The B-type cytochrome family comprises electron
transport proteins containing heme. The redox-active center of
these proteins is iron protoporphyrin IX, which can be
non-covalently bound to other protein matrices. Cytochrome b561
(Cytb561) is a member of the B-type cytochrome family, and is a
transmembrane protein containing two heme-b subunits embedded
within the membrane. It has a maximum absorbance wavelength in the
redox absorption spectrum of ~561 nm, which is reflected in its
name. The Cytb561 protein consists of 200–300 amino acids,
approximately half of which are embedded within the membrane
bilayer. Cytb561 can transmit electrons across chromaffin granule
membranes (1,2) and facilitate transmembrane electron
transfer (3).
The Cytb561 family is named after the specific
cytochrome b561 (CYB561), which was identified and named in bovine
chromaffin granule membranes in 1971 by Flatmark et al
(4). Based on an analysis of the
CYB561 gene sequence from chromaffin granules of the bovine adrenal
gland, it was discovered that this protein family exists in various
organs and cells across multiple species, of animals, including
humans (5), mice (6), Drosophila melanogaster
(7), Anopheles gambiae
(8), Caenorhabditis elegans
(9) and planarian species (10), and plants such as Arabidopsis
thalania (11) and cultivated
rice (12). Cytb561, unique to
eukaryotes, exhibits a high degree of conservation, implying
similar structures and functions across different species (13). Mammalian Cytb561 proteins and
predicted plant Cytb561 proteins are highly hydrophobic and can
transfer electrons from the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane
to the extracellular space or intracellular vesicles. They have
important roles in various physiological processes, including iron
absorption, cellular defense, nitrate reduction and signal
transduction. Through multiple sequence alignment, Cytb561 family
members from various sources have been categorized into seven
categories (14):
Animals/neuroendocrine, plants, insects, fungi, animals/tumor
suppression factor (TSF), plants containing a DoH domain, and
stromal cell-derived receptor 2 (SDR2). In 1974, Silsand and
Flatmark (15) purified Cyb561 from
bovine chromaffin granules; however, other natural Cytb561 proteins
have not been purified due to their low abundance in natural
sources. Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, six members
of the human Cytb561 (hCytb561) family (16) have been identified: CYB561 encoded
by CYB561A1; duodenal CYB561 (Dcytb) encoded by CYB561A2 (17); lysosomal CYB561 (LCytb) encoded by
CYB561A3; SDR2 encoded by ferric chelate reductase 1 (FRRS1);
101F6/human TSF encoded by CYB561D2 (14); and 101F6 analogs (16). To date, the most extensively studied
members of this family, which are associated with tumors, are
CYB561, Dcytb, LCytb, SDR2 and 101F6.
In the present article, the structures of the
Cytb561 family, basic functional characteristics of hCytb561 family
members, and the roles of the five key family members in various
diseases and tumors are reviewed.
Iron metabolism in the human body is a tightly
regulated system, involving iron absorption, transport and
distribution, the formation of various important functional
ferritin molecules, storage and excretion (18). Iron is absorbed into the bloodstream
via active transport by mucosal cells in the duodenum and upper
segment of the jejunum. In the bloodstream, ferric ions
(Fe3+) are bound and transported by transferrin. After
entering cells through transferrin receptor 1 (TFRC), these ions
are reduced and released into the cytoplasmic labile iron pool
(LIP), and excess iron is stored in ferritin (19). TFRC is an iron import protein that
is post-transcriptionally regulated by iron levels; it contributes
to iron absorption and is the main means of iron uptake in
proliferating cells (20). Ferritin
is an iron-binding protein that primarily functions to store and
stabilize iron, and also acts as an iron oxidase, converting
ferrous ions (Fe2+) to Fe3+ during iron ion
internalization and storage (21).
Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) is a proton-coupled
transmembrane metal ion transporter in mammals, which mediates iron
absorption in the small intestine and facilitates iron transport
from the endosome (22).
Fe2+ transported from the endosome by DMT1 contributes
to the LIP, which is involved in cellular metabolism (23). Iron absorption is regulated by
multifactorial feedback, and the synthesis of ferritin, transferrin
and its receptor TFRC is regulated by iron levels in the body.
Ascorbic acid (ASC) acts as a cofactor for numerous
important enzymes involved in mammalian metabolism (24), including dopamine β-hydroxylase in
the vesicles of catecholamine storage granules (25) and peptide-amide monooxygenase in
neuropeptide storage granules (24). The regeneration of ASC in
neuropeptide storage vesicles is necessary to sustain amidated
peptide biosynthesis. The cyclical regeneration of ASC contributes
to cell physiology and serves as a key regulator of iron metabolism
(26). This vitamin affects iron
metabolism by promoting the intestinal absorption of non-heme iron
(27), increasing
transferrin-dependent iron uptake, and promoting the
ASC/dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) cycle at the plasma membrane to
increase the uptake of non-transferrin-bound iron (28–30).
It also promotes ferritin synthesis by increasing or maintaining
the level of iron regulatory protein 1 in its non-iron-bound form
to promote cytoplasmic aconitase reactivity (31,32).
Additionally, ASC regulates iron metabolism by inhibiting the
autophagy of ferritin (33),
inhibiting lysosomal ferritin degradation (33,34)
and regulating cell iron efflux (30,35).
Iron is one of the most important trace elements in
mammals due to its important role in cell replication, metabolism
and growth (36). Iron also
contributes to the generation of free radicals via oxidation and
reduction, such as in the Fenton reaction (37), the destruction of lipids and
proteins, DNA base modification, DNA strand breakage and other
mutations associated with oxidative DNA damage (38), as well as the occurrence and
development of cancer (39). To
sustain high intracellular iron levels and promote the function of
iron-dependent proteins, malignant tumor cells modulate the
expression or activity of various iron-related proteins. For
example, elevated plasma ferritin levels are associated with
advanced clinical stages and poor prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma (40) and
hepatobiliary cancer (41). DMT1 is
highly expressed in colorectal cancer, and inhibiting its activity
can restrict tumor growth by inhibiting the Janus kinase-signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway
(42). Increased serum
concentrations of heavy-chain ferritin (FTH) in patients with
melanoma are associated with increased numbers of circulating
CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells, which
contribute to the suppression of antitumor immune function
(43). Moreover, the proliferation
of CD8+ T cells, critical in the antitumor immune
response, requires iron stored in FTH (44). As highlighted in a previous review,
disrupted iron homeostasis can be observed at all stages of cancer
development (45). Various iron
metabolism-related proteins have been demonstrated to be involved
in the initiation, proliferation and metastasis of malignant tumors
(46). The expression levels of
certain genes associated with iron metabolism have been indicated
to be powerful indicators of tumor prognosis. For example,
upregulated TFRC expression in breast cancer (20,47)
and downregulated ferritin (48) or
ferriportin expression (49) are
associated with a poor prognosis. The regulation of iron
homeostasis, by iron depletion and the targeting of iron
metabolism, has shown strong and extensive antitumor effects,
suggesting that iron metabolism is a potential target for cancer
therapy (50). As the hCytb561
family plays an important role in iron metabolism and cancer, it is
expected to become a key target for the treatment of malignant
tumors.
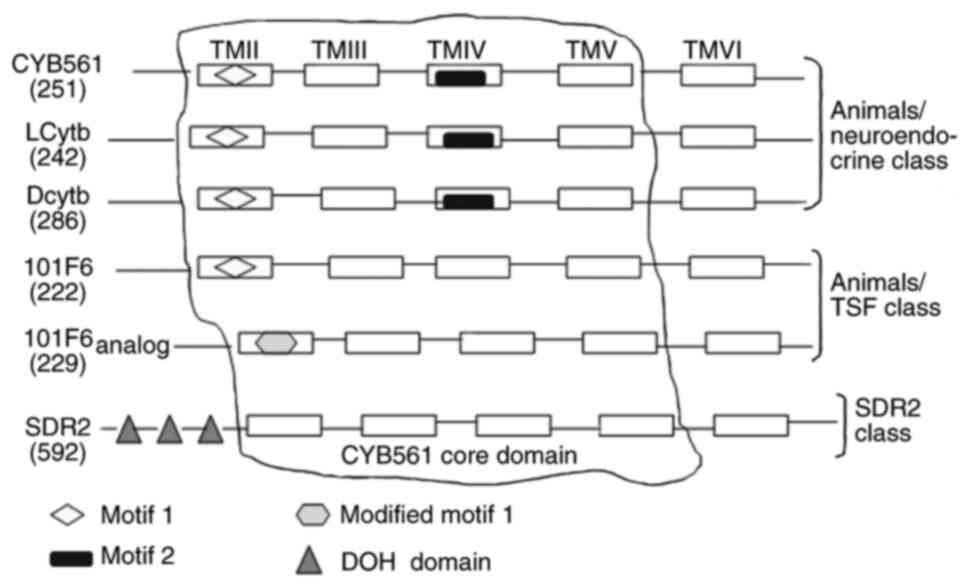
The Cytb561 family of transmembrane proteins
typically contain six transmembrane α-helix domains (51–53).
Sequence alignment indicates that all retrieved sequences exhibit
four completely conserved sequences located in the second to fifth
transmembrane segments (14). Four
consecutive central helices form the core domain of CYB561
(Fig. 1). The core of the four
helices comprises two pairs of histidine (His) residues (14,51);
the first and third residues are located on the cytoplasmic side,
while the second and fourth are located at the boundary region of
the outer (or intravesicular) hydrophilic ring and transmembrane
helix (54–56). The CYB561 core domain, via its four
His residues, coordinates to heme-b groups on both sides of the
membrane (57–59). The core domain facilitates
intramolecular electron transfer by accepting electrons from ASC
(60). It is structurally similar
to other redox domains, such as dopamine β-monoxygenase redox
domains and the dopamine β-monooxygenase N-terminal (DOMON) domain
(24), and can be a component of
other proteins. The basic characteristics of hCytb561 family
members, including their genomic locations and sequence sizes, are
shown in Table I. They are divided
into different categories according to their specific motifs
(Fig. 1). CYB561, Dcytb and LCytb
have been assigned to the animals/neuroendocrine class due to
presence of motif 1
[FN(X)HP(X)2M(X)2G(X)5G(X)ALLVYR]
and motif 2 [YSLHSW(X)G] in their core structures (15). 101F6 and its analogs have been
classified in the animals/TSF class due to the presence of modified
motif 1
[LFSWHP(X)2M(X)3F(X)3M(X)EAIL(X)SP(X)2SS]
in their structures. SDR2 belongs to the SDR2 class due to the
presence of three DOH domains or a DOMON domain (14), which is homologous to a domain found
in dopamine-β-hydroxylase (61).
All family members have transmembrane electron transfer activity or
contain at least two heme groups that may contribute to the
integrity or binding of the transmembrane protein structure
(56). The double-electrode
voltage-clamp technique has demonstrated the ability of SDR2 to
conduct electric current (62).
Human CYB561 is estimated to lack the first 22 amino
acids at the N-terminal of the cytoplasmic side predicted for the
bovine cell sequence. Srivastava et al (63) hypothesized that the gene product of
human CYB561 contains five transmembrane helical structures. The
crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana Cytb561 suggests
that this protein may function as a dimer (13). Additionally, two highly conserved
amino acids, Lys-81 and His-106, have been demonstrated to be
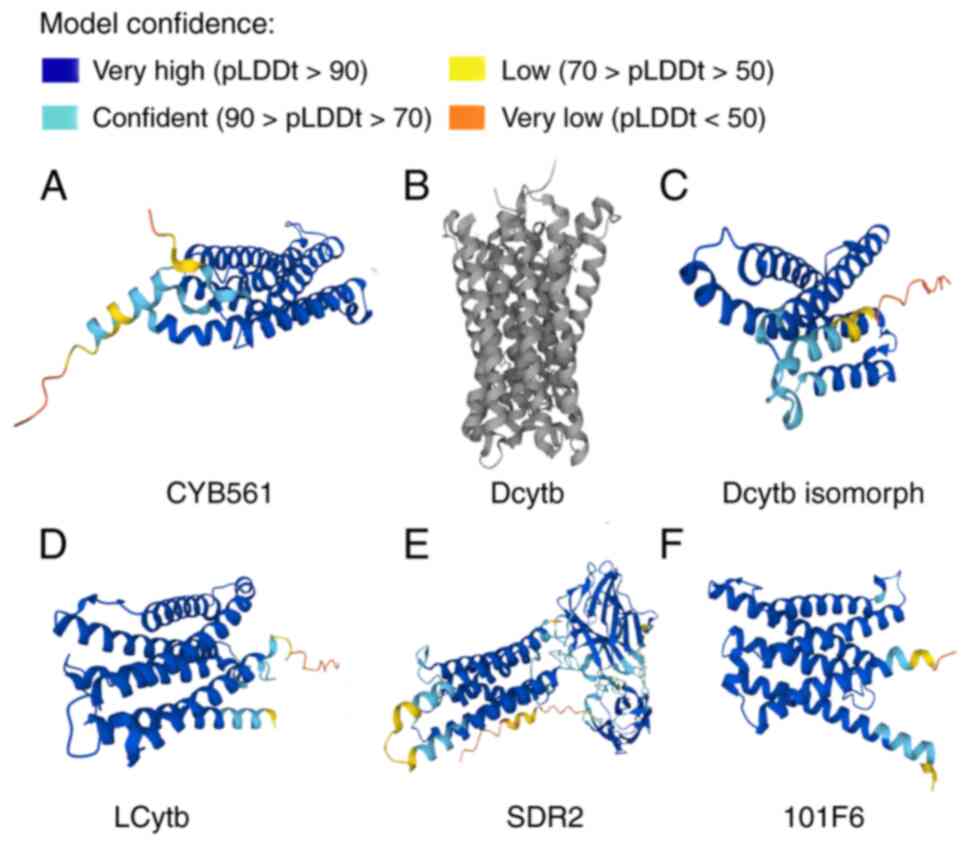
important in substrate recognition and catalysis (64). To illustrate the structures of
hCytb561 family members, data on their 3-dimensional structures
have been obtained from the UniProt (Universal Protein Resource)
website (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb) and are presented
in Fig. 2.
The Cytb561 family uses ASC, an extracapsular
electron donor, on one side of the membrane to provide electrons,
catalyze transmembrane electron transport, and reduce
monodehydroascorbate (MDA), a partially oxidized form of ASC that
acts as an intracapsular electron receptor, thereby facilitating
the regeneration of ASC (64,65).
Motif 2 was originally thought to be an MDA free-radical-binding
sequence (60). The reduced
expression of the CYB561 homologue in Drosophila memory
mutant (nemy) has been shown to lead to defective memory retention,
confirming the role of Cytb561 in memory retention and its
influence on neural function (66).
In addition, the role of Cytb561 in ASC regeneration has been
confirmed by the fact that ASC in erythrocytes can reduce
extracellular MDA (67,68). ASC has been confirmed to function as
an electron donor for mouse DCytb (67). Furthermore, B-type cytochromes with
biophysical properties similar to those of Cytb561 from bovine
chromaffin granules have been reported to reduce ASC in the cell
membranes of certain plants (69,70).
First identified in chromaffin vesicles that
synthesize catecholamines, CYB561 was later confirmed to be present
in neuroendocrine tissues (74).
RNA sequencing has shown that CYB561 is widely expressed in eight
systems (locomotion, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, urinary,
reproductive, endocrine and nervous systems) of the normal human
body. According to gene expression data from the Bgee database
(https://bgee.org), the CYB561 gene is expressed in the
adrenal gland and 223 other tissues. Pathologically, CYB561 is
expressed in HeLa cervical cancer cells and melanoma cells
(74). In addition, its mRNA levels
are significantly upregulated in SW480 colon cancer, HL-60 T-cell
lymphoma and K-562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells but not in
Burkitt's lymphoma (75). Under
physiological conditions, CYB561 in natural chromaffin granules,
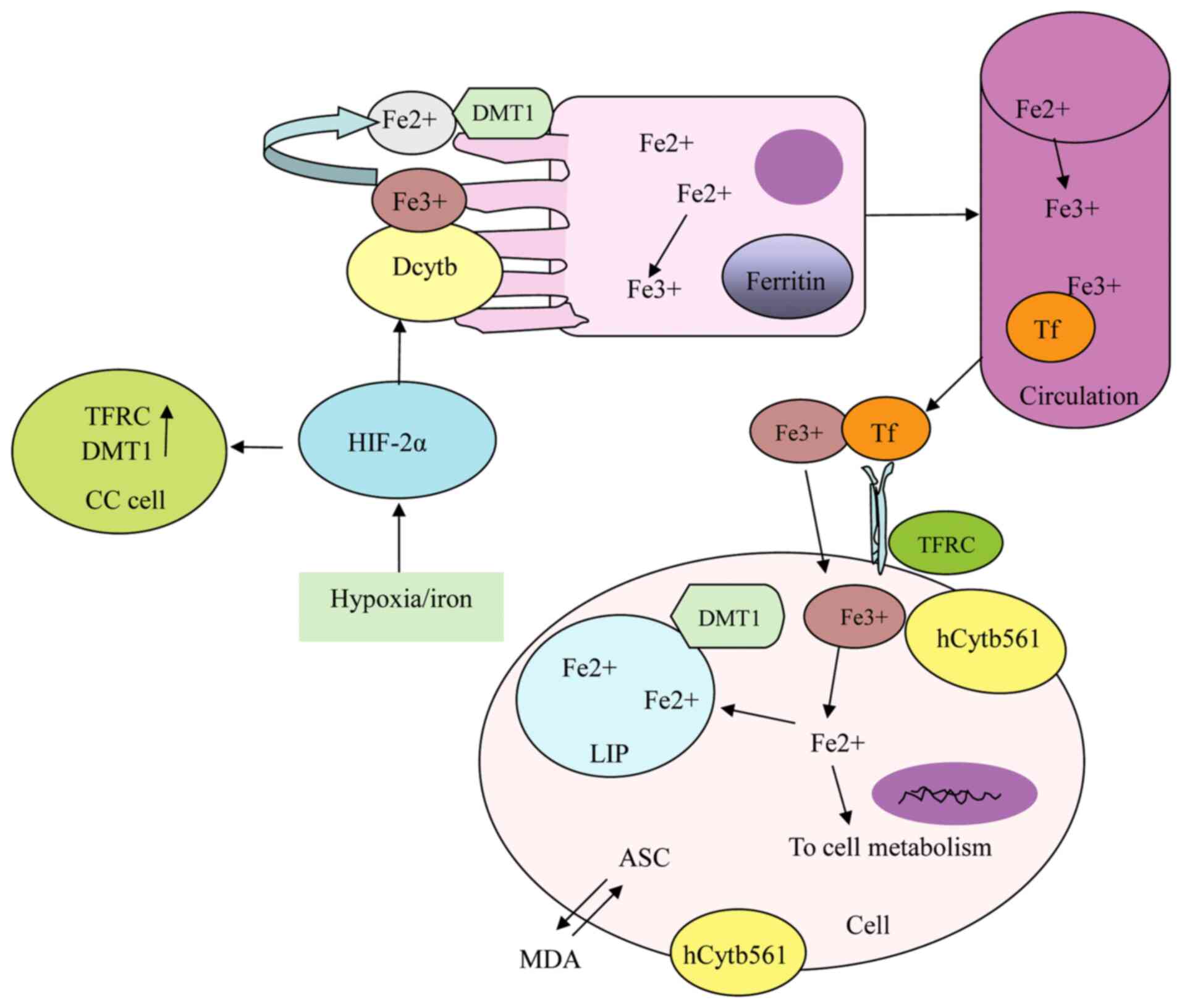
vesicles and recombinant membrane systems exhibits ‘electron
shuttle’ activity between ASC and membrane permeable ferricyanide
or MDA (57,76), which is associated with cell
metabolism and mitochondrial activation (77) (Fig.
3), and affects heart rate and blood pressure through
regulation of the adrenaline pathway (78).
Pathogenic homozygous mutations in the CYB561 gene
have been reported to lead to ASC deficiency in
catecholamine-secreting vesicles and functional dopamine
b-hydroxylase deficiency, resulting in orthostatic hypotension
syndrome (78). In
CYB561(−/-) mice, it was found that the concentration of
norepinephrine in whole brain homogenate and adrenal glands was
reduced compared with that in wild-type mice (78). CYB561 is also involved in the
progression of certain tumors and influences their prognosis. For
example, a low expression level of CYB561 mRNA was found to be
associated with a poor prognosis in patients with ovarian cancer,
suggesting that CYB561 may be a single-gene prognostic biomarker
(79). In addition, in another
study CYB561 was demonstrated to promote the growth and metastatic
potential of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer
(80). Our previous study found
that CYB561 expression was upregulated in breast cancer; associated
with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), immune cells,
histological grade and molecular subtypes; and associated with the
poor prognosis of patients (81),
which is consistent with other results reported in the literature
(82). Moreover, our previous study
demonstrated that CYB561 promotes the proliferation, migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells and inhibits apoptosis (83). The knockdown of CYB561 changes the
Fe2+ and total iron content of cancer cells and the
expression of the iron absorption and transport-related proteins
TFRC and DMT1, indicating that it is involved in the iron
metabolism of breast cancer cells (83). In addition, recent literature shows
that CYB561 plays a role in promoting the proliferation of
HER2-positive breast cancer cells by inhibiting the degradation of
H2A histone family member Y (84).
This reductase is present in the late
endolysosome-lysosome membrane; it is expressed at high levels in
the adrenal gland, lymph nodes, B lymphocytes and monocytes, but is
downregulated in sepsis (98) and
skin warts caused by human papillomavirus infection (99).
SDR2, encoded by the gene FRRS1, is a homolog of
CYB561 and Dcytb, which is localized in the cell membrane and
expressed at high levels in the liver (62), kidney (62), esophageal mucosa, oral epithelium,
gallbladder, testicles and heart, as well as in lesions associated
with asthma, dermatitis, and rhinitis (102). A recent study found that FRRS1 is
upregulated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (103). SDR2 exhibits iron chelate
reductase activity and functions as an active iron reductase that
regulates catecholamines in the brain. It reduces Fe3+
to Fe2+ prior to transportation from the endosome to the
cytoplasm (67,104) (Fig.
3).
FRRS1 has been predicted by machine learning methods
to be upregulated in the brain tissue of patients with Alzheimer's
disease and suggested to be a potential risk gene for Alzheimer's
disease (105). Linton et
al (106) found that the
expression of FRRS1 is downregulated in primary soft tissue sarcoma
of the extremities and is negatively correlated with metastatic
recurrence. In addition, they tested the combined prognostic
effects of FRRS1, helicase 4, complement Factor H and
mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor using a simple
equal-weight scoring system, and found that they had a greater
prognostic effect than tumor grading. However, by contrast, other
researchers found that FRRS1 is upregulated in SiHa and HeLa
cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells, and transfection with short
hairpin-FRRS1 inhibited the growth of these cells and promoted
their apoptosis (103).
Encoded by CYB561D2, 101F6 is highly expressed in
the pancreas, nervous system, granulocytes and human glioma
(107). It is a transmembrane
reductase with iron reductase activity (108), which uses ASC in the cytoplasm as
an electron donor to transfer electrons through the endoplasmic
reticulum for reduction of lumenal MDA and Fe3+
(109–111) (Fig.
3).
CYB561D2 is a putative tumor suppressor gene that is
located in the 3p21.3 region of the human chromosome, where allelic
deletions and genomic changes are frequently found in lung cancer
and numerous other cancers (112–114). The overlap of heterozygosity
deletion and homozygosity deletion in this region occurs frequently
in lung and breast cancer, suggesting that one or more genes in
this region play an important role in the pathogenesis of these
cancers (112–115). Recombinant adenovirus-mediated
transfection of 101F6 demonstrated that 101F6 inhibits cell growth
alters the cell cycle and induces apoptosis in human lung cancer
cells (116). In addition, the
exogenous expression of 101F6 enhances the uptake of ASC by lung
cancer cells, leading to the accumulation of cytotoxic
H2O2. This cooperatively kills tumor cells
through apoptosis and autophagy pathways, independently of caspase
activation (116). By contrast,
the upregulated expression of CYB561D2 has been found to be
associated with a higher clinical grade and shorter survival time
in patients with glioma. In vitro experiments revealed that
the overexpression of CYB561D2 in glioma increased the expression
of the immunosuppressive genes PD-L1, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand
2 and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase in co-cultured T cells (117), while CYB561D2 knockout inhibited
the growth, colony formation and migration of glioma cells and
promoted cell apoptosis (117).
The Cytb561 family is a class of transmembrane
proteins characterized by six transmembrane helices and two heme
groups, which exhibit electron transfer and ferric reductase
activities. The main members of this family, namely CYB561, Dcytb,
LCytb, SDR2 and 101F6, are involved in ASC recycling and iron
metabolism. They are widely expressed in human tissues, upregulated
or downregulated in different tumors, and involved in the
pathogenesis of a variety of diseases and tumors. In addition, they
are potential prognostic indicator for certain cancers. Although
all members of this family theoretically exhibit iron reductase
activity, they are not necessarily involved in iron metabolism in
tumors, and Dcytb is a notable example. Members of the Cytb561
family play crucial roles in the promotion or suppression of
numerous types of malignant tumors; for example, CYB561 promotes
breast cancer growth, Dcytb facilitates glioma invasion and
inhibits the growth of breast cancer and bladder cancer, CYB561A3
is crucial in the proliferation of Burkitt's lymphoma cells, and
SDR2 accelerates cervical squamous cell carcinoma growth. In
addition, 101F6 represses the growth of human lung cancer cells but
contributes to the growth of glioma cells. These transmembrane
proteins also have the potential to serve as therapeutic targets in
various tumors. The reasons are as follows: i) Their expression
levels are up- or downregulated in various tumor tissues compared
with corresponding normal tissues, and this differential expression
is associated with the prognosis of patients; for example, the
upregulated expression of CYB561 in breast cancer is a poor
prognostic factor. ii) At the cellular level, altering their
expression levels can alter the functional status of tumor cells,
such as by promoting or inhibiting cell proliferation, migration,
invasion and apoptosis. iii) At the animal level, modulating their
expression levels in tumor cells can affect the tumor size in nude
mice; for example, the knockdown of CYB561 expression level in
HER2-positive breast cancer cells reduced tumorigenicity compared
with that in the control (84). The
seemingly contradictory roles and tumor specificity of the members
of the Cytb561 family suggest that their intricate mechanisms of
action in tumors merit further study. At present, the role of this
family in tumors and the associated mechanisms are still under
investigation. To develop precise targeted treatments for patients
with tumors, it is essential to conduct further research to
elucidate the role of these iron metabolism-related proteins.
Not applicable.
This review was supported by grants from the Department of
Science and Technology of Qinghai Province in China (project no.
2024-SF-L01) and the Thousand Talents of Program of High-end
Innovation of Qinghai Province in China.
Not applicable.
XZ and ZA conceived of the review and acted as
mentors and guarantors of the work. XZ wrote the manuscript. HLe
was involved in drafting the manuscript. HLi modified the
manuscript. XG reviewed and revised the text. Data authentication
is not applicable. All authors read and approved the final version
of the manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Kelley PM and Njus D: Cytochrome b561
spectral changes associated with electron transfer in
chromaffin-vesicle ghosts. J Biol Chem. 261:6429–6432. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Srivastava M: Xenopus cytochrome b561:
Molecular confirmation of a general five transmembrane structure
and developmental regulation at the gastrula stage. DNA Cell Biol.
15:1075–1080. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asard H, Horemans N and Caubergs RJ:
Transmembrane electron transport in ascorbate-loaded plasma
membrane vesicles from higher plants involves a b-type cytochrome.
FEBS Lett. 306:143–146. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Flatmark T, Terland O and Helle KB:
Electron carriers of the bovine adrenal chromaffin granules.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 226:9–19. 1971.
|
|
5
|
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW,
Mural RJ, Sutton GG, Smith HO, Yandell M, Evans CA, Holt RA, et al:
The sequence of the human genome. Science. 291:1304–1351. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium, .
Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF, Agarwal
P, Agarwala R, Ainscough R, Alexandersson M, et al: Initial
sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature.
420:520–562. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA,
Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF,
et al: The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster.
Science. 287:2185–2195. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Holt RA, Subramanian GM, Halpern A, Sutton
GG, Charlab R, Nusskern DR, Wincker P, Clark AG, Ribeiro JM, Wides
R, et al: The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles
gambiae. Science. 298:129–149. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
C. elegans Sequencing Consortium, . Genome
sequence of the nematode C. elegans: A platform for investigating
biology. Science. 282:2012–2018. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Asada A, Kusakawa T, Orii H, Agata K,
Watanabe K and Tsubaki M: Planarian cytochrome b561: Conservation
of a six transmembrane structure and localization along the central
and peripheral nervous system. J Biochem. 131:175–182. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative, . Analysis
of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
Nature. 408:796–815. 2004.
|
|
12
|
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang
R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, et al: A
draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp.
japonica). Science. 296:92–100. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu P, Ma D, Yan C, Gong X, Du M and Shi Y:
Structure and mechanism of a eukaryotic transmembrane
ascorbate-dependent oxidoreductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:1813–1818. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsubaki M, Takeuchi F and Nakanishi N:
Cytochrome b561 protein family: Expanding roles and versatile
transmembrane electron transfer abilities as predicted by a new
classification system and protein sequence motif analyses. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1753:174–190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silsand T and Flatmark T: Purification of
cytochrome b-561: An integral heme protein of the adrenal
chromaffin granule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 359:257–266.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bérczi A and Zimányi L: The trans-membrane
cytochrome b561 proteins: Structural information and biological
function. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 15:745–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McKie AT, Barrow D, Latunde-Dada GO, Rolfs
A, Sager G, Mudaly E, Mudaly M, Richardson C, Barlow D, Bomford A,
et al: An iron-regulated ferric reductase associated with the
absorption of dietary iron. Science. 291:1755–1759. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abbate V and Hider R: Iron in biology.
Metallomics. 9:1467–1469. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galy B, Conrad M and Muckenthaler M:
Mechanisms controlling cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 25:133–155. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawabata H: Transferrin and transferrin
receptors update. Free Radic Biol Med. 133:46–54. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Srai SK and Sharp P: Proteins of Iron
Homeostasis. Iron Physiology and Pathophysiology in Humans.
Anderson GJ and McLaren GD: Humana Press; Totowa NJ, USA: pp.
pp3–25. 2012, ISBN 978-1-60327-484-5. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hubert N and Hentze MW: Previously
uncharacterized isoforms of divalent metal transporter (DMT)-1:
Implications for regulation and cellular function. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:12345–12350. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lemler DJ, Lynch ML, Tesfay L, Deng Z,
Paul BT, Wang X, Hegde P, Manz DH, Torti SV and Torti FM: DCYTB is
a predictor of outcome in breast cancer that functions via
iron-independent mechanisms. Breast Cancer Res. 19:252017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Menniti FS, Knoth J and Diliberto EJ Jr:
Role of ascorbic acid in dopamine beta-hydroxylation. The
endogenous enzyme cofactor and putative electron donor for cofactor
regeneration. J Biol Chem. 261:16901–16908. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kent UM and Fleming PJ: Purified
cytochrome b561 catalyzes transmembrane electron transfer for
dopamine beta-hydroxylase and peptidyl glycine alpha-amidating
monooxygenase activities in reconstituted systems. J Biol Chem.
262:8174–8178. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lane DJ and Richardson DR: The active role
of vitamin C in mammalian iron metabolism:. Much more than just
enhanced iron absorption! = Free Radic Biol Med. 75:69–83.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Atanassova BD and Tzatchev KN: Ascorbic
acid-important for iron metabolism. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 50:11–16.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lane DJR and Lawen A: Non-transferrin iron
reduction and uptake are regulated by transmembrane ascorbate
cycling in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 283:12701–12708. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lane DJ, Robinson SR, Czerwinska H, Bishop
GM and Lawen A: Two routes of iron accumulation in astrocytes:
Ascorbate-dependent ferrous iron uptake via the divalent metal
transporter (DMT1) plus an independent route for ferric iron.
Biochem J. 432:123–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lane DJ, Chikhani S, Richardson V and
Richardson DR: Transferrin iron uptake is stimulated by ascorbate
via an intracellular reductive mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1833:1527–1541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toth I, Rogers JT, McPhee JA, Elliott SM,
Abramson SL and Bridges KR: Ascorbic acid enhances iron-induced
ferritin translation in human leukemia and hepatoma cells. J Biol
Chem. 270:2846–2852. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Toth I and Bridges KR: Ascorbic acid
enhances ferritin mRNA translation by an IRP/aconitase switch. J
Biol Chem. 270:19540–19544. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bridges KR: Ascorbic acid inhibits
lysosomal autophagy of ferritin. J Biol Chem. 262:14773–1478. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hoffman KE, Yanelli K and Bridges KR:
Ascorbic acid and iron metabolism: Alterations in lysosomal
function. Am J Clin Nutr. 54 (6 Suppl):S1188S–S1192S. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Richardson DR: Role of ceruloplasmin and
ascorbate in cellular iron release. J Lab Clin Med. 134:454–465.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Crichton R: In Iron Metabolism: From
Molecular Mechanisms to Cinical Consequences. pp. 17–58. John Wiley
and Sons; 2009
|
|
37
|
Sun H, Zhang C, Cao S, Sheng T, Dong N and
Xu Y: Fenton reactions drive nucleotide and ATP syntheses in
cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 10:448–459. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Akatsuka S, Yamashita Y, Ohara H, Liu YT,
Izumiya M, Abe K, Ochiai M, Jiang L, Nagai H, Okazaki Y, et al:
Fenton reaction induced cancer in wild type rats recapitulates
genomic alterations observed in human cancer. PLoS One.
7:e434032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Torti SV and Torti FM: Iron and cancer:
2020 vision. Cancer Res. 80:5435–5448. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bian Z, Hann HW, Ye Z, Yin C, Wang Y, Fang
W, Wan S, Wang C and Tao K: Ferritin level prospectively predicts
hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus
infection. Oncol Lett. 16:3499–3508. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Song A, Eo W, Kim S, Shim B and Lee S:
Significance of serum ferritin as a prognostic factor in advanced
hepatobiliary cancer patients treated with Korean medicine: A
retrospective cohort study. BMC Complement Altern Med. 18:1762018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xue X, Ramakrishnan SK, Weisz K, Triner D,
Xie L, Attili D, Pant A, Győrffy B, Zhan M, Carter-Su C, et al:
Iron uptake via DMT1 integrates cell cycle with JAK-STAT3 signaling
to promote colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell Metab. 24:447–461. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gray CP, Arosio P and Hersey P:
Association of increased levels of heavy-chain ferritin with
increased CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cell levels in patients with
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 9:2551–2559. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu NQ, De Marchi T, Timmermans AM,
Beekhof R, Trapman-Jansen AM, Foekens R, Look MP, van Deurzen CH,
Span PN, Sweep FC, et al: Ferritin heavy chain in triple negative
breast cancer: A favorable prognostic marker that relates to a
cluster of differentiation 8 positive (CD8+) effector T-cell
response. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:1814–1827. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lelièvre P, Sancey L, Coll JL, Deniaud A
and Busser B: Iron dysregulation in human cancer: Altered
metabolism, biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring and
rationale for therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:35242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Yu L, Ding J and Chen Y: Iron
metabolism in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Staka CM, Rakha EA,
Ball G, Green AR, Aleskandarany M, Paish EC, Douglas Macmillan R,
Nicholson RI, et al: Transferrin receptor (CD71) is a marker of
poor prognosis in breast cancer and can predict response to
tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 119:283–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Alkhateeb AA, Han B and Connor JR:
Ferritin stimulates breast cancer cells through an iron-independent
mechanism and is localized within tumor-associated macrophages.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 137:733–744. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pinnix ZK, Miller LD, Wang W, D'Agostino R
Jr, Kute T, Willingham MC, Farris M, Petty WJ, de Hoyos A, Weaver
KE and Wentworth S: Ferroportin and iron regulation in breast
cancer progression and prognosis. Sci Transl Med. 2:43ra562010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Morales M and Xue X: Targeting iron
metabolism in cancer therapy. Theranostics. 11:8412–8429. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bashtovyy D, Bérczi A, Asard H and Páli T:
Structure prediction for the di-heme cytochrome b561 protein
family. Protoplasma. 221:31–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Perin MS, Fried VA, Slaughter CA and
Südhof TC: The structure of cytochrome b561, a secretory
vesicle-specific electron transport protein. EMBO J. 7:2697–2703.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Asard H, Kapila J, Verelst W and Bérczi A:
Higher-plant plasma membrane cytochrome b561: A protein in search
of a function. Protoplasma. 217:77–93. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Degli Esposti M, Kamensky YuA, Arutjunjan
AM and Konstantinov AA: A model for the molecular organization of
cytochrome beta-561 in chromaffin granule membranes. FEBS Lett.
254:74–78. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tsubaki M, Nakayama M, Okuyama E, Ichikawa
Y and Hori H: Existence of two heme B centers in cytochrome b561
from bovine adrenal chromaffin vesicles as revealed by a new
purification procedure and EPR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem.
272:23206–23210. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Oakhill JS, Marritt SJ, Gareta EG, Cammack
R and McKie AT: Functional characterization of human duodenal
cytochrome b (Cybrd1): Redox properties in relation to iron and
ascorbate metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1777:260–268. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bérczi A, Su D, Lakshminarasimhan M,
Vargas A and Asard H: Heterologous expression and site-directed
mutagenesis of an ascorbate-reducible cytochrome b561. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 443:82–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kamensky Y, Liu W, Tsai AL, Kulmacz RJ and
Palmer G: Axial ligation and stoichiometry of heme centers in
adrenal cytochrome b561. Biochemistry. 46:8647–8658. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Okuyama E, Yamamoto R, Ichikawa Y and
Tsubaki M: Structural basis for the electron transfer across the
chromaffin vesicle membranes catalyzed by cytochrome b561: Analyses
of cDNA nucleotide sequences and visible absorption spectra.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1383:269–278. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Takeuchi F, Kobayashi K, Tagawa S and
Tsubaki M: Ascorbate inhibits the carbethoxylation of two histidyl
and one tyrosyl residues indispensable for the transmembrane
electron transfer reaction of cytochrome b561. Biochemistry.
40:4067–4076. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Aravind L: DOMON: An ancient extracellular
domain in dopamine beta-monooxygenase and other proteins. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:524–526. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Picco C, Scholz-Starke J, Naso A, Preger
V, Sparla F, Trost P and Carpaneto A: How are cytochrome b561
electron currents controlled by membrane voltage and substrate
availability? Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:384–391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Srivastava M, Gibson KR, Pollard HB and
Fleming PJ: Human cytochrome b561: A revised hypothesis for
conformation in membranes which reconciles sequence and functional
information. Biochem J. 303:915–921. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Nakanishi N, Takeuchi F and Tsubaki M:
Histidine cycle mechanism for the concerted proton/electron
transfer from ascorbate to the cytosolic haem b centre of
cytochrome b561: A unique machinery for the biological
transmembrane electron transfer. J Biochem. 142:553–560. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kipp BH, Kelley PM and Njus D: Evidence
for an essential histidine residue in the ascorbate-binding site of
cytochrome b561. Biochemistry. 40:3931–3937. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Iliadi KG, Avivi A, Iliadi NN, Knight D,
Korol AB, Nevo E, Taylor P, Moran MF, Kamyshev NG and Boulianne GL:
Nemy encodes a cytochrome b561 that is required for Drosophila
learning and memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19986–19991. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Su D and Asard H: Three mammalian
cytochromes b561 are ascorbate-dependent ferrireductases. FEBS J.
273:3722–3734. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
VanDuijn MM, Tijssen K, VanSteveninck J,
Van Den Broek PJ and Van Der Zee J: Erythrocytes reduce
extracellular ascorbate free radicals using intracellular ascorbate
as an electron donor. J Biol Chem. 275:27720–27725. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Asard H, Venken M, Caubergs R, Reijnders
W, Oltmann FL and De Greef JA: b-Type cytochromes in higher plant
plasma membranes. Plant Physiol. 90:1077–1083. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Askerlund P, Larsson C and Widell S:
Cytochromes of plant plasma membranes. Characterization by
absorbance difference spectroscopy and redox titration. Physiol
Plant. 76:123–134. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Vargas JD, Herpers B, McKie AT, Gledhill
S, McDonnell J, van den Heuvel M, Davies KE and Ponting CP: Stromal
cell-derived receptor 2 and cytochrome b561 are functional ferric
reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1651:116–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Herrmann T, Muckenthaler M, van der Hoeven
F, Brennan K, Gehrke SG, Hubert N, Sergi C, Gröne HJ, Kaiser I,
Gosch I, et al: Iron overload in adult Hfe-deficient mice
independent of changes in the steady-state expression of the
duodenal iron transporters DMT1 and Ireg1/ferroportin. J Mol Med.
82:39–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Escriou V, Laporte F, Garin J, Brandolin G
and Vignais PV: Purification and physical properties of a novel
type of cytochrome b from rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol
Chem. 269:14007–14014. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pruss RM and Shepard EA: Cytochrome b561
can be detected in many neuroendocrine tissues using a specific
monoclonal antibody. Neuroscience. 22:149–157. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Srivastava M: Genomic structure and
expression of the human gene encoding cytochrome b561, an integral
protein of the chromaffin granule membrane. J Biol Chem.
270:22714–22720. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Njus D and Kelley PM: The
secretory-vesicle ascorbate-regenerating system: A chain of
concerted H+/e(−)-transfer reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1144:235–248. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Olak ME, Thirdborough SM, Ung CY, Elliott
T, Healy E, Freeman TC and Ardern-Jones MR: Distinct molecular
signature of human skin langerhans cells denotes critical
differences in cutaneous dendritic cell immune regulation. J Invest
Dermatol. 134:695–703. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Van den Berg MP, Almomani R, Biaggioni I,
van Faassen M, van der Harst P, Silljé HHW, Mateo Leach I,
Hemmelder MH, Navis G, Luijckx GJ, et al: Mutations in CYB561
causing a novel orthostatic hypotension syndrome. Circ Res.
122:846–854. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Willis S, Villalobos VM, Gevaert O,
Abramovitz M, Williams C, Sikic BI and Leyland-Jones B: Single gene
prognostic biomarkers in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
11:e01491832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Olarte CK and Bagamasbad DP: SAT-132 the
secretory vesicle membrane protein, CYB561, promotes the growth and
metastatic potential of castration-resistant neuroendocrine
prostate cancer. J Endocr Soc. 4 (Suppl 1):SAT–132. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zhou X, Shen G, Ren D, Guo X, Han J, Guo
Q, Zhao F, Wang M, Dong Q, Li Z and Zhao J: Expression and clinical
prognostic value of CYB561 in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 148:1879–1892. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yang X, Zhao Y, Shao Q and Jiang G:
Cytochrome b561 serves as a potential prognostic biomarker and
target for breast cancer. Int J Gen Med. 14:10447–10464. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhou X, Guo X, Han J, Wang M, Liu Z, Ren
D, Zhao J and Li Z: Cytochrome b561 regulates iron metabolism by
activating the Akt/mTOR pathway to promote Breast Cancer Cells
proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 431:1137602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhao T, Wang C, Zhao N, Qiao G, Hua J,
Meng D, Liu L, Zhong B, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: CYB561 promotes HER2+
breast cancer proliferation by inhibiting H2AFY degradation. Cell
Death Discov. 10:382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ganasen M, Togashi H, Takeda H, Asakura H,
Tosha T, Yamashita K, Hirata K, Nariai Y, Urano T, Yuan X, et al:
Structural basis for promotion of duodenal iron absorption by
enteric ferric reductase with ascorbate. Commun Biol. 1:1202018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Su D, May JM, Koury MJ and Asard H: Human
erythrocyte membranes contain a cytochrome b561 that may be
involved in extracellular ascorbate recycling. J Biol Chem.
281:39852–39859. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wyman S, Simpson RJ, McKie AT and Sharp
PA: Dcytb (Cybrd1) functions as both a ferric and a cupric
reductase in vitro. FEBS Lett. 582:1901–1906. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Asard H, Barbaro R, Trost P and Bérczi A:
Cytochromes b561: Ascorbate-mediated trans-membrane electron
transport. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:1026–1035. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Choi J, Masaratana P, Latunde-Dada GO,
Arno M, Simpson RJ and McKie AT: Duodenal reductase activity and
spleen iron stores are reduced and erythropoiesis is abnormal in
Dcytb knockout mice exposed to hypoxic conditions. J Nutr.
142:1929–1934. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Xue X, Taylor M, Anderson E, Hao C, Qu A,
Greenson JK, Zimmermann EM, Gonzalez FJ and Shah YM:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α activation promotes colorectal cancer
progression by dysregulating iron homeostasis. Cancer Res.
72:2285–2293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Brookes MJ, Hughes S, Turner FE, Reynolds
G, Sharma N, Ismail T, Berx G, McKie AT, Hotchin N, Anderson GJ, et
al: Modulation of iron transport proteins in human colorectal
carcinogenesis. Gut. 55:1449–1460. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen R, Cao J, Jiang W, Wang S and Cheng
J: Upregulated expression of CYBRD1 predicts poor prognosis of
patients with ovarian cancer. J Oncol. 2021:75484062021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Qing M, Zhou J, Chen W and Cheng L: Highly
expressed CYBRD1 associated with glioma recurrence regulates the
immune response of glioma cells to interferon. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2021:27932222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Boult J, Roberts K, Brookes MJ, Hughes S,
Bury JP, Cross SS, Anderson GJ, Spychal R, Iqbal T and Tselepis C:
Overexpression of cellular iron import proteins is associated with
malignant progression of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:379–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Rychtarcikova Z, Lettlova S, Tomkova V,
Korenkova V, Langerova L, Simonova E, Zjablovskaja P,
Alberich-Jorda M, Neuzil J and Truksa J: Tumor-initiating cells of
breast and prostate origin show alterations in the expression of
genes related to iron metabolism. Oncotarget. 8:6376–6398. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lee HY, Li CC, Li WM, Hsu YL, Yeh HC, Ke
HL, Yeh BW, Huang CN, Li CF, Kuo PL and Wu WJ: Identification of
potential genes in upper tract urothelial carcinoma using
next-generation sequencing with bioinformatics and in vitro
analyses. PeerJ. 9:e113432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ma J, Huang W, Zhu C, Sun X, Zhang Q,
Zhang L, Qi Q, Bai X, Feng Y and Wang C: miR-423-3p activates FAK
signaling pathway to drive EMT process and tumor growth in lung
adenocarcinoma through targeting CYBRD1. J Clin Lab Anal.
35:e240442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhang J, Cheng Y, Duan M, Qi N and Liu J:
Unveiling differentially expressed genes upon regulation of
transcription factors in sepsis. Biotech. 7:462017.
|
|
99
|
Al-Eitan LN, Tarkhan AH, Alghamdi MA,
Al-Qarqaz FA and Al-Kofahi HS: Transcriptome analysis of
HPV-induced warts and healthy skin in humans. BMC Med Genomics.
13:352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Meng F, Fleming BA, Jia X, Rousek AA,
Mulvey MA and Ward DM: Lysosomal iron recycling in mouse
macrophages is dependent upon both LcytB and Steap3 reductases.
Blood Adv. 6:1692–1707. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang Z, Guo R, Trudeau SJ, Wolinsky E, Ast
T, Liang JH, Jiang C, Ma Y, Teng M, Mootha VK and Gewurz BE:
CYB561A3 is the key lysosomal iron reductase required for Burkitt
B-cell growth and survival. Blood. 138:2216–2230. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lemonnier N, Melén E, Jiang Y, Joly S,
Ménard C, Aguilar D, Acosta-Perez E, Bergström A, Boutaoui N,
Bustamante M, et al: A novel whole blood gene expression signature
for asthma, dermatitis, and rhinitis multimorbidity in children and
adolescents. Allergy. 75:3248–3260. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Liu H, Liu L, Liu Q, He F and Zhu H:
LncRNA HOXD-AS1 affects proliferation and apoptosis of cervical
cancer cells by promoting FRRS1 expression via transcription factor
ELF1. Cell Cycle. 21:416–426. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ponting CP: Domain homologues of dopamine
b-hydroxylase and ferric reductase: Roles for iron metabolism in
neurodegenerative disorders? Hum Mol Genet. 10:1853–1858. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Binder J, Ursu O, Bologa C, Jiang S,
Maphis N, Dadras S, Chisholm D, Weick J, Myers O, Kumar P, et al:
Machine learning prediction and tau-based screening identifies
potential Alzheimer's disease genes relevant to immunity. Commun
Biol. 5:1252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Linton KM, Hey Y, Saunders E, Jeziorska M,
Denton J, Wilson CL, Swindell R, Dibben S, Miller CJ, Pepper SD, et
al: Acquisition of biologically relevant gene expression data by
Affymetrix microarray analysis of archival formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded tumours. Br J Cancer. 98:1403–1414. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Li S, Shi J, Gao H, Yuan Y, Chen Q, Zhao
Z, Wang X, Li B, Ming L, Zhong J, et al: Identification of a gene
signature associated with radiotherapy and prognosis in gliomas.
Oncotarget. 8:88974–88987. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
El Behery M, Fujimura M, Kimura T and
Tsubaki M: Direct measurements of ferric reductase activity of
human 101F6 and its enhancement upon reconstitution into
phospholipid bilayer nanodisc. Biochem Biophys Rep.
21:1007302020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Mizutani A, Sanuki R, Kakimoto K, Kojo S
and Taketani S: Involvement of 101F6, a homologue of cytochrome
b561, in the reduction of ferric ions. J Biochem. 142:699–705.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Recuenco MC, Fujito M, Rahman MM, Sakamoto
Y, Takeuchi F and Tsubaki M: Functional expression and
characterization of human 101F6 protein, a homologue of cytochrome
b561 and a candidate tumor suppressor gene product. Biofactors.
34:219–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Recuenco MC, Rahman MM, Takeuchi F,
Kobayashi K and Tsubaki M: Electron transfer reactions of candidate
tumor suppressor 101F6 protein, a cytochrome b561 homologue, with
ascorbate and monodehydroascorbate radical. Biochemistry.
52:3660–3668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ji L, Nishizaki M, Gao B, Burbee D, Kondo
M, Kamibayashi C, Xu K, Yen N, Atkinson EN, Fang B, et al:
Expression of several genes in the human chromosome 3p21.3
homozygous deletion region by an adenovirus vector results in tumor
suppressor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res.
62:2715–2720. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ji L, Minna JD and Roth JA: 3p21.3 tumor
suppressor cluster: Prospects for translational applications.
Future Oncol. 1:79–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lerman MI and Minna JD: The international
lung cancer chromosome 3p21.3 tumor suppressor gene consortium. The
630-kb lung cancer homozygous deletion region on human chromosome
3p21.3: Identification and evaluation of the resident candidate
tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Res. 60:6116–6133. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zabarovsky ER, Lerman MI and Minna JD:
Tumor suppressor genes on chromosome 3p involved in the
pathogenesis of lung and other cancers. Oncogene. 21:6915–6935.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ohtani S, Iwamaru A, Deng W, Ueda K, Wu G,
Jayachandran G, Kondo S, Atkinson EN, Minna JD, Roth JA and Ji L:
Tumor suppressor 101F6 and ascorbate synergistically and
selectively inhibit non-small cell lung cancer growth by
caspase-independent apoptosis and autophagy. Cancer Res.
67:6293–6303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Tao B, Shi J, Shuai S, Zhou H, Zhang H, Li
B, Wang X, Li G, He H and Zhong J: CYB561D2 up-regulation activates
STAT3 to induce immunosuppression and aggression in gliomas. J
Transl Med. 19:3382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|