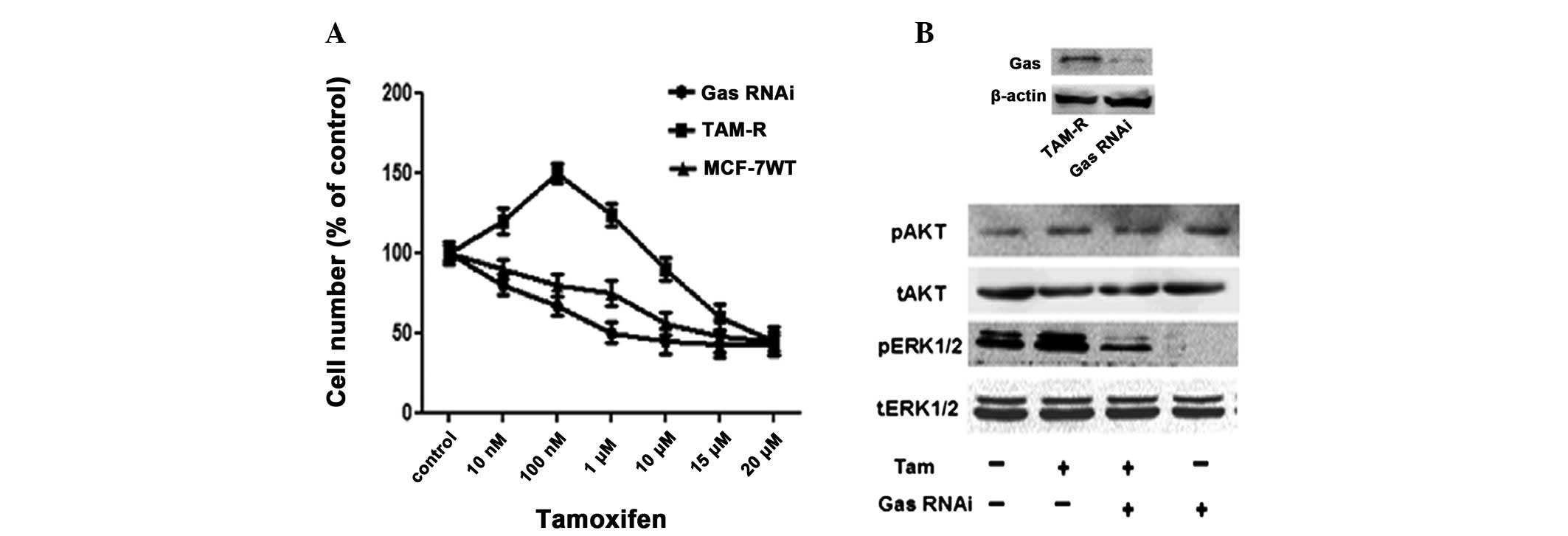
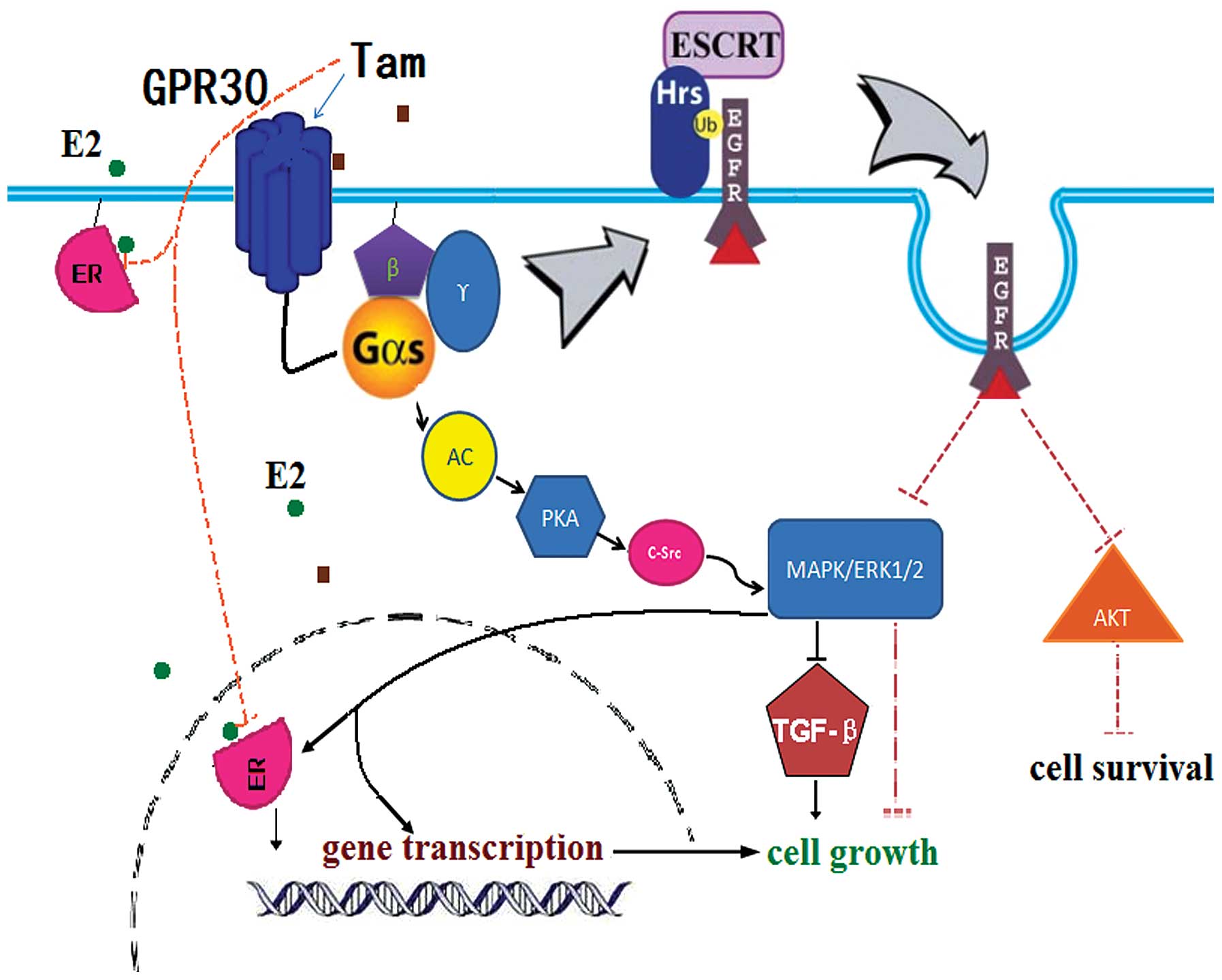
|
1
|
Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an
overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group. Lancet. 351:1451–1467. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Powles TJ, Ashley S, Tidy A, Smith IE and
Dowsett M: Twenty-year follow-up of the Royal Marsden randomized,
double-blinded tamoxifen breast cancer prevention trial. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 99:283–290. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cuzick J, Powles T, Veronesi U, et al:
Overview of the main outcomes in breast-cancer prevention trials.
Lancet. 361:296–300. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurebayashi J: Resistance to endocrine
therapy in breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 56(Suppl 1):
39–46. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM,
Constantinidou D, Ali S and Nakshatri H: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new
model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem. 276:9817–9824.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO and
Nicholson RI: Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein
kinase is associated with poor response to anti-hormonal therapy
and decreased patient survival in clinical breast cancer. Int J
Cancer. 95:247–254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Weissenborn C, et
al: G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPR30 and tamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:457–466.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller TW, Balko JM and Arteaga CL:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and antiestrogen resistance in breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:4452–4461. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brunner N, Frandsen TL, Holst-Hansen C, et
al: MCF7/LCC2: a 4-hydroxytamoxifen resistant human breast cancer
variant that retains sensitivity to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI
182,780. Cancer Res. 53:3229–3232. 1993.
|
|
10
|
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Roessner A, Costa SD
and Kalinski T: Role of GPR30 in the mechanisms of tamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
123:87–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, et al:
Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen
receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 96:926–935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, et al:
Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7
cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 24:85–95.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ward A, Balwierz A, Zhang JD, et al:
Re-expression of microRNA-375 reverses both tamoxifen resistance
and accompanying EMT-like properties in breast cancer. Oncogene.
Apr 16–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
14
|
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Geistlinger TR, et
al: Regulation of ERBB2 by oestrogen receptor-PAX2 determines
response to tamoxifen. Nature. 456:663–666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, et
al: Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling
pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 96:131–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clark AS, West K, Streicher S and Dennis
PA: Constitutive and inducible Akt activity promotes resistance to
chemotherapy, trastuzumab, or tamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 1:707–717. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gerits N, Kostenko S, Shiryaev A,
Johannessen M and Moens U: Relations between the mitogen-activated
protein kinase and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathways:
comradeship and hostility. Cell Signal. 20:1592–1607. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu AM, Lo RK, Wong CS, Morris C, Wise H
and Wong YH: Activation of STAT3 by G alpha(s) distinctively
requires protein kinase A, JNK, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
J Biol Chem. 281:35812–35825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Selever J, Gu G, Lewis MT, et al:
Dicer-mediated upregulation of BCRP confers tamoxifen resistance in
human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6510–6521. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schafer JM, Bentrem DJ, Takei H, Gajdos C,
Badve S and Jordan VC: A mechanism of drug resistance to tamoxifen
in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 83:75–83. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wiebe VJ, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA and
DeGregorio MW: Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 14:173–188. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clarke R, Liu MC, Bouker KB, et al:
Antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer and the role of estrogen
receptor signaling. Oncogene. 22:7316–7339. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schwartz JL, Shajahan AN and Clarke R: The
role of interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF1) in overcoming
antiestrogen resistance in the treatment of breast cancer. Int J
Breast Cancer. 2011:9121022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou C, Zhong Q, Rhodes LV, et al:
Proteomic analysis of acquired tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 cells
reveals expression signatures associated with enhanced migration.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R452012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Canney PA, Griffiths T, Latief TN and
Priestman TJ: Clinical significance of tamoxifen withdrawal
response. Lancet. 1:361987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Howell A, Dodwell DJ, Anderson H and
Redford J: Response after withdrawal of tamoxifen and progestogens
in advanced breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 3:611–617. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Banerjee S, Kambhampati S, Haque I and
Banerjee SK: Pomegranate sensitizes tamoxifen action in ER-alpha
positive breast cancer cells. J Cell Commun Signal. 5:317–324.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leung E, Kannan N, Krissansen GW, Findlay
MP and Baguley BC: MCF-7 breast cancer cells selected for tamoxifen
resistance acquire new phenotypes differing in DNA content,
phospho-HER2 and PAX2 expression, and rapamycin sensitivity. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:717–724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
deGraffenried LA, Friedrichs WE, Russell
DH, et al: Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response
in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt Activity. Clin Cancer Res.
10:8059–8067. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vivacqua A, Bonofiglio D, Recchia AG, et
al: The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates the proliferative
effects induced by 17beta-estradiol and hydroxytamoxifen in
endometrial cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 20:631–646. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carmeci C, Thompson DA, Ring HZ, Francke U
and Weigel RJ: Identification of a gene (GPR30) with homology to
the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily associated with estrogen
receptor expression in breast cancer. Genomics. 45:607–617. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Filardo EJ, Graeber CT, Quinn JA, et al:
Distribution of GPR30, a seven membrane-spanning estrogen receptor,
in primary breast cancer and its association with clinicopathologic
determinants of tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6359–6366.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Birnbaumer L and Teng CT: Regulation
of ERRalpha gene expression by estrogen receptor agonists and
antagonists in SKBR3 breast cancer cells: differential molecular
mechanisms mediated by g protein-coupled receptor GPR30/GPER-1. Mol
Endocrinol. 24:969–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kleuser B, Malek D, Gust R, Pertz HH and
Potteck H: 17-Beta-estradiol inhibits transforming growth
factor-beta signaling and function in breast cancer cells via
activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase through the G
protein-coupled receptor 30. Mol Pharmacol. 74:1533–1543. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, et
al: Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth
factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen
receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 68:826–833. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Madden TA, et
al: Oestrogen receptor-mediated modulation of the EGFR/MAPK pathway
in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
81:81–93. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng B, Lavoie C, Tang TD, et al:
Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor degradation by
heterotrimeric Galphas protein. Mol Biol Cell. 15:5538–5550. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stryjek-Kaminska D, Piiper A and Zeuzem S:
Epidermal growth factor regulates adenylate cyclase activity via Gs
and Gi1–2 proteins in pancreatic acinar membranes. Biochem J.
316:87–91. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maggiolini M and Picard D: The unfolding
stories of GPR30, a new membrane-bound estrogen receptor. J
Endocrinol. 204:105–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huiart L, Dell'Aniello S and Suissa S: Use
of tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors in a large population-based
cohort of women with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:1558–1563.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|