|
1
|
Arnold M, Abnet CC, Neale RE, Vignat J,
Giovannucci EL, McGlynn KA and Bray F: Global burden of 5 major
types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology.
159:335–349.e15. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang FF, Luo YH, Wang H and Zhao L:
Metastasis-associated long noncoding RNAs in gastrointestinal
cancer: Implications for novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:8735–8749. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grady WM: Epigenetic alterations in the
gastrointestinal tract: Current and emerging use for biomarkers of
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 151:425–468. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
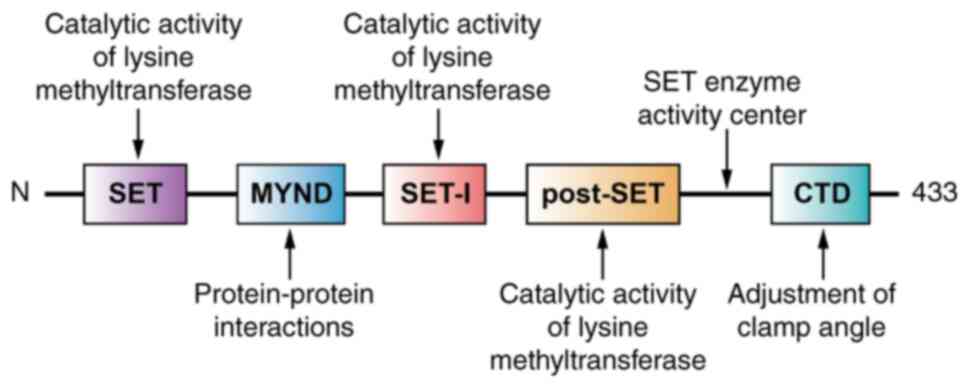
4
|
Wang DK, Zuo Q, He QY and Li B: Targeted
immunotherapies in gastrointestinal cancer: From molecular
mechanisms to implications. Front Immunol. 12:7059992021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao Z, Shu Y, Wang J, Wang C, Feng T, Yang
L, Shao J and Zou L: Super enhancers: Pathogenic roles and
potential therapeutic targets for acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Genes Dis. 9:1466–1477. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brown MA, Sims RJ III, Gottlieb PD and
Tucker PW: Identification and characterization of Smyd2: A split
SET/MYND domain-containing histone H3 lysine 36-specific
methyltransferase that interacts with the Sin3 histone deacetylase
complex. Mol Cancer. 5:262006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
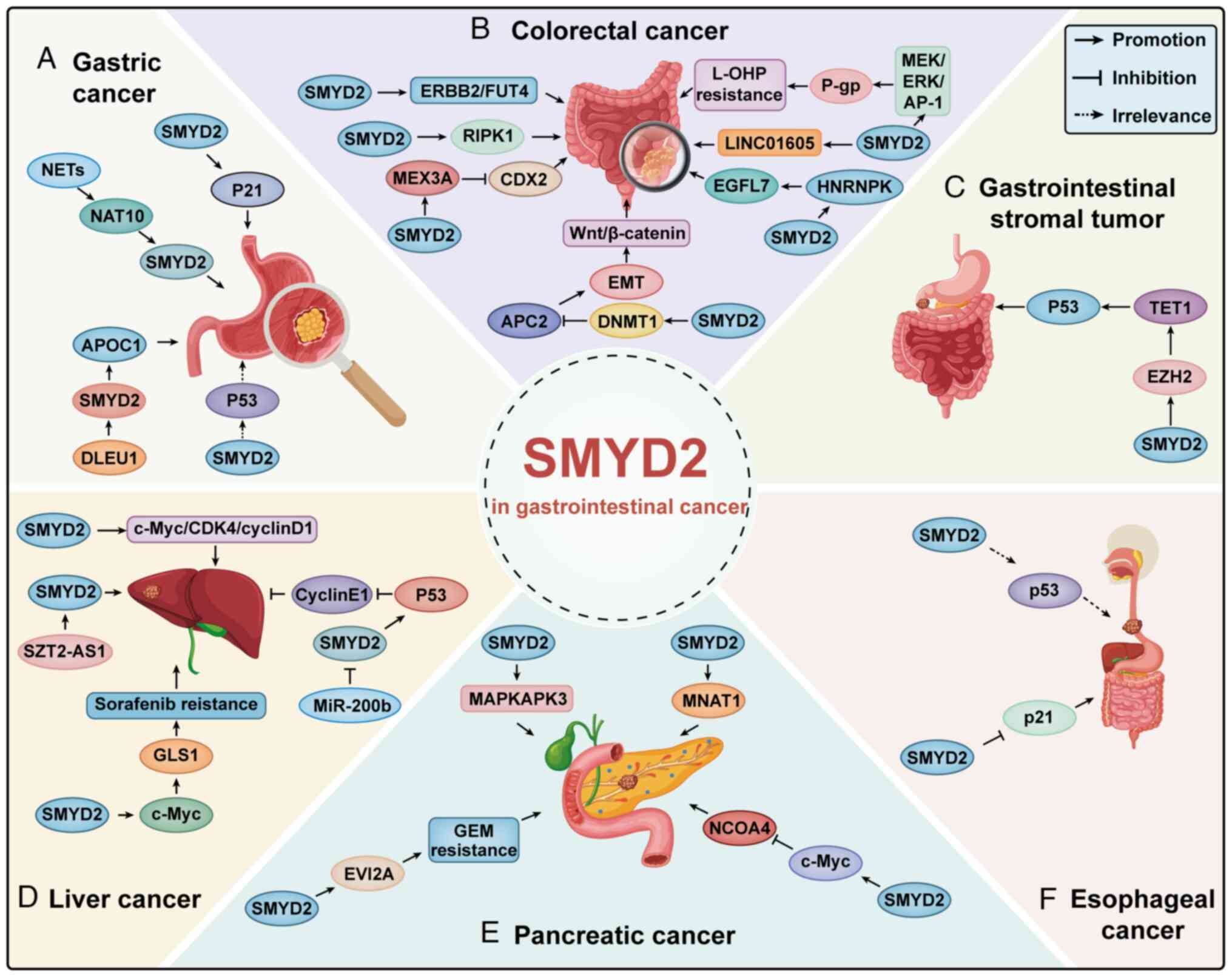
Huang J, Perez-Burgos L, Placek BJ,
Sengupta R, Richter M, Dorsey JA, Kubicek S, Opravil S, Jenuwein T
and Berger SL: Repression of p53 activity by Smyd2-mediated
methylation. Nature. 444:629–632. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng Y, Qiu R, Yang Y, Gao T, Zheng Y,
Huang W, Gao J, Zhang K, Liu R, Wang S, et al: Regulation of EZH2
by SMYD2-mediated lysine methylation is implicated in
tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 29:1482–1498.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sajjad A, Novoyatleva T, Vergarajauregui
S, Troidl C, Schermuly RT, Tucker HO and Engel FB: Lysine
methyltransferase Smyd2 suppresses p53-dependent cardiomyocyte
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2556–2562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Hirajima S, Nagata
H, Nishimura Y, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, Okajima W, Ohashi T,
Konishi H, et al: Overexpression of SMYD2 contributes to malignant
outcome in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:357–364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamamoto R, Toyokawa G, Nakakido M, Ueda K
and Nakamura Y: SMYD2-dependent HSP90 methylation promotes cancer
cell proliferation by regulating the chaperone complex formation.
Cancer Lett. 351:126–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reynoird N, Mazur PK, Stellfeld T, Flores
NM, Lofgren SM, Carlson SM, Brambilla E, Hainaut P, Kaznowska EB,
Arrowsmith CH, et al: Coordination of stress signals by the lysine
methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes pancreatic cancer. Genes Dev.
30:772–785. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eggert E, Hillig RC, Koehr S, Stöckigt D,
Weiske J, Barak N, Mowat J, Brumby T, Christ CD, Ter Laak A, et al:
Discovery and characterization of a highly potent and selective
aminopyrazoline-based in vivo probe (BAY-598) for the protein
lysine methyltransferase SMYD2. J Med Chem. 59:4578–4600. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hamamoto R, Saloura V and Nakamura Y:
Critical roles of non-histone protein lysine methylation in human
tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:110–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng Q, Zhang W and Rao GW: Protein
lysine methyltransferase SMYD2: A promising small molecule target
for cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 65:10119–10132. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Copeland RA: Protein methyltransferase
inhibitors as precision cancer therapeutics: A decade of discovery.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 373:201700802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Copeland RA: Epigenetic medicinal
chemistry. ACS Med Chem Lett. 7:124–127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang M, Chen G, Tu B, Hu Z, Huang Y,
DuFort CC, Wan X, Mao Z, Liu Y, Zhu WG and Lu W: SMYD2
inhibition-mediated hypomethylation of Ku70 contributes to impaired
nonhomologous end joining repair and antitumor immunity. Sci Adv.
9:eade66242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng J, Yang W, Li C and Li F: Synergistic
anticancer effects of SMYD2 inhibitor BAY-598 and doxorubicin in
non-small cell lung cancer. Heliyon. 10:e320152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Razmi M, Yazdanpanah A, Etemad-Moghadam S,
Alaeddini M, Angelini S and Eini L: Clinical prognostic value of
the SMYD2/3 as new epigenetic biomarkers in solid cancer patients:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 1–15.
2022.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rubio-Tomás T: Novel insights into SMYD2
and SMYD3 inhibitors: From potential anti-tumoural therapy to a
variety of new applications. Mol Biol Rep. 48:7499–7508. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu D, Yang X and Wang X: Neutrophil
extracellular traps promote gastric cancer cell metastasis via the
NAT10-mediated N4-acetylcytidine modification of SMYD2. Cell
Signal. 116:1110142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carr SR, Akerley W, Hashibe M and
Cannon-Albright LA: Evidence for a genetical contribution to
non-smoking-related lung cancer. Thorax. 70:1033–1039. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Spellmon N, Holcomb J, Trescott L,
Sirinupong N and Yang Z: Structure and function of SET and MYND
domain-containing proteins. Int J Mol Sci. 16:1406–1428. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leinhart K and Brown M: SET/MYND lysine
methyltransferases regulate gene transcription and protein
activity. Genes (Basel). 2:210–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ferguson AD, Larsen NA, Howard T, Pollard
H, Green I, Grande C, Cheung T, Garcia-Arenas R, Cowen S, Wu J, et
al: Structural basis of substrate methylation and inhibition of
SMYD2. Structure. 19:1262–1273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu S, Zhong C, Zhang T and Ding J:
Structure of human lysine methyltransferase Smyd2 reveals insights
into the substrate divergence in Smyd proteins. J Mol Cell Biol.
3:293–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
‘SMYD2-SET and MYND domain-containing
protein 2’. UniProt; Geneva: 2024, https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NRG4
|
|
29
|
Herz HM, Garruss A and Shilatifard A: SET
for life: Biochemical activities and biological functions of SET
domain-containing proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:621–639. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu J, Cheung T, Grande C, Ferguson AD, Zhu
X, Theriault K, Code E, Birr C, Keen N and Chen H: Biochemical
characterization of human SET and MYND domain-containing protein 2
methyltransferase. Biochemistry. 50:6488–6497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Al-Madhoun AS,
Elisma F, Skerjanc IS and Figeys D: The tale of two domains:
Proteomics and genomics analysis of SMYD2, a new histone
methyltransferase. Mol Cell Proteomics. 7:560–572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spellmon N, Sun X, Sirinupong N, Edwards
B, Li C and Yang Z: Molecular dynamics simulation reveals
correlated inter-lobe motion in protein lysine methyltransferase
SMYD2. PLoS One. 10:e01457582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu S, Wu J, Sun B, Zhong C and Ding J:
Structural and biochemical studies of human lysine
methyltransferase Smyd3 reveal the important functional roles of
its post-SET and TPR domains and the regulation of its activity by
DNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:4438–4449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sirinupong N, Brunzelle J, Ye J, Pirzada
A, Nico L and Yang Z: Crystal structure of cardiac-specific histone
methyltransferase SmyD1 reveals unusual active site architecture. J
Biol Chem. 285:40635–40644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chandramouli B and Chillemi G:
Conformational dynamics of lysine methyltransferase Smyd2. insights
into the different substrate crevice characteristics of Smyd2 and
Smyd3. J Chem Inf Model. 56:2467–2475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Alshammari E, Sobota J, Spellmon
N, Perry E, Cao T, Mugunamalwaththa T, Smith S, Brunzelle J, Wu G,
et al: Structure of the SMYD2-PARP1 complex reveals both productive
and allosteric modes of peptide binding. bioRxiv [Preprint].
2024.12.03.626679. 2024.
|
|
37
|
Gottlieb PD, Pierce SA, Sims RJ, Yamagishi
H, Weihe EK, Harriss JV, Maika SD, Kuziel WA, King HL, Olson EN, et
al: Bop encodes a muscle-restricted protein containing MYND and SET
domains and is essential for cardiac differentiation and
morphogenesis. Nat Genet. 31:25–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sesé B, Barrero MJ, Fabregat MC, Sander V
and Izpisua Belmonte JC: SMYD2 is induced during cell
differentiation and participates in early development. Int J Dev
Biol. 57:357–364. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Diehl F, Brown MA, van Amerongen MJ,
Novoyatleva T, Wietelmann A, Harriss J, Ferrazzi F, Böttger T,
Harvey RP, Tucker PW and Engel FB: Cardiac deletion of Smyd2 is
dispensable for mouse heart development. PLoS One. 5:e97482010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawamura S, Yoshigai E, Kuhara S and
Tashiro K: smyd1 and smyd2 are expressed in muscle tissue in
Xenopus laevis. Cytotechnology. 57:161–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alshammari E, Zhang YX and Yang Z:
Mechanistic and functional extrapolation of SET and MYND
domain-containing protein 2 to pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 28:3753–3766. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Boehm D, Jeng M, Camus G, Gramatica A,
Schwarzer R, Johnson JR, Hull PA, Montan M, Sakane N, Pagans S, et
al: SMYD2-mediated histone methylation contributes to HIV-1
latency. Cell Host Microbe. 21:569–579.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Olsen JB, Cao XJ, Han B, Chen LH, Horvath
A, Richardson TI, Campbell RM, Garcia BA and Nguyen H: Quantitative
profiling of the activity of protein lysine methyltransferase SMYD2
using SILAC-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 15:892–905.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weirich S, Schuhmacher MK, Kudithipudi S,
Lungu C, Ferguson AD and Jeltsch A: Analysis of the substrate
specificity of the SMYD2 protein lysine methyltransferase and
discovery of novel non-histone substrates. Chembiochem. 21:256–264.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li LX, Fan LX, Zhou JX, Grantham JJ,
Calvet JP, Sage J and Li X: Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes
cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Clin
Invest. 127:2751–2764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Piao L, Kang D, Suzuki T, Masuda A, Dohmae
N, Nakamura Y and Hamamoto R: The histone methyltransferase SMYD2
methylates PARP1 and promotes poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity in
cancer cells. Neoplasia. 16:257–264. 264.e22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nakakido M, Deng Z, Suzuki T, Dohmae N,
Nakamura Y and Hamamoto R: Dysregulation of AKT pathway by
SMYD2-mediated lysine methylation on PTEN. Neoplasia. 17:367–373.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Saddic LA, West LE, Aslanian A, Yates JR
III, Rubin SM, Gozani O and Sage J: Methylation of the
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by SMYD2. J Biol Chem.
285:37733–37740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cho HS, Hayami S, Toyokawa G, Maejima K,
Yamane Y, Suzuki T, Dohmae N, Kogure M, Kang D, Neal DE, et al: RB1
methylation by SMYD2 enhances cell cycle progression through an
increase of RB1 phosphorylation. Neoplasia. 14:476–486. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Obermann WMJ: A motif in HSP90 and P23
that links molecular chaperones to efficient estrogen receptor α
methylation by the lysine methyltransferase SMYD2. J Biol Chem.
293:16479–16487. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ji K, Jia H, Liu Z, Yu G, Wen R, Zhang T,
Peng Z, Man W, Tian Y, Wang C, et al: New insight in immunotherapy
and combine therapy in colorectal cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
12:14536302025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Meng F, Liu X, Lin C, Xu L, Liu J, Zhang
P, Zhang X, Song J, Yan Y, Ren Z and Zhang Y: SMYD2 suppresses APC2
expression to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer
Res. 10:997–1011. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu YQ, Thonn V, Patankar JV, Thoma OM,
Waldner M, Zielinska M, Bao LL, Gonzalez-Acera M, Wallmüller S,
Engel FB, et al: SMYD2 targets RIPK1 and restricts TNF-induced
apoptosis and necroptosis to support colon tumor growth. Cell Death
Dis. 13:522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang Y, Zhou L, Xu Y, Zhou J, Jiang T,
Wang J, Li C, Sun X, Song H and Song J: Targeting SMYD2 inhibits
angiogenesis and increases the efficiency of apatinib by
suppressing EGFL7 in colorectal cancer. Angiogenesis. 26:1–18.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lai Y and Yang Y: SMYD2 facilitates cancer
cell malignancy and xenograft tumor development through
ERBB2-mediated FUT4 expression in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem.
477:2149–2159. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ren H, Wang Z, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang S,
Zhang T and Li Y: SMYD2-OE promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colon
cancer through MDR1/P-glycoprotein via MEK/ERK/AP1 pathway. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:2585–2594. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yue M, Liu T, Yan G, Luo X and Wang L:
LINC01605, regulated by the EP300-SMYD2 complex, potentiates the
binding between METTL3 and SPTBN2 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 21:5042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pan L, Fan Y and Zhou L: SMYD2
epigenetically activates MEX3A and suppresses CDX2 in colorectal
cancer cells to augment cancer growth. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
49:959–969. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Deng X, Hamamoto R, Vougiouklakis T, Wang
R, Yoshioka Y, Suzuki T, Dohmae N, Matsuo Y, Park JH and Nakamura
Y: Critical roles of SMYD2-mediated β-catenin methylation for
nuclear translocation and activation of Wnt signaling. Oncotarget.
8:55837–55847. 2027. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ma X, Xu W, Qi L, Zhang Q, Sun X and Zhang
S: Clinical outcome of non-curative endoscopic submucosal
dissection for early gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol.
15:566–576. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Z, Xu H, You W, Pan K and Li W:
Helicobacter pylori eradication for primary prevention of gastric
cancer: Progresses and challenges. J Natl Cancer Cent. 4:299–310.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu D, Liu M, Wang W, Li X, Shi E, Zhang
C, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang L and Wang X: SMYD family members serve as
potential prognostic markers and correlate with immune infiltrates
in gastric cancer. J Oncol. 2023:60328642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu D, Wang X, Shi E, Wang L, Nie M, Li L,
Jiang Q, Kong P, Shi S, Wang C, et al: Comprehensive analysis of
the value of SMYD family members in the prognosis and immune
infiltration of malignant digestive system tumors. Front Genet.
12:6999102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xu H, Ba Z, Liu C and Yu X: Long noncoding
RNA DLEU1 promotes proliferation and glycolysis of gastric cancer
cells via APOC1 upregulation by recruiting SMYD2 to induce
trimethylation of H3K4 modification. Transl Oncol. 36:1017312023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
He C, Wang Z, Yu J, Mao S and Xiang X:
Current drug resistance mechanisms and treatment options in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Summary and update. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 25:1390–1405. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ji Y, Xu X, Long C, Wang J, Ding L, Zheng
Z, Wu H, Yang L, Tao L and Gao F: SMYD2 aggravates gastrointestinal
stromal tumor via upregulation of EZH2 and downregulation of TET1.
Cell Death Discov. 8:2742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yu Y, Qi J, Xiong J, Jiang L, Cui D, He J,
Chen P, Li L, Wu C, Ma T, et al: Epigenetic co-deregulation of
EZH2/TET1 is a senescence-countering, actionable vulnerability in
triple-negative breast cancer. Theranostics. 9:761–777. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hwang SY, Danpanichkul P, Agopian V, Mehta
N, Parikh ND, Abou-Alfa GK, Singal AG and Yang JD: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Updates on epidemiology, surveillance, diagnosis and
treatment. Clin Mol Hepatol. 31 (Suppl):S228–S254. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zuo SR, Zuo XC, He Y, Fang WJ, Wang CJ,
Zou H, Chen P, Huang LF, Huang LH, Xiang H and Liu SK: Positive
expression of SMYD2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients
with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 9:321–330. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fang W, Song L, Li Z, Meng P, Zuo S and
Liu S: Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation of liver cancer
cells via targeting SMYD2/p53 signaling pathway. Zhong Nan Da Xue
Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 47:1303–1314. 2022.(In English, Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xu K, Ding J, Zhou L, Li D, Luo J, Wang W,
Shang M, Lin B, Zhou L and Zheng S: SMYD2 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by reprogramming glutamine metabolism via
c-Myc/GLS1 axis. Cells. 12:252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu R, Guo Y, Wang L, Yin G, Tuo H, Zhu Y,
Yang W, Liu Q and Wang Y: A novel hypoxia-induced lncRNA, SZT2-AS1,
boosts HCC progression by mediating HIF heterodimerization and
histone trimethylation under a hypoxic microenvironment. Cell Death
Differ. Nov 22–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
73
|
Jiang Z, Zheng X, Li M and Liu M:
Improving the prognosis of pancreatic cancer: Insights from
epidemiology, genomic alterations, and therapeutic challenges.
Front Med. 17:1135–1169. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tan J, Liao S, Yuan B, Liu X, Yu W, Zhan
H, Jiang Y and Liu Y: Targeting SMYD2 promotes ferroptosis and
impacts the progression of pancreatic cancer through the
c-Myc/NCOA4 axis-mediated ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen
Subj. 1868:1306832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW and
Kimmelman AC: Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo
receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature. 509:105–109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jin Y, Qiu J, Lu X and Li G: C-MYC
inhibited ferroptosis and promoted immune evasion in ovarian cancer
cells through NCOA4 mediated ferritin autophagy. Cells.
11:41272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lenkiewicz E, Malasi S, Hogenson TL,
Flores LF, Barham W, Phillips WJ, Roesler AS, Chambers KR,
Rajbhandari N, Hayashi A, et al: Genomic and epigenomic landscaping
defines new therapeutic targets for adenosquamous carcinoma of the
pancreas. Cancer Res. 80:4324–4334. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhao Q, Ye Y, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Wang G, Gui Z
and Zhang M: PANoptosis-related long non-coding RNA signature to
predict the prognosis and immune landscapes of pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep. 37:1016002023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xu Z, Liu Y, Pan Z and Qin L: Epigenetic
upregulation of MNAT1 by SMYD2 is linked to PI3K/AKT activation and
tumorigenesis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Histol Histopathol.
39:263–277. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jin L, Qian D, Tang X, Huang Y, Zou J and
Wu Z: SMYD2 imparts gemcitabine resistance to pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cells by upregulating EVI2A. Mol Biotechnol.
66:2920–2933. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jiang W, Zhang B, Xu J, Xue L and Wang L:
Current status and perspectives of esophageal cancer: A
comprehensive review. Cancer Commun (Lond). 45:281–331. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Komatsu S, Imoto I, Tsuda H, Kozaki KI,
Muramatsu T, Shimada Y, Aiko S, Yoshizumi Y, Ichikawa D, Otsuji E
and Inazawa J: Overexpression of SMYD2 relates to tumor cell
proliferation and malignant outcome of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 30:1139–1146. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|