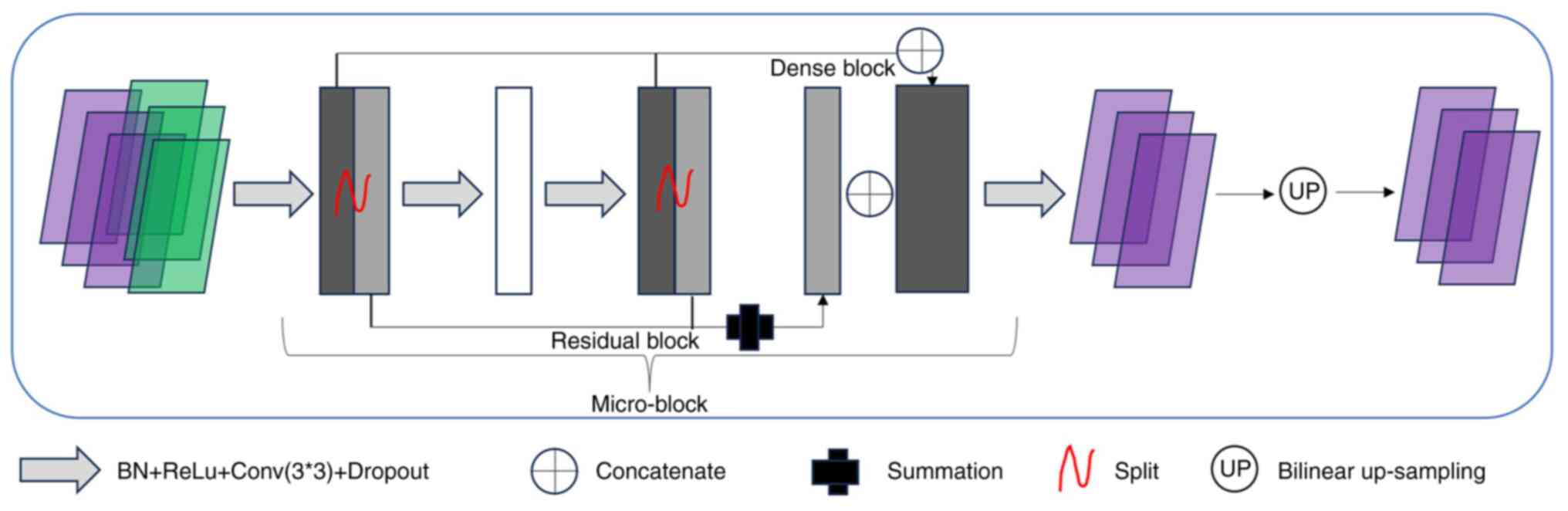
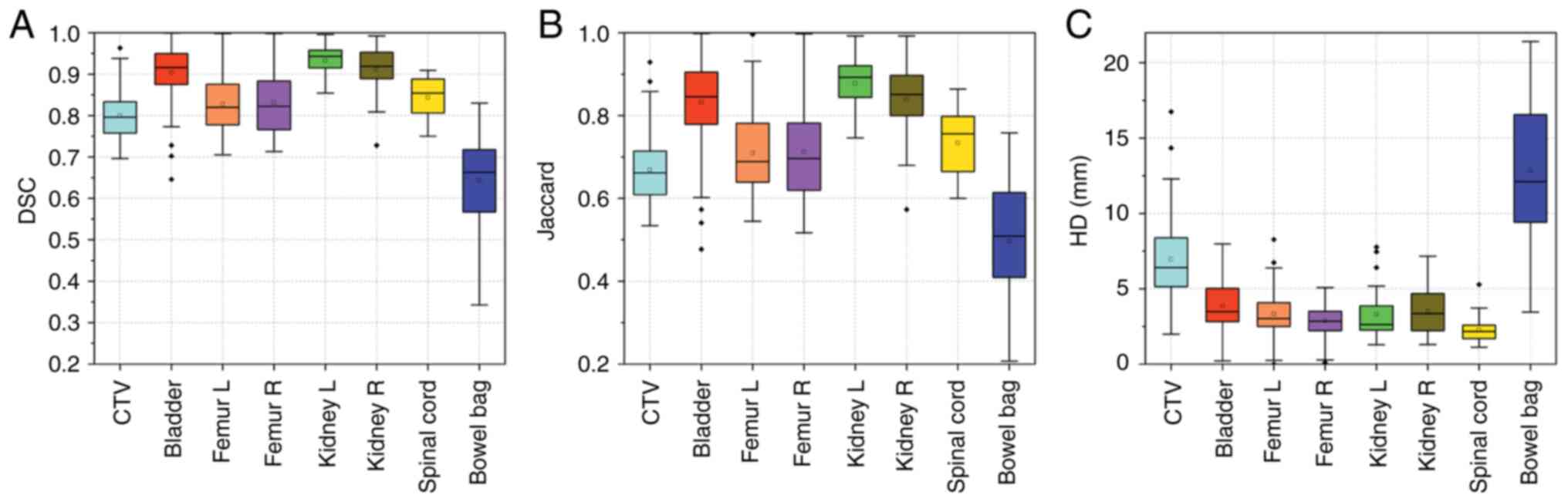
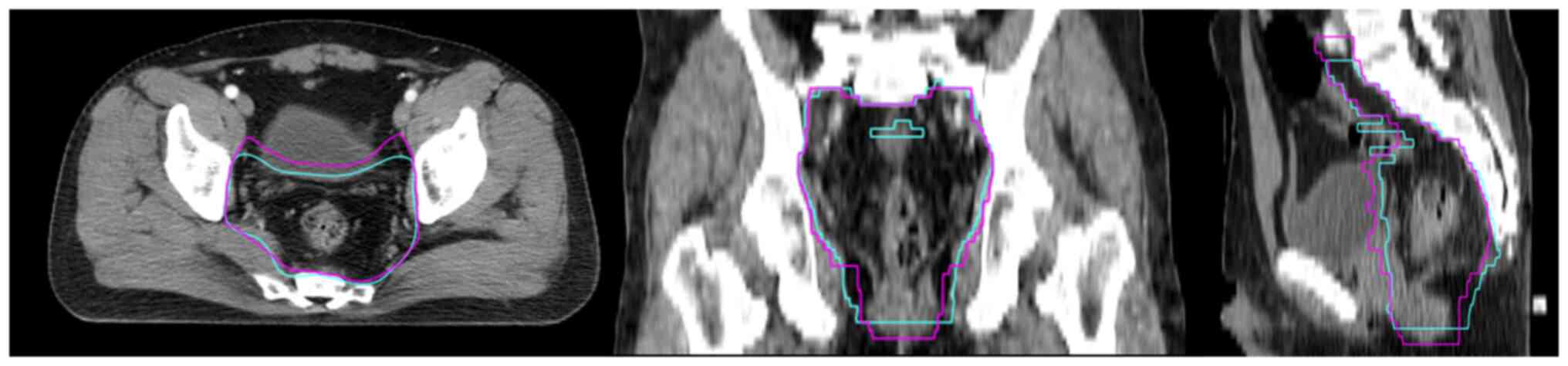
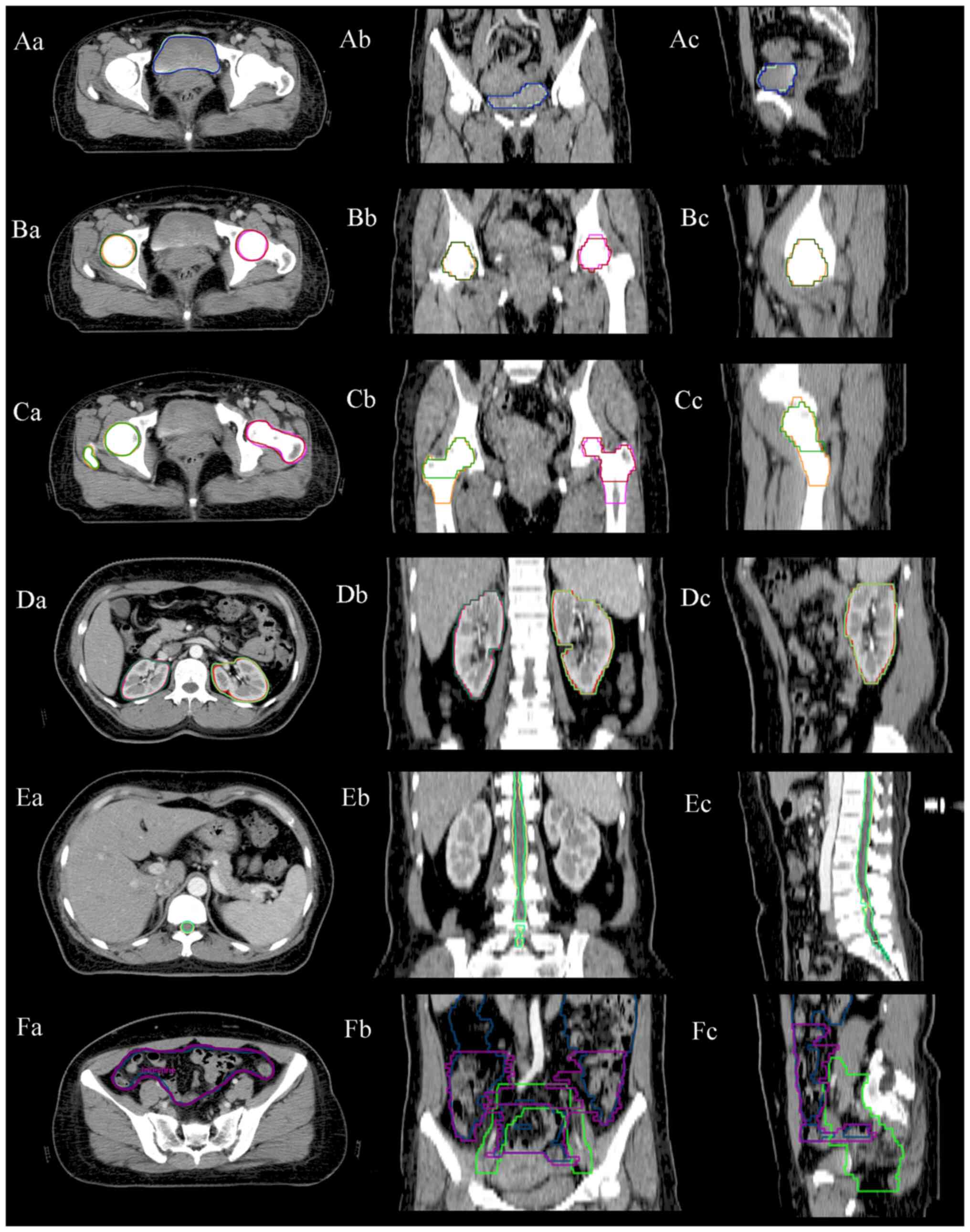
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N and Chen WQ:
Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A
secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J
(Engl). 134:783–791. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanna CR, Slevin F, Appelt A, Beavon M,
Adams R, Arthur C, Beasley M, Duffton A, Gilbert A, Gollins S, et
al: Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for rectal cancer in the UK in
2020. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 33:214–223. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen AM, Chin R, Beron P, Yoshizaki T,
Mikaeilian AG and Cao M: Inadequate target volume delineation and
local-regional recurrence after intensity-modulated radiotherapy
for human papillomavirus-positive oropharynx cancer. Radiother
Oncol. 123:412–418. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Walker GV, Awan M, Tao R, Koay EJ,
Boehling NS, Grant JD, Sittig DF, Gunn GB, Garden AS, Phan J, et
al: Prospective randomized double-blind study of atlas-based
organ-at-risk autosegmentation-assisted radiation planning in head
and neck cancer. Radiother Oncol. 112:321–325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rezaeijo SM, Jafarpoor Nesheli S, Fatan
Serj M and Tahmasebi Birgani MJ: Segmentation of the prostate, its
zones, anterior fibromuscular stroma, and urethra on the MRIs and
multimodality image fusion using U-Net model. Quant Imaging Med
Surg. 12:4786–4804. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Voet PWJ, Dirkx MLP, Teguh DN, Hoogeman
MS, Levendag PC and Heijmen BJM: Does atlas-based autosegmentation
of neck levels require subsequent manual contour editing to avoid
risk of severe target underdosage? A dosimetric analysis. Radiother
Oncol. 98:373–377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Daisne JF and Blumhofer A: Atlas-based
automatic segmentation of head and neck organs at risk and nodal
target volumes: A clinical validation. Radiat Oncol. 8:1542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma CY, Zhou JY, Xu XT, Guo J, Han MF, Gao
YZ, Du H, Stahl JN and Maltz JS: Deep learning-based
auto-segmentation of clinical target volumes for radiotherapy
treatment of cervical cancer. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 23:e134702022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marin T, Zhuo Y, Lahoud RM, Tian F, Ma X,
Xing F, Moteabbed M, Liu X, Grogg K, Shusharina N, et al: Deep
learning-based GTV contouring modeling inter- and intra-observer
variability in sarcomas. Radiother Oncol. 167:269–276. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Casati M, Piffer S, Calusi S, Marrazzo L,
Simontacchi G, Di Cataldo V, Greto D, Desideri I, Vernaleone M,
Francolini G, et al: Clinical validation of an automatic
atlas-based segmentation tool for male pelvis CT images. J Appl
Clin Med Phys. 23:e135072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vinod SK, Min M, Jameson MG and Holloway
LC: A review of interventions to reduce inter-observer variability
in volume delineation in radiation oncology. J Med Imaging Radiat
Oncol. 60:393–406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Chang Y, Peng Z, Lv Y, Shi W, Wang
F, Pei X and Xu XG: Evaluation of deep learning-based
auto-segmentation algorithms for delineating clinical target volume
and organs at risk involving data for 125 cervical cancer patients.
J Appl Clin Med Phys. 21:272–279. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Young AV, Wortham A, Wernick I, Evans A
and Ennis RD: Atlas-based segmentation improves consistency and
decreases time required for contouring postoperative endometrial
cancer nodal volumes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:943–947.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song Y, Hu J, Wu Q, Xu F, Nie S, Zhao Y,
Bai S and Yi Z: Automatic delineation of the clinical target volume
and organs at risk by deep learning for rectal cancer postoperative
radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 145:186–192. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen W, Wang C, Zhan W, Jia Y, Ruan F, Qiu
L, Yang S and Li Y: A comparative study of auto-contouring
softwares in delineation of organs at risk in lung cancer and
rectal cancer. Sci Rep. 11:230022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Piqeur F, Hupkens BJP, Nordkamp S, Witte
MG, Meijnen P, Ceha HM, Berbee M, Dieters M, Heyman S, Valdman A,
et al: Development of a consensus-based delineation guideline for
locally recurrent rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 177:214–221.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mackay K, Bernstein D, Glocker B,
Kamnitsas K and Taylor A: A review of the metrics used to assess
auto-contouring systems in radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll
Radiol). 35:354–369. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Y, Wu W, Sun Y, Yu D, Zhang Y, Wang L,
Wang Y, Zhang X and Lu Y: The clinical evaluation of atlas-based
auto-segmentation for automatic contouring during cervical cancer
radiotherapy. Front Oncol. 12:9450532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Men K, Dai J and Li Y: Automatic
segmentation of the clinical target volume and organs at risk in
the planning CT for rectal cancer using deep dilated convolutional
neural networks. Med Phys. 44:6377–6389. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ronneberger O, Fischer P and Brox T:
U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation:
Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI
2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5–9,
2015, Proceedings Part III. Springer International Publishing;
Cham: pp. 234–241. 2015
|
|
22
|
Shen G, Jin X, Sun C and Li Q: Artificial
intelligence radiotherapy planning: Automatic segmentation of human
organs in CT images based on a modified convolutional neural
network. Front Public Health. 10:8131352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luan S, Xue X, Ding Y, Wei W and Zhu B:
Adaptive attention convolutional neural network for liver tumor
segmentation. Front Oncol. 11:6808072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu Y, Kang K, Han C, Wang S, Chen Q, Chen
Y, Zhang F and Liu Z: A blind randomized validated convolutional
neural network for auto-segmentation of clinical target volume in
rectal cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant radiotherapy. Cancer
Med. 11:166–175. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Gardner SJ, Wen N, Elshaikh MA,
Siddiqui F, Movsas B and Chetty IJ: Automatic segmentation of the
prostate on CT images using deep neural networks (DNN). Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 104:924–932. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Z, Liu X, Xiao B, Wang S, Miao Z, Sun
Y and Zhang F: Segmentation of organs-at-risk in cervical cancer CT
images with a convolutional neural network. Phys Med. 69:184–191.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
To MNN, Vu DQ, Turkbey B, Choyke PL and
Kwak JT: Deep dense multi-path neural network for prostate
segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Comput Assist
Radiol Surg. 13:1687–1696. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Breto A, Zavala-Romero O, Asher D,
Baikovitz J, Ford J, Stoyanova R and Portelance L: A deep learning
pipeline for per-fraction automatic segmentation of GTV and OAR in
cervical cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 105 (Suppl
1):S2022019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bi N, Wang J, Zhang T, Chen X, Xia W, Miao
J, Xu K, Wu L, Fan Q, Wang L, et al: Deep learning improved
clinical target volume contouring quality and efficiency for
postoperative radiation therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Front Oncol. 9:11922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sha X, Wang H, Sha H, Xie L, Zhou Q, Zhang
W and Yin Y: Clinical target volume and organs at risk segmentation
for rectal cancer radiotherapy using the Flex U-Net network. Front
Oncol. 13:11724242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Song Y, Wu Y, Liang L, Li G and Bai
S: Clinical evaluation on automatic segmentation results of
convolutional neural networks in rectal cancer radiotherapy. Front
Oncol. 13:11583152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Li J, Xiao H, Jin X, Yan S and
Feng J: Dual path networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst.
30:2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Z, Liu X, Guan H, Zhen H, Sun Y, Chen
Q, Chen Y, Wang S and Qiu J: Development and validation of a deep
learning algorithm for auto-delineation of clinical target volume
and organs at risk in cervical cancer radiotherapy. Radiother
Oncol. 153:172–179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Liu F, Chen W, Liu X, Hou X, Shen
J, Guan H, Zhen H, Wang S, Chen Q, et al: Automatic segmentation of
clinical target volumes for post-modified radical mastectomy
radiotherapy using convolutional neural networks. Front Oncol.
10:5813472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Valentini V, Gambacorta MA, Barbaro B,
Chiloiro G, Coco C, Das P, Fanfani F, Joye I, Kachnic L, Maingon P,
et al: International consensus guidelines on clinical target volume
delineation in rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 120:195–201. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gay HA, Barthold HJ, O'Meara E, Bosch WR,
El Naqa I, Al-Lozi R, Rosenthal SA, Lawton C, Lee WR, Sandler H, et
al: Pelvic normal tissue contouring guidelines for radiation
therapy: A radiation therapy oncology group consensus panel atlas.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:e353–e362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yeghiazaryan V and Voiculescu I: Family of
boundary overlap metrics for the evaluation of medical image
segmentation. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 5:0150062018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Geets X, Daisne JF, Arcangeli S, Coche E,
De Poel M, Duprez T, Nardella G and Grégoire V: Inter-observer
variability in the delineation of pharyngo-laryngeal tumor and
parotid glands and cervical spinal cord: Comparison between CT-scan
and MRI. Radiother Oncol. 77:25–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brouwer CL, Steenbakkers RJHM, Bourhis J,
Budach W, Grau C, Grégoire V, Van Herk M, Lee A, Maingon P, Nutting
C, et al: CT-based delineation of organs at risk in the head and
neck region: DAHANCA, EORTC, GORTEC, HKNPCSG, NCIC CTG, NCRI, NRG
oncology and TROG consensus guidelines. Radiother Oncol. 117:83–90.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rhee DJ, Jhingran A, Rigaud B, Netherton
T, Cardenas CE, Zhang L, Vedam S, Kry S, Brock KK, Shaw W, et al:
Automatic contouring system for cervical cancer using convolutional
neural networks. Med Phys. 47:5648–5658. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zabihollahy F, Viswanathan AN, Schmidt EJ
and Lee J: Fully automated segmentation of clinical target volume
in cervical cancer from magnetic resonance imaging with
convolutional neural network. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 23:e137252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mohammadi R, Shokatian I, Salehi M, Arabi
H, Shiri I and Zaidi H: Deep learning-based auto-segmentation of
organs at risk in high-dose rate brachytherapy of cervical cancer.
Radiother Oncol. 159:231–240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ju Z, Guo W, Gu S, Zhou J, Yang W, Cong X,
Dai X, Quan H, Liu J, Qu B and Liu G: CT based automatic clinical
target volume delineation using a dense-fully connected convolution
network for cervical Cancer radiation therapy. BMC Cancer.
21:2432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chan JW, Kearney V, Haaf S, Wu S, Bogdanov
M, Reddick M, Dixit N, Sudhyadhom A, Chen J, Yom SS and Solberg TD:
A convolutional neural network algorithm for automatic segmentation
of head and neck organs at risk using deep lifelong learning. Med
Phys. 46:2204–2213. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ginn JS, Gay HA, Hilliard J, Shah J,
Mistry N, Möhler C, Hugo GD and Hao Y: A clinical and time savings
evaluation of a deep learning automatic contouring algorithm. Med
Dosim. 48:55–60. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Åström LM, Behrens CP, Calmels L, Sjöström
D, Geertsen P, Mouritsen LS, Serup-Hansen E, Lindberg H and Sibolt
P: Online adaptive radiotherapy of urinary bladder cancer with full
re-optimization to the anatomy of the day: Initial experience and
dosimetric benefits. Radiother Oncol. 171:37–42. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
D'Aviero A, Re A, Catucci F, Piccari D,
Votta C, Piro D, Piras A, Di Dio C, Iezzi M, Preziosi F, et al:
Clinical validation of a deep-learning segmentation software in
head neck: An early analysis in a developing radiation oncology
center. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 19:90572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lustberg T, van Soest J, Gooding M,
Peressutti D, Aljabar P, van der Stoep J, van Elmpt W and Dekker A:
Clinical evaluation of atlas and deep learning based automatic
contouring for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 126:312–317. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu Y, Nguyen H, Smith C, Chen T, Byrne M,
Archibald-Heeren B, Rijken J and Aland T: Clinical assessment of a
novel machine-learning automated contouring tool for radiotherapy
planning. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 24:e139492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|