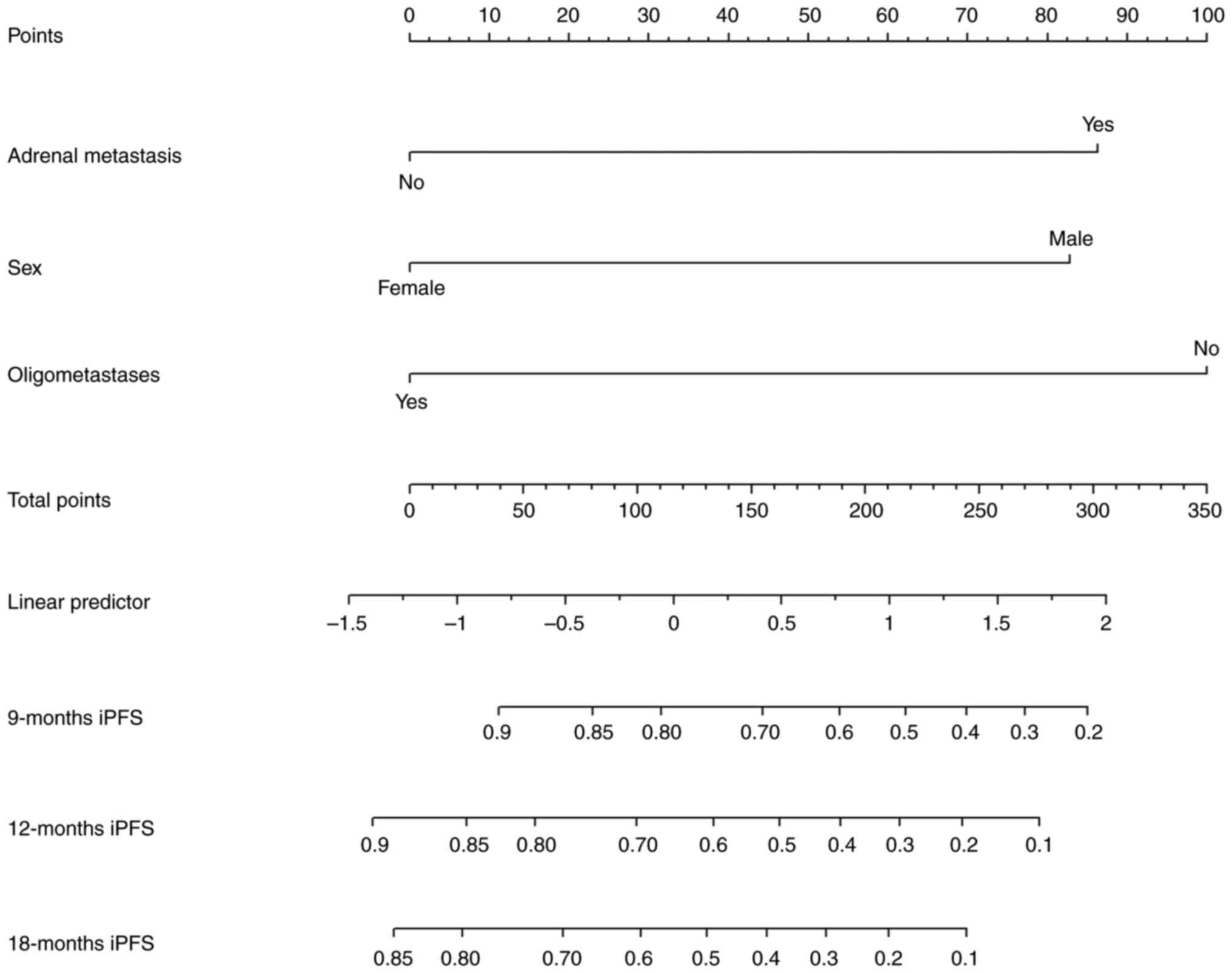
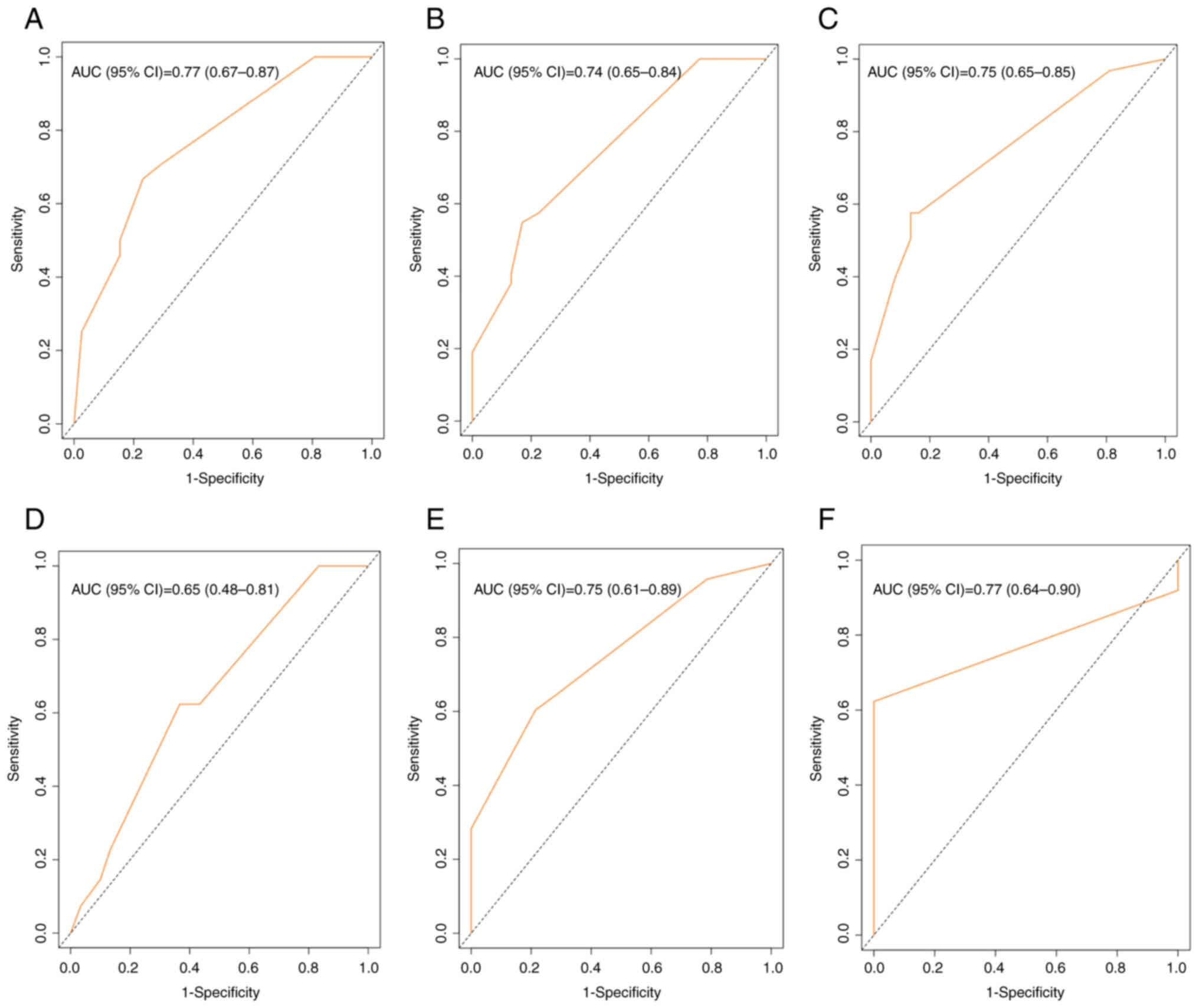
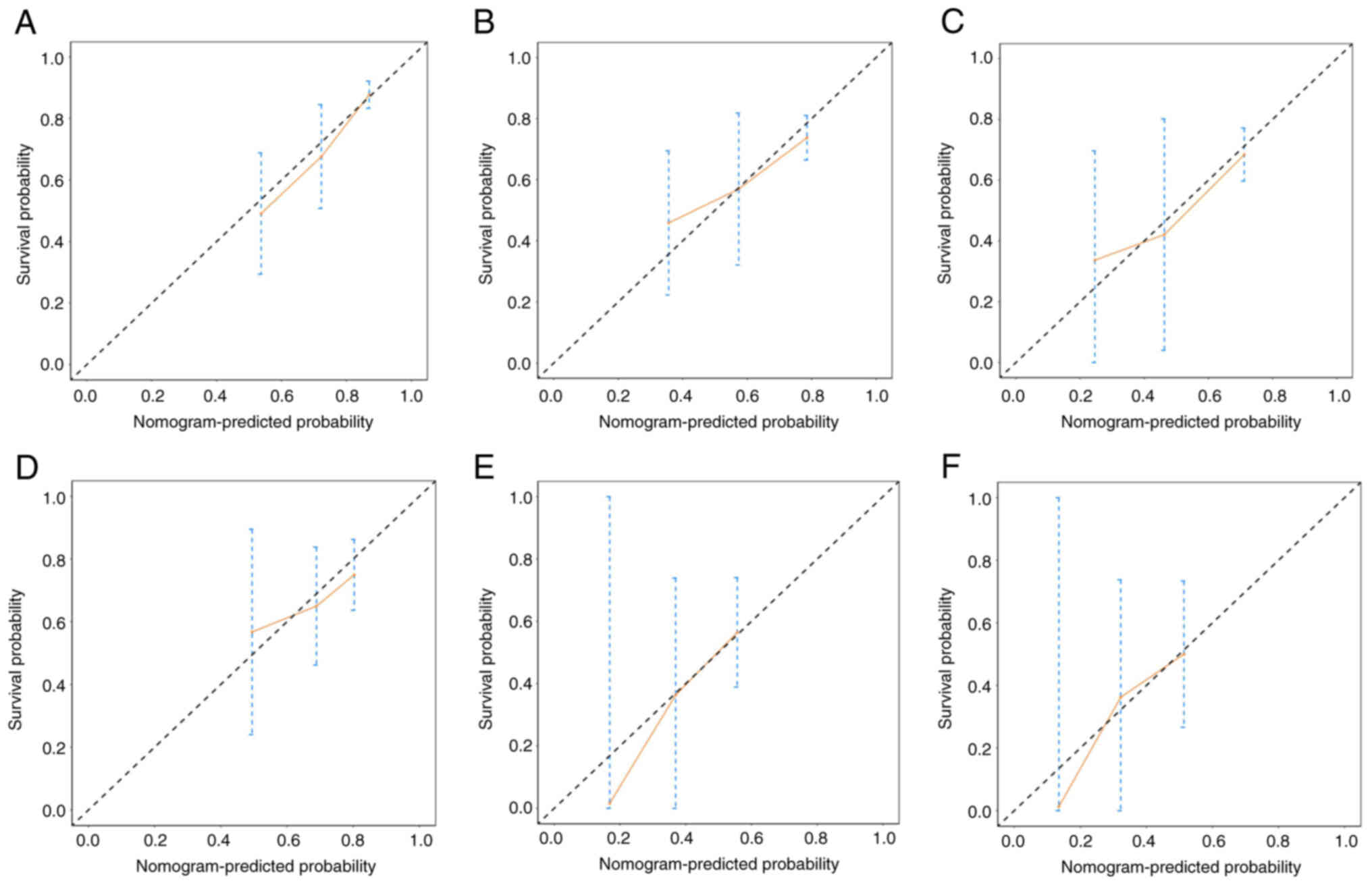
|
1
|
Gazdar AF, Bunn PA and Minna JD:
Small-cell lung cancer: What we know, what we need to know and the
path forward. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:725–737. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Manapov F, Kasmann L, Roengvoraphoj O,
Dantes M, Schmidt-Hegemann NS, Belka C and Eze C: Prophylactic
cranial irradiation in small-cell lung cancer: Update on patient
selection, efficacy and outcomes. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 9:49–55.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu S, Guo X, Li Y, Liu H, Zhang Y and Zhu
H: Antiprogrammed death ligand 1 therapy failed to reduce the risk
of developing brain metastases in patients with extensive-stage
small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Cancer.
130:18–30. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Upton DH, Ung C, George SM, Tsoli M,
Kavallaris M and Ziegler DS: Challenges and opportunities to
penetrate the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy.
Theranostics. 12:4734–4752. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slotman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, Rankin
E, Snee M, Hatton M, Postmus P, Collette L, Musat E and Senan S;
EORTC Radiation Oncology Group and Lung Cancer Group, :
Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 357:664–672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takahashi T, Yamanaka T, Seto T, Harada H,
Nokihara H, Saka H, Nishio M, Kaneda H, Takayama K, Ishimoto O, et
al: Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients
with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre,
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:663–671.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Slotman BJ, Mauer ME, Bottomley A,
Faivre-Finn C, Kramer GW, Rankin EM, Snee M, Hatton M, Postmus PE,
Collette L and Senan S: Prophylactic cranial irradiation in
extensive disease small-cell lung cancer: Short-term health-related
quality of life and patient reported symptoms: Results of an
international phase III randomized controlled trial by the EORTC
Radiation Oncology and Lung Cancer Groups. J Clin Oncol. 27:78–84.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP and Tome WA:
Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment
after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or
low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
85:348–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gondi V, Paulus R, Bruner DW, Meyers CA,
Gore EM, Wolfson A, Werner-Wasik M, Sun AY, Choy H and Movsas B:
Decline in tested and self-reported cognitive functioning after
prophylactic cranial irradiation for lung cancer: Pooled secondary
analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group randomized trials 0212
and 0214. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 86:656–664. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, Caine C, Corn
B, Kanner A, Rowley H, Kundapur V, DeNittis A, Greenspoon JN, et
al: Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the
hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain
radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): A phase II
multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol. 32:3810–3816. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brown PD, Gondi V, Pugh S, Tome WA, Wefel
JS, Armstrong TS, Bovi JA, Robinson C, Konski A, Khuntia D, et al:
Hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy plus
memantine for patients with brain metastases: Phase III trial NRG
oncology CC001. J Clin Oncol. 38:1019–1029. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Belderbos JSA, De Ruysscher DKM, De Jaeger
K, Koppe F, Lambrecht MLF, Lievens YN, Dieleman EMT, Jaspers JPM,
Van Meerbeeck JP, Ubbels F, et al: Phase 3 randomized trial of
prophylactic cranial irradiation with or without hippocampus
avoidance in SCLC (NCT01780675). J Thorac Oncol. 16:840–849. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dingemans AC, Fruh M, Ardizzoni A, Besse
B, Faivre-Finn C, Hendriks LE, Lantuejoul S, Peters S, Reguart N,
Rudin CM, et al: Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice
guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up✩. Ann
Oncol. 32:839–853. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rusthoven CG and Kavanagh BD: Prophylactic
Cranial Irradiation (PCI) versus active MRI surveillance for small
cell lung cancer: The case for Equipoise. J Thorac Oncol.
12:1746–1754. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in
Oncology (NCCN Guidelines), . Small Cell Lung Cancer Version
2.2024. November 21–2023
|
|
16
|
Greenspoon JN, Evans WK, Cai W and Wright
JR: Selecting patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
for prophylactic cranial irradiation by predicting brain
metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 6:808–812. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chung JH, Kang SY, Wu HG, Seo YS, Kim DW,
Kang KW, Kim HJ and Cheon GJ: Risk stratification of symptomatic
brain metastases by clinical and FDG PET parameters for selective
use of prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with extensive
disease of small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 143:81–87.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li W, Ding C, Sheng W, Wan Q, Cui Z, Qi G
and Liu Y: Development and validation of a nomogram for the
prediction of brain metastases in small cell lung cancer. Clin
Respir J. 17:456–467. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ, Kim AW and Tanoue
LT: The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest.
151:193–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murray N and Sheehan F: Limited stage
small cell lung cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2:63–70. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee JJ, Bekele BN, Zhou X, Cantor SB,
Komaki R and Lee JS: Decision analysis for prophylactic cranial
irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
24:3597–3603. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ankolekar A, De Ruysscher D, Reymen B,
Houben R, Dekker A, Roumen C and Fijten R: Shared decision-making
for prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive-stage small-cell
lung cancer: An exploratory study. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
10:3120–3131. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An N, Jing W, Wang H, Li J, Liu Y, Yu J
and Zhu H: Risk factors for brain metastases in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 7:6357–6364. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Wu D, Shen B, Chen M, Zhou X, Zhang
P, Qiu G, Ji Y, Du X and Yang Y: A nomogram to predict the
cumulative risk for brain metastases in patients with limited-stage
small cell lung cancer without prophylactic cranial irradiation.
Strahlenther Onkol. 199:727–738. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ueki K, Matsuo Y, Kishi N, Yoneyama M,
Yoshida H, Sakamori Y, Ozasa H, Hirai T and Mizowaki T: Usefulness
of pro-gastrin-releasing peptide as a predictor of the incidence of
brain metastasis and effect of prophylactic cranial irradiation in
patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Radiat Res.
63:636–645. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hou Q, Sun B, Yao N, Liang Y, Cao X, Wei L
and Cao J: Construction of brain metastasis prediction model and
optimization of prophylactic cranial irradiation selection for
limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14:49062022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu H, Bi Y, Han A, Luo J, Li M, Shi F,
Kong L and Yu J: Risk factors for brain metastases in completely
resected small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study to identify
patients most likely to benefit from prophylactic cranial
irradiation. Radiat Oncol. 9:2162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bang A, Kendal WS, Laurie SA, Cook G and
MacRae RM: Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation in extensive stage
small cell lung cancer: Outcomes at a comprehensive cancer centre.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 101:1133–1140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oliver DE, Donnelly OG, Grass GD, Naghavi
AO, Yang GQ, Dilling TJ and Perez BA: Extracranial metastatic
burden in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: Implications for
prophylactic cranial irradiation. J Thorac Dis. 10:4321–4327. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Y, Li J, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Lin Z, Zhao Z
and Jiao S: Prophylactic cranial irradiation could improve overall
survival in patients with extensive small cell lung cancer: A
retrospective study. Strahlenther Onkol. 192:905–912. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Megyesfalvi Z, Tallosy B, Pipek O,
Fillinger J, Lang C, Klikovits T, Schwendenwein A, Hoda MA,
Renyi-Vamos F, Laszlo V, et al: The landscape of small cell lung
cancer metastases: Organ specificity and timing. Thorac Cancer.
12:914–923. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao Y, Bado I, Wang H, Zhang W, Rosen JM
and Zhang XH: Metastasis Organotropism: Redefining the congenial
soil. Dev Cell. 49:375–391. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Furlan A, Dyachuk V, Kastriti ME,
Calvo-Enrique L, Abdo H, Hadjab S, Chontorotzea T, Akkuratova N,
Usoskin D, Kamenev D, et al: Multipotent peripheral glial cells
generate neuroendocrine cells of the adrenal medulla. Science.
357:eaal37532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim TG, Pyo H, Ahn YC, Noh JM and Oh D:
Role of prophylactic cranial irradiation for elderly patients with
limited-disease small-cell lung cancer: Inverse probability of
treatment weighting using propensity score. J Radiat Res.
60:630–638. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reddy SP, Dowell JE and Pan E: Predictors
of prognosis of synchronous brain metastases in small-cell lung
cancer patients. Clin Exp Metastasis. 37:531–539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee JS, Kim S, Sung SY, Kim YH, Lee HW,
Hong JH and Ko YH: Treatment outcomes of 9,994 patients with
extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer from a retrospective
nationwide population-based cohort in the Korean HIRA database.
Front Oncol. 11:5466722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang J, Zhou C, Yao W, Wang Q, Min X, Chen
G, Xu X, Li X, Xu F, Fang Y, et al: Adebrelimab or placebo plus
carboplatin and etoposide as first-line treatment for
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CAPSTONE-1): A multicentre,
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 23:739–747. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu SV, Reck M, Mansfield AS, Mok T,
Scherpereel A, Reinmuth N, Garassino MC, De Castro Carpeno J,
Califano R, Nishio M, et al: Updated overall survival and PD-L1
subgroup analysis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung
cancer treated with Atezolizumab, Carboplatin, and Etoposide
(IMpower133). J Clin Oncol. 39:619–630. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goldman JW, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N,
Hotta K, TDDDrukhin D, Statsenko G, Hochmair MJ, Özgüroğlu M, Ji
JH, et al: Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus
platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line
treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN):
Updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:51–65. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gadgeel SM, Lukas RV, Goldschmidt J,
Conkling P, Park K, Cortinovis D, de Marinis F, Rittmeyer A, Patel
JD, von Pawel J, et al: Atezolizumab in patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer and history of asymptomatic, treated
brain metastases: Exploratory analyses of the phase III OAK study.
Lung Cancer. 128:105–112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|