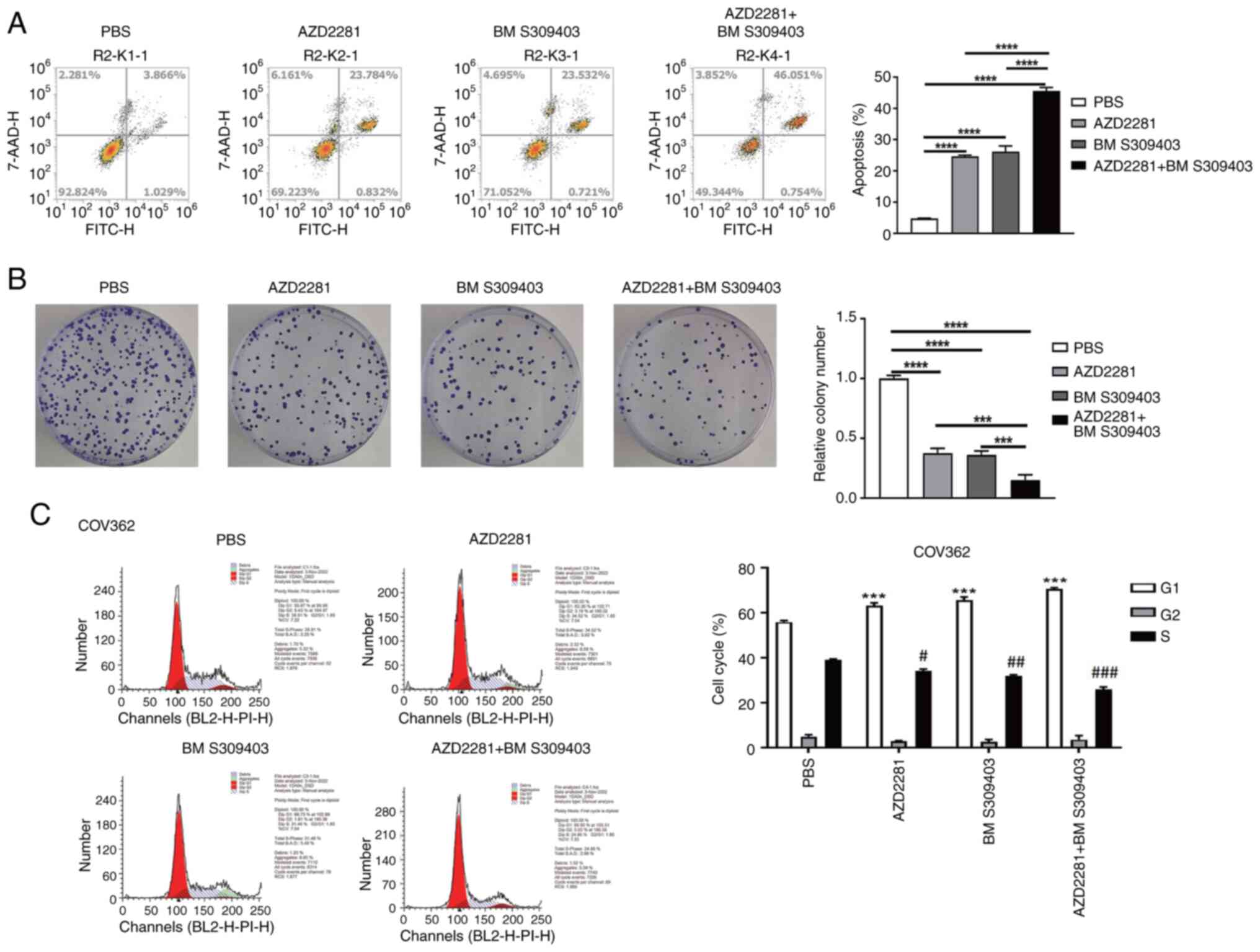
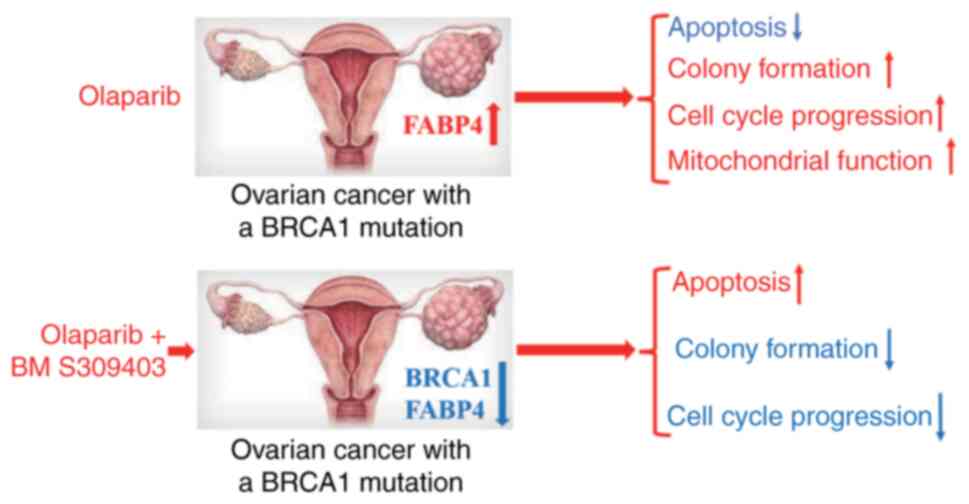
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harter P, Johnson T, Berton-Rigaud D, Park
SY, Friedlander M, Del Campo JM, Shimada M, Forget F, Mirza MR,
Colombo N, et al: BRCA1/2 mutations associated with
progression-free survival in ovarian cancer patients in the
AGO-OVAR 16 study. Gynecol. Oncol. 140:443–449. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Tewari KS, Burger RA, Enserro D, Norquist
BM, Swisher EM, Brady MF, Bookman MA, Fleming GF, Huang H, Homesley
HD, et al: Final Overall Survival of a Randomized Trial of
Bevacizumab for Primary Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. J Clin Oncol.
37:2317–2328. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sunar V, Korkmaz V, Topcu V, Cavdarli B,
Arik Z, Ozdal B and Ustun YE: Frequency of germline BRCA1/2
mutations and association with clinicopathological characteristics
in Turkish women with epithelial ovarian cancer. Asia Pac J Clin
Oncol. 18:84–92. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Daly MB, Pal T, Berry MP, Buys SS, Dickson
P, Domchek SM, Elkhanany A, Friedman S, Goggins M, Hutton ML, et
al: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and
Pancreatic, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in
Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 19:77–102. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Walker M, Jacobson M and Sobel M:
Management of ovarian cancer risk in women with BRCA1/2 pathogenic
variants. CMAJ. 191:E886–E893. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Langelier MF, Planck JL, Roy S and Pascal
JM: Structural basis for DNA damage-dependent
poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by human PARP-1. Science. 336:728–732. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zimmer AS, Gillard M, Lipkowitz S and Lee
JM: Update on PARP inhibitors in breast cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 19:212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Layman RM and Arun B: PARP inhibitors in
triple-negative breast cancer including those With BRCA Mutations.
Cancer J. 27:67–75. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tung NM, Zakalik D and Somerfield MR;
Hereditary Breast Cancer Guideline Expert Panel, : Adjuvant PARP
Inhibitors in Patients With High-Risk Early-Stage HER2-Negative
Breast Cancer and Germline BRCA Mutations: ASCO Hereditary Breast
Cancer Guideline Rapid Recommendation Update. J Clin Oncol.
39:2959–2961. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mirza MR, Coleman RL, Gonzalez-Martin A,
Moore KN, Colombo N, Ray-Coquard I and Pignata S: The forefront of
ovarian cancer therapy: Update on PARP inhibitors. Ann Oncol.
31:1148–1159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hong T, Lei G, Chen X, Li H, Zhang X, Wu
N, Zhao Y, Zhang Y and Wang J: PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis
via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in
BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. Redox Biol. 42:1019282021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Banerjee S, Moore KN, Colombo N, Scambia
G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, Friedlander M, Lisyanskaya A, Floquet A, Leary
A, et al: Maintenance olaparib for patients with newly diagnosed
advanced ovarian cancer and a BRCA mutation (SOLO1/GOG 3004):
5-year follow-up of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:1721–1731. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedlander M, Moore KN, Colombo N,
Scambia G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, Lisyanskaya A, Sonke GS, Gourley C,
Banerjee S, et al: Patient-centred outcomes and effect of disease
progression on health status in patients with newly diagnosed
advanced ovarian cancer and a BRCA mutation receiving maintenance
olaparib or placebo (SOLO1): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 22:632–642. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ray-Coquard I, Pautier P, Pignata S, Pérol
D, González-Martín A, Berger R, Fujiwara K, Vergote I, Colombo N,
Mäenpää J, et al: Olaparib plus Bevacizumab as First-Line
Maintenance in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl J Med. 381:2416–2428. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pujade-Lauraine E, Ledermann JA, Selle F,
Gebski V, Penson RT, Oza AM, Korach J, Huzarski T, Poveda A,
Pignata S, et al: Olaparib tablets as maintenance therapy in
patients with platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer and a
BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): A double-blind, randomised,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1274–1284.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C,
Friedlander M, Vergote I, Rustin G, Scott CL, Meier W,
Shapira-Frommer R, Safra T, et al: Olaparib maintenance therapy in
patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: A
preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a
randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:852–861. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
DiSilvestro P, Colombo N, Scambia G, Kim
BG, Oaknin A, Friedlander M, Lisyanskaya A, Floquet A, Leary A,
Sonke GS, et al: Efficacy of maintenance olaparib for patients with
newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer with a BRCA Mutation:
Subgroup analysis findings from the SOLO1 Trial. J Clin Oncol.
38:3528–3537. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Noordermeer SM and van Attikum H: PARP
Inhibitor Resistance: A Tug-of-War in BRCA-Mutated Cells. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:820–834. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dias MP, Moser SC, Ganesan S and Jonkers
J: Understanding and overcoming resistance to PARP inhibitors in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 18:773–791. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang X, Li X, Li W, Bai H and Zhang Z:
PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer: Sensitivity prediction and
resistance mechanisms. J Cell Mol Med. 23:2303–2313. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang N, Yang Y, Jin D, Zhang Z, Shen K,
Yang J, Chen H, Zhao X, Yang L and Lu H: PARP inhibitor resistance
in breast and gynecological cancer: Resistance mechanisms and
combination therapy strategies. Front Pharmacol. 13:9676332022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang PB, Hou PP, Liu FY, Hong WB, Chen HZ,
Sun XY, Li P, Zhang Y, Ju CY, Luo LJ, et al: Blocking PPARү
interaction facilitates Nur77 interdiction of fatty acid uptake and
suppresses breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:27412–27422. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jabs M, Rose AJ, Lehmann LH, Taylor J,
Moll I, Sijmonsma TP, Herberich SE, Sauer SW, Poschet G, Federico
G, et al: Inhibition of endothelial notch signaling impairs fatty
acid transport and leads to metabolic and vascular remodeling of
the adult Heart. Circulation. 137:2592–2608. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luis G, Godfroid A, Nishiumi S, Cimino J,
Blacher S, Maquoi E, Wery C, Collignon A, Longuespée R,
Montero-Ruiz L, et al: Tumor resistance to ferroptosis driven by
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1) in cancer cells and Fatty Acid
Biding Protein-4 (FABP4) in tumor microenvironment promote tumor
recurrence. Redox Biol. 43:1020062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gyamfi J, Yeo JH, Kwon D, Min BS, Cha YJ,
Koo JS, Jeong J, Lee J and Choi J: Interaction between CD36 and
FABP4 modulates adipocyte-induced fatty acid import and metabolism
in breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 7:1292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang H, Deng Q, Ni T, Liu Y, Lu L, Dai H,
Wang H and Yang W: Targeted Inhibition of LPL/FABP4/CPT1 fatty acid
metabolic axis can effectively prevent the progression of
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis to liver cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
17:4207–4222. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian W, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Zhu T, Hua Y, Li
H, Zhang Q and Xia M: FABP4 promotes invasion and metastasis of
colon cancer by regulating fatty acid transport. Cancer Cell Int.
20:5122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Zhao X, Deng L, Li X, Wang G, Li
Y and Chen M: High expression of FABP4 and FABP6 in patients with
colorectal cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 17:1712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li G, Wu Q, Gong L, Xu X, Cai J, Xu L,
Zeng Y, He X and Wang Z: FABP4 is an independent risk factor for
lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with cervical
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 21:5682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen QY, Huang XB, Zhao YJ, Wang HG, Wang
JB, Liu LC, Wang LQ, Zhong Q, Xie JW, Lin JX, et al: The peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor agonist rosiglitazone specifically
represses tumour metastatic potential in chromatin
inaccessibility-mediated FABP4-deficient gastric cancer.
Theranostics. 12:1904–1920. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mukherjee A, Chiang CY, Daifotis HA,
Nieman KM, Fahrmann JF, Lastra RR, Romero IL, Fiehn O and Lengyel
E: Adipocyte-Induced FABP4 expression in ovarian cancer cells
promotes metastasis and mediates carboplatin resistance. Cancer
Res. 80:1748–1761. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gharpure KM, Pradeep S, Sans M, Rupaimoole
R, Ivan C, Wu SY, Bayraktar E, Nagaraja AS, Mangala LS, Zhang X,
Haemmerle M, et al: FABP4 as a key determinant of metastatic
potential of ovarian cancer. Nat Commun. 9:29232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo X, Ryu KW, Kim DS, Nandu T, Medina CJ,
Gupte R, Gibson BA, Soccio RE, Yu Y, Gupta RK and Kraus WL: PARP-1
Controls the Adipogenic Transcriptional Program by PARylating
C/EBPβ and modulating its transcriptional activity. Mol Cell.
65:260–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pan J, Liu F, Xiao X, Xu R, Dai L, Zhu M,
Xu H, Xu Y, Zhao A, Zhou W, et al: METTL3 promotes colorectal
carcinoma progression by regulating the m6A-CRB3-Hippo axis. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 41:192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dang Y, Xu R, Pan J, Xiao X, Zhang S, Zhou
W, Xu Y and Ji G: Dynamic changes in DNA methylation and
hydroxymethylation revealed the transformation of advanced adenoma
into colorectal carcinoma. Clin Transl Med. 13:e12022023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ryu KW, Nandu T, Kim J, Challa S,
DeBerardinis RJ and Kraus WL: Metabolic regulation of transcription
through compartmentalized NAD(+) biosynthesis. Science.
360:eaan57802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Su X, Jin M, Xu C, Gao Y, Yang Y, Qi H,
Zhang Q, Yang X, Ya W, Zhang Y and Yang R: FABP4 in Paneth cells
regulates antimicrobial protein expression to reprogram gut
microbiota. Gut Microbes. 14:21399782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moreno-Vedia J, Girona J, Ibarretxe D,
Masana L and Rodriguez-Calvo R: Unveiling the role of the fatty
acid binding protein 4 in the metabolic-associated fatty liver
disease. Biomedicines. 10:1972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang M, Shu W, Zhai X, Yang X, Zhou H, Pan
B, Li C, Lu D, Cai J, Zheng S, et al: Integrated multi-omic
analysis identifies fatty acid binding protein 4 as a biomarker and
therapeutic target of ischemia-reperfusion injury in steatotic
liver transplantation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 81:832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sekine M, Nishino K and Enomoto T:
Differences in ovarian and other cancers risks by population and
BRCA Mutation Location. Genes (Basel). 12:10502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schouten PC, Richters L, Vis DJ, Kommoss
S, van Dijk E, Ernst C, Kluin RJC, Marmé F, Lips EH, Schmidt S, et
al: Ovarian Cancer-Specific BRCA-like Copy-number aberration
classifiers detect mutations associated with homologous
recombination deficiency in the AGO-TR1 Trial. Clin Cancer Res.
27:6559–6569. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Samuel D, Diaz-Barbe A, Pinto A,
Schlumbrecht M and George S: Hereditary Ovarian Carcinoma: Cancer
Pathogenesis Looking beyond BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cells. 11:5392022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vidakovic M, Dinic S, Grdovic N,
Mihailović M, Uskoković A, Quesada P and Poznanović G: Regulation
of rat haptoglobin gene expression is coordinated by the nuclear
matrix. J Cell Biochem. 107:1205–1221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gui L, Raza SHA, Ma B, Easa AA, Althobaiti
F, Shukry M, Alotaibi MA, Al Hazani TMI, Dawood MAO, Khan R, et al:
CEBPβ binding directly to the promoter region drives CEBPa
transcription and improves FABP4 transcriptional activity in
adipose tissue of yak (Bos grunniens). Res Vet Sci. 141:174–179.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Regassa A, Park KW and Kim WK: Phenamil
enhances the adipogenic differentiation of hen preadipocytes. Cell
Biol Int. 40:1123–1128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mandal SK, Puri S, Kumar BK,
Muzaffar-Ur-Rehman M, Sharma PK, Sankaranarayanan M and Deepa PR:
Targeting lipid-sensing nuclear receptors PPAR (α, ү, β/δ): HTVS
and molecular docking/dynamics analysis of pharmacological ligands
as potential pan-PPAR agonists. Mol Divers. 28:1423–1438. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Baczewska M, Bojczuk K, Kołakowski A,
Dobroch J, Guzik P and Knapp P: Obesity and energy substrate
transporters in ovarian cancer-review. Molecules. 26:16592021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Arora S, Balasubramaniam S, Zhang H,
Berman T, Narayan P, Suzman D, Bloomquist E, Tang S, Gong Y,
Sridhara R, et al: FDA Approval Summary: Olaparib monotherapy or in
combination with bevacizumab for the maintenance treatment of
patients with advanced ovarian cancer. Oncologist. 26:e164–e172.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gonzalez-Martin A, Desauw C, Heitz F,
Cropet C, Gargiulo P, Berger R, Ochi H, Vergote I, Colombo N, Mirza
MR, et al: Maintenance olaparib plus bevacizumab in patients with
newly diagnosed advanced high-grade ovarian cancer: Main analysis
of second progression-free survival in the phase III
PAOLA-1/ENGOT-ov25 trial. Eur J Cancer. 174:221–231. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moore K, Colombo N, Scambia G, Kim BG,
Oaknin A, Friedlander M, Lisyanskaya A, Floquet A, Leary A, Sonke
GS, et al: Maintenance olaparib in patients with newly diagnosed
advanced ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 379:2495–2505. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nikolaou M, Pavlopoulou A, Georgakilas AG
and Kyrodimos E: The challenge of drug resistance in cancer
treatment: A current overview. Clin Exp Metastasis. 35:309–318.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang X, Zhang H and Chen X: Drug
resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug
Resist. 2:141–160. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Biegala L, Gajek A, Marczak A and Rogalska
A: Olaparib-Resistant BRCA2(MUT) Ovarian Cancer Cells with Restored
BRCA2 Abrogate Olaparib-Induced DNA Damage and G2/M Arrest
Controlled by the ATR/CHK1 Pathway for Survival. Cells.
12:10382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Biegala L, Gajek A, Szymczak-Pajor I,
Marczak A, Sliwinska A and Rogalska A: Targeted inhibition of the
ATR/CHK1 pathway overcomes resistance to olaparib and dysregulates
DNA damage response protein expression in BRCA2(MUT) ovarian cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 13:226592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|