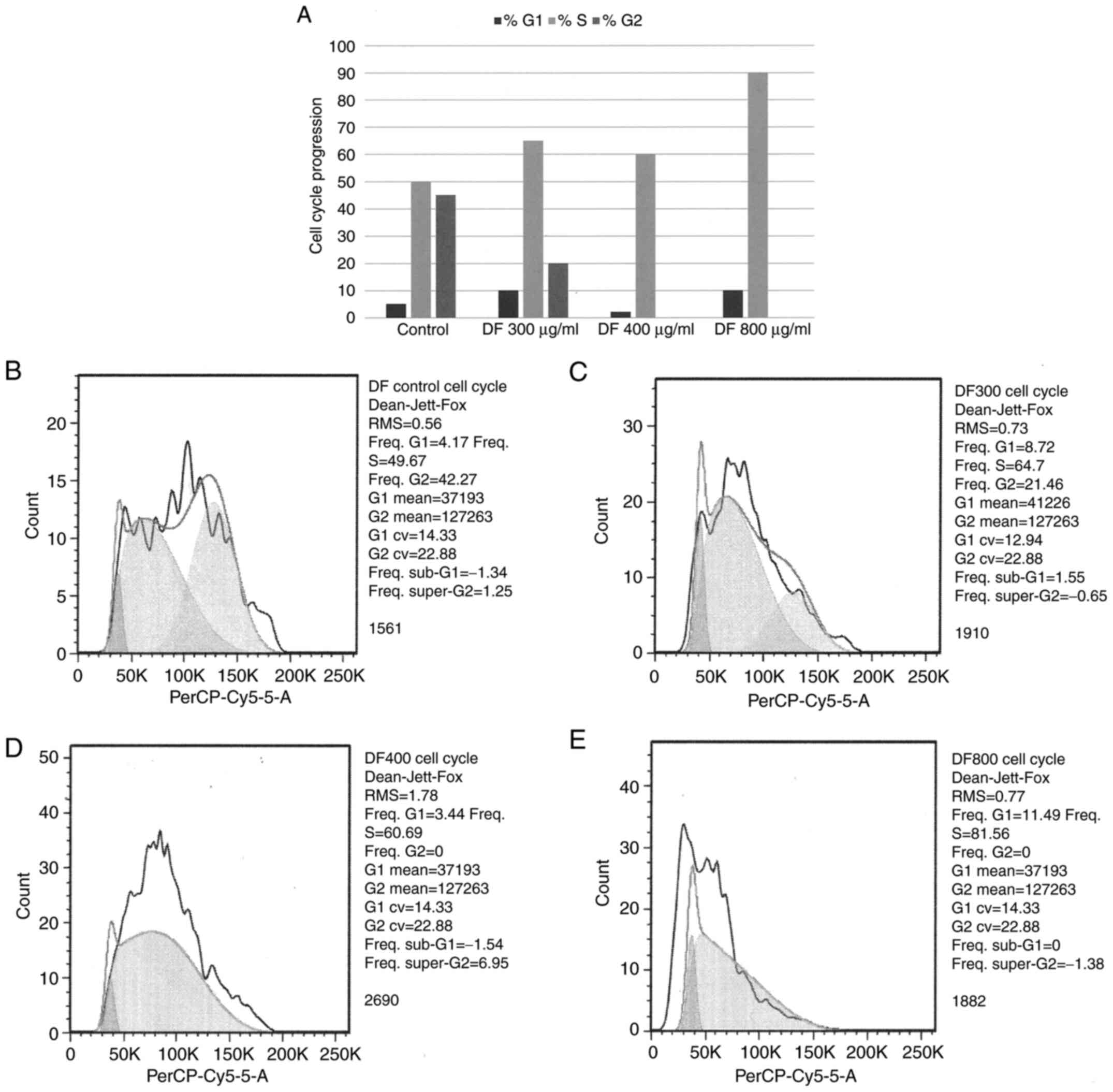
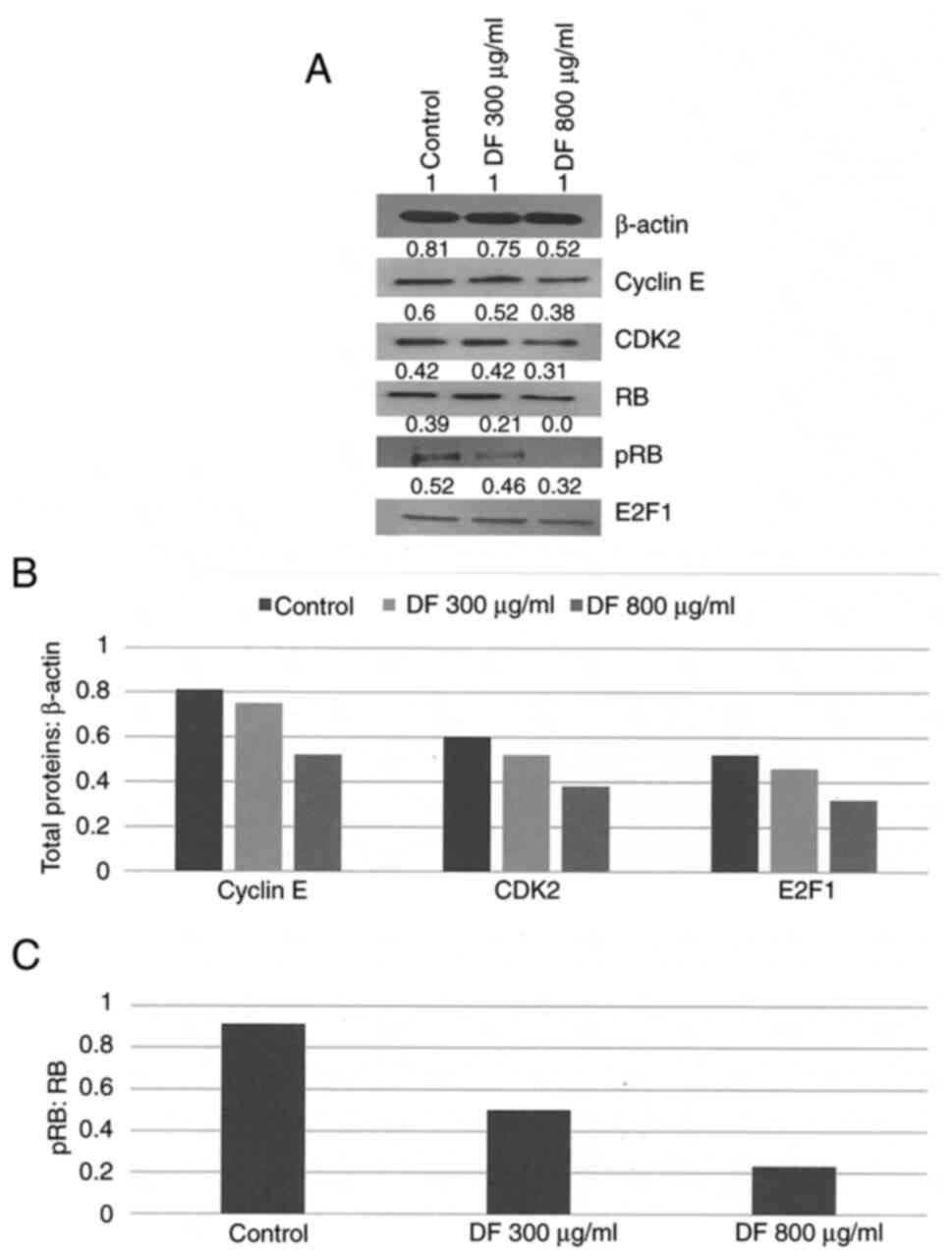
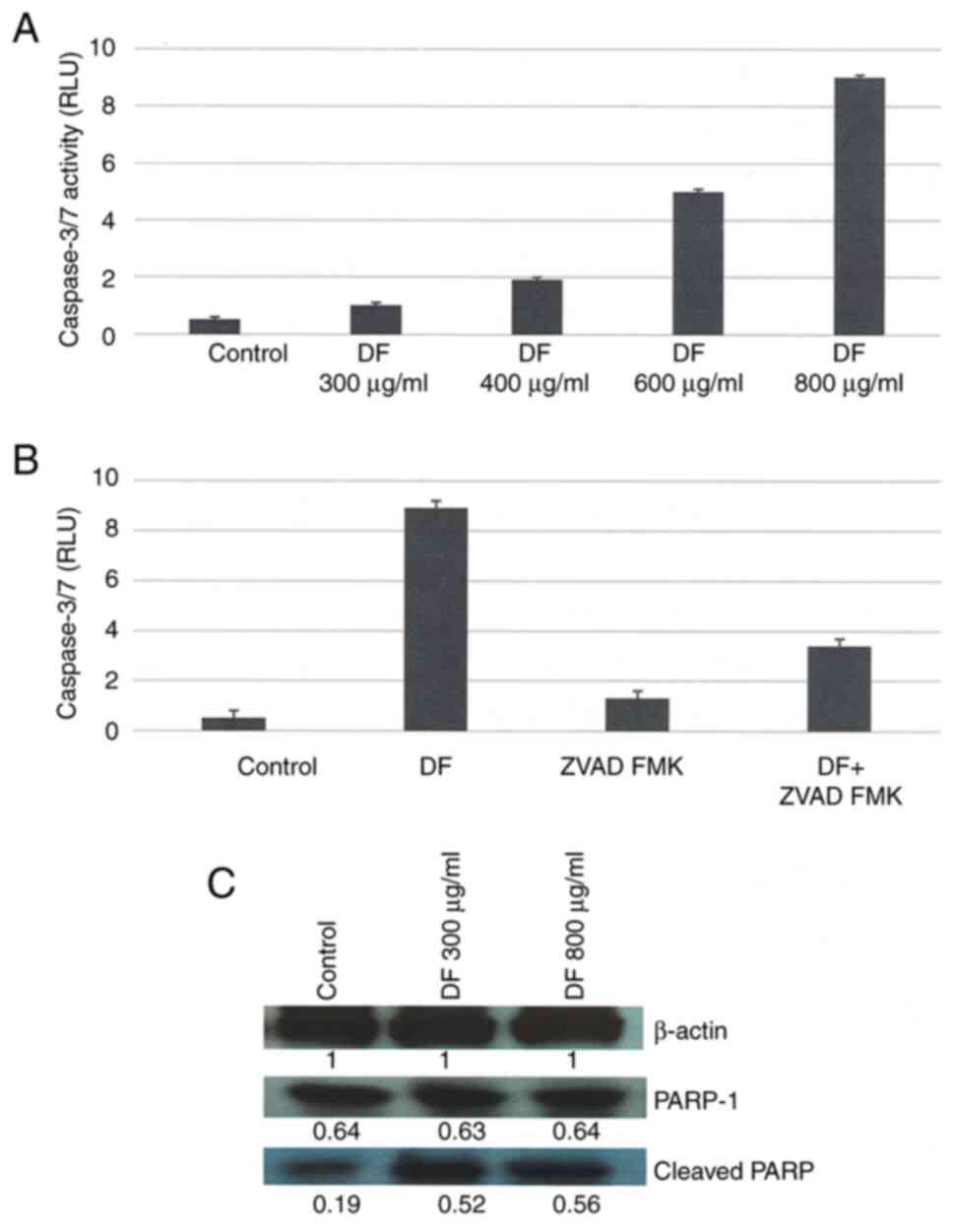
|
1
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts
& Figures 2022. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2022/2022-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdfJune
7–2024
|
|
2
|
Lin NU, Vanderplas A, Hughes ME, Theriault
RL, Edge SB, Wong YN, Blayney DW, Niland JC, Winer EP and Weeks JC:
Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival
among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the National
Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer. 118:5463–5472. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Velloso FJ, Bianco FJR, Farias JO, Torres
NE, Ferruzo PY, Anschau V, Jessus-Farreira HC, Chng TH, Sogayar MC,
Zerbini LF and Correa RG: The crossroads of breast cancer
progression: Insights into the modulation of major signaling
pathways. Onco Targets Ther. 10:5491–5524. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Won KI and Spruck C: Triple-negative
breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (Review).
Int J Oncol. 57:1245–1261. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gradishar WJ, Moran MS and Abraham J: NCCN
Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast Cancer Version 4.
2022.Available from:. www.nccn.org
|
|
6
|
Ye L, Jia Y, Ji KE, Saunders AJ, Xue K, Ji
J, Mason MD and Jiang WG: Traditional Chinese medicine in
prevention and treatment of breast cancer and metastasis. Oncol
Lett. 10:1240–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Z, Zhang Q, Yu L, Zhu J, Cao Y and
Gao X: The signaling pathways and targets of traditional Chinese
medicine and natural medicine in triple-negative breast cancer. J
Ethnopharmacol. 264:1132492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Telang NT, Li G, Sepkovic DW, Bradlow HL
and Wong GYC: Anti-proliferative effects of Chinese herb Cornus
officinalis in a cell culture model for estrogen receptor positive
clinical breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 5:22–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Telang N, Li G, Katdare M, Sepkovic D,
Bradlow L and Wong G: Inhibitory effects of Chinese nutritional
herbs in isogenic breast carcinoma cells with modulated estrogen
receptor function. Oncol Lett. 12:3949–3957. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Telang NT, Li G, Katdare M, Sepkovic DW,
Bradlow HL and Wong GYC: The nutritional herb Epimedium
grandiflorum inhibits the growth in a model for the Luminal A
molecular subtype of breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:2477–2482. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Telang NT, Nair HB and Wong GYC: Growth
inhibitory efficacy of Cornus officinalis in a cell culture model
for triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 17:5261–5266.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Telang NT, Nair HB and Wong GYC: Growth
inhibitory efficacy of the nutritional herb Psoralia corylifolia in
a model of triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Funct Nutr.
2:82021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Telang NT, Nair HB and Wong GYC: Growth
inhibitory efficacy of Chinese herbs in a cellular model for
triple-negative breast cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14:13182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Telang N, Nair HB and Wong GYC:
Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of Dipsacus asperoides
in a cellular model for triple-negative breast cancer. Arch Breast
Cancer. 9:66–75. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J,
Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark I, Bayani N, Cope JP, Tong F, et al: A
collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of
functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 10:515–527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxret I, Strzepak T,
Costello D, Crowley P, Xing L, Hung MC, Bonfiglio T, Hicks DG and
Tang P: The expression pattwerns of ER, PR, HER-2, CK 5/6, EGFR, Ki
67 and AR by immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell
lines. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 4:35–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lehmann BD, Colaprico A, Silva TC, Chen J,
An H, Ban Y, Huang H, Wang L, James JL, Balko JM, et al:
Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes. Nat Commun. 12:62762021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burkhart DL and Sage J: Cellular
mechanisms of tumor suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat Rev
Cancer. 8:671–682. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Otto T and Sicinski P: Cell cycle proteins
as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:93–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang EJ, Lee WJ, Cho SH and Choi SW:
Proliferative effects of flavan-3-olsand propelargonidins from
rhizomes of Drynaria fortunei on MCF-7 and osteoblastic cells. Arch
Pharmacol Res. 26:620–630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wong KC, Pang WY, Wang XL, Mok SK, Lai WP,
Chow HK, Leung PC, Yao SX and Wong MS: Drynaria fortunei-derived
total flavonoid fraction and isolated compounds exert
oestrogen-like protective effects in bone. Br J Nutr. 110:475–485.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang ST, Chang CC, Pang JH, Huang HS,
Chou SC, Kao MC and You HL: Drynaria fortunei promoted angiogenesis
associated with modified MMP-2/TMP-2 balance and activation of VEGF
ligand/receptors expression. Front Pharmacol. 9:9792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiao X, Lin XH, Liang YH, Dong J, Guo DA
and Ye M: Comprehensive chemical analysis of the rhizomes of
Drynaria fortune by orthogonal pre-separation and liquid
chromatography mass spectrometry. Planta Med. 80:330–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie L, Zhao S, Zhang X, Huang W, Qiao L,
Zhan D, Ma C, Gong W, Dang H and Lu H: Wenshengyang recipe treats
infertility through hormonal regulation and inflammatory responses
revealed by transcriptome analysis and network pharmacology. Front
Pharmacol. 13:9175442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Telang NT: Stem cell models for breast and
colon cancer: Experimental approach for drug discovery. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:92232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Telang NT: Natural products as drug
candidates for breast cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 26:3492023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hannen R and Bartsch JW: Essential roles
of telomerase reverse transcriptase hTERT in cancer stemness and
metastasis. FEBS Lett. 592:2023–2031. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kumar VE, Nambiar R, De Souza C, Nguyen A,
Chien J and Lam KS: Targeting epigenetic modifiers of tumor
plasticity and cancer stem cell behavior. Cells. 11:14032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gooding AJ and Scheiman WP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition programs and cancer stem cell
phenotypes Mediators of breast cancer therapy resistance. Mol
Cancer Res. 18:1257–1270. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ganeshan K and Xu B: Telomerase inhibitors
from natural products and their anticancer potential. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:132017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liskova A, Kubatka P, Samec M, Zubor P,
Mlyneck M, Bielik T, Samuel SM, Zulli A, Kwon TK and Busselberg D:
Dietary phytochemicals targeting cancer stem cells. Molecules.
24:8992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin W: Role of JAK/STAT 3 signaling in the
regulation of metastasis, the transition of cancer stem cells and
chemo-resistance of cancer by epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Cells. 9:2172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|