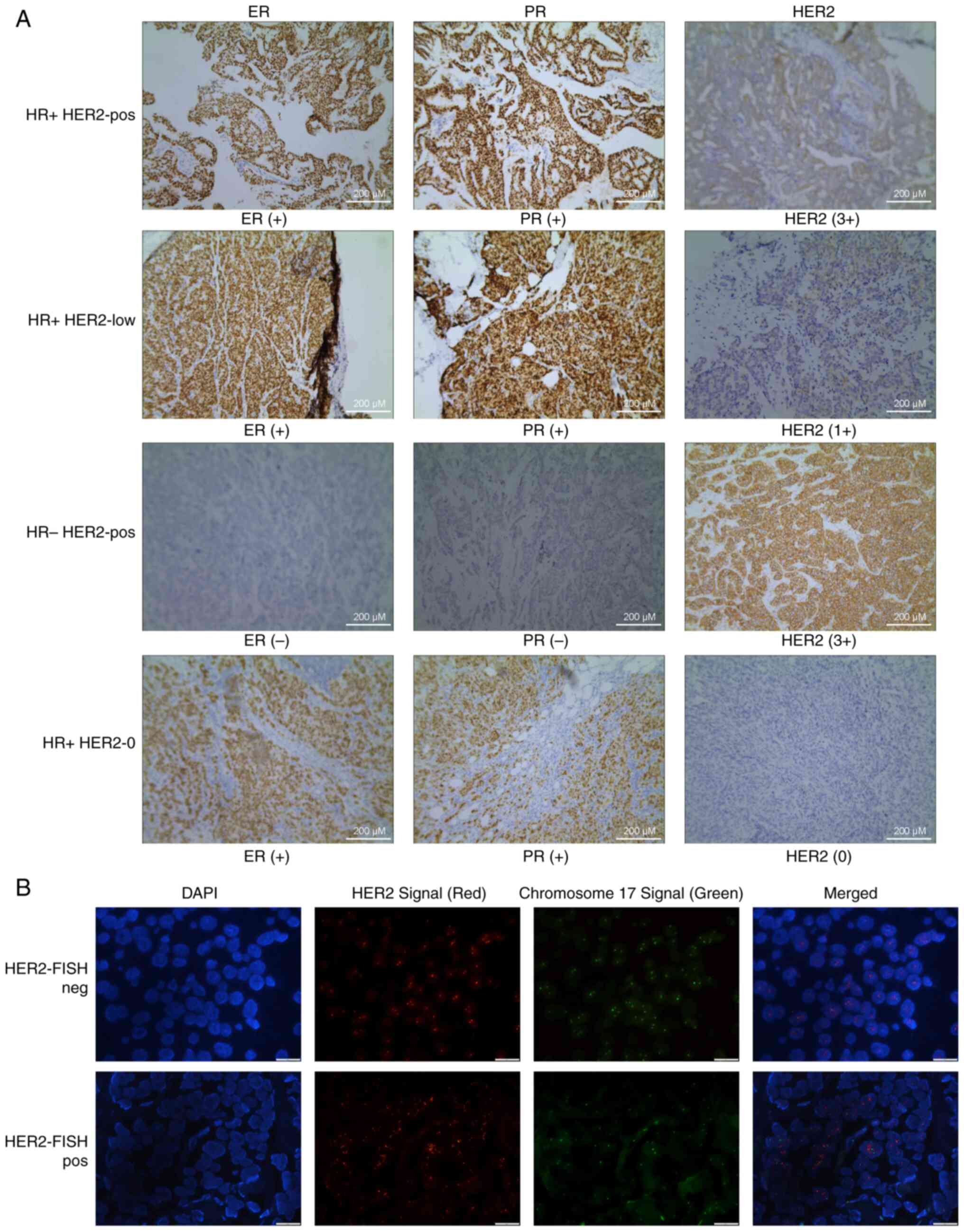
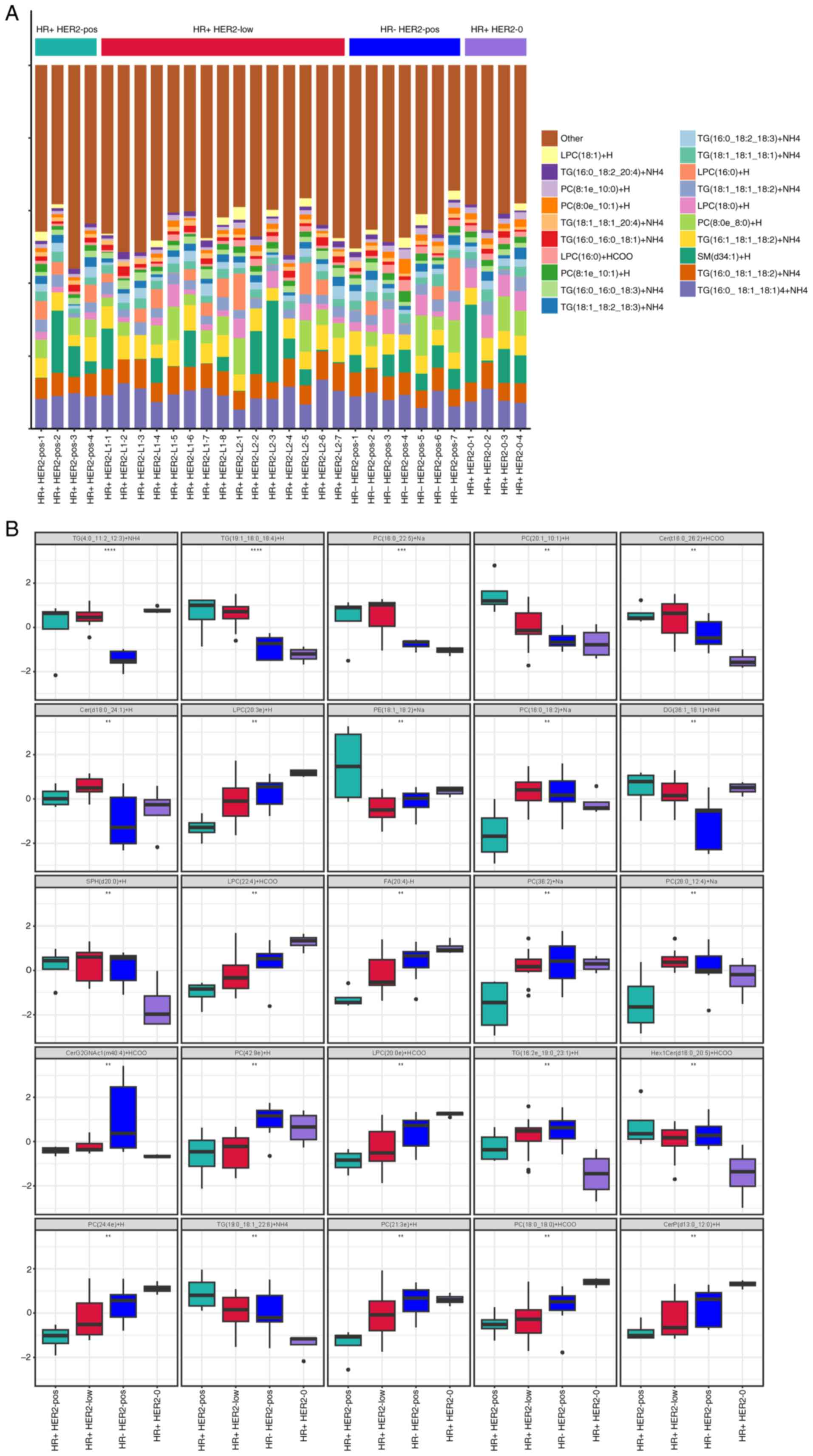
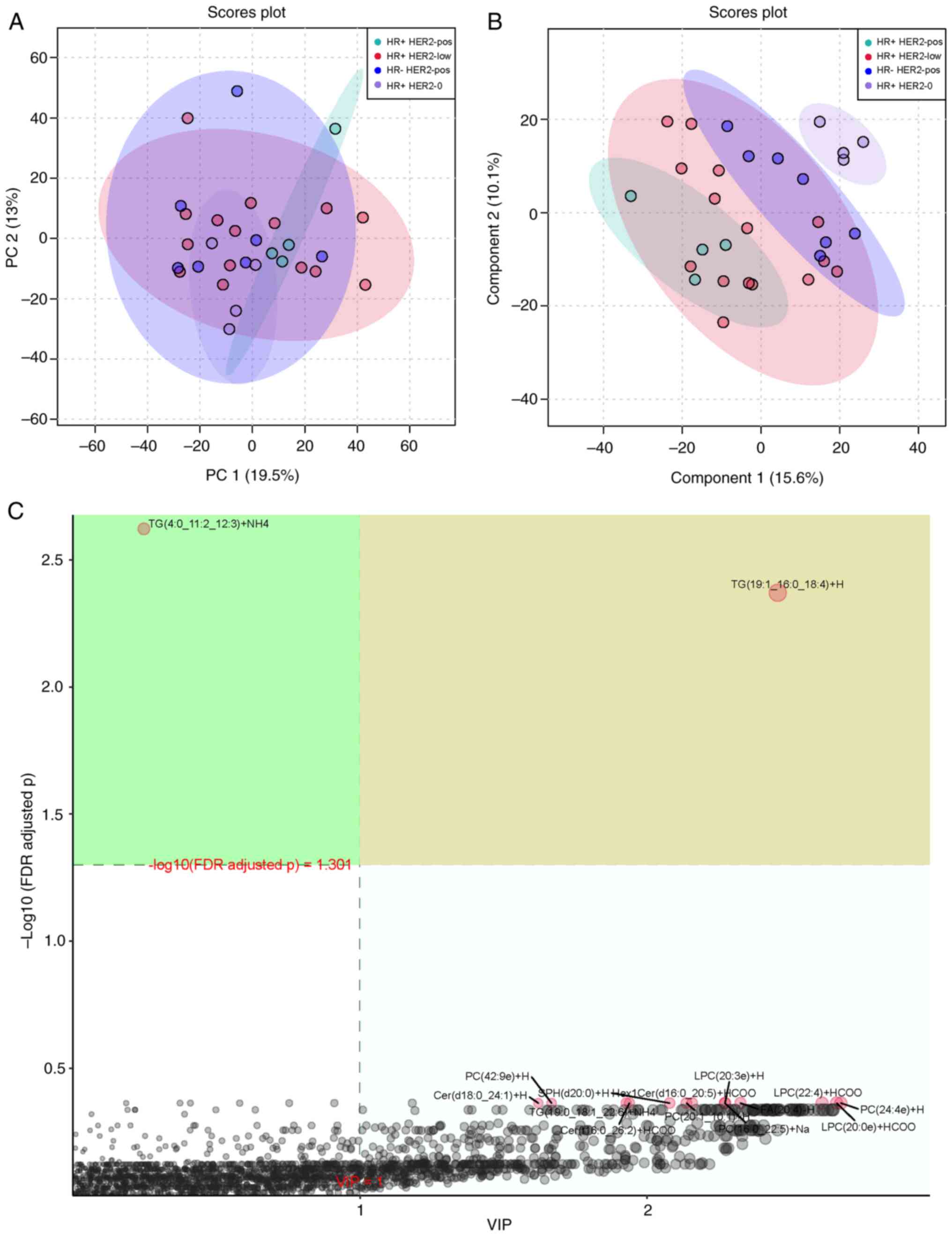
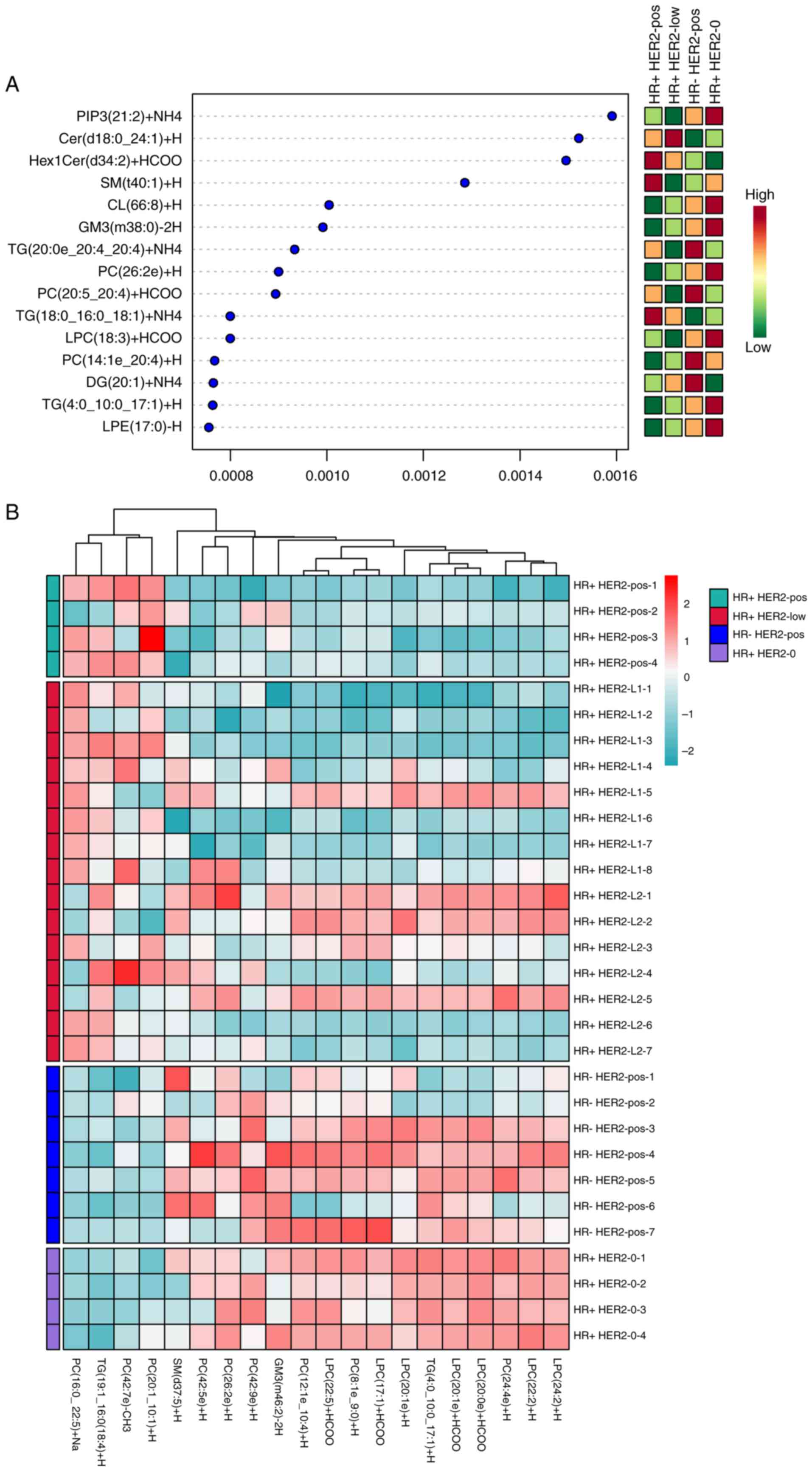
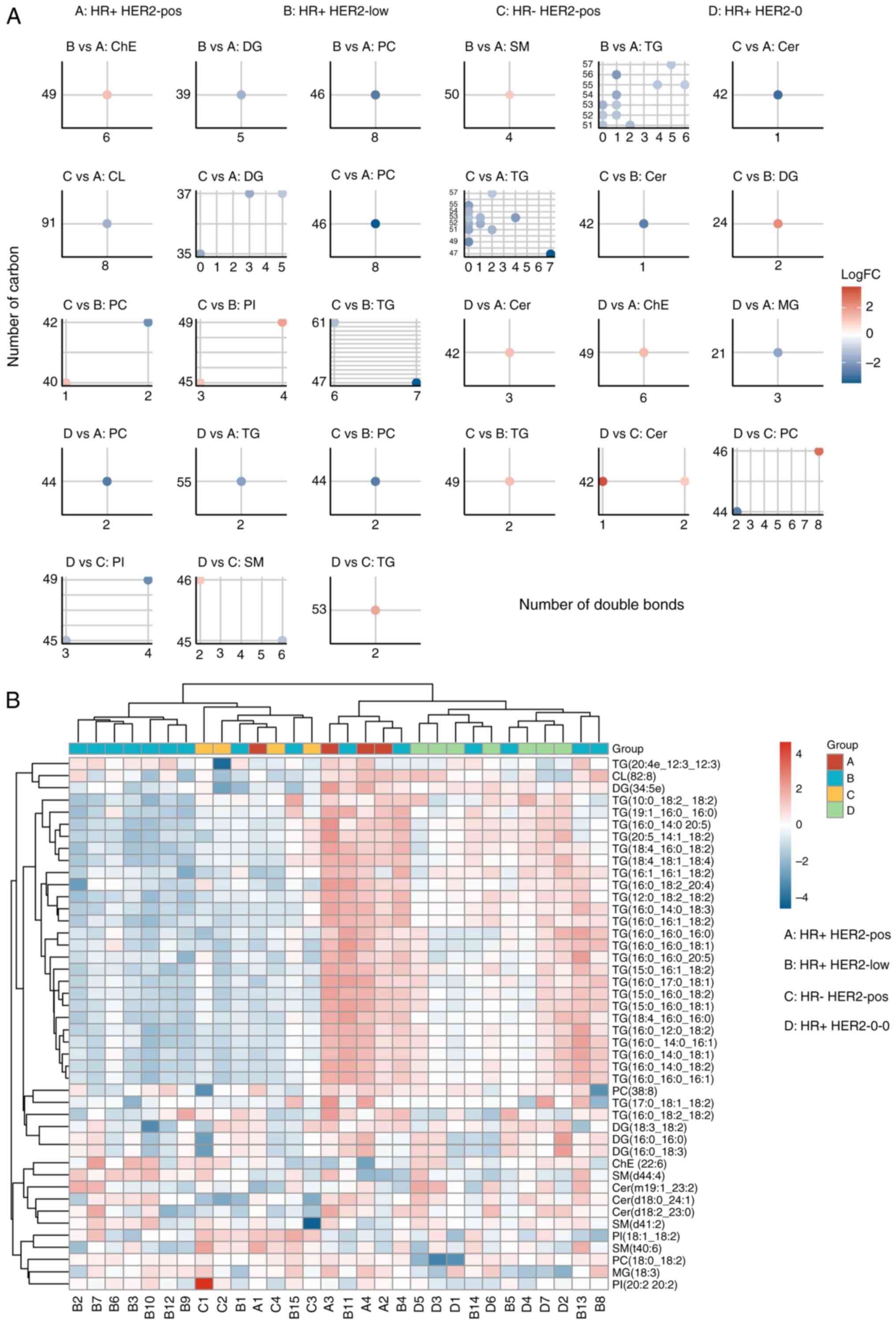
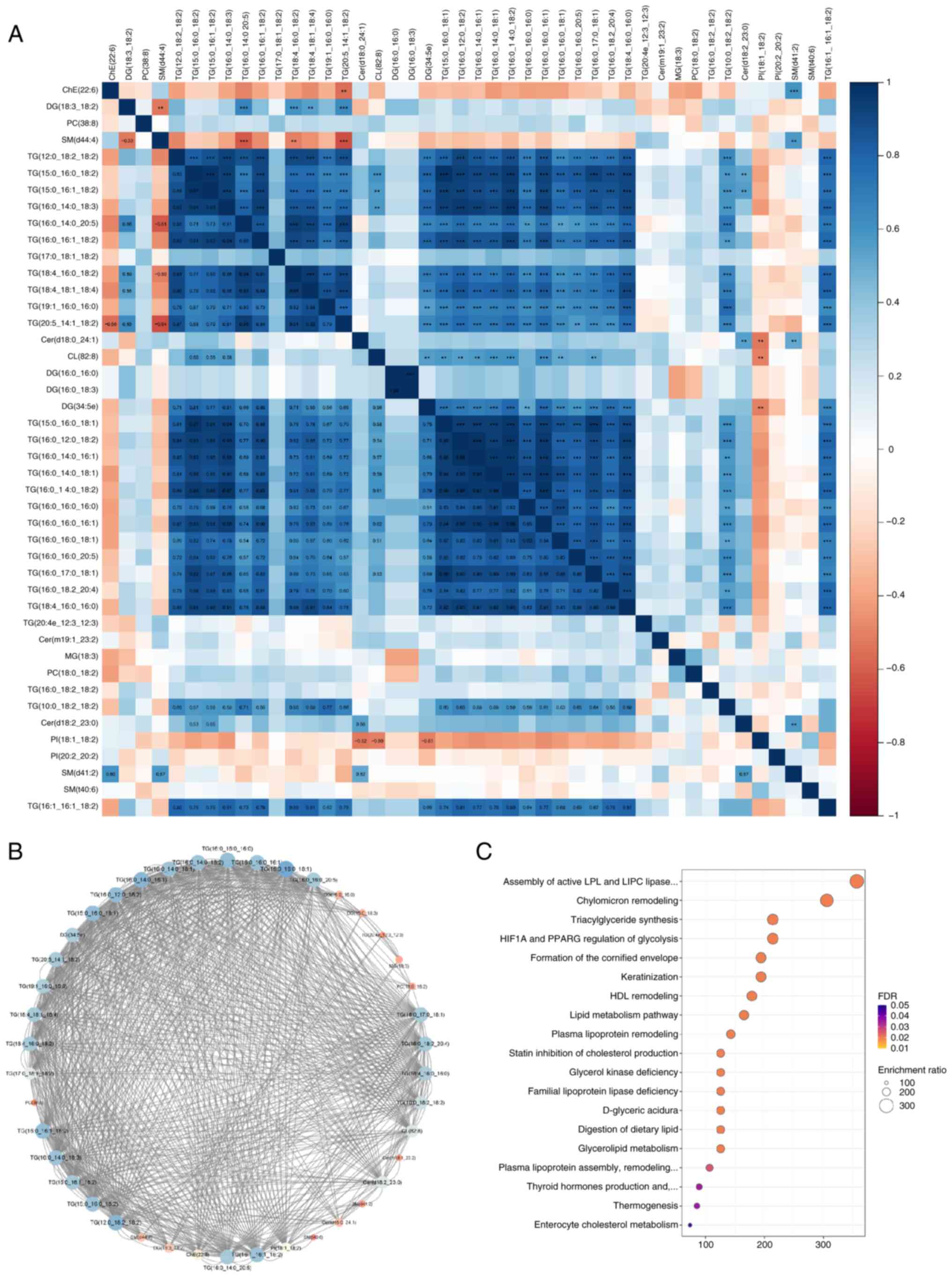
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M,
Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I and Bray F:
Global cancer observatory: Cancer today. International Agency for
Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2020
|
|
2
|
Wolf-Yadlin A, Kumar N, Zhang Y,
Hautaniemi S, Zaman M, Kim HD, Grantcharova V, Lauffenburger DA and
White FM: Effects of HER2 overexpression on cell signaling networks
governing proliferation and migration. Mol Syst Biol. 2:542006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eladdadi A and Isaacson D: A mathematical
model for the effects of HER2 overexpression on cell proliferation
in breast cancer. Bull Math Biol. 70:1707–1729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tagliabue E, Agresti R, Carcangiu ML,
Ghirelli C, Morelli D, Campiglio M, Martel M, Giovanazzi R, Greco
M, Balsari A and Ménard S: Role of HER2 in wound-induced breast
carcinoma proliferation. Lancet. 362:527–533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Freudenberg JA, Wang Q, Katsumata M,
Drebin J, Nagatomo I and Greene MI: The role of HER2 in early
breast cancer metastasis and the origins of resistance to
HER2-targeted therapies. Exp Mol Pathol. 87:1–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan
M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D and Hung MC: Upregulation of
CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell.
6:459–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harris C, Ward R, Dobbins T, Drew A and
Pearson S: The efficacy of HER2-targeted agents in metastatic
breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 22:1308–1317. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin NU and Winer EP: Brain metastases: The
HER2 paradigm. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1648–1655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Merkhofer EC, Cogswell P and Baldwin AS:
Her2 activates NF-kappaB and induces invasion through the canonical
pathway involving IKKalpha. Oncogene. 29:1238–1248. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo X, He Y, Tang H, Cao Y, Gao M, Liu B
and Hu Z: Effects of HER2 on the invasion and migration of gastric
cancer. Am J Transl Res. 11:7604–7613. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Juboori SI, Vadakekolathu J, Idri S,
Wagner S, Zafeiris D, Pearson J, Almshayakhchi R, Caraglia M,
Desiderio V, Miles AK, et al: PYK2 promotes HER2-positive breast
cancer invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1–14. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chi F, Wu R, Jin X, Jiang M and Zhu X:
HER2 induces cell proliferation and invasion of non-small-cell lung
cancer by upregulating COX-2 expression via MEK/ERK signaling
pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 5:2709–2716. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alameddine RS, Otrock ZK, Awada A and
Shamseddine A: Crosstalk between HER2 signaling and angiogenesis in
breast cancer: Molecular basis, clinical applications and
challenges. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vogl G, Bartel H, Dietze O and
Hauser-Kronberger C: HER2 is unlikely to be involved in directly
regulating angiogenesis in human breast cancer. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 14:138–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tarantino P, Hamilton E, Tolaney SM,
Cortes J, Morganti S, Ferraro E, Marra A, Viale G, Trapani D,
Cardoso F, et al: HER2-low breast cancer: Pathological and clinical
landscape. J Clin Oncol. 38:1951–1962. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan M, Schwaederle M, Arguello D, Millis
SZ, Gatalica Z and Kurzrock R: HER2 expression status in diverse
cancers: Review of results from 37,992 patients. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 34:157–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maximiano S, Magalhaes P, Guerreiro MP and
Morgado M: Trastuzumab in the treatment of breast cancer. BioDrugs.
30:75–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vu T and Claret FX: Trastuzumab: Updated
mechanisms of action and resistance in breast cancer. Front Oncol.
2:622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, Sohn J,
Vidal M, Tokunaga E, Tsurutani J, Ueno NT, Prat A, Chae YS, et al:
Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 387:9–20. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Skidmore L, Sakamuri S, Knudsen NA, Hewet
AG, Milutinovic S, Barkho W, Biroc SL, Kirtley J, Marsden R, Storey
K, et al: ARX788, a site-specific anti-HER2 antibody-drug
conjugate, demonstrates potent and selective activity in HER2-low
and T-DM1-resistant breast and gastric cancers. Mol Cancer Ther.
19:1833–1843. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ogitani Y, Aida T, Hagihara K, Yamaguchi
J, Ishii C, Harada N, Soma M, Okamoto H, Oitate M, Arakawa S, et
al: DS-8201a, a novel HER2-targeting ADC with a novel DNA
Topoisomerase I inhibitor, demonstrates a promising antitumor
efficacy with differentiation from T-DM1. Clin Cancer Res.
22:5097–5108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai LJ, Ma D, Xu YZ, Li M, Li YW, Xiao Y,
Jin X, Wu SY, Zhao YX, Wang H, et al: Molecular features and
clinical implications of the heterogeneity in Chinese patients with
HER2-low breast cancer. Nat Commun. 14:51122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Nonneville A, Houvenaeghel G, Cohen M,
Sabiani L, Bannier M, Viret F, Gonçalves A and Bertucci F:
Pathological complete response rate and disease-free survival after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with HER2-low and HER2-0
breast cancers. Eur J Cancer. 176:181–188. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu L, Kawashima M, Sugimoto M, Sonomura
K, Pu F, Li W, Takeda M, Goto T, Kawaguchi K, Sato TA and Toi M:
Discovery of lipid profiles in plasma-derived extracellular
vesicles as biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Sci.
114:4020–4031. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vitaliti A, Roccatani I, Iorio E, Perta N,
Gismondi A, Chirico M, Pisanu ME, Di Marino D, Canini A, De Luca A
and Rossi L: AKT-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition is
affected by copper bioavailability in HER2 negative breast cancer
cells via a LOXL2-independent mechanism. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
46:93–115. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiao Y, Ma D, Yang YS, Yang F, Ding JH,
Gong Y, Jiang L, Ge LP, Wu SY, Yu Q, et al: Comprehensive
metabolomics expands precision medicine for triple-negative breast
cancer. Cell Res. 32:477–490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li S, Zeng H, Fan J, Wang F, Xu C, Li Y,
Tu J, Nephew KP and Long X: Glutamine metabolism in breast cancer
and possible therapeutic targets. Biochem Pharmacol.
210:1154642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen L, Huang H, Li J, Chen W, Yao Y, Hu
J, Zhou J, Huang F and Ni C: Exploration of prognosis and
immunometabolism landscapes in ER+ breast cancer based on a novel
lipid metabolism-related signature. Front Immunol. 14:11994652023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Azam A and Sounni NE: Lipid metabolism
heterogeneity and crosstalk with mitochondria functions drive
breast cancer progression and drug resistance. Cancers (Basel).
14:62672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zipinotti Dos Santos D, de Souza JC,
Pimenta TM, da Silva Martins B, Junior RSR, Butzene SMS, Tessarolo
NG, Cilas PML Jr, Silva IV and Rangel LBA: The impact of lipid
metabolism on breast cancer: A review about its role in
tumorigenesis and immune escape. Cell Commun Signal. 21:1612023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ward AV, Anderson SM and Sartorius CA:
Advances in analyzing the breast cancer lipidome and its relevance
to disease progression and treatment. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 26:399–417. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
World Health Organization (WHO), . WHO
classification of tumours editorial board: Breast tumours. WHO;
Geneva: 2019
|
|
33
|
Chong J, Soufan O, Li C, Caraus I, Li S,
Bourque G, Wishart DS and Xia J: MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more
transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:W486–W494. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duan Y, Du Y, Gu Z, Zheng X and Wang C:
prognostic value, immune signature, and molecular mechanisms of the
PHLDA family in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
23:103162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Breast Cancer Professional Committee of
the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association and Breast Tumor Group of the
Oncology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, . Guidelines
for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment by China Anti-cancer
Association (2024 edition) (Chinese version). China Oncology.
33:1092–1187. 2023.
|
|
36
|
Zhang R, Yang M, Hou X, Hou R, Wang L, Shi
L, Zhao F, Liu X, Meng Q, Wang L and Zhang L: Characterization and
difference of lipids and metabolites from Jianhe White Xiang and
Large White pork by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem
mass spectrometry. Food Res Int. 162:1119462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Z, Liao Q, Sun Y, Pan T, Liu S, Miao
W, Li Y, Zhou L and Xu G: Lipidomic and transcriptomic analysis of
the longissimus muscle of luchuan and duroc pigs. Front Nutr.
8:6676222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:4–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yousuf U, Sofi S, Makhdoomi A and Mir MA:
Identification and analysis of dysregulated fatty acid metabolism
genes in breast cancer subtypes. Med Oncol. 39:2562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang F and Du G: Dysregulated lipid
metabolism in cancer. World J Biol Chem. 3:167–174. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang M, Han J, Xing H, Zhang H, Li Z,
Liang L, Li C, Dai S, Wu M, Shen F and Yang T: Dysregulated fatty
acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Oncol.
3:241–251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou X, Huang F, Ma G, Wei W, Wu N and Liu
Z: Dysregulated ceramides metabolism by fatty acid 2-hydroxylase
exposes a metabolic vulnerability to target cancer metastasis.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:3702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Monaco ME: Fatty acid metabolism in breast
cancer subtypes. Oncotarget. 8:29487–29500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Qin L, An N, Yuan B, Zhu Q and Feng Y: The
metabolomic characteristics and dysregulation of fatty acid esters
of hydroxy fatty acids in breast cancer. Metabolites. 13:11082023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weiss L, Hoffmann GE, Schreiber R, Andres
H, Fuchs E, Körber E and Kolb HJ: Fatty-acid biosynthesis in man, a
pathway of minor importance. Purification, optimal assay
conditions, and organ distribution of fatty-acid synthase. Biol
Chem Hoppe Seyler. 367:905–912. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ribas HT, Sogayar MC, Dolga AM,
Winnischofer SM and Trombetta-Lima M: Lipid profile in breast
cancer: From signaling pathways to treatment strategies. Biochimie.
219:118–129. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Aramaki S, Tsuge S, Islam A, Eto F,
Sakamoto T, Oyama S, Li W, Zhang C, Yamaguchi S, Takatsuka D, et
al: Lipidomics-based tissue heterogeneity in specimens of luminal
breast cancer revealed by clustering analysis of mass spectrometry
imaging: A preliminary study. PLoS One. 18:e02831552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bavis MM, Nicholas AM, Tobin AJ, Christian
SL and Brown RJ: The breast cancer microenvironment and lipoprotein
lipase: Another negative notch for a beneficial enzyme? FEBS Open
Bio. 13:586–596. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|