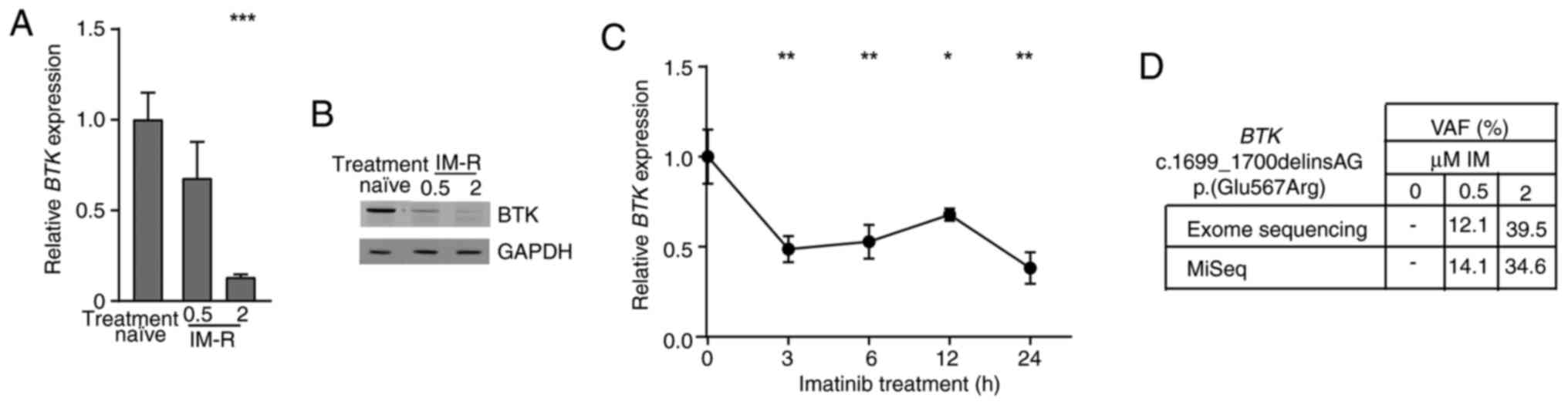
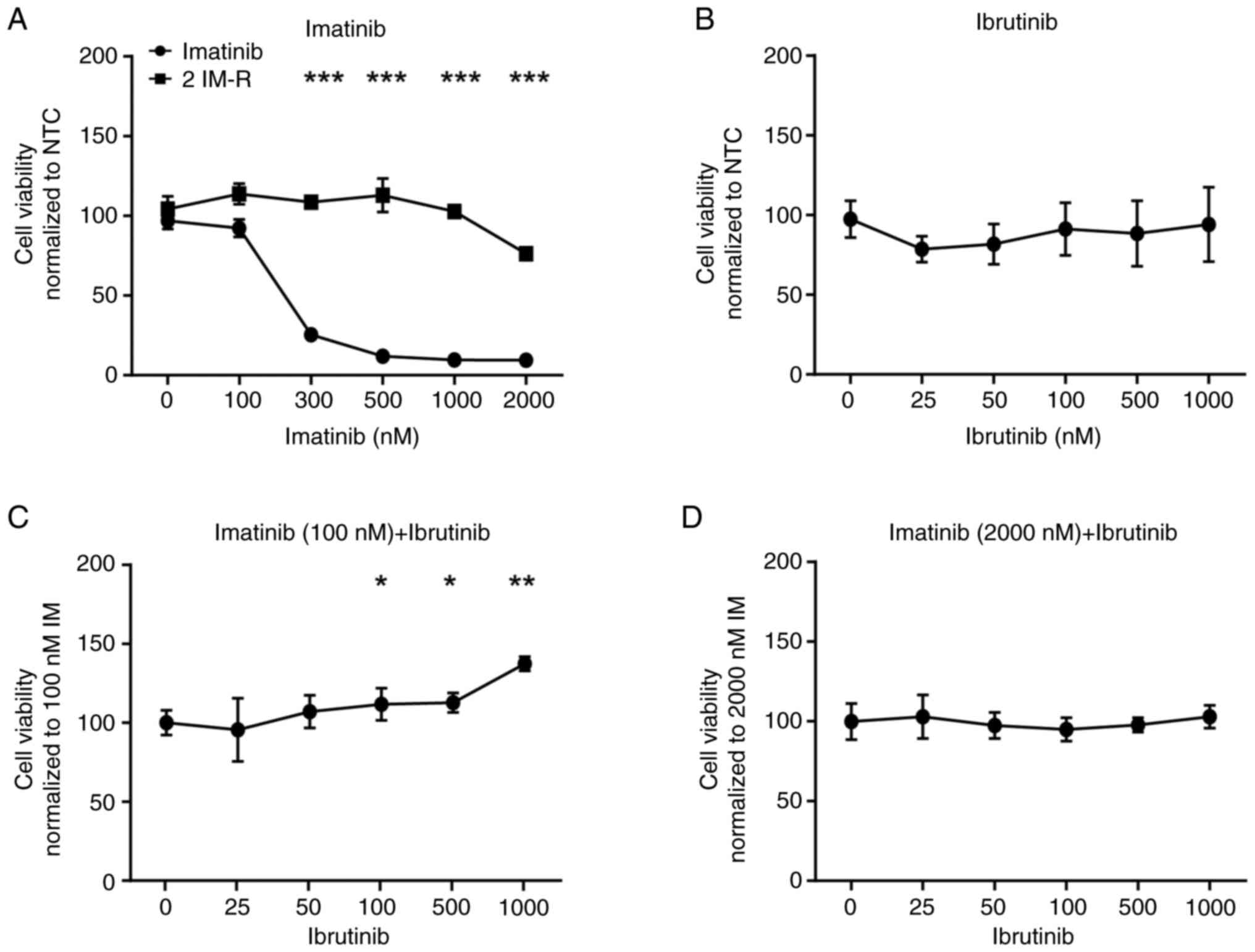
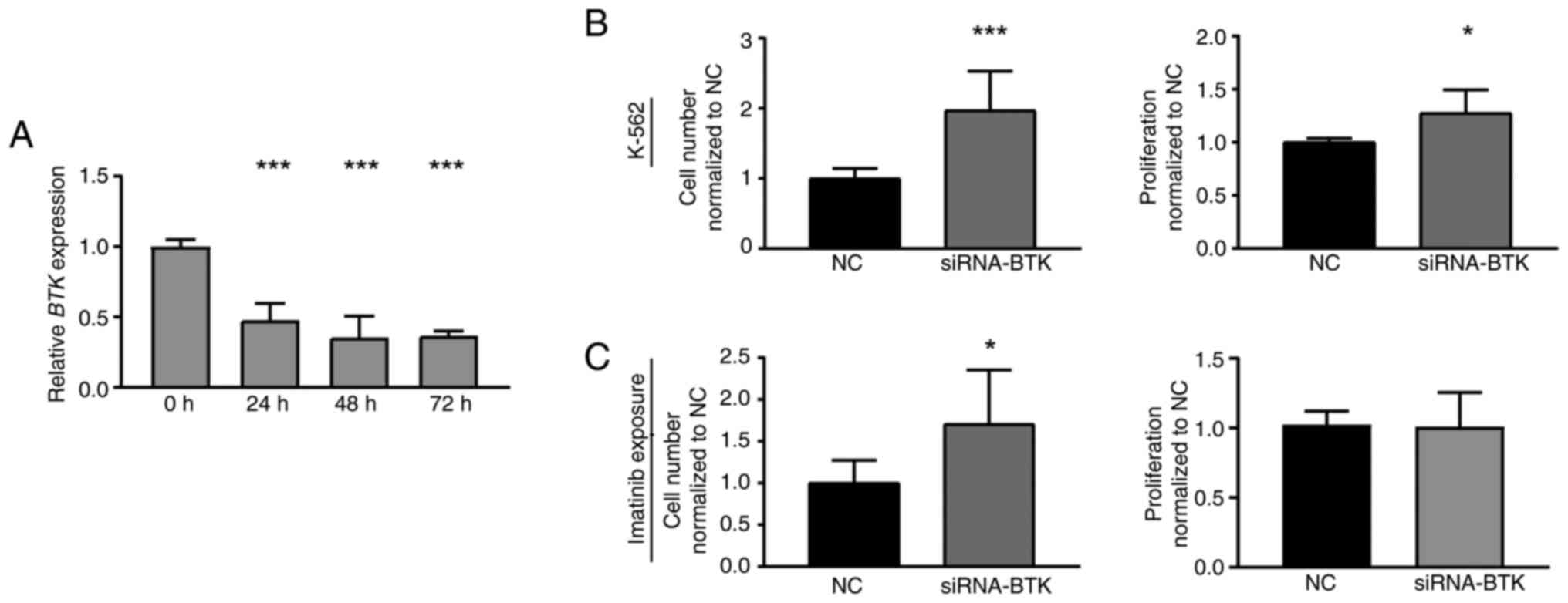
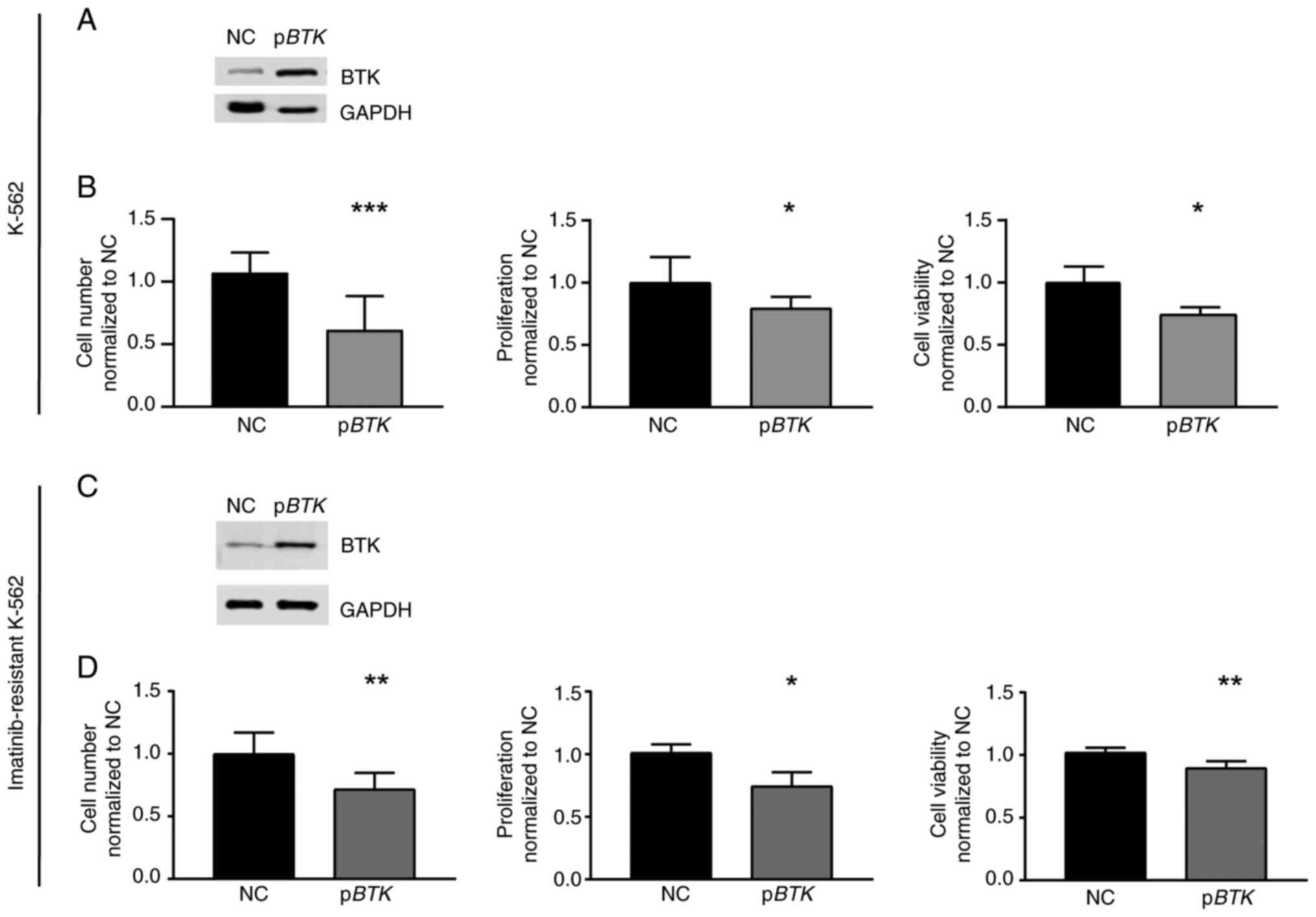
|
1
|
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S,
Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J and Lydon NB: Effects of a
selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of
Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 2:561–566. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deininger MW, Goldman JM and Melo JV: The
molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 96:3343–3356.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quintás-Cardama A and Cortes J: Molecular
biology of bcr-abl1-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood.
113:1619–1630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Milojkovic D and Apperley J: Mechanisms of
resistance to imatinib and second-generation tyrosine inhibitors in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7519–7527. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Silver RT,
Schiffer C, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE,
Deininger MW, Guilhot F, et al: European LeukemiaNet 2020
recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
34:966–984. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cortes J, Jabbour E, Kantarjian H, Yin CC,
Shan J, O'Brien S, Garcia-Manero G, Giles F, Breeden M, Reeves N,
et al: Dynamics of BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in chronic
myeloid leukemia after sequential treatment with multiple tyrosine
kinase inhibitors. Blood. 110:4005–4011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N,
Paquette R, Rao PN and Sawyers CL: Clinical resistance to STI-571
cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification.
Science. 293:876–880. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jabbour E, Parikh SA, Kantarjian H and
Cortes J: Chronic myeloid leukemia: Mechanisms of resistance and
treatment. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 25:981–995. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G,
Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes
JE, Guilhot F, et al: European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the
management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 122:872–884.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Hare T, Zabriskie MS, Eiring AM and
Deininger MW: Pushing the limits of targeted therapy in chronic
myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:513–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Braun TP, Eide CA and Druker BJ: Response
and resistance to BCR-ABL1-targeted therapies. Cancer Cell.
37:530–542. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaehler M and Cascorbi I: Pharmacogenomics
of impaired tyrosine kinase inhibitor response: Lessons learned
from chronic myelogenous leukemia. Front Pharmacol. 12:6969602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Lavallade H and Kizilors A: The
Importance of mutational analyses in chronic myeloid leukaemia for
treatment choice. Eur Med J Oncol. 4:86–95. 2016.
|
|
14
|
Cilloni D and Saglio G: Molecular
pathways: BCR-ABL. Clin Cancer Res. 18:930–937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaehler M, Litterst M, Kolarova J, Böhm R,
Bruckmueller H, Ammerpohl O, Cascorbi I and Nagel I: Genome-wide
expression and methylation analyses reveal aberrant cell adhesion
signaling in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant CML cells. Oncol
Rep. 48:1442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaehler M, Osteresch P, Künstner A, Vieth
S, Esser D, Möller M, Busch H, Vater I, Spielmann M, Cascorbi I and
Nagel I: Clonal evolution in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistance:
Lessons from in vitro-models. Front Oncol. 13:12008972023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen T, Wang J, Shi Y, Qian H and Liu P:
Inhibitors targeting Bruton's tyrosine kinase in cancers: Drug
development advances. Leukemia. 35:312–332. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pal Singh S, Dammeijer F and Hendriks RW:
Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol
Cancer. 17:572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mattsson PT, Vihinen M and Smith CI:
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA): A genetic tyrosine kinase (Btk)
disease. Bioessays. 18:825–834. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hendriks RW, Yuvaraj S and Kil LP:
Targeting Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:219–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Gavriatopoulou M,
Fotiou D and Dimopoulos MA: Current and novel BTK inhibitors in
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Ther Adv Hematol.
12:20406207219895862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Palma M, Mulder TA and Österborg A: BTK
inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Biological activity and
immune effects. Front Immunol. 12:6867682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bond DA, Alinari L and Maddocks K: Bruton
tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of mantle cell
lymphoma: Review of current evidence and future directions. Clin
Adv Hematol Oncol. 17:223–233. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Byrd JC, Hillmen P, Ghia P, Kater AP,
Chanan-Khan A, Furman RR, O'Brien S, Yenerel MN, Illés A, Kay N, et
al: Acalabrutinib versus ibrutinib in previously treated chronic
lymphocytic leukemia: Results of the first randomized phase III
trial. J Clin Oncol. 39:3441–3452. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hillmen P, Eichhorst B, Brown JR, Lamanna
N, O'Brien SM, Tam CS, Qiu L, Kazmierczak M, Zhou K, Šimkovič M, et
al: Zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory chronic
lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma: Interim
analysis of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol.
41:1035–1045. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lozzio CB and Lozzio BB: Human chronic
myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia
chromosome. Blood. 45:321–334. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kaehler M, Dworschak M, Rodin JP,
Ruemenapp J, Vater I, Penas EMM, Liu C, Cascorbi I and Nagel I:
ZFP36L1 plays an ambiguous role in the regulation of cell expansion
and negatively regulates CDKN1A in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
Exp Hematol. 99:54–64.e7. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaehler M, Ruemenapp J, Gonnermann D,
Nagel I, Bruhn O, Haenisch S, Ammerpohl O, Wesch D, Cascorbi I and
Bruckmueller H: MicroRNA-212/ABCG2-axis contributes to development
of imatinib-resistance in leukemic cells. Oncotarget.
8:92018–92031. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waetzig V, Haeusgen W, Andres C, Frehse S,
Reinecke K, Bruckmueller H, Boehm R, Herdegen T and Cascorbi I:
Retinoic acid-induced survival effects in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma
cells. J Cell Biochem. 120:5974–5986. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bruhn O, Lindsay M, Wiebel F, Kaehler M,
Nagel I, Böhm R, Röder C and Cascorbi I: Alternative
polyadenylation of ABC transporters of the C-family (ABCC1, ABCC2,
ABCC3) and implications on posttranscriptional Micro-RNA
regulation. Mol Pharmacol. 97:112–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rentzsch P, Schubach M, Shendure J and
Kircher M: CADD-Splice-improving genome-wide variant effect
prediction using deep learning-derived splice scores. Genome Med.
13:312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ito M, Shichita T, Okada M, Komine R,
Noguchi Y, Yoshimura A and Morita R: Bruton's tyrosine kinase is
essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation and contributes to
ischaemic brain injury. Nat Commun. 6:73602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Uckun FM and Venkatachalam T: Targeting
solid tumors with BTK inhibitors. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6504142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Treon SP, Xu L, Guerrera ML, Jimenez C,
Hunter ZR, Liu X, Demos M, Gustine J, Chan G, Munshi M, et al:
Genomic landscape of waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and its impact
on treatment strategies. J Clin Oncol. 38:1198–1208. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith CIE and Burger JA: Resistance
mutations to BTK inhibitors originate from the NF-κB but not from
the PI3K-RAS-MAPK Arm of the B cell receptor signaling pathway.
Front Immunol. 12:6894722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ahn IE and Brown JR: Targeting Bruton's
tyrosine kinase in CLL. Front Immunol. 12:6874582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chiron D, Di Liberto M, Martin P, Huang X,
Sharman J, Blecua P, Mathew S, Vijay P, Eng K, Ali S, et al:
Cell-cycle reprogramming for PI3K inhibition overrides a
relapse-specific C481S BTK mutation revealed by longitudinal
functional genomics in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov.
4:1022–1035. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gu D, Tang H, Wu J, Li J and Miao Y:
Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase using non-covalent inhibitors in B
cell malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 14:402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Väliaho J, Faisal I, Ortutay C, Smith CI
and Vihinen M: Characterization of all possible single-nucleotide
change caused amino acid substitutions in the kinase domain of
Bruton tyrosine kinase. Hum Mutat. 36:638–647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Speletas M, Kanariou M,
Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F, Papadopoulou Alataki E, Arvanitidis K,
Pardali E, Constantopoulos A, Kartalis G, Vihinen M, Sideras P and
Ritis K: Analysis of Btk mutations in patients with X-linked
agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) and determination of carrier status in
normal female relatives: A nationwide study of Btk deficiency in
Greece. Scand J Immunol. 54:321–327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Burger JA, Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, Ghia
P, Tedeschi A, Bairey O, Hillmen P, Coutre SE, Devereux S, et al:
Long-term efficacy and safety of first-line ibrutinib treatment for
patients with CLL/SLL: 5 years of follow-up from the phase 3
RESONATE-2 study. Leukemia. 34:787–798. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Broccoli A, Argnani L, Morigi A, Nanni L,
Casadei B, Pellegrini C, Stefoni V and Zinzani PL: Long-term
efficacy and safety of ibrutinib in the treatment of CLL patients:
A real life experience. J Clin Med. 10:58452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hantschel O, Rix U, Schmidt U,
Bürckstümmer T, Kneidinger M, Schütze G, Colinge J, Bennett KL,
Ellmeier W, Valent P and Superti-Furga G: The Btk tyrosine kinase
is a major target of the Bcr-Abl inhibitor dasatinib. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:13283–13288. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Parting O, Langer S, Kuepper MK, Wessling
C, Li S, Braunschweig T, Chatain N, Maié T, Costa IG, Crysandt M,
et al: Therapeutic inhibition of FcγRIIb signaling targets leukemic
stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 34:2635–2647.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shea LK, Mikhail FM, Forero-Torres A and
Davis RS: Concomitant imatinib and ibrutinib in a patient with
chronic myelogenous leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin
Case Rep. 5:899–901. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
MacPartlin M, Smith AM, Druker BJ,
Honigberg LA and Deininger MW: Bruton's tyrosine kinase is not
essential for Bcr-Abl-mediated transformation of lymphoid or
myeloid cells. Leukemia. 22:1354–1360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peng B, Lloyd P and Schran H: Clinical
pharmacokinetics of imatinib. Clinl Pharmacokinet. 44:879–894.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Villuendas R, Steegmann JL, Pollán M,
Tracey L, Granda A, Fernández-Ruiz E, Casado LF, Martínez J,
Martínez P, Lombardía L, et al: Identification of genes involved in
imatinib resistance in CML: A gene-expression profiling approach.
Leukemia. 20:1047–1054. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu S, Gokhale S, Jung J, Spirollari E,
Tsai J, Arceo J, Wu BW, Victor E and Xie P: Multifaceted
immunomodulatory effects of the BTK inhibitors ibrutinib and
acalabrutinib on different immune cell subsets-beyond B
lymphocytes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7275312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rada M, Barlev N and Macip S: BTK: A
two-faced effector in cancer and tumour suppression. Cell Death
Dis. 9:10642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|