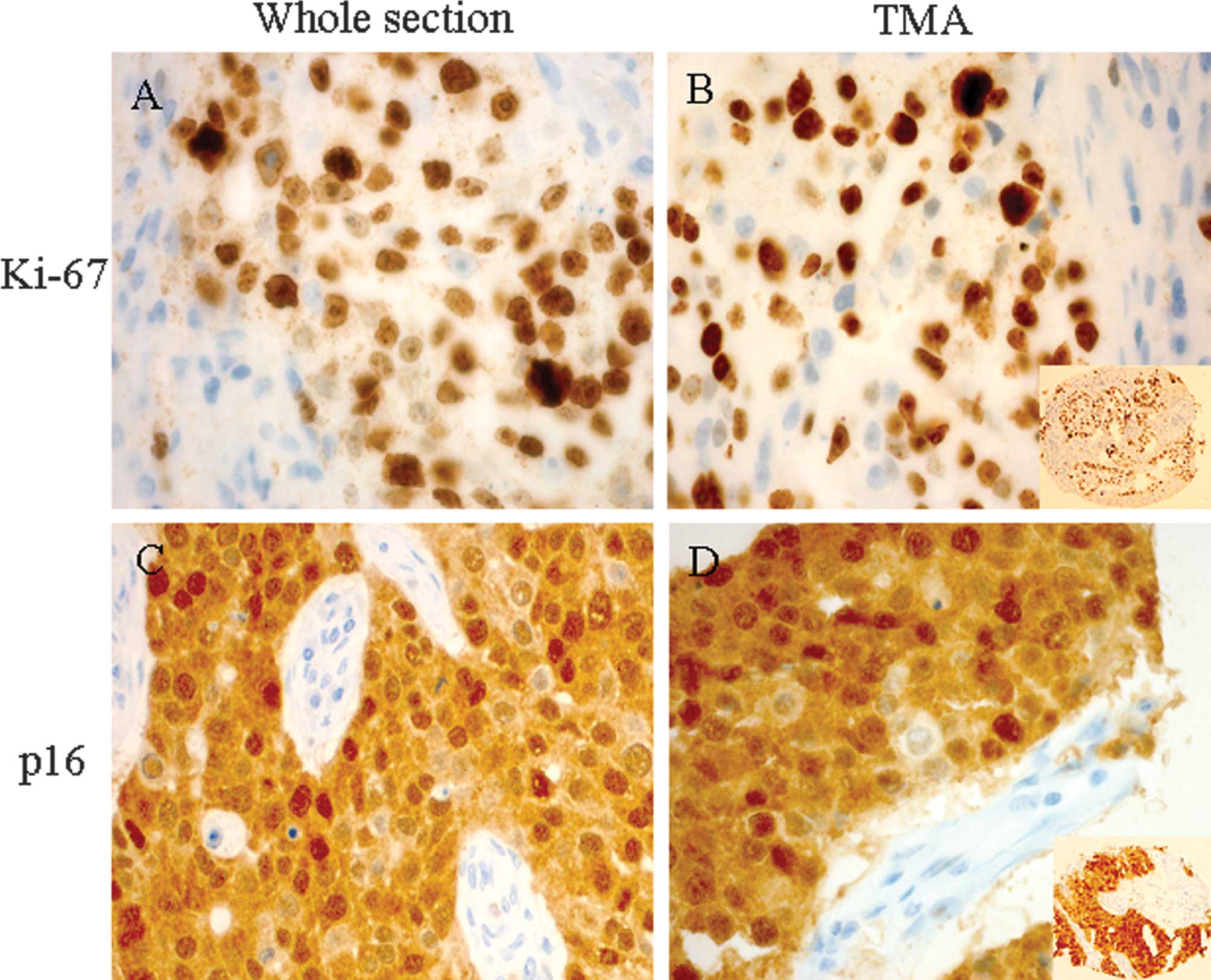
|
1
|
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A,
Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G
and Kallioniemi OP: Tissue microarrays for high-throughput
molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 4:844–847. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mills SE, Fechner RE, Frierson HF, Kempson
RL, Wick MR, Dehner LP, Swanson PE and Humphrey PA: Guardians of
the wax and the patient. Am J Clin Pathol. 104:365–367.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Camp RL, Charette LA and Rimm DL:
Validation of tissue microarray technology in breast carcinoma. Lab
Invest. 80:1943–1949. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tolgay OI, Dolled-Filhart M, D’Aquila TG,
Camp RL and Rimm DL: Tissue microarray-based studies of patients
with lymph node negative breast carcinoma show that met expression
is associated with worse outcome but is not correlated with
epidermal growth factor family receptors. Cancer. 97:1841–1848.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Korsching E, Packeisen J, Agelopoulos K,
Eisenacher M, Voss R, Isola J, van Diest PJ, Brandt B, Boecker W
and Buerger H: Cytogenetic alterations and cytokeratin expression
patterns in breast cancer: integrating a new model of breast
differentiation into cytogenetic pathways of breast carcinogenesis.
Lab Invest. 82:1525–1533. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Griffin MC, Robinson RA and Trask DK:
Validation of tissue microarrays using p53 immunohistochemical
studies of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Mod Pathol.
16:1181–1188. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuwabara S, Ajioka Y, Watanabe H, Hitomi
J, Nishikura K and Hatakeyama K: Heterogeneity of p53 mutational
status in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res.
89:405–410. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baisse B, Bouzourene H, Saraga EP, Bosman
FT and Benhattar J: Intratumor genetic heterogeneity in advanced
human colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 93:346–352. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jourdan F, Sebbagh N, Comperat E, Mourra
N, Flahault A, Olschwang S, Duval A, Hamelin R and Flejou JF:
Tissue microarray technology: validation in colorectal carcinoma
and analysis of p53, hMLH1, and hMSH2 immunohistochemical
expression. Virchows Arch. 443:115–121. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gomaa W, Ke Y, Fujii H and Helliwell T:
Tissue microarray of head and neck squamous carcinoma: validation
of the methodology for the study of cutaneous fatty acid-binding
protein, vascular endothelial growth factor, involucrin and Ki-67.
Virchows Arch. 447:701–709. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rosen DG, Huang X, Deavers MT, Malpica A,
Silva EG and Liu J: Validation of tissue microarray technology in
ovarian carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 17:790–797. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nocito A, Bubendorf L, Tinner EM, et al:
Microarrays of bladder cancer tissue are highly representative of
proliferation index and histological grade. J Pathol. 194:349–357.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Merseburger AS, Kuczyk MA, Serth J, et al:
Limitations of tissue microarrays in the evaluation of focal
alterations of bcl-2 and p53 in whole mount derived prostate
tissues. Oncol Rep. 10:223–228. 2003.
|
|
14
|
Torhorst J, Bucher C, Kononen J, Haas P,
Zuber M, Kochli OR, Mross F, Dieterich H, Moch H, Mihatsch M,
Kallioniemi OP and Sauter G: Tissue microarrays for rapid linking
of molecular changes to clinical endpoints. Am J Pathol.
159:2249–2256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khouja MH, Baekelandt M, Nesland JM and
Holm R: The clinical importance of Ki-67, p16, p14, and p57
expression in patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma. Int J
Gynecol Pathol. 26:418–425. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaplan EL and Meier P: Nonparametric
estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc.
53:457–481. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cox DR: Regression models and life tables.
J R Stat Soc B. 34:187–220. 1972.
|
|
18
|
Sapino A, Marchio C, Senetta R, Castellano
I, Macri L, Cassoni P, Ghisolfi G, Cerrato M, D’Ambrosio E and
Bussolati G: Routine assessment of prognostic factors in breast
cancer using a multicore tissue microarray procedure. Virchows
Arch. 449:288–296. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Su Y, Shrubsole MJ, Ness RM, Cai Q,
Kataoka N, Washington K and Zheng W: Immunohistochemical
expressions of Ki-67, cyclin D1, beta-catenin, cyclooxygenase-2,
and epidermal growth factor receptor in human colorectal adenoma: a
validation study of tissue microarrays. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 15:1719–1726. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Leversha MA, Fielding P, Watson S, Gosney
JR and Field JK: Expression of p53, pRB, and p16 in lung tumours: a
validation study on tissue microarrays. J Pathol. 200:610–619.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tawfik El-Mansi M and Williams AR:
Validation of tissue microarray technology using cervical
adenocarcinoma and its precursors as a model system. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 16:1225–1233. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kallioniemi OP, Wagner U, Kononen J and
Sauter G: Tissue microarray technology for high-throughput
molecular profiling of cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 10:657–662. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fernebro E, Dictor M, Bendahl PO, Ferno M
and Nilbert M: Evaluation of the tissue microarray technique for
immunohistochemical analysis in rectal cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
126:702–705. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fons G, Hasibuan SM, van der Velden J and
ten Kate FJ: Validation of tissue microarray technology in
endometrioid cancer of the endometrium. J Clin Pathol. 60:500–503.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zerkowski MP, Camp RL, Burtness BA, Rimm
DL and Chung GG: Quantitative analysis of breast cancer tissue
microarrays shows high cox-2 expression is associated with poor
outcome. Cancer Invest. 25:19–26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|