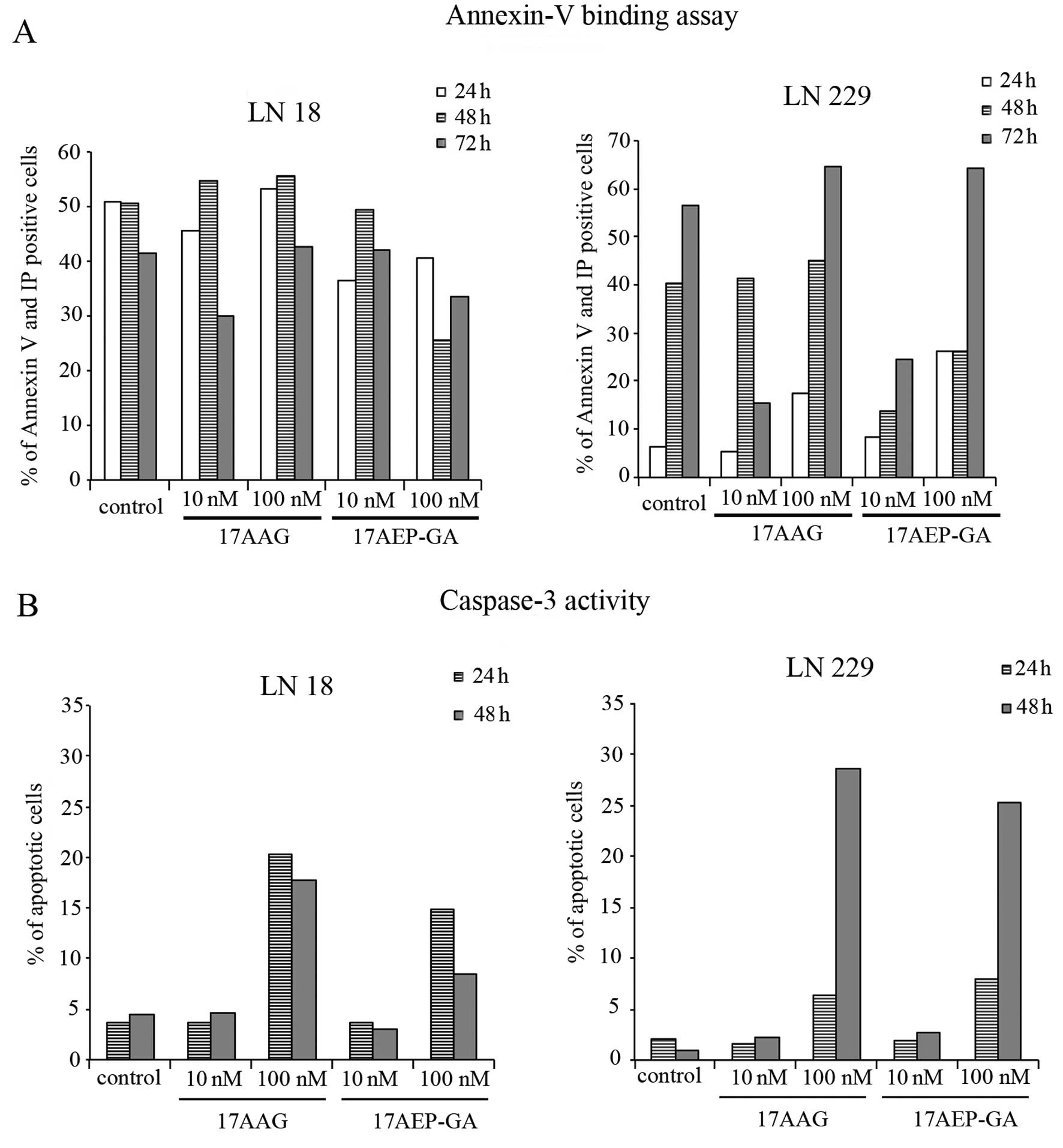
|
1
|
McLendon RE and Halperin EC: Is the
long-term survival of patients with intracranial glioblastoma
multiforme overstated? Cancer. 98:1745–1748. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Navas-Acién A, Pollán M, Gustavsson P,
Floderus B, Plato N and Dosemeci M: Interactive effect of chemical
substances and occupational electromagnetic field exposure on the
risk of gliomas and meningiomas in Swedish men. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 11:1678–1683. 2002.
|
|
3
|
Galloway TJ, Indelicato DJ, Amdur RJ,
Swanson EL, Smith AA and Marcus RB: Second tumors in pediatric
patients treated with radiotherapy to the central nervous system.
Am J Clin Oncol. 35:279–283. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krishnan S, Wade R and Moorman AV:
Temporal changes in the incidence and pattern of central nervous
system relapses in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
treated on four consecutive Medical Research Council trials,
1985–2001. Leukemia. 24:450–459. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cordier S, Monfort C, Filippini G, et al:
Parental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the risk
of childhood brain tumors: The SEARCH International Childhood Brain
Tumor Study. Am J Epidemiol. 159:1109–1116. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Molina JR, Hayashi Y, Stephens C and
Georgescu MM: Invasive glioblastoma cells acquire stemness and
increased Akt activation. Neoplasia. 12:453–463. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sauvageot CM, Weatherbee JL, Kesari S, et
al: Efficacy of the HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG in human glioma cell
lines and tumorigenic glioma stem cells. Neuro Oncol. 11:109–121.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abounader R and Laterra J: Scatter
factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and
angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 7:436–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mazzone M and Comoglio PM: The Met
pathway: master switch and drug target in cancer progression. FASEB
J. 20:1611–1621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lesko E and Majka M: The biological role
of HGF-MET axis in tumor growth and development of metastasis.
Front Biosci. 13:1271–1280. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang W, Hiscox S, Matsumoto K and
Nakamura T: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, its molecular,
cellular and clinical implications in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 29:209–248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weidner KM, Sachs M and Birchmeier W: The
Met receptor tyrosine kinase transduces motility, proliferation,
and morphogenic signals of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor
in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 121:145–154. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pratt WB and Toft DO: Regulation of
signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based
chaperone machinery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:111–133.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maulik G, Kijima T, Ma PC, et al:
Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:620–627. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Workman P: Altered states: selectively
drugging the Hsp90 cancer chaperone. Trends Mol Med. 10:47–51.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Whitesell L, Mimnaugh EG, De Costa B,
Myers CE and Neckers LM: Inhibition of heat shock protein
HSP90-pp60v-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone
ansamycins: essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic
transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:8324–8328. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Goetz MP, Toft DO, Ames MM and Erlichman
C: The Hsp90 chaperone complex as a novel target for cancer
therapy. Ann Oncol. 14:1169–1176. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ochel HJ, Eichhorn K and Gademann G:
Geldanamycin: the prototype of a class of antitumor drugs targeting
the heat shock protein 90 family of molecular chaperones. Cell
Stress Chaperones. 6:105–112. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lesko E, Gozdzik J, Kijowski J, Jenner B,
Wiecha O and Majka M: HSP90 antagonist, geldanamycin, inhibits
proliferation, induces apoptosis and blocks migration of
rhabdomysoracoma cells in vitro and seeding into bone marrow in
vivo. Anticancer Drugs. 18:1173–1181. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramanathan RK, Trump DL, Eiseman JL, et
al: Phase I pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of
17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17AAG, NSC 330507), a
novel inhibitor of heat shock protein 90, in patients with
refractory advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3385–3391. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xie Q, Thompson R, Hardy K, et al: A
highly invasive human glioblastoma pre-clinical model for testing
therapeutics. J Transl Med. 6:772008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zagzag D, Nomura M, Friedlander DR, Blanco
CY, Gagner JP, Nomura N and Newcomb EW: Geldanamycin inhibits
migration of glioma cells in vitro: a potential role for
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1alpha) in glioma cell invasion. J
Cell Physiol. 196:394–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lukasiewicz E, Miekus K, Kijowski J, et
al: High anti tumor activity against rhabdomyosarcoma cells and low
normal cells cytotoxicity of heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, with
special emphasis on 17-
(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl)-aminno-17-demethoxy-geldanamycin. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 60:161–166. 2009.
|
|
24
|
Solit DB, Basso AD, Olshen AB, Scher HI
and Rosen N: Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 function
down-regulates Akt kinase and sensitizes tumors to Taxol. Cancer
Res. 63:2139–2144. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC,
Schutte B and Reutelingsperger CP: Annexin V-affinity assay: a
review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine
exposure. Cytometry. 31:1–9. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hardy KM, Yatskievych TA, Konieczka J,
Bobbs AS and Antin PB: FGF signalling through RAS/MAPK and PI3K
pathways regulates cell movement and gene expression in the chicken
primitive streak without affecting E-cadherin expression. BMC Dev
Biol. 11:202011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Miekus K, Jarocha D, Trzyna E and Majka M:
Role of I-TAC-binding receptors CXCR3 and CXCR7 in proliferation,
activation of intracellular signaling pathways and migration of
various tumor cell lines. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 48:104–111.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie Q, Gao CF, Shinomiya N, et al:
Geldanamycins exquisitely inhibit HGF/SF-mediated tumor cell
invasion. Oncogene. 24:3697–3707. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Supko JG, Hickman RL, Grever MR and
Malspeis L: Preclinical pharmacologic evaluation of geldanamycin as
an antitumor agent. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 36:305–315. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|