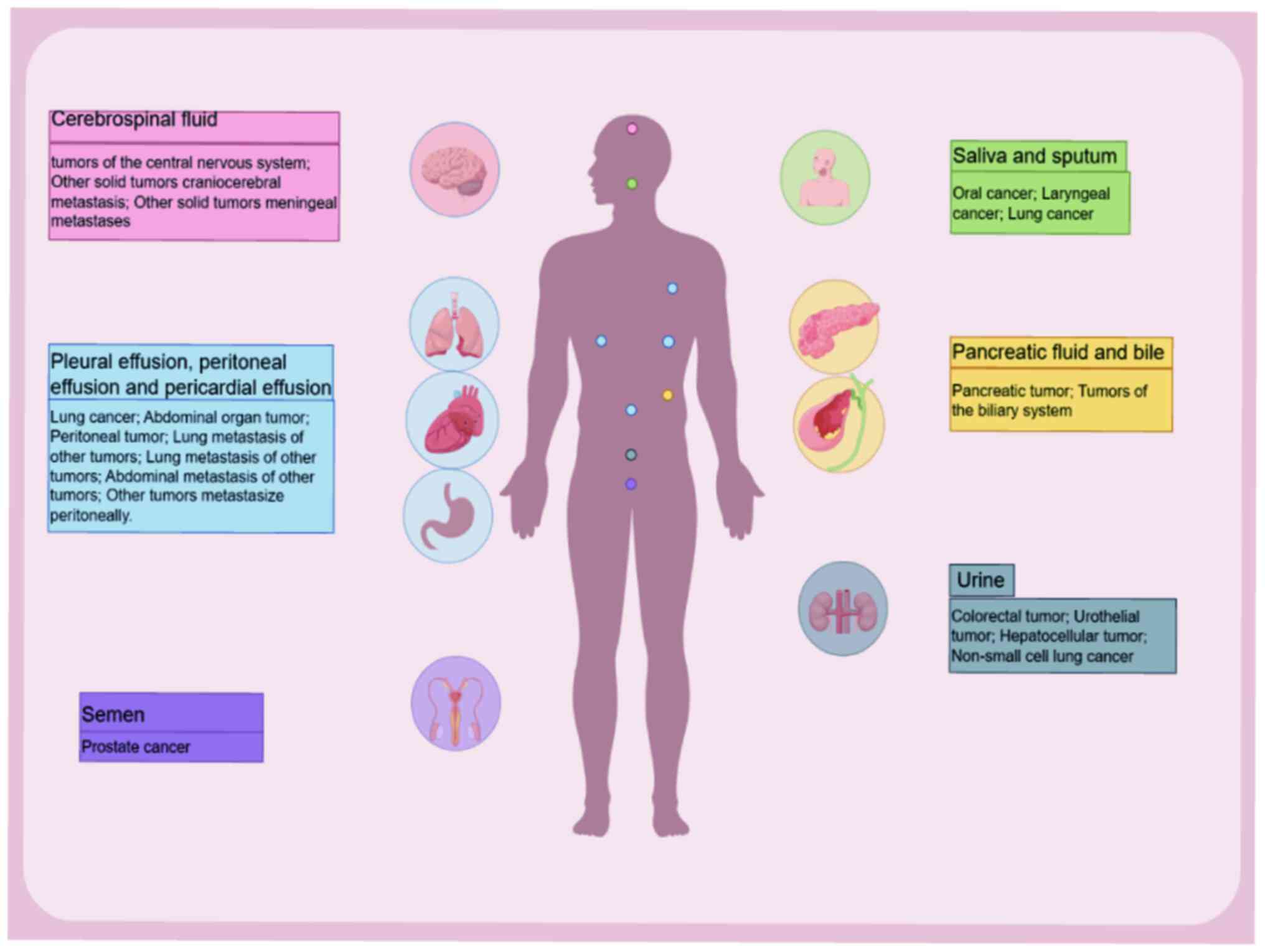
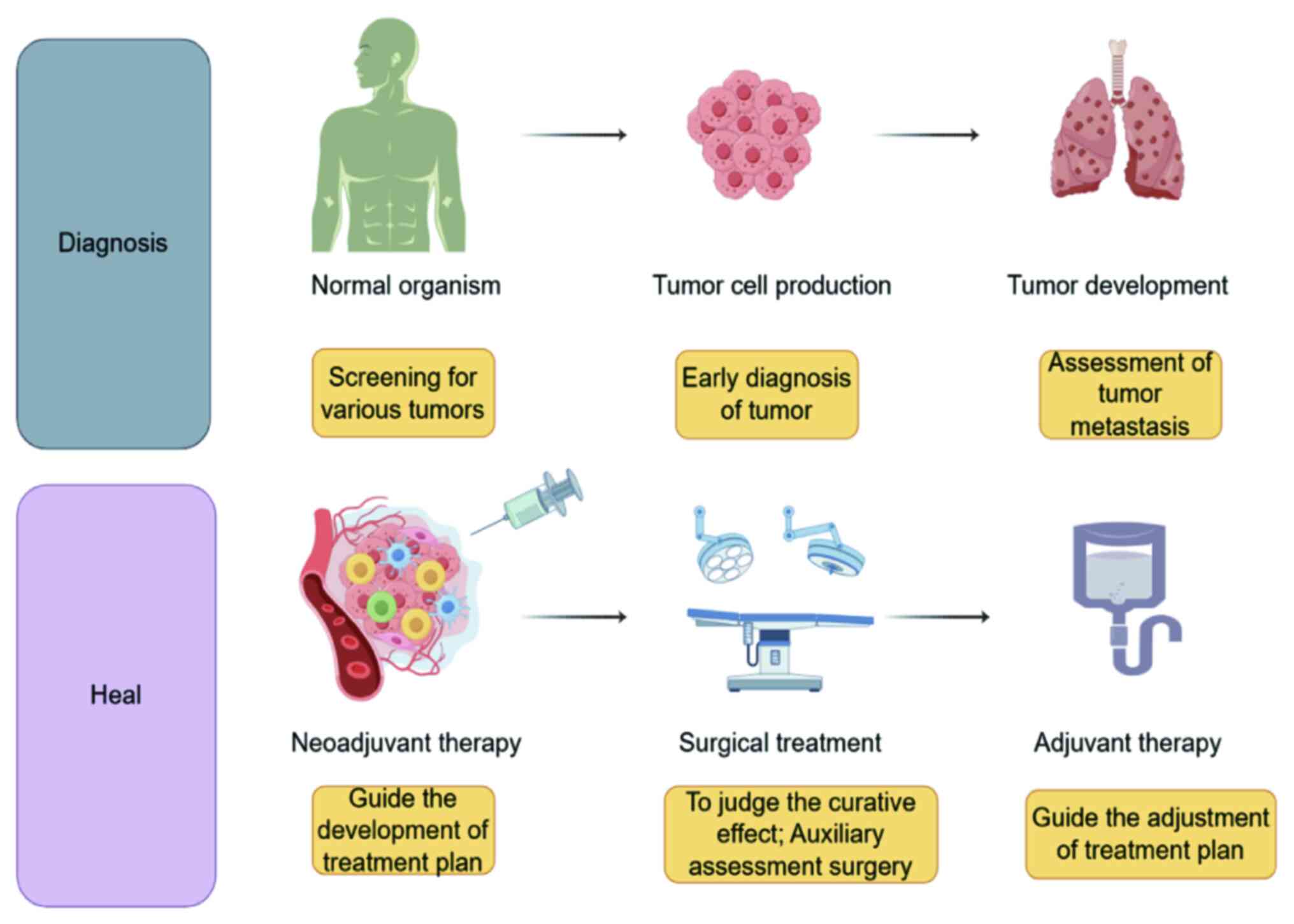
|
1
|
Schoop R, Roode LM, de Boer LL and
Dashtbozorg B: Framework for deep learning based Multi-Modality
image registration of snapshot and pathology images. IEEE J Biomed
Health Inform. Aug 16–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pritzker K and Nieminen HJ: Needle biopsy
adequacy in the era of precision medicine and value-based health
care. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 143:1399–1415. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nikanjam M, Kato S and Kurzrock R: Liquid
biopsy: Current technology and clinical applications. J Hematol
Oncol. 15:1312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tivey A, Church M, Rothwell D, Dive C and
Cook N: Circulating tumour DNA-looking beyond the blood. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 19:600–612. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alix-Panabieres C and Pantel K: Liquid
biopsy: From discovery to clinical application. Cancer Discov.
11:858–873. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen SA, Liu MC and Aleshin A: Practical
recommendations for using ctDNA in clinical decision making.
Nature. 619:259–268. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mandel P and Metais P: Nuclear acids in
human blood plasma. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 142:241–243. 1948.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hobbs KJ, Cooper BL, Dembek K and Sheats
MK: Investigation of extracted plasma cell-free DNA as a biomarker
in foals with sepsis. Vet Sci. 11:3462024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang LX, Jiang YZ, Qiu LJ and Huang DP:
Quantitative detection and integrality analysis of plasma
circulating Cell-free DNA in multiple myeloma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 32:1106–1111. 2024.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joshi J, Raval A, Desai U, Upadhyay V,
Bhavsar M, Shah K, Rawal R, Panchal H and Shah F: EGFR mutation
analysis in Non-small cell lung carcinoma patients: A liquid biopsy
approach. Indian J Clin Biochem. 36:51–58. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Volik S, Alcaide M, Morin RD and Collins
C: Cell-free DNA (cfDNA): Clinical significance and utility in
cancer shaped by emerging technologies. Mol Cancer Res. 14:898–908.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan EM, Schur PH, Carr RI and Kunkel HG:
Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest.
45:1732–1740. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koffler D, Agnello V, Winchester R and
Kunkel HG: The occurrence of single-stranded DNA in the serum of
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. J
Clin Invest. 52:198–204. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giacona MB, Ruben GC, Iczkowski KA, Roos
TB, Porter DM and Sorenson GD: Cell-free DNA in human blood plasma:
Length measurements in patients with pancreatic cancer and healthy
controls. Pancreas. 17:89–97. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Szilagyi M, Pos O, Marton E, Buglyo G,
Soltesz B, Keseru J, Penyige A, Szemes T and Nagy B: Circulating
cell-free nucleic acids: Main characteristics and clinical
application. Int J Mol Sci. 21:68272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biro O, Fothi A, Alasztics B, Nagy B,
Orban TI and Rigo JJ: Circulating exosomal and Argonaute-bound
microRNAs in preeclampsia. Gene. 692:138–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fernando MR, Jiang C, Krzyzanowski GD and
Ryan WL: New evidence that a large proportion of human blood plasma
cell-free DNA is localized in exosomes. PLoS One. 12:e01839152017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aucamp J, Bronkhorst AJ, Badenhorst C and
Pretorius PJ: The diverse origins of circulating cell-free DNA in
the human body: A critical re-evaluation of the literature. Biol
Rev Camb Philos Soc. 93:1649–1683. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moss J, Magenheim J, Neiman D, Zemmour H,
Loyfer N, Korach A, Samet Y, Maoz M, Druid H, Arner P, et al:
Comprehensive human cell-type methylation atlas reveals origins of
circulating cell-free DNA in health and disease. Nat Commun.
9:50682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Teo YV, Capri M, Morsiani C, Pizza G,
Faria A, Franceschi C and Neretti N: Cell-free DNA as a biomarker
of aging. Aging Cell. 18:e128902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hummel EM, Hessas E, Muller S, Beiter T,
Fisch M, Eibl A, Wolf OT, Giebel B, Platen P, Kumsta R and Moser
DA: Cell-free DNA release under psychosocial and physical stress
conditions. Transl Psychiatry. 8:2362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ai B, Liu H, Huang Y and Peng P:
Circulating cell-free DNA as a prognostic and predictive biomarker
in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:44583–44595. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim DY, Cho EH, Kim JS, Chie EK and Kang
HC: Plasma Circulating Cell-free DNa in advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma patients treated with radiation therapy. In Vivo.
37:2306–2313. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gianni C, Palleschi M, Merloni F, Di Menna
G, Sirico M, Sarti S, Virga A, Ulivi P, Cecconetto L, Mariotti M
and De Giorgi U: Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomics: A promising biomarker
for diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of response in breast
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 23:141972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Al SN, Messaoudi SA, Babu SR, Chaudhary
AB, Alsharm AA, Alrefaei AF, Kadasah S, Abu-Elmagd M, Assidi M,
Buhmeida A, et al: Utility of circulating Cell-free DNA in
assessing microsatellite instability and loss of Heterozygosity in
breast cancer using human identification approach. Genes (Basel).
13:5902022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bahado-Singh RO, Turkoglu O, Aydas B and
Vishweswaraiah S: Precision oncology: Artificial intelligence,
circulating cell-free DNA, and the minimally invasive detection of
pancreatic cancer-A pilot study. Cancer Med. 12:19644–19655. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin LH, Chang KW, Kao SY, Cheng HW and Liu
CJ: Increased plasma circulating Cell-Free DNA could be a potential
marker for oral cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:33032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang Q, Yuan Z, Hu H, Zhang W, Wang G and
Wang X: Genome-wide discovery of circulating cell-free DNA
methylation biomarkers for colorectal cancer detection. Clin
Epigenetics. 15:1192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eskander NS, Mansour L, Abdelaal A, Saad E
and Mohamed D: Circulating cell free DNA integrity index as a
biomarker for response to chemotherapy in patients with metastatic
colorectal carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 23:339–348. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Heidrich I and Pantel K: Liquid biopsy:
Blood-based analyses of circulating cell-free DNA in xenografts.
EMBO Mol Med. 14:e163262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kroeze A, Cornelissen AS, Pascutti MF,
Verheij M, Bulder I, Klarenbeek S, Ait SA, Hazenberg MD, Nur E, van
der Schoot CE, et al: Cell-free DNA levels are increased in acute
graft-versus-host disease. Eur J Haematol. 109:271–281. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kustanovich A, Schwartz R, Peretz T and
Grinshpun A: Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer
Biol Ther. 20:1057–1067. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stewart CM and Tsui D: Circulating
cell-free DNA for non-invasive cancer management. Cancer Genet.
228–229. 169–179. 2018.
|
|
34
|
Yu SC, Lee SW, Jiang P, Leung TY, Chan KC,
Chiu RW and Lo YM: High-resolution profiling of fetal DNA clearance
from maternal plasma by massively parallel sequencing. Clin Chem.
59:1228–1237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Butler TM, Spellman PT and Gray J:
Circulating-tumor DNA as an early detection and diagnostic tool.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 42:14–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jahr S, Hentze H, Englisch S, Hardt D,
Fackelmayer FO, Hesch RD and Knippers R: DNA fragments in the blood
plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their
origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 61:1659–1665.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miller AM and Karajannis MA: Current role
and future potential of CSF ctDNA for the diagnosis and clinical
management of pediatric central nervous system tumors. J Natl Compr
Canc Netw. 20:1363–1369. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diehl F, Schmidt K, Choti MA, Romans K,
Goodman S, Li M, Thornton K, Agrawal N, Sokoll L, Szabo SA, et al:
Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat Med.
14:985–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han JY, Ahn KS, Kim TS, Kim YH, Cho KB,
Shin DW, Baek WK, Suh SI, Jang BC and Kang KJ: Liquid biopsy from
Bile-Circulating tumor DNA in patients with biliary tract cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 13:45812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I,
Wang Y, Agrawal N, Bartlett BR, Wang H, Luber B, Alani RM, et al:
Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human
malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 6:224ra242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Diehl F, Li M, Dressman D, He Y, Shen D,
Szabo S, Diaz LJ, Goodman SN, David KA, Juhl H, et al: Detection
and quantification of mutations in the plasma of patients with
colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:16368–16373. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Murtaza M, Biggs H,
Rueda OM, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Gale D, Forshew T, Mahler-Araujo B,
et al: Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:1199–1209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sato S, Nakamura Y, Oki E and Yoshino T:
Molecular residual Disease-guided adjuvant treatment in resected
colorectal cancer: Focus on CIRCULATE-Japan. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 22:53–58. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yi K, Wang X, Filippov SK and Zhang H:
Emerging ctDNA detection strategies in clinical cancer
theranostics. Smart Med. 2:e202300312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheng F, Su L and Qian C: Circulating
tumor DNA: A promising biomarker in the liquid biopsy of cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:48832–48841. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee TH, Montalvo L, Chrebtow V and Busch
MP: Quantitation of genomic DNA in plasma and serum samples: Higher
concentrations of genomic DNA found in serum than in plasma.
Transfusion. 41:276–282. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Heger JM, Mattlener J, Schneider J, Godel
P, Sieg N, Ullrich F, Lewis RI, Bucaciuc-Mracica T, Schwarz RF,
Ruess D, et al: Entirely noninvasive outcome prediction in central
nervous system lymphomas using circulating tumor DNA. Blood.
143:522–534. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Werner B, Warton K and Ford CE:
Transcending Blood-Opportunities for alternate liquid biopsies in
oncology. Cancers (Basel). 14:13092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Seyhan AA: Circulating liquid biopsy
biomarkers in glioblastoma: Advances and challenges. Int J Mol Sci.
25:79742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zheng MM, Li YS, Jiang BY, Tu HY, Tang WF,
Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Ye JY, Yan HH, Su J, et al: Clinical utility of
cerebrospinal fluid Cell-Free DNA as liquid biopsy for
leptomeningeal metastases in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
14:924–932. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu J, Liu Z, Huang T, Wang Y, Song MM,
Song T, Long G, Zhang X, Li X and Zhang L: Cerebrospinal fluid
circulating tumor DNA depicts profiling of brain metastasis in
NSCLC. Mol Oncol. 17:810–824. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
De Mattos-Arruda L, Mayor R, Ng C, Weigelt
B, Martinez-Ricarte F, Torrejon D, Oliveira M, Arias A, Raventos C,
Tang J, et al: Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumour DNA
better represents the genomic alterations of brain tumours than
plasma. Nat Commun. 6:88392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Luo N, Gao Y, Wu Y, Qin X, Qi Y,
Sun T, Tao R, Qi C, Liu B and Yuan S: The joint detection of CEA
and ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid: An auxiliary tool for the
diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastases in cancer. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 149:1679–1690. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bai Y, Yu Q, Liu N, Liu J, Wang D, Liu X
and Yuan S: Case report: Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating
tumor DNA diagnoses and guides the treatment of a lung
adenocarcinoma case with leptomeningeal metastasis. Front Oncol.
12:9449632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
van der Wel J, Boelens MC, Jebbink M,
Smulders SA, Maas KW, Luitse M, Compter A, Boltjes R, Sol N,
Monkhorst K, et al: Osimertinib-induced DNA resistance mutations in
cerebrospinal fluid of EGFR mutated NSCLC patients developing
leptomeningeal metastases: ORA-LM study. Neuro Oncol. Aug
7–2024.doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noae138 (Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Azad TD, Nanjo S, Jin MC, Chabon JJ, Kurtz
DM, Chaudhuri AA, Connolly ID, Hui AB, Liu CL, Merriott D, et al:
Quantification of cerebrospinal fluid tumor DNA in lung cancer
patients with suspected leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. NPJ Precis
Oncol. 8:1212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Valerius AR, Webb MJ, Hammad N, Sener U
and Malani R: Cerebrospinal fluid liquid biopsies in the evaluation
of adult gliomas. Curr Oncol Rep. 26:377–390. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dai L, Liu Z, Zhu Y and Ma L: Genome-wide
methylation analysis of circulating tumor DNA: A new biomarker for
recurrent glioblastom. Heliyon. 9:e143392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kojic M, Maybury MK, Waddell N,
Koufariotis LT, Addala V, Millar A, Wood S, Pearson JV, Hansford
JR, Hassall T, et al: Efficient detection and monitoring of
pediatric brain malignancies with liquid biopsy based on
patient-specific somatic mutation screening. Neuro Oncol.
25:1507–1517. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Izquierdo E, Proszek P, Pericoli G,
Temelso S, Clarke M, Carvalho DM, Mackay A, Marshall LV, Carceller
F, Hargrave D, et al: Droplet digital PCR-based detection of
circulating tumor DNA from pediatric high grade and diffuse midline
glioma patients. Neurooncol Adv. 3:vdab0132021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li J, Zhao S, Lee M, Yin Y, Li J, Zhou Y,
Ballester LY, Esquenazi Y, Dashwood RH, Davies P, et al: Reliable
tumor detection by whole-genome methylation sequencing of cell-free
DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of pediatric medulloblastoma. Sci Adv.
6:eabb54272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pages M, Rotem D, Gydush G, Reed S,
Rhoades J, Ha G, Lo C, Fleharty M, Duran M, Jones R, et al: Liquid
biopsy detection of genomic alterations in pediatric brain tumors
from cell-free DNA in peripheral blood, CSF, and urine. Neuro
Oncol. 24:1352–1363. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ding S and Song X, Geng X, Liu L, Ma H,
Wang X, Wei L, Xie L and Song X: Saliva-derived cfDNA is applicable
for EGFR mutation detection but not for quantitation analysis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 10:1973–1983. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang Z, Zhang L, Li L, Li X, Xu Y, Wang M,
Liang L, Jiao P, Li Y, He S, et al: Sputum Cell-Free DNA: Valued
surrogate sample for detection of EGFR mutation in patients with
advanced lung adenocarcinoma. J Mol Diagn. 22:934–942. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang Z, Li X, Zhang L, Xu Y, Wang M, Liang
L, Jiao P, Li Y, He S, Du J, et al: Sputum cell-free DNA: Valued
surrogate sample for the detection of EGFR exon 20 p.T790M mutation
in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma and acquired
resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Cancer Med. 10:3323–3331. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ferrier ST, Tsering T, Sadeghi N, Zeitouni
A and Burnier JV: Blood and saliva-derived ctDNA is a marker of
residual disease after treatment and correlates with recurrence in
human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer. Cancer Med.
12:15777–15787. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Britze TE, Jakobsen KK, Gronhoj C and von
Buchwald C: A systematic review on the role of biomarkers in liquid
biopsies and saliva samples in the monitoring of salivary gland
cancer. Acta Otolaryngol. 143:709–713. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gupta S, Singh B, Abhishek R, Gupta S and
Sachan M: The emerging role of liquid biopsy in oral squamous cell
carcinoma detection: Advantages and challenges. Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 24:311–331. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Perrone ME, Alvarez R, Vo TT, Chung MW,
Chhieng DC, Paulson VA, Colbert BG, Q Konnick E and Huang EC:
Validating cell-free DNA from supernatant for molecular diagnostics
on cytology specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 129:956–965. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang SR, Mooney KL, Libiran P, Jones CD,
Joshi R, Lau HD, Stehr H, Berry GJ, Zehnder JL, Long SR, et al:
Targeted deep sequencing of cell-free DNA in serous body cavity
fluids with malignant, suspicious, and benign cytology. Cancer
Cytopathol. 128:43–56. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Leick KM, Kazarian AG, Rajput M,
Tomanek-Chalkley A, Miller A, Shrader HR, Mccarthy A, Coleman KL,
Kasi PM and Chan C: Peritoneal Cell-free tumor DNA as biomarker for
peritoneal surface malignancies. Ann Surg Oncol. 27:5065–5071.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kinugasa H, Nouso K, Ako S, Dohi C,
Matsushita H, Matsumoto K, Kato H and Okada H: Liquid biopsy of
bile for the molecular diagnosis of gallbladder cancer. Cancer Biol
Ther. 19:934–938. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Takai E, Totoki Y, Nakamura H, Morizane C,
Nara S, Hama N, Suzuki M, Furukawa E, Kato M, Hayashi H, et al:
Clinical utility of circulating tumor DNA for molecular assessment
in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 5:184252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Levink I, Jansen M, Azmani Z, van Ijcken
W, van Marion R, Peppelenbosch MP, Cahen DL, Fuhler GM and Bruno
MJ: Mutation analysis of pancreatic juice and plasma for the
detection of pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:131162023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Fitzgerald JM, Ramchurren N, Rieger K,
Levesque P, Silverman M, Libertino JA and Summerhayes IC:
Identification of H-ras mutations in urine sediments complements
cytology in the detection of bladder tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst.
87:129–133. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jain S, Lin SY, Song W and Su YH:
Urine-based liquid biopsy for nonurological cancers. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 23:277–283. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Su YH, Wang M, Block TM, Landt O, Botezatu
I, Serdyuk O, Lichtenstein A, Melkonyan H, Tomei LD and Umansky S:
Transrenal DNA as a diagnostic tool: Important technical notes. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 1022:81–89. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Su YH, Wang M, Brenner DE, Norton PA and
Block TM: Detection of mutated K-ras DNA in urine, plasma, and
serum of patients with colorectal carcinoma or adenomatous polyps.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1137:197–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xiao Y, Ju L, Qian K, Jin W, Wang G, Zhao
Y, Jiang W, Liu N, Wu K, Peng M, et al: Non-invasive diagnosis and
surveillance of bladder cancer with driver and passenger DNA
methylation in a prospective cohort study. Clin Transl Med.
12:e10082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Christensen E, Nordentoft I,
Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Elbaek SK, Lindskrog SV, Taber A, Andreasen
TG, Strandgaard T, Knudsen M, Lamy P, et al: Cell-Free urine and
plasma DNA mutational analysis predicts neoadjuvant chemotherapy
response and outcome in patients with muscle-invasive bladder
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 29:1582–1591. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Tamura D, Abe M, Hiraki H, Sasaki N,
Yashima-Abo A, Ikarashi D, Kato R, Kato Y, Maekawa S, Kanehira M,
et al: Postoperative recurrence detection using individualized
circulating tumor DNA in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Cancer
Sci. 115:529–539. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kim AK, Hamilton JP, Lin SY, Chang TT,
Hann HW, Hu CT, Lou Y, Lin YJ, Gade TP, Park G, et al: Urine DNA
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma screening. Br J Cancer.
126:1432–1438. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Adrogue HJ and Madias NE: Assessing
Acid-base status: Physiologic versus physicochemical approach. Am J
Kidney Dis. 68:793–802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Dermody SM, Bhambhani C, Swiecicki PL,
Brenner JC and Tewari M: Trans-renal cell-free tumor DNA for
Urine-based liquid biopsy of cancer. Front Genet. 13:8791082022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Alahdal M, Perera RA, Moschovas MC, Patel
V and Perera RJ: Current advances of liquid biopsies in prostate
cancer: Molecular biomarkers. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 30:27–38. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fonseca NM, Maurice-Dror C, Herberts C, Tu
W, Fan W, Murtha AJ, Kollmannsberger C, Kwan EM, Parekh K, Schonlau
E, et al: Prediction of plasma ctDNA fraction and prognostic
implications of liquid biopsy in advanced prostate cancer. Nat
Commun. 15:18282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tolmeijer SH, Boerrigter E, Van Erp NP and
Mehra N: Using early on-treatment circulating tumor DNA
measurements as response assessment in metastatic castration
resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 15:421–423. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ponti G, Maccaferri M, Manfredini M,
Micali S, Torricelli F, Milandri R, Del PC, Ciarrocchi A, Ruini C,
Benassi L, et al: Quick assessment of cell-free DNA in seminal
fluid and fragment size for early non-invasive prostate cancer
diagnosis. Clin Chim Acta. 497:76–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ponti G, Maccaferri M, Percesepe A, Tomasi
A and Ozben T: Liquid biopsy with cell free DNA: New horizons for
prostate cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 58:60–76. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yu B and Ma W: Biomarker discovery in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for personalized treatment and
enhanced prognosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. Aug 24–2024.doi:
10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.08.006 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhu L, Xu R, Yang L, Shi W, Zhang Y, Liu
J, Li X, Zhou J and Bing P: Minimal residual disease (MRD)
detection in solid tumors using circulating tumor DNA: A systematic
review. Front Genet. 14:11721082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li S, Li H, Li X, Zhu M, Li H and Xia F:
Hybridization Chain Reaction-amplified electrochemical DNA-based
sensors enable calibration-free measurements of nucleic acids
directly in whole blood. Anal Chem. 93:8354–8361. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ho HY, Chung KK, Kan CM and Wong SC:
Liquid biopsy in the clinical management of cancers. Int J Mol Sci.
25:85942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Phallen J, Sausen M, Adleff V, Leal A,
Hruban C, White J, Anagnostou V, Fiksel J, Cristiano S, Papp E, et
al: Direct detection of early-stage cancers using circulating tumor
DNA. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaan24152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bittla P, Kaur S, Sojitra V, Zahra A,
Hutchinson J, Folawemi O and Khan S: Exploring Circulating tumor
DNA (CtDNA) and its role in early detection of cancer: A systematic
review. Cureus. 15:e457842023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty
SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M, Breakefield XO and Skog JK:
Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and
challenges. Ann Oncol. 32:466–477. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kemper M, Krekeler C, Menck K, Lenz G,
Evers G, Schulze AB and Bleckmann A: Liquid Biopsies in Lung
Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:14302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lin C, Liu X, Zheng B, Ke R and Tzeng CM:
Liquid biopsy, ctDNA diagnosis through NGS. Life (Basel).
11:8902021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Fernandes M, Cruz-Martins N, Souto MC,
Guimaraes S, Pereira RJ, Justino A, Pina MJ, Magalhaes A, Queiroga
H, Machado JC, et al: Clinical application of Next-generation
sequencing of plasma Cell-free DNA for genotyping untreated
advanced Non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:27072021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Roberto TM, Jorge MA, Francisco GV, Noelia
T, Pilar RG and Andres C: Strategies for improving detection of
circulating tumor DNA using next generation sequencing. Cancer
Treat Rev. 119:1025952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Grada A and Weinbrecht K: Next-generation
sequencing: Methodology and application. J Invest Dermatol.
133:e112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Cheng ML, Pectasides E, Hanna GJ, Parsons
HA, Choudhury AD and Oxnard GR: Circulating tumor DNA in advanced
solid tumors: Clinical relevance and future directions. CA Cancer J
Clin. 71:176–190. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ma M, Zhu H, Zhang C, Sun X, Gao X and
Chen G: ‘Liquid biopsy’-ctDNA detection with great potential and
challenges. Ann Transl Med. 3:2352015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Gale D, Lawson A, Howarth K, Madi M,
Durham B, Smalley S, Calaway J, Blais S, Jones G, Clark J, et al:
Development of a highly sensitive liquid biopsy platform to detect
clinically-relevant cancer mutations at low allele fractions in
cell-free DNA. PLoS One. 13:e01946302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Forshew T, Murtaza M, Parkinson C, Gale D,
Tsui DW, Kaper F, Dawson SJ, Piskorz AM, Jimenez-Linan M, Bentley
D, et al: Noninvasive identification and monitoring of cancer
mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA. Sci Transl
Med. 4:136ra682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Cabalag CS, Yates M, Corrales MB, Yeh P,
Wong SQ, Zhang BZ, Fujihara KM, Chong L, Hii MW, Dawson SJ, et al:
Potential clinical utility of a targeted circulating tumor DNA
Assay in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 276:e120–e126. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Newman AM, Bratman SV, To J, Wynne JF,
Eclov NC, Modlin LA, Liu CL, Neal JW, Wakelee HA, Merritt RE, et
al: An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA
with broad patient coverage. Nat Med. 20:548–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Azad TD, Chaudhuri AA, Fang P, Qiao Y,
Esfahani MS, Chabon JJ, Hamilton EG, Yang YD, Lovejoy A, Newman AM,
et al: Circulating tumor DNA analysis for detection of minimal
residual disease after chemoradiotherapy for localized esophageal
cancer. Gastroenterology. 158:494–505. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Noguchi T, Sakai K, Iwahashi N, Matsuda K,
Matsukawa H, Yahata T, Toujima S, Nishio K and Ino K: Changes in
the gene mutation profiles of circulating tumor DNA detected using
CAPP-Seq in neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated advanced ovarian
cancer. Oncol Lett. 19:2713–2720. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Jung D, Jain P, Yao Y and Wang M: Advances
in the assessment of minimal residual disease in mantle cell
lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Satyal U, Srivastava A and Abbosh PH:
Urine biopsy-liquid gold for molecular detection and surveillance
of bladder cancer. Front Oncol. 9:12662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Taylor K, Zou J, Magalhaes M, Oliva M,
Spreafico A, Hansen AR, Mcdade SS, Coyle VM, Lawler M, Elimova E,
et al: Circulating tumour DNA kinetics in recurrent/metastatic head
and neck squamous cell cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 188:29–38.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Aoude LG, Brosda S, Ng J, Lonie JM, Belle
CJ, Patel K, Koufariotis LT, Wood S, Atkinson V, Smithers BM, et
al: Circulating tumor DNA: A promising biomarker for predicting
recurrence in patients with BRAF-Negative melanoma. J Mol Diagn.
25:771–781. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Grassi T, Harris FR, Smadbeck JB, Murphy
SJ, Block MS, Multinu F, Schaefer KJ, Zhang P, Karagouga G, Liu MC,
et al: Personalized tumor-specific DNA junctions to detect
circulating tumor in patients with endometrial cancer. PLoS One.
16:e02523902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Mansson CT, Vad-Nielsen J, Meldgaard P,
Nielsen AL and Sorensen BS: EGFR transcription in non-small-cell
lung cancer tumours can be revealed in ctDNA by cell-free chromatin
immunoprecipitation (cfChIP). Mol Oncol. 15:2868–2876. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jafri H, Mushtaq S, Baig S, Bhatty A and
Siraj S: Comparison of KRAS gene in circulating tumor DNA levels vs
histological grading of colorectal cancer patients through liquid
biopsy. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 29:371–375. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
FDA, . Summary of Safety and Effectiveness
Data (SSED) P150047. Cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2®.
2016.
|
|
118
|
Biglari N, Soltani-Zangbar MS, Mohammadian
J, Mehdizadeh A and Abbasi K: ctDNA as a novel and promising
approach for cancer diagnosis: A focus on hepatocellular carcinoma.
EXCLI J. 22:752–780. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Hickman RA, Miller AM and Arcila ME:
Cerebrospinal fluid: A unique source of circulating tumor DNA with
broad clinical applications. Transl Oncol. 33:1016882023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Rimelen V, Ahle G, Pencreach E, Zinniger
N, Debliquis A, Zalmai L, Harzallah I, Hurstel R, Alamome I, Lamy
F, et al: Tumor cell-free DNA detection in CSF for primary CNS
lymphoma diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 7:432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Venetis K, Pepe F, Pescia C, Cursano G,
Criscitiello C, Frascarelli C, Mane E, Russo G, Taurelli SB,
Troncone G, et al: ESR1 mutations in HR+/HER2-metastatic breast
cancer: Enhancing the accuracy of ctDNA testing. Cancer Treat Rev.
121:1026422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Teh SY, Lin R, Hung LH and Lee AP: Droplet
microfluidics. Lab Chip. 8:198–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Taniguchi K, Uchida J, Nishino K, Kumagai
T, Okuyama T, Okami J, Higashiyama M, Kodama K, Imamura F and Kato
K: Quantitative detection of EGFR mutations in circulating tumor
DNA derived from lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
17:7808–7815. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fang J, Yuan C, Luo X, He Z and Fu W: A
Thermus thermophilus argonaute-coupling exponential
amplification assay for ultrarapid analysis of circulating tumor
DNA. Talanta. 266:1250342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Cappello F, Angerilli V, Munari G, Ceccon
C, Sabbadin M, Pagni F, Fusco N, Malapelle U and Fassan M:
FFPE-Based NGS approaches into clinical practice: The limits of
glory from a pathologist viewpoint. J Pers Med. 12:1026422022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Mantilla WA, Sanabria-Salas MC, Baldion
AM, Sua LF, Gonzalez DM and Lema M: NGS in lung, breast, and
unknown primary cancer in colombia: A multidisciplinary consensus
on challenges and opportunities. JCO Glob Oncol. 7:1012–1023. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Lin YH, Liao XJ, Chang W and Chiou CC:
Ultrafast DNA amplification using microchannel Flow-through PCR
device. Biosensors (Basel). 12:3032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xu J, Han X, Xu W, Liu J, Zhu A, Song D
and Long F: Development of a hybridization chain reaction-powered
lab-on-fiber device for ultrafast point-of-care testing of
circulating tuor DNA in whole blood. Talanta. 259:1244752023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Wu J, Lv J, Zheng X and Wu ZS:
Hybridization chain reaction and its applications in biosensing.
Talanta. 234:1226372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Kim J, Shim JS, Han BH, Kim HJ, Park J,
Cho IJ, Kang SG, Kang JY, Bong KW and Choi N: Hydrogel-based
hybridization chain reaction (HCR) for detection of urinary
exosomal miRNAs as a diagnostic tool of prostate cancer. Biosens
Bioelectron. 192:1135042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Papakonstantinou A, Gonzalez NS, Pimentel
I, Sunol A, Zamora E, Ortiz C, Espinosa-Bravo M, Peg V, Vivancos A,
Saura C, et al: Prognostic value of ctDNA detection in patients
with early breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant therapy: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev.
104:1023622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wang D, Zhao P, Lu T, Ren J, Zhu L, Han X,
Zhang G, Dong X, Ma H, Yu M and Cai H: ctDNA as a prognostic
biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Open Life Sci. 18:202206152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Wei J, Feng J, Weng Y, Xu Z, Jin Y, Wang
P, Cui X, Ruan P, Luo R, Li N and Peng M: The prognostic value of
ctDNA and bTMB on immune checkpoint inhibitors in human cancer.
Front Oncol. 11:7069102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Markou A, Tzanikou E and Lianidou E: The
potential of liquid biopsy in the management of cancer patients.
Semin Cancer Biol. 84:69–79. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Bratman SV, Yang S, Iafolla M, Liu Z,
Hansen AR, Bedard PL, Lheureux S, Spreafico A, Razak AA, Shchegrova
S, et al: Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis as a
predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with
pembrolizumab. Nat Cancer. 1:873–881. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Gale D, Heider K, Ruiz-Valdepenas A,
Hackinger S, Perry M, Marsico G, Rundell V, Wulff J, Sharma G,
Knock H, et al: Residual ctDNA after treatment predicts early
relapse in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Ann Oncol. 33:500–510. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Borcoman E, Kanjanapan Y, Champiat S, Kato
S, Servois V, Kurzrock R, Goel S, Bedard P and Le Tourneau C: Novel
patterns of response under immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 30:385–396.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Young JS, Al-Adli N, Scotford K, Cha S and
Berger MS: Pseudoprogression versus true progression in
glioblastoma: What neurosurgeons need to know. J Neurosurg.
139:748–759. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Zheng J, Zhou X, Fu Y and Chen Q: Advances
in the study of hyperprogression of different tumors treated with
PD-1/PD-L1 antibody and the mechanisms of its occurrence. Cancers
(Basel). 15:13142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Vellanki PJ, Ghosh S, Pathak A, Fusco MJ,
Bloomquist EW, Tang S, Singh H, Philip R, Pazdur R and Beaver JA:
Regulatory implications of ctDNA in Immuno-oncology for solid
tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0053442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Mahuron KM and Fong Y: Applications of
liquid biopsy for surgical patients with cancer: A review. JAMA
Surg. 159:96–103. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Juarez-Avendano G, Mendez-Ramirez N,
Luna-Silva NC, Gomez-Almaguer D, Pelayo R and Balandran JC:
Molecular and cellular markers for measurable residual disease in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 78:159–170.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Li Y, Solis-Ruiz J, Yang F, Long N, Tong
CH, Lacbawan FL, Racke FK and Press RD: NGS-defined measurable
residual disease (MRD) after initial chemotherapy as a prognostic
biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 13:592023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Gutman JA, Winters A, Kent A, Amaya M,
Mcmahon C, Smith C, Jordan CT, Stevens B, Minhajuddin M, Pei S, et
al: Higher-dose venetoclax with measurable residual disease-guided
azacitidine discontinuation in newly diagnosed acute myeloid
leukemia. Haematologica. 108:2616–2625. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Munir T, Cairns DA, Bloor A, Allsup D,
Cwynarski K, Pettitt A, Paneesha S, Fox CP, Eyre TA, Forconi F, et
al: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia therapy guided by measurable
residual disease. N Engl J Med. 390:326–337. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Zhang JT, Liu SY, Gao W, Liu SM, Yan HH,
Ji L, Chen Y, Gong Y, Lu HL, Lin JT, et al: Longitudinal
undetectable molecular residual disease defines potentially cured
population in localized non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov.
12:1690–1701. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Jung HA, Ku BM, Kim YJ, Park S, Sun JM,
Lee SH, Ahn JS, Cho JH, Kim HK, Choi YS, et al: Longitudinal
monitoring of circulating tumor DNA from plasma in patients with
curative resected Stages I to IIIA EGFR-Mutant Non-Small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 18:1199–1208. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Costa LJ, Chhabra S, Medvedova E, Dholaria
BR, Schmidt TM, Godby KN, Silbermann R, Dhakal B, Bal S, Giri S, et
al: Daratumumab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and dexamethasone with
minimal residual disease Response-Adapted therapy in newly
diagnosed multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 40:2901–2912. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
San-Miguel J, Avet-Loiseau H, Paiva B,
Kumar S, Dimopoulos MA, Facon T, Mateos MV, Touzeau C, Jakubowiak
A, Usmani SZ, et al: Sustained minimal residual disease negativity
in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma and the impact of daratumumab
in MAIA and ALCYONE. Blood. 139:492–501. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Costa LJ, Chhabra S, Medvedova E, Dholaria
BR, Schmidt TM, Godby KN, Silbermann R, Dhakal B, Bal S, Giri S, et
al: Minimal residual disease response-adapted therapy in newly
diagnosed multiple myeloma (MASTER): Final report of the
multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol.
10:e890–e901. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
D'Agostino M, Bertuglia G, Rota-Scalabrini
D, Belotti A, More S, Corradini P, Oliva S, Ledda A, Grasso M,
Pavone V, et al: Predictors of unsustained minimal residual disease
negativity in multiple myeloma (MM) Patients. Blood.
1432023.doi:10.1182/blood.2023022080.
|
|
152
|
Medford AJ, Moy B, Spring LM, Hurvitz SA,
Turner NC and Bardia A: Molecular residual disease in breast
cancer: Detection and therapeutic interception. Clin Cancer Res.
29:4540–4548. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Patel RP, Somasundram PM, Smith LK,
Sheppard KE and Mcarthur GA: The therapeutic potential of targeting
minimal residual disease in melanoma. Clin Transl Med.
13:e11972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Honore N, van Marcke C, Galot R, Helaers
R, Ambroise J, van Maanen A, Mendola A, Dahou H, Marbaix E, Van
Eeckhout P, et al: Tumor-agnostic plasma assay for circulating
tumor DNA detects minimal residual disease and predicts outcome in
locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann
Oncol. 34:1175–1186. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Pott C, Jurinovic V, Trotman J, Kehden B,
Unterhalt M, Herold M, Jagt RV, Janssens A, Kneba M, Mayer J, et
al: Minimal residual disease status predicts outcome in patients
with previously untreated follicular lymphoma: A prospective
analysis of the Phase III GALLIUM study. J Clin Oncol. 42:550–561.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Yang K, Hu H, Wu J, Wang H, Guo Z, Yu W,
Yao L, Ding F, Zhou T, Wang W, et al: Letter to the Editor:
Clinical utility of urine DNA for noninvasive detection and minimal
residual disease monitoring in urothelial carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
22:252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Mo S, Ye L, Wang D, Han L, Zhou S, Wang H,
Dai W, Wang Y, Luo W, Wang R, et al: Early detection of molecular
residual disease and risk stratification for stage I to III
colorectal cancer via circulating tumor DNA Methylation. JAMA
Oncol. 9:770–778. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Slater S, Bryant A, Chen HC, Begum R, Rana
I, Aresu M, Peckitt C, Zhitkov O, Lazaro-Alcausi R, Borja V, et al:
ctDNA guided adjuvant chemotherapy versus standard of care adjuvant
chemotherapy after curative surgery in patients with high risk
stage II or stage III colorectal cancer: A multi-centre,
prospective, randomised control trial (TRACC Part C). BMC Cancer.
23:2572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Armakolas A, Kotsari M and Koskinas J:
Liquid biopsies, novel approaches and future directions. Cancers
(Basel). 15:15792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Xie J, Yao W, Chen L, Zhu W, Liu Q, Geng
G, Fang J, Zhao Y, Xiao L, Huang Z and Zhao J: Plasma ctDNA
increases tissue NGS-based detection of therapeutically targetable
mutations in lung cancers. BMC Cancer. 23:2942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|