biol Drug
Des. 101:1113–1137. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Si C, Yang L and Cai X: LncRNA LINC00649
aggravates the progression of cervical cancer through sponging
miR-216a-3p. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 48:2853–2862. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang D, Zhao L, Peng C, Ran K, Mu R and Ao
Y: LncRNA CRNDE promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
upregulating SIX1 through modulating miR-337-3p. J Cell Biochem.
120:16128–16142. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cai Y, Lyu T, Li H, Liu C, Xie K, Xu L, Li
W, Liu H, Zhu J, Lyu Y, et al: LncRNA CEBPA-DT promotes liver
cancer metastasis through DDR2/β-catenin activation via interacting
with hnRNPC. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:3352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao Z, Gao J and Huang S: LncRNA SNHG7
promotes the HCC progression through miR-122-5p/FOXK2 axis. Dig Dis
Sci. 67:925–935. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji Y, Sun H, Liang H, Wang Y, Lu M, Guo Z,
Lv Z and Ren W: Evaluation of LncRNA ANRIL potential in hepatic
cancer progression. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 38:119–131.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dai D, Wang H, Zhu L, Jin H and Wang X:
N6-methyladenosine links RNA metabolism to cancer progression. Cell
Death Dis. 9:1242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma S, Chen C, Ji X, Liu J, Zhou Q, Wang G,
Yuan W, Kan Q and Sun Z: The interplay between m6A RNA methylation
and noncoding RNA in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1212019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Burchard J, Zhang C, Liu AM, Poon RT, Lee
NP, Wong KF, Sham PC, Lam BY, Ferguson MD, Tokiwa G, et al:
microRNA-122 as a regulator of mitochondrial metabolic gene network
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Syst Biol. 6:4022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, Chen R, Liu X, Li
Y, Lee NP, Lee WH, Ariyaratne PN, Tennakoon C, et al: Genome-wide
survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Nat Genet. 44:765–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Makowska Z, Boldanova T, Adametz D,
Quagliata L, Vogt JE, Dill MT, Matter MS, Roth V, Terracciano L and
Heim MH: Gene expression analysis of biopsy samples reveals
critical limitations of transcriptome-based molecular
classifications of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol Clin Res.
2:80–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL,
Pietroni MC and Williams R: Transection of the oesophagus for
bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 60:646–649. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Müller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12:772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney J:
GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data.
BMC Bioinformatics. 14:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Newman AM, Steen CB, Liu CL, Gentles AJ,
Chaudhuri AA, Scherer F, Khodadoust MS, Esfahani MS, Luca BA,
Steiner D, et al: Determining cell type abundance and expression
from bulk tissues with digital cytometry. Nat Biotechnol.
37:773–782. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Salmaninejad A, Valilou SF, Shabgah AG,
Aslani S, Alimardani M, Pasdar A and Sahebkar A: PD-1/PD-L1
pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy. J Cell
Physiol. 234:16824–16837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Malta TM, Sokolov A, Gentles AJ,
Burzykowski T, Poisson L, Weinstein JN, Kamińska B, Huelsken J,
Omberg L, Gevaert O, et al: Machine learning identifies stemness
features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation. Cell.
173:338–354.e15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E,
Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, Treviño V, Shen H, Laird PW,
Levine DA, et al: Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune
cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun. 4:26122013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M,
Mayer C, Efremova M, Rieder D, Hackl H and Trajanoski Z: Pan-cancer
immunogenomic analyses reveal genotype-immunophenotype
relationships and predictors of response to checkpoint blockade.
Cell Rep. 18:248–262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J, Sahu A, Hu X,
Li Z, Traugh N, Bu X, Li B, et al: Signatures of T cell dysfunction
and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med.
24:1550–1558. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maeser D, Gruener RF and Huang RS:
oncoPredict: An R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient
drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief
Bioinform. 22:bbab2602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chew V, Lai L, Pan L, Lim CJ, Li J, Ong R,
Chua C, Leong JY, Lim KH, Toh HC, et al: Delineation of an
immunosuppressive gradient in hepatocellular carcinoma using
high-dimensional proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:E5900–E5909. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ and
Schreiber RD: Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to
tumor escape. Nat Immunol. 3:991–998. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shlomai A, de Jong YP and Rice CM: Virus
associated malignancies: The role of viral hepatitis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 26:78–88. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Margetts J, Ogle LF, Chan SL, Chan AWH,
Chan KCA, Jamieson D, Willoughby CE, Mann DA, Wilson CL, Manas DM,
et al: Neutrophils: Driving progression and poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma? Br J Cancer. 118:248–257. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arvanitakis K, Mitroulis I and Germanidis
G: Tumor-associated neutrophils in hepatocellular carcinoma
pathogenesis, prognosis, and therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:28992021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang HC, Haung LY, Wang CJ, Chao YJ, Hou
YC, Yen CJ and Shan YS: Tumor-associated macrophages promote
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells against sorafenib by
activating CXCR2 signaling. J Biomed Sci. 29:992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
You M, Gao Y, Fu J, Xie R, Zhu Z, Hong Z,
Meng L, Du S, Liu J, Wang FS, et al: Epigenetic regulation of
HBV-specific tumor-infiltrating T cells in HBV-related HCC.
Hepatology. 78:943–958. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S,
Ogasawara S, Palmer D, Verslype C, Zagonel V, Fartoux L, Vogel A,
et al: Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A
non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:940–952.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Romano E, Kusio-Kobialka M, Foukas PG,
Baumgaertner P, Meyer C, Ballabeni P, Michielin O, Weide B, Romero
P and Speiser DE: Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma
patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:6140–6145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS,
Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, Teng SL, et
al: MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in
metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 515:558–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rotte A, Jin JY and Lemaire V: Mechanistic
overview of immune checkpoints to support the rational design of
their combinations in cancer immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 29:71–83.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shi J, Liu J, Tu X, Li B, Tong Z, Wang T,
Zheng Y, Shi H, Zeng X, Chen W, et al: Single-cell immune signature
for detecting early-stage HCC and early assessing anti-PD-1
immunotherapy efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0031332022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pfister D, Núñez NG, Pinyol R, Govaere O,
Pinter M, Szydlowska M, Gupta R, Qiu M, Deczkowska A, Weiner A, et
al: NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated
HCC. Nature. 592:450–456. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheng AL, Hsu C, Chan SL, Choo SP and Kudo
M: Challenges of combination therapy with immune checkpoint
inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 72:307–319.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Benson AB, D'Angelica MI, Abbott DE, Anaya
DA, Anders R, Are C, Bachini M, Borad M, Brown D, Burgoyne A, et
al: Hepatobiliary cancers, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice
guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 19:541–565. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Federico P, Petrillo A, Giordano P, Bosso
D, Fabbrocini A, Ottaviano M, Rosanova M, Silvestri A, Tufo A,
Cozzolino A and Daniele B: Immune checkpoint inhibitors in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and novel perspectives.
Cancers (Basel). 12:30252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|