Introduction
Melanoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer, with
an estimated 324,635 new cases and 57,043 cancer-related deaths
worldwide in 2020 (1,2). Generally, risk factors for melanoma
include the number of nevi, genetic susceptibility, sun exposure
and family history of the disease (3–6). The
treatment strategy for melanoma depends on the stage of cancer
(7–9). For early-stage melanoma, surgery is
the standard therapy (7,10,11);
however, when the tumor spreads, other therapies, such as immune
checkpoint inhibitors, are recommended for patients with advanced
melanoma (8,12–15).
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are a type
of immunotherapy, which have achieved unprecedented progress in
treating advanced melanoma (16).
However, the therapeutic response rate is only ~40–50% and the
response is unsatisfactory in ~60% of patients with advanced
melanoma who receive PD-1 inhibitors, which is a crucial cause of
poor prognosis in these patients (16–19).
Therefore, investigating potential markers that predict therapeutic
response to PD-1 inhibitors is necessary to improve the management
of patients with advanced melanoma.
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 (MALT1) is
intimately involved in the regulation of immune escape, which can
further affect the response to PD-1 inhibitors and accelerate
cancer progression (20–22). According to a previous study, MALT1
regulates the activation of CD8+ T cells to facilitate
immune escape and can further affect the antitumor effect of PD-1
inhibitors in mice models (21). At
the same time, MALT1 is essential for maintaining the homeostasis
and immunosuppressive function of regulatory T (Treg) cells, which
may reduce the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors (23). Furthermore, another study reported
that MALT1 inhibition enhances antitumor immune responses,
resulting in the attenuation of melanoma progression (22). Consequently, we hypothesize that
MALT1 may possess a prognostic value for patients with advanced
melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. Relevant studies are
scarce; therefore, the present research aimed to assess the ability
of MALT1 to predict therapeutic response and survival in patients
with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy.
Patients and methods
Patients and healthy subjects
The present prospective, multicenter cohort study
was performed at the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Engineering
University (Handan, China), Handan Central Hospital (Handan, China)
and Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital (Beijing, China). A total
of 49 patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy were recruited from the aforementioned centers between
July 2019 and April 2023. The inclusion criteria were as follows:
i) Diagnosis of advanced melanoma with a tumor-node-metastasis
(TNM) stage of III or IV; ii) aged ≥18 years; iii) inability to
have a surgical resection; iv) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
Performance Status (ECOG PS) ≤1 (24); v) ≥1 measurable lesion according to
the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria
v.1.1 (25); vi) ability to provide
peripheral blood; and vii) willingness to cooperate with follow-up.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: i) Other primary solid
tumors or malignant hematologic diseases; ii) previous systematic
anticancer treatment; iii) presence of an autoimmune disease; iv)
previous organ transplantation; and v) serious liver or kidney
failure. A total of 20 healthy subjects were enrolled as healthy
controls (HCs), who were matched to the patients with advanced
melanoma by age and sex. The inclusion criteria of the HCs were as
follows: i) normal results of the physical examination; ii) aged
≥18 years; and iii) ability to provide peripheral blood. The
exclusion criteria for HCs were the same as for the patients with
advanced melanoma. The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Engineering
University (Handan, China; approval no. 2018K037; February 17,
2018). It should be clarified that three centers were involved, and
we only obtained one ethics approval from one ethic committee,
rather than three ethic committees. The reason was that: according
to Guidelines for the Construction of Ethical Review Boards for
Clinical Research Involving Human Subjects (https://www.cha.org.cn/site/content/393b419e529469ef3f4c0ddaddb347ca.html),
a single review model could be implemented in multicenter studies.
Specifically, single review referred to that in multicenter
studies, participating centers only needed to obtain a single
ethics approval from one ethics committee, rather than obtaining
ethics approvals from every ethics committee. The patients with
advanced melanoma and HCs provided written informed consent at the
time of enrollment.
Data collection and treatment
The clinical characteristics of the patients with
advanced melanoma were collected after enrollment. The PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy that each patient received was based on a
combination of the patient's situation, their willingness and the
physician's suggestions. The specific treatment of PD-1 inhibitors
was as follows: Nivolumab (3 mg/kg, once every 2 weeks),
camrelizumab (200 mg, once every 2 weeks) and pembrolizumab (200
mg, once every 2 weeks). The PD-1 inhibitor was administered until
the patient's disease progressed or they became intolerant, or it
was administered for two years.
Peripheral blood collection and
detection
Peripheral blood was collected from the patients
with advanced melanoma before treatment (T0), after 2
months of treatment (T1) and after 4 months of treatment
(T2). Peripheral blood was only collected once from HCs
after enrollment. The peripheral blood was processed (centrifuged
at 1,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C) to obtain peripheral blood
mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and reverse transcription
(RT)-quantitative (q)PCR was used to detect the level of MALT1 in
the PBMCs. Total RNA of PBMC was extracted using TRIzol™
reagent (Invitrogen™; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit (Perfect Real Time; cat. no.
RR037A; Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was then used to obtain
cDNA from the total RNA (1 cycle of 37°C for 15 min and 85°C for 5
sec). MALT1 levels were measured by qPCR (fluorophore: TB Green;
Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; 1 cycle of 95°C for 30 sec, 40
cycles of 95°C for 5 sec and 60°C for 10–15 sec) and quantified
using the 2−ΔΔCq method with GAPDH used as an internal
reference (26). The primer
sequences for MALT1 were as follows: Forward,
5′-TCTTGGCTGGACAGTTTGTGA-3′; reverse, 5′-GCTCTCTGGGATGTCGCAA-3′
(27). The primer sequences for
GAPDH were as follows: Forward, 5′-GGAAGCTTGTCATCAATGGAAATC-3′;
reverse, 5′-TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC-3′ (28).
Follow-up and evaluations
Disease progression was assessed every 2 cycles
(about 1 month) during the first 4 months after treatment.
Subsequently, disease progression was evaluated every 2 months. The
therapeutic response rates of the patients with advanced melanoma
were calculated based on the assessment data of the third month
using RECIST criteria v.1.1 (25).
The objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR)
were also calculated.
The patients with advanced melanoma had a normal
follow-up. In detail, patients were followed up every 3–6 months
for the first 2 years, every 3–12 months at 3–5 years and annually
after 5 years. The median follow-up period was 9.1 months.
Progress-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were
calculated based on the follow-up data.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 (IBM Corp.)
software. Comparisons between MALT1 levels at T0 between
the HCs and patients with advanced melanoma were analyzed using the
Mann-Whitney U test. Comparisons between MALT1 levels at
T0, T1 and T2 in patients with
advanced melanoma was analyzed using the Friedman test.
Bonferroni's correction was applied to adjust the comparison (the
current P-values had already been multiplied by 2 for adjustment).
The correlation between MALT1 levels and the therapeutic response
of the patients was analyzed using the Spearman's rank correlation
coefficient test. The association between MALT1 levels at different
times (T0, T1 and T2) and the
prognosis of the patients with advanced melanoma was assessed using
Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test. The maximum level of
MALT1 in HCs (3.100, relative value) was used as the cut-off value
of MALT1 in the patients with advanced melanoma. The association
between factors (MALT1 and all clinical characteristics) and PFS or
OS was analyzed using univariate and backward stepwise multivariate
Cox regression analyses. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
MALT1 levels in patients with advanced
melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy compared with
HCs
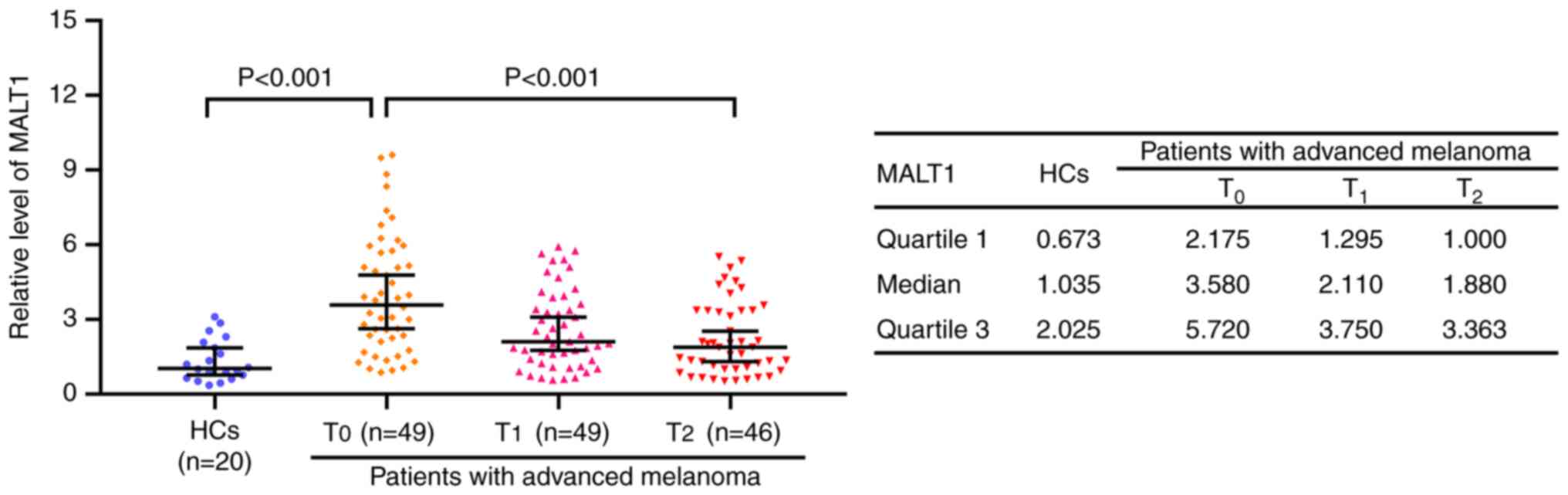
MALT1 levels at T0 were significantly
increased in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy compared with that in HCs, with the median
[interquartile range (IQR)], 3.580 (2.175–5.720) and 1.035
(0.673–2.025), respectively (P<0.001). In patients with advanced
melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy, MALT1 levels were
the highest at T0 [median (IQR), 3.580 (2.175–5.720)],
followed by T1 [median (IQR), 2.110 (1.295–3.750)] and
the lowest at T2 [median (IQR), 1.880 (1.000–3.363);
P<0.001; Fig. 1].
Comparison of MALT1 levels in patients
with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy with
different clinical features
MALT1 levels were significantly increased in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy with an ECOG PS score of 1 (vs. 0; P=0.018), total
tumor size >5 cm (vs. ≤5 cm; P=0.015) and TNM stage IV (vs. TNM
stage III; P=0.030). However, MALT1 levels were not significantly
different in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy for other clinical features, including age
(≤60 vs. >60 years; P=0.645), sex (female vs. male; P=0.337),
lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (normal vs. abnormal; P=0.263)
and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) level (negative vs.
positive; P=0.607; Table I). The
clinical characteristics of the HCs are presented in Table SI.
 | Table I.Association between MALT1 levels and
clinical characteristics in patients with advanced melanoma
(n=49). |
Table I.
Association between MALT1 levels and
clinical characteristics in patients with advanced melanoma
(n=49).
| Clinical
characteristics | Patients with
advanced melanoma, n (%) | MALT1, median
(IQR) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.645 |
|
≤60 | 26 (53.1) | 3.660
(1.995–6.015) |
|
|
>60 | 23 (46.9) | 3.580
(2.350–5.080) |
|
| Sex |
|
| 0.337 |
|
Female | 24 (49.0) | 4.020
(2.278–6.125) |
|
|
Male | 25 (51.0) | 3.260
(1.930–5.040) |
|
| ECOG PS |
|
| 0.018 |
| 0 | 29 (59.2) | 3.000
1.600–4.700) |
|
| 1 | 20 (40.8) | 4.935
(3.043–6.188) |
|
| Total tumor size,
cm |
|
| 0.015 |
| ≤5 | 23 (46.9) | 2.580
(1.490–4.470) |
|
|
>5 | 26 (53.1) | 4.420
(2.758–6.393) |
|
| TNM stage |
|
| 0.030 |
|
III | 8 (16.3) | 2.425
(1.320–3.645) |
|
| IV | 41 (83.7) | 3.910
(2.355–5.965) |
|
| LDH level |
|
| 0.263 |
|
Normal | 29 (59.2) | 3.260
(1.585–5.385) |
|
|
Abnormal | 20 (40.8) | 3.675
(2.650–6.583) |
|
| PD-L1 level |
|
| 0.607 |
|
Negative | 7 (14.3) | 3.490
(1.520–5.760) |
|
|
Positive | 42 (85.7) | 3.815
(2.325–5.750) |
|
Association between MALT1 levels at
T0, T1 and T2, and therapeutic
response in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy
In patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy, the complete response (CR), partial response
(PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD) was
demonstrated to be 3 (6.1%), 11 (22.4%), 15 (30.7%) and 20 (40.8%)
patients, respectively. Notably, 14 (28.6%) and 29 (59.2%) patients
achieved ORR and DCR, respectively (Table II).
 | Table II.Relationship between MALT1 levels at
different time points and the therapeutic response in patients with
advanced melanoma (n=49). |
Table II.
Relationship between MALT1 levels at
different time points and the therapeutic response in patients with
advanced melanoma (n=49).
|
| Patients with
advanced melanomaa, n (%) | MALT1, median
(IQR) |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Items | T0
(n=49) | P-value | T1
(n=49) | P-value | T2
(n=46) | P-value |
|---|
| Response |
|
| 0.053a |
| 0.001a |
| 0.021a |
| CR | 3 (6.1) | 2.250 |
| 1.410 |
| 1.580 |
|
|
|
| (0.870–4.930) |
| (0.640–2.110) |
| (0.590–1.880) |
|
| PR | 11 (22.4) | 3.000 |
| 1.610 |
| 1.300 |
|
|
|
| (2.100–5.080) |
| (0.900–2.380) |
| (0.680–2.530) |
|
| SD | 15 (30.7) | 3.315 |
| 1.730 |
| 1.405 |
|
|
|
| (1.340–5.705) |
| (1.103–4.403) |
| (0.965–4.780) |
|
| PD | 20 (40.8) | 3.985 |
| 3.155 |
| 2.130 |
|
|
|
| (2.745–6.333) |
| (2.410–4.853) |
| (1.750–3.420) |
|
| ORR |
|
| 0.163b |
| 0.009b |
| 0.036b |
|
Yes | 14 (28.6) | 2.800 |
| 1.510 |
| 1.315 |
|
|
|
| (1.830–4.968) |
| (0.840–2.178) |
| (0.678–2.163) |
|
| No | 35 (71.4) | 3.840 |
| 2.890 |
| 2.080 |
|
|
|
| (1.910–6.125) |
| (1.670–4.568) |
| (1.180–3.930) |
|
| DCR |
|
| 0.070b |
| 0.004b |
| 0.059b |
|
Yes | 29 (59.2) | 3.025 |
| 1.680 |
| 1.340 |
|
|
|
| (1.433–5.088) |
| (1.025–3.153) |
| (0.748–3.153) |
|
| No | 20 (40.8) | 3.985 |
| 3.155 |
| 2.130 |
|
|
|
| (2.745–6.333) |
| (2.410–4.853) |
| (1.750–3.420) |
|
MALT1 levels at T0 were not different
among patients with CR, PR, SD or PD (P=0.053). Meanwhile, MALT1
levels at T0 were not significantly associated with ORR
(yes vs. no; P=0.163) or DCR (yes vs. no; P=0.070) in patients with
advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. MALT1
levels at T1 were the highest in patients with PD,
followed by patients with SD and PR, and the lowest in patients
with CR (P=0.001). Additionally, MALT1 levels at T1 were
significantly associated with non-ORR (vs. yes, P=0.009) and
non-DCR (vs. yes, P=0.004) in patients with advanced melanoma
receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. MALT1 levels at T2
were the highest in patients with PD, followed by patients with CR
and SD, and the lowest in patients with PR (P=0.021). MALT1 levels
at T2 were significantly associated with non-ORR (vs.
yes, P=0.036); however, it was not significantly associated with
DCR in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy (yes vs. no; P=0.059; Table II).
Association between MALT1 levels at
T0, T1 and T2, and PFS and OS in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy
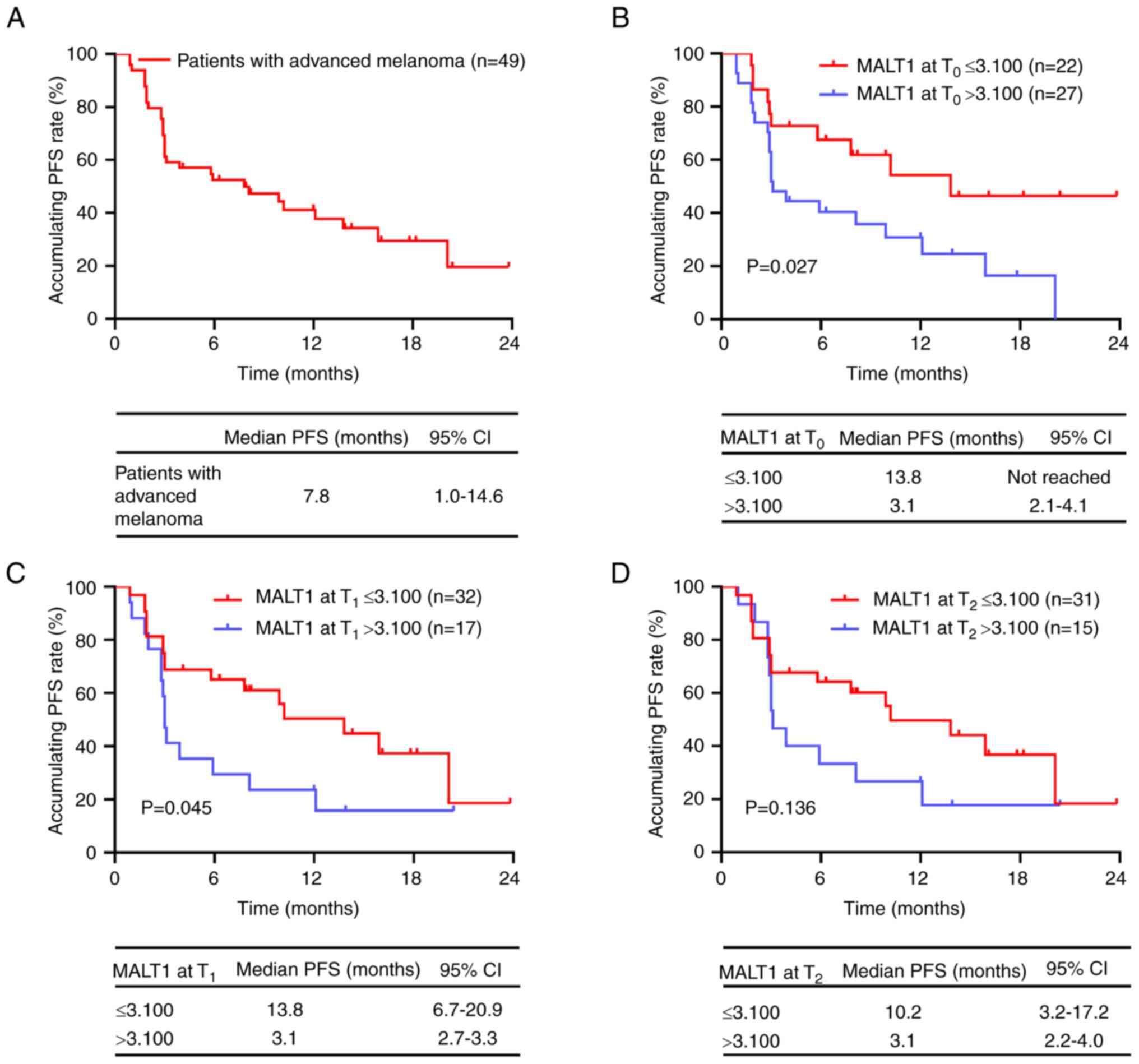
The median [95% confidence interval (CI)] PFS was
7.8 (1.0–14.6) months in patients with advanced melanoma receiving
PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy (Fig.
2A). The maximum value of MALT1 in HCs (3.100) was used as the
cut-off value in patients with advanced melanoma, and this value
was applied for subsequent analyses. MALT1 levels at T0
(P=0.027; Fig. 2B) and
T1 (P=0.045; Fig. 2C)
>3.100 were significantly associated with a shorter PFS in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy, in comparison with MALT1 levels at T0 and
T1 ≤3.100. However, MALT1 levels at T2 were
not significantly associated with PFS in patients with advanced
melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy (P=0.136; Fig. 2D).
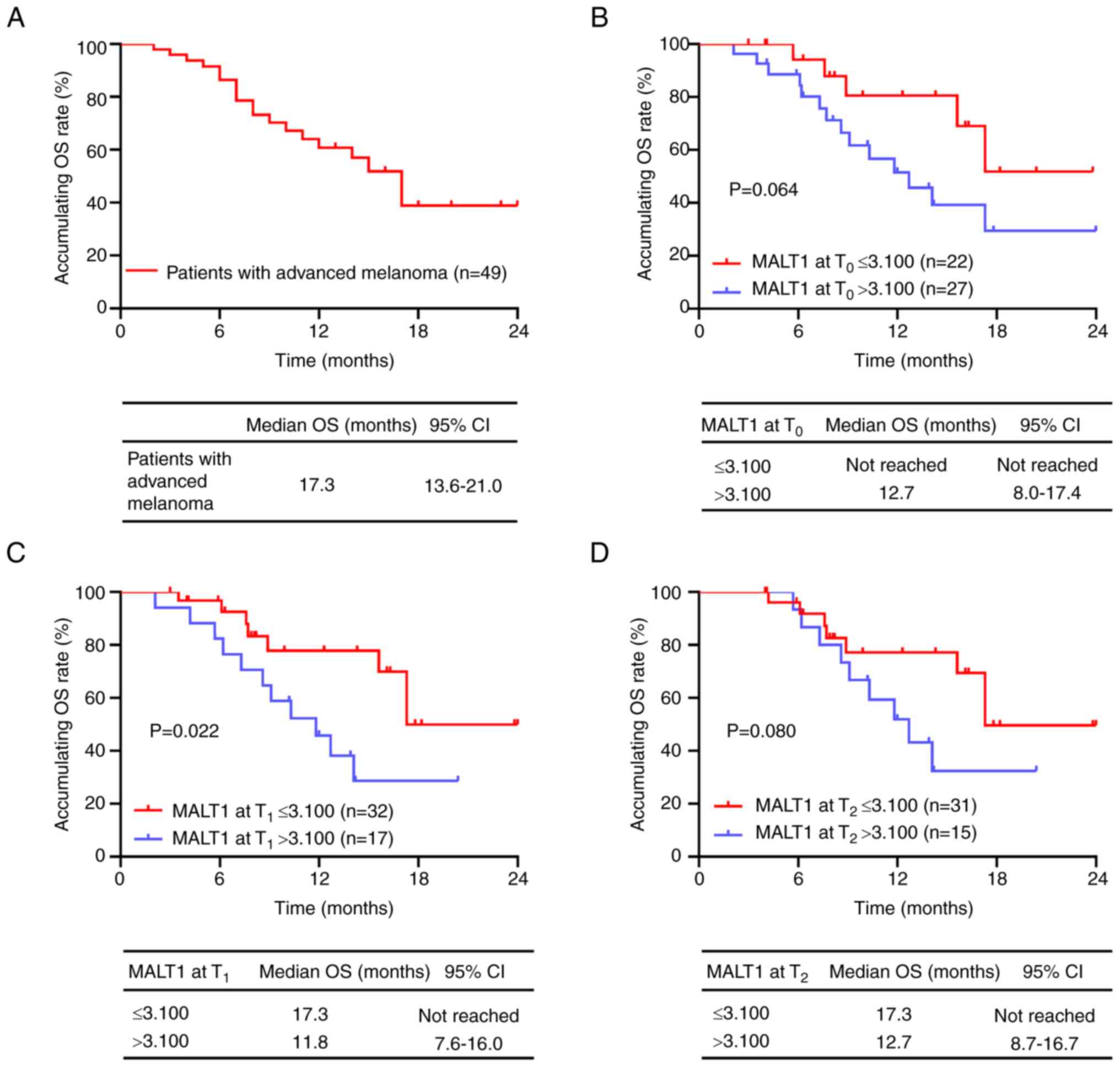
The median (95% CI) OS was 17.3 (13.6–21.0) months
in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy (Fig. 3A). MALT1 levels
at T0 were not significantly associated with OS in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy (P=0.064; Fig. 3B).
MALT1 levels at T1 >3.100 were significantly
associated with a poor OS in patients with advanced melanoma
receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy, in comparison with those with
MALT1 levels at T1 ≤3.100 (P=0.022; Fig. 3C); however, MALT1 levels at
T2 were not significantly associated with OS (P=0.080;
Fig. 3D).
Independent factors for predicting PFS
and OS in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy
According to univariate Cox regression analysis,
MALT1 levels at T0 (>3.100 vs. ≤3.100; P=0.034), TNM
stage (IV vs. III; P=0.020) and LDH level (abnormal vs. normal;
P=0.020) were significantly associated with a shorter PFS in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy. In contrast, PD-L1 level (positive vs. negative) was
significantly associated with a prolonged PFS (P=0.048; Fig. 4A). After adjustment, MALT1 levels at
T0 [>3.100 vs. ≤3.100; hazard ratio (HR)=2.248;
P=0.037] and LDH level (abnormal vs. normal; HR=2.303; P=0.022)
were significantly independently associated with a shorter PFS in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy (Fig. 4B).
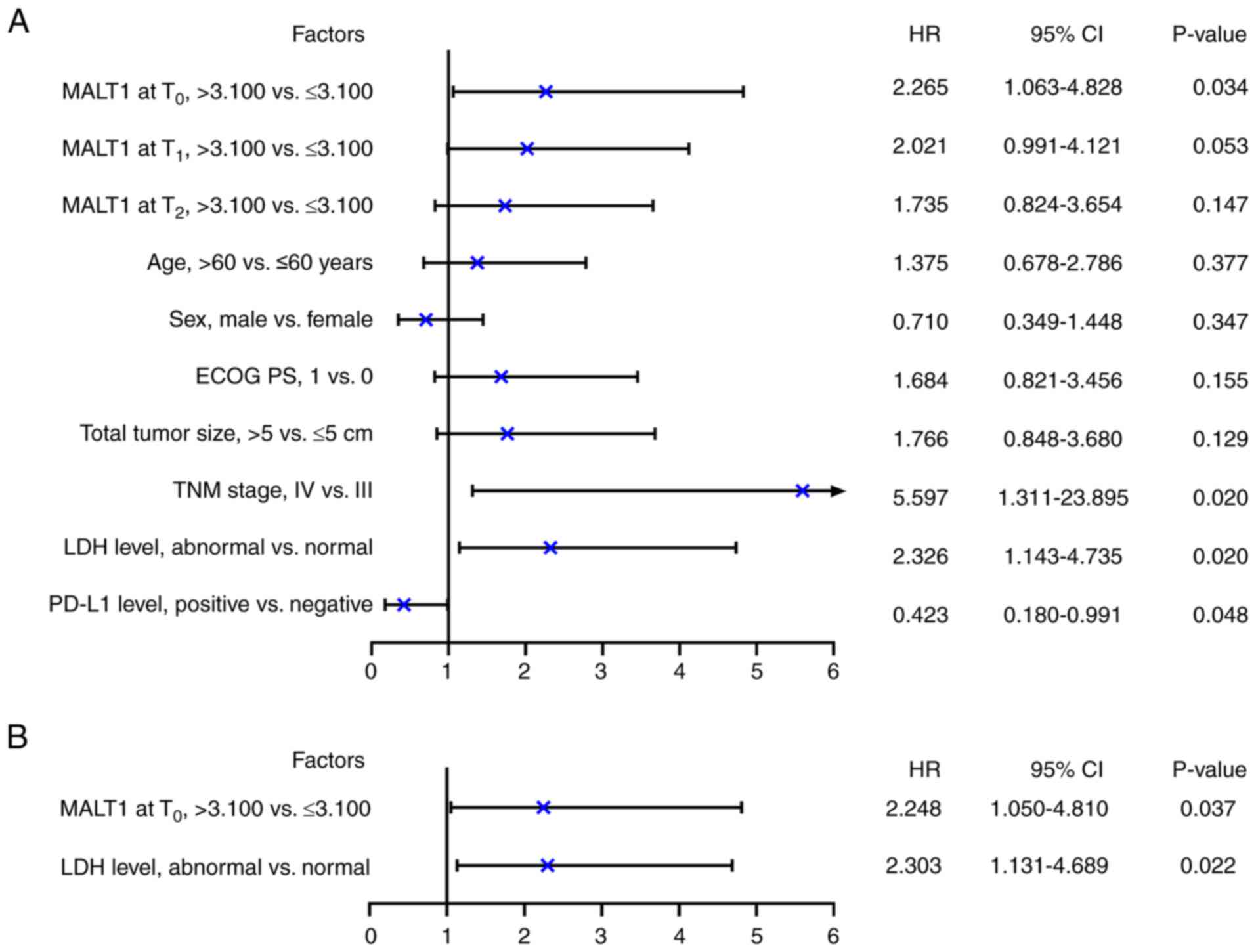 | Figure 4.Independent factors associated with
PFS in patients with advanced melanoma receiving programmed cell
death-1 inhibitor monotherapy. (A) Univariate and (B) backward
stepwise multivariate Cox regression analyses of PFS. PFS,
progression-free survival; MALT1, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
1; T0, before treatment; T1, 2 months after
treatment; T2, 4 months after treatment; Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; TNM,
tumor-node-metastasis; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PD-L1,
programmed cell death-ligand 1; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence
interval. |
Univariate Cox regression analysis revealed that
MALT1 levels at T1 (>3.100 vs. ≤3.100; P=0.028), ECOG
PS score (1 vs. 0; P=0.014) and TNM stage (IV vs. III; P=0.042)
were significantly associated with a poor OS (Fig. 5A). After adjustment, only MALT1
levels at T1 (>3.100 vs. ≤3.100; HR=4.332; P=0.007)
were significantly associated with a shorter OS. Furthermore, PD-L1
level (positive vs. negative; HR=0.244, P=0.018) was significantly
associated with a prolonged OS in patients with advanced melanoma
receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy (Fig. 5B).
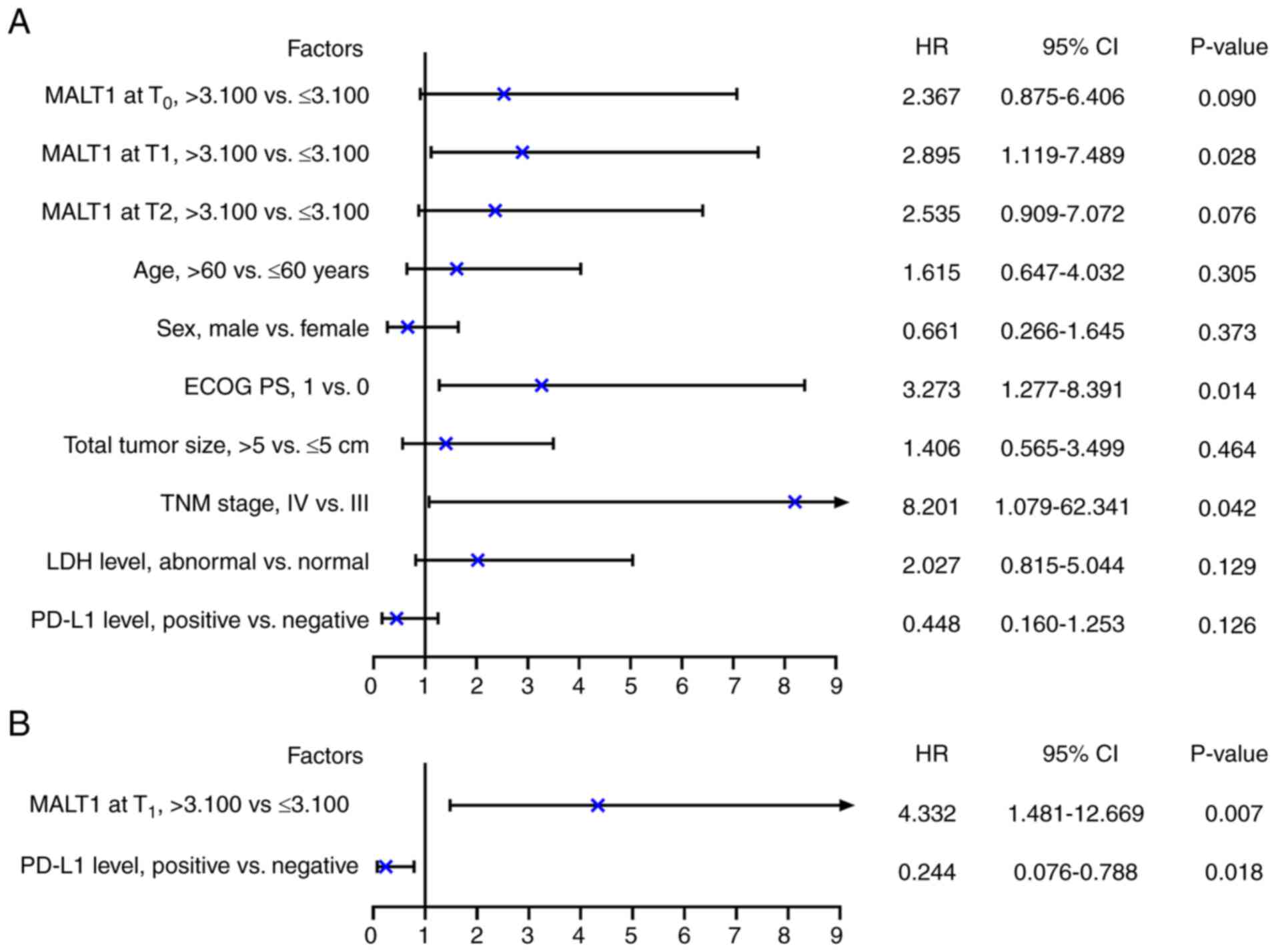 | Figure 5.Independent factors associated with
OS in patients with advanced melanoma receiving programmed cell
death-1 inhibitor monotherapy. (A) Univariate and (B) backward
stepwise multivariate Cox regression analyses of OS. OS, overall
survival; MALT1, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1;
T0, before treatment; T1, 2 months after
treatment; T2, 4 months after treatment; Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; TNM,
tumor-node-metastasis; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PD-L1,
programmed cell death-ligand 1; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence
interval. |
Discussion
MALT1 regulates the behaviors of malignant tumor
cells and immune escape, thereby playing a role in the pathology of
various cancers. Studies have reported the dysregulation of MALT1
in several cancers, such as metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC),
hepatocellular cancer and prostate cancer (29–32).
In the present study, it was observed that MALT1 levels was
elevated in patients with advanced melanoma compared with in HCs.
Potential explanations for this are as follows: i) MALT1 may
strengthen melanoma cell proliferation, motility and survival by
activating the Jun N-terminal Kinase/c-Jun and nuclear factor-κB
pathways (33) and; ii) MALT1 may
impair the activation of CD8+ T cells, leading to immune
escape and further induction of melanoma (21). In addition, the present demonstrated
that MALT1 levels were reduced from T0 to T2
in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy. A possible reason may be that MALT1 can induce immune
escape and after treatment with PD-1 inhibitors, CD8+ T
cells were activated, which attenuated the immune escape, leading
to a decrease in MALT1 levels (21). Therefore, MALT1 was decreased after
treatment of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with advanced melanoma.
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that MALT1 levels were associated
with an ECOG PS score of 1, a total tumor size >5 cm and TNM
stage IV in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy. This may be explained by the potential for
MALT1 to facilitate melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis to
aggravate the disease conditions, leading to a higher ECOG PS
score, larger tumor size and higher TNM stage (33).
Benefiting from the development of PD-1 inhibitors,
the median OS of patients with advanced melanoma has been prolonged
to more than 35 months (16,34,35).
However, certain patients still lack therapeutic responses, and the
corresponding markers that reflect therapeutic responses to PD-1
inhibitors are still limited (17).
In the current study, it was demonstrated that MALT1 levels at
T1 were negatively associated with overall therapeutic
response, ORR and DCR, and its level at T2 was also
negatively associated to overall therapeutic response and ORR in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy. The possible reasons may be as follows: i) MALT1 may
impair the activation of CD8+ T cells, which reduces the
effect of PD-1 inhibitors and resulted in a poor therapeutic
response to this treatment (21);
and ii) MALT1 may maintain the immune-suppressive function of Treg
cells in the tumor microenvironment, which facilitates immune
escape and reduces the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors (36). Taken together, MALT1 levels were
associated with a poor therapeutic response to PD-1 inhibitors in
patients with advanced melanoma.
The estimation of survival of patients with solid
cancers receiving PD-1 inhibitors using their MALT1 levels was
assessed by a previous study, which reported that high MALT1 levels
before and after PD-1 inhibitor-based treatment was associated with
a poor PFS and OS in patients with mCRC (32). The current study demonstrated that
MALT1 levels at T0 and T1 were associated
with a shortened PFS, and its level at T1 was associated
with a poor OS in patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1
inhibitor monotherapy. Multivariate Cox regression analysis further
suggested that MALT1 levels at T0 independently
estimated poor PFS, and MALT1 levels at T1 independently
estimated worse OS in patients with advanced melanoma receiving
PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. The possible reasons may be as follows:
i) MALT1 may facilitate the progression of melanoma, leading to
poor survival (33); and ii) MALT1
may enhance the immune escape, leading to reduced PD-1 inhibitor
efficacy and ultimately contributing to a worse prognosis (21,36).
Therefore, MALT1 levels were associated with poor survival in
patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy. Notably, in patients with a MALT1 level >3.100, the
median PFS and OS values at T2 were increased compared
with those at T1. We hypothesize that the potential
reason is that 3 patients were not analyzed at T2,
including 2 patients who experienced disease progression or death,
and 1 patient who was lost to follow-up, which affected the
results. Moreover, after searching relevant studies, only one
previous study was identified that classified MALT1 into high and
low levels based on its median value (2.529) in patients with mCRC
receiving PD-1 inhibitors (32).
This study reported that MALT1 >2.529 was independently
associated with a shorter PFS in these patients with a HR of 1.981
(32). In comparison, the HR of
MALT1 >3.100 for predicting PFS was higher in the present study,
calculated to be 2.248. Therefore, according to the findings of the
aforementioned previous study and the present study, MALT1
>3.100 may possess an improved effect for predicting poor
prognosis in patients with several cancers who receive PD-1
inhibitors (32). However, both
2.529 and 3.100 were relative expression levels; therefore, their
significance for clinical applications may be limited.
There are several limitations of the current study.
Firstly, the sample size was small, which may have induced low
statistical power. Secondly, the number of HCs was unmatched to the
number of patients with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor
monotherapy. This may have affected the results. Thirdly, the type
of PD-1 inhibitors was not unified; thus, the generalization of the
findings of the present study should be further validated.
In summary, MALT1 levels were decreased after PD-1
inhibitor treatment, and a high level estimated a poor therapeutic
response and unsatisfactory survival in patients with advanced
melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. Clinically, the
present study proposes that MALT1 may serve as a potential marker
to predict the prognosis of patients with advanced melanoma
receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. Notably, using 3.100 as a
threshold value for MALT1, and detecting it after 2 months of PD-1
inhibitor treatment yields a satisfactory predictive ability of
MALT1 for prognosis in patients with advanced melanoma. MALT1 level
detection may help physicians improve the management of patients
with advanced melanoma receiving PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy;
however, the prognostic role of MALT1 in patients with advanced
melanoma receiving other treatments, and whether 3.100 could serve
as the clinical normal level of MALT1, should be validated by
further large-scale studies.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Experimental Study on
Adipose Stem Cells Assisting Autologous Hair Transplantation of
Monomer Hair Follicles (grant no. 19422083011-9).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
YT conceived and designed the present study. XM
performed the experiments. KZ and JC collected and analyzed the
experimental data. JY, ZG and GM were responsible for the
interpretation of the data. YT and XM confirm the authenticity of
all the raw data. All authors have read and approved the final
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Engineering
University (Handan, China; approval no. 2018K037; February 17,
2018). The patients with advanced melanoma and healthy controls
provided written informed consent at the time of enrolment.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schadendorf D, van Akkooi ACJ, Berking C,
Griewank KG, Gutzmer R, Hauschild A, Stang A, Roesch A and Ugurel
S: Melanoma. Lancet. 392:971–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Teixido C, Castillo P, Martinez-Vila C,
Arance A and Alos L: Molecular markers and targets in melanoma.
Cells. 10:23202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shreberk-Hassidim R, Ostrowski SM and
Fisher DE: The complex interplay between nevi and melanoma: Risk
factors and precursors. Int J Mol Sci. 24:35412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Serman N, Vranic S, Glibo M, Serman L and
Bukvic Mokos Z: Genetic risk factors in melanoma etiopathogenesis
and the role of genetic counseling: A concise review. Bosn J Basic
Med Sci. 22:673–682. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raimondi S, Suppa M and Gandini S:
Melanoma epidemio-logy and sun exposure. Acta Derm Venereol.
100:adv001362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Majem M, Manzano JL, Marquez-Rodas I,
Mujika K, Muñoz-Couselo E, Pérez-Ruiz E, de la Cruz-Merino L,
Espinosa E, Gonzalez-Cao M and Berrocal A: SEOM clinical guideline
for the management of cutaneous melanoma (2020). Clin Transl Oncol.
23:948–960. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Villani A, Potestio L, Fabbrocini G,
Troncone G, Malapelle U and Scalvenzi M: The treatment of advanced
melanoma: Therapeutic update. Int J Mol Sci. 23:63882022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Curti BD and Faries MB: Recent advances in
the treatment of melanoma. N Engl J Med. 384:2229–2240. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Santamaria-Barria JA and Mammen JMV:
Surgical management of melanoma: Advances and updates. Curr Oncol
Rep. 24:1425–1432. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wollina U: Melanoma surgery-An update.
Dermatol Ther. 35:e159662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jenkins RW and Fisher DE: Treatment of
advanced melanoma in 2020 and beyond. J Invest Dermatol. 141:23–31.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang AC and Zappasodi R: A decade of
checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in melanoma: Understanding the
molecular basis for immune sensitivity and resistance. Nat Immunol.
23:660–670. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fujimura T, Muto Y and Asano Y:
Immunotherapy for melanoma: The significance of immune checkpoint
inhibitors for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Int J Mol Sci.
23:157202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sabbatino F, Liguori L, Pepe S and Ferrone
S: Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 22:563–576. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carlino MS, Larkin J and Long GV: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet. 398:1002–1014. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eddy K and Chen S: Overcoming immune
evasion in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:89842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brown LJ, da Silva IP, Moujaber T, Gao B,
Hui R, Gurney H, Carlino M and Nagrial A: Five-year survival and
clinical correlates among patients with advanced non-small cell
lung cancer, melanoma and renal cell carcinoma treated with immune
check-point inhibitors in Australian tertiary oncology centres.
Cancer Med. 12:6788–6801. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zaremba A, Eggermont AMM, Robert C, Dummer
R, Ugurel S, Livingstone E, Ascierto PA, Long GV, Schadendorf D and
Zimmer L: The concepts of rechallenge and retreatment with immune
checkpoint blockade in melanoma patients. Eur J Cancer.
155:268–280. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Neill TJ, Tofaute MJ and Krappmann D:
Function and targeting of MALT1 paracaspase in cancer. Cancer Treat
Rev. 117:1025682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang N, Ji F, Cheng L, Lu J, Sun X, Lin X
and Lan X: Knockout of immunotherapy prognostic marker genes
eliminates the effect of the anti-PD-1 treatment. NPJ Precis Oncol.
5:372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rosenbaum M, Gewies A, Pechloff K, Heuser
C, Engleitner T, Gehring T, Hartjes L, Krebs S, Krappmann D,
Kriegsmann M, et al: Bcl10-controlled Malt1 paracaspase activity is
key for the immune suppressive function of regulatory T cells. Nat
Commun. 10:23522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng L, Deng N, Yang N, Zhao X and Lin X:
Malt1 protease is critical in maintaining function of regulatory T
cells and may be a therapeutic target for antitumor immunity. J
Immunol. 202:3008–3019. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Azam F, Latif MF, Farooq A, Tirmazy SH,
AlShahrani S, Bashir S and Bukhari N: Performance status assessment
by using ECOG (eastern cooperative oncology group) score for cancer
patients by oncology healthcare professionals. Case Rep Oncol.
12:728–736. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu Q, Chu Y, Mi R, Jiang
F, Zhao J, Hu K, Luo R, Feng Y, et al: MALT1 regulates Th2 and Th17
differentiation via NF-κB and JNK pathways, as well as correlates
with disease activity and treatment outcome in rheumatoid
arthritis. Front Immunol. 13:9138302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Song C, Liu X, Lin W, Lai K, Pan S, Lu Z,
Li D, Li N and Geng Q: Systematic analysis of histone acetylation
regulators across human cancers. BMC Cancer. 23:7332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qian R, Niu X, Wang Y, Guo Z, Deng X, Ding
Z, Zhou M and Deng H: Targeting MALT1 suppresses the malignant
progression of colorectal cancer via miR-375/miR-365a-3p/NF-κB
axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8450482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kurden-Pekmezci A, Cakiroglu E, Eris S,
Mazi FA, Coskun-Deniz OS, Dalgic E, Oz O and Senturk S: MALT1
paracaspase is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and
promotes cancer cell survival and growth. Life Sci. 323:1216902023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsui KH, Chang KS, Sung HC, Hsu SY, Lin
YH, Hou CP, Yang PS, Chen CL, Feng TH and Juang HH:
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 is an oncogene inducing cell
proliferation, invasion, and tumor growth via the upregulation of
NF-κB activity in human prostate carcinoma cells. Biomedicines.
9:2502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li C, Yu F and Xu W: Early low blood MALT1
expression levels forecast better efficacy of PD-1 inhibitor-based
treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncol
Lett. 26:3292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Zhang G, Jin J, Degan S, Tameze Y
and Zhang JY: MALT1 promotes melanoma progression through JNK/c-Jun
signaling. Oncogenesis. 6:e3652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moreira RS, Bicker J, Musicco F,
Persichetti A and Pereira AMPT: Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in advanced
metastatic melanoma: State of the art and future challenges. Life
Sci. 240:1170932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luke JJ, Flaherty KT, Ribas A and Long GV:
Targeted agents and immunotherapies: Optimizing outcomes in
melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:463–482. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Di Pilato M, Kim EY, Cadilha BL, Prüßmann
JN, Nasrallah MN, Seruggia D, Usmani SM, Misale S, Zappulli V,
Carrizosa E, et al: Targeting the CBM complex causes
Treg cells to prime tumours for immune checkpoint
therapy. Nature. 570:112–116. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|