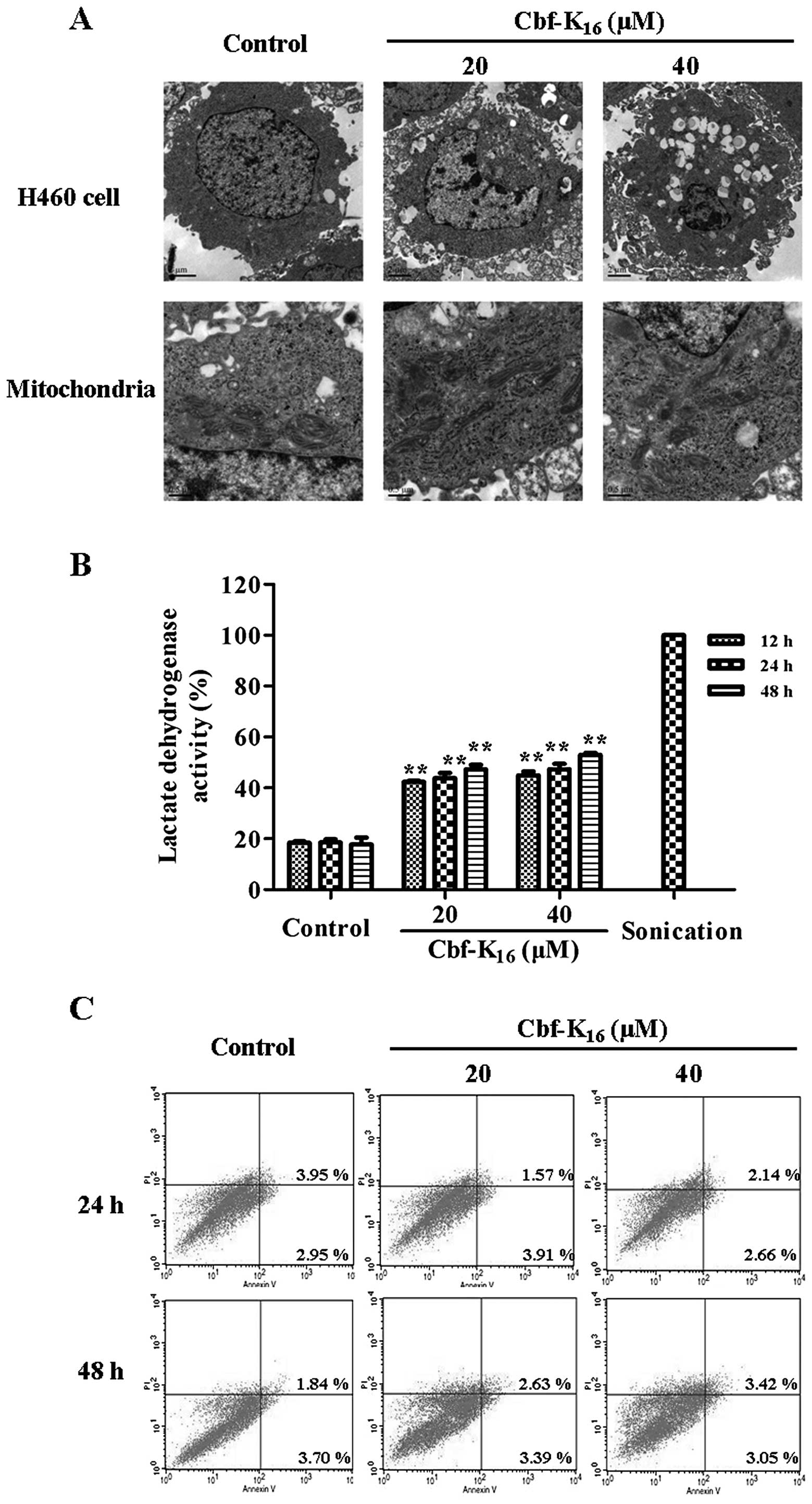
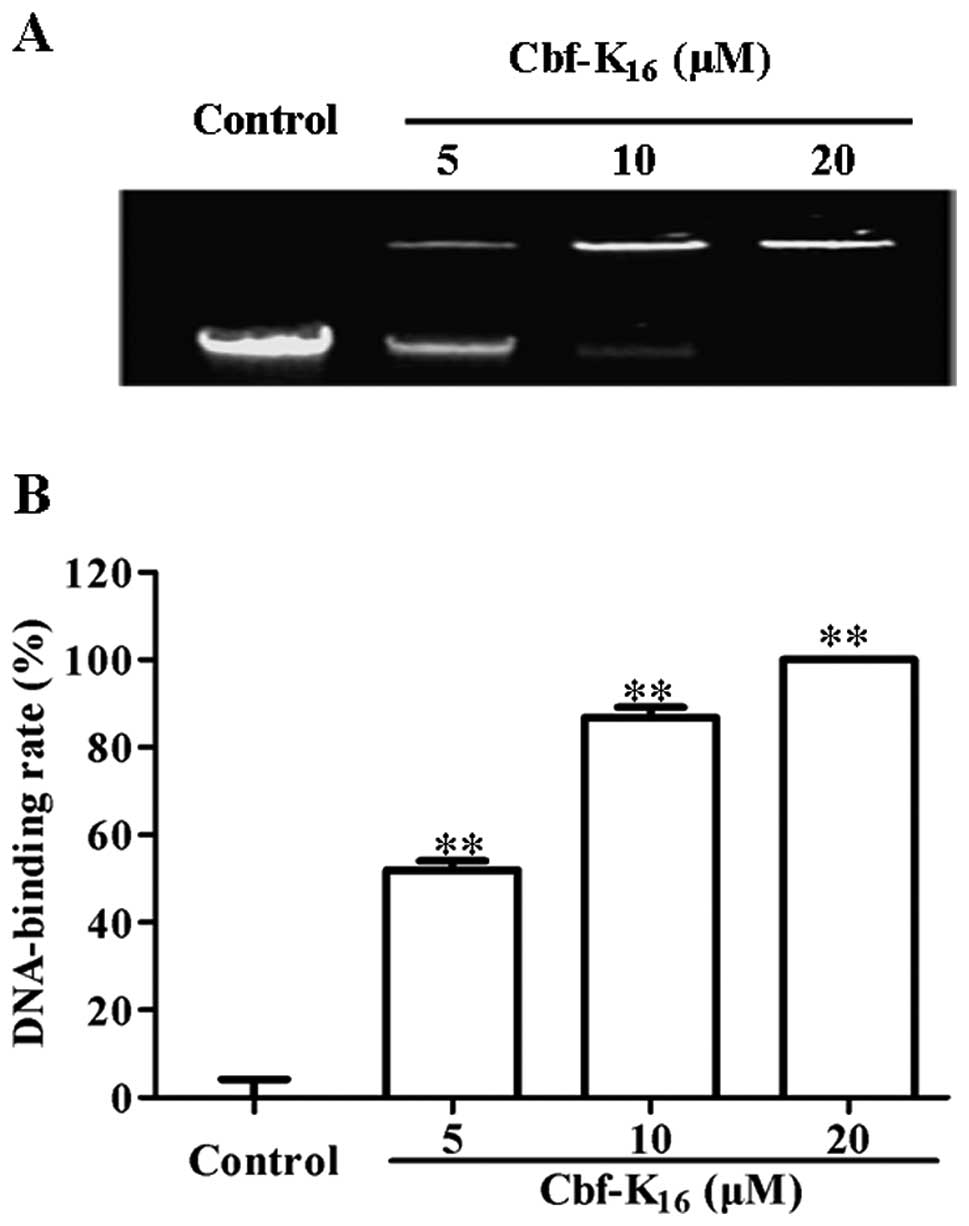
|
1
|
Yan JX, Wang KR, Chen R, Song JJ, Zhang
BZ, Dang W, Zhang W and Wang R: Membrane active antitumor activity
of NK-18, a mammalian NK-lysin-derived cationic antimicrobial
peptide. Biochimie. 94:184–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lehmann J, Retz M, Sidhu SS, Suttmann H,
Sell M, Paulsen F, Harder J, Unteregger G and Stöckle M: Antitumor
activity of the antimicrobial peptide magainin II against bladder
cancer cell lines. Eur Urol. 50:141–147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hoskin DW and Ramamoorthy A: Studies on
anticancer activities of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophysica
Acta. 1778:357–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vanajothi R, Sudha A, Manikandan R,
Rameshthangam P and Srinivasan P: Luffa acutangula and
lippia nodiflora leaf extract induces growth inhibitory
effect through induction of apoptosis on human lung cancer cell
line. Biomed Prev Nutr. 2:287–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Quadrelli S, Lyons G, Colt H, Chimondeguy
D and Silva C: Lung cancer as a second primary malignancy:
increasing prevalence and its influence on survival. Ann Surg
Oncol. 16:1033–1038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim HM, Lim J, Park SK, Kang JS, Lee K,
Lee CW, Lee KH, Yun MJ, Yang KH, Han G, Kwon SW, Kim Y and Han SB:
Antitumor activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against human
lung cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1802–1807. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Doroshow JH, Juhasz A, Ge Y, Holbeck S, Lu
J, Antony S, Wu Y, Jiang G and Roy K: Antiproliferative mechanisms
of action of the flavin dehydrogenase inhibitors diphenylene
iodonium and di-2-thienyliodonium based on molecular profiling of
the NCI-60 human tumor cell panel. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1195–1207.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Maione P, Rossi A, Airoma G, Ferrara C,
Castaldo V and Gridelli C: The role of targeted therapy in
non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 51:29–44. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koh PK, Faivre-Finn C, Blackhall FH and
Ruysscher D: Targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
clinical developments and rationale for the combination with
thoracic radiotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:626–640. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang W, Shi Y, Chen Y, Yu S, Hao J, Luo
J, Sha X and Fang X: Enhanced antitumor efficacy by
paclitaxel-loaded pluronic P123/F127 mixed micelles against
non-small cell lung cancer based on passive tumor targeting and
modulation of drug resistance. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 75:341–353.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dempke WC, Suto T and Reck M: Targeted
therapies for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 67:257–274.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang K, Yan J, Liu X, Zhang J, Chen R,
Zhang B, Dang W, Zhang W, Kai M, Song J and Wang R: Novel
cytotoxity exhibition mode of polybia-CP, a novel antimicrobial
peptide from the venom of the social wasp Polybia paulista.
Toxicology. 288:27–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zasloff M: Antimicrobial peptides of
multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Hu J, Zhang S, Zhou P, Zhao X, Xu
H, Zhao X, Yaseen M and Lu JR: Molecular mechanisms of
antibacterial and antitumor actions of designed surfactant-like
peptides. Biomaterials. 33:592–603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou H, Dou J, Wang J, Chen L, Wang H,
Zhou W, Li Y and Zhou C: The antibacterial activity of BF-30 in
vitro and in infected burned rats is through interference with
cytoplasmic membrane integrity. Peptides. 32:1131–1138. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Almaaytah A, Zhou M, Wang L, Chen T,
Walker B and Shaw C: Antimicrobial/cytolytic peptides from the
venom of the North African scorpion, Androctonus amoreuxi:
biochemical and functional characterization of natural peptides and
a single site-substituted analog. Peptides. 35:291–299.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okumura K: Cathelicidins - Therapeutic
antimicrobial and antitumor host defense peptides for oral
diseases. Jpn Dental Sci Rev. 47:67–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chan DI, Prenner EJ and Vogel HJ:
Tryptophan- and arginine-rich antimicrobial peptides: structures
and mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1758:1184–1202.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Hong J, Liu X, Yang H, Liu R, Wu
J, Wang A, Lin D and Lai R: Snake cathelicidin from Bungarus
fasciatus is a potent peptide antibiotics. PLoS One.
3:e32172008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chen L, Guang H, Li Z,
Yang H, Li J, You D, Yu H and Lai R: Cathelicidin-BF, a snake
cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide, could be an excellent
therapeutic agent for Acne Vulgaris. PLoS One. 6:e221202011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hao Q, Wang H, Wang J, Dou J, Zhang M,
Zhou W and Zhou C: Effective antimicrobial activity of
Cbf-K16 and Cbf-A7A13 against
NDM-1-carrying Escherichia coli by DNA binding after
penetrating the cytoplasmic membrane in vitro. J Pept Sci.
19:173–180. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang H, Ke M, Tian Y, Wang J, Li B, Wang
Y, Dou J and Zhou C: BF-30 selectively inhibits melanoma cell
proliferation via cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization and
DNA-binding in vitro and in B16F10-bearing mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 707:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin WJ, Chien YL, Pan CY, Lin TL, Chen JY,
Chiu SJ and Hui CF: Epinecidin-1, an antimicrobial peptide from
fish (Epinephelus coioides) which has an antitumor effect
like lytic peptides in human fibrosarcoma cells. Peptides.
30:283–290. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen JY, Lin WJ and Lin TL: A fish
antimicrobial peptide, tilapia hepcidin TH2-3, shows potent
antitumor activity against human fibrosarcoma cells. Peptides.
30:1636–1642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang C, Li HB, Li S, Tian LL and Shang DJ:
Antitumor effects and cell selectivity of temporin-1CEa, an
antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretions of the Chinese brown
frog (Rana chensinensis). Biochimie. 94:434–441. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Qu Y, Zhang J and Wang X:
Ardipusilloside I purified from Ardisia pusilla
competitively binds VEGFR and induces apoptosis in NCI-H460 cells.
Phytomedicine. 17:519–526. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Bolt AM, Byrd RM and Klimecki WT:
Autophagy is the predominant process induced by arsenite in human
lymphoblastoid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 244:366–373. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang WT, Pan CY, Rajanbabu V, Cheng CW
and Chen JY: Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) antimicrobial
peptide, hepcidin 1–5, shows antitumor activity in cancer cells.
Peptides. 32:342–352. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsu JC, Lin LC, Tzen JT and Chen JY:
Characteristics of the antitumor activities in tumor cells and
modulation of the inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells of a
novel antimicrobial peptide, chrysophsin-1, from the red sea bream
(Chrysophrys major). Peptides. 32:900–910. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen JY, Lin WJ, Wu JL, Her GM and Hui CF:
Epinecidin-1 peptide induces apoptosis which enhances antitumor
effects in human leukemia U937 cells. Peptides. 30:2365–2373. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paredes-Gamero EJ, Martins MN, Cappabianco
FA, Ide JS and Miranda A: Characterization of dual effects induced
by antimicrobial peptides: regulated cell death or membrane
disruption. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:1062–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu H, Zhou BH, Qiu X, Wang HS, Zhang F,
Fang R, Wang XF, Cai SH, Du J and Bu XZ: T63, a new 4-arylidene
curcumin analogue, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through
activation of the reactive oxygen species-FOXO3a pathway in lung
cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:2204–2217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang YQ, Su J, Wu F, Lu P, Yuan LF, Yuan
WE, Sheng J and Jin T: Biscarbamate cross-linked polyethylenimine
derivative with low molecular weight, low cytotoxicity, and high
efficiency for gene delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:693–704.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu JC, Lin LC, Tzen JT and Chen JY:
Pardaxin-induced apoptosis enhances antitumor activity in HeLa
cells. Peptides. 32:1110–1116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim YS, Jin HO, Seo SK, Woo SH, Choe TB,
An S, Hong SI, Lee SJ, Lee KH and Park IC: Sorafenib induces
apoptotic cell death in human non-small cell lung cancer cells by
down-regulating mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent
survivin expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:216–226. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Custodio A, Méndez M and Provencio M:
Targeted therapies for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current
status and future implications. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:36–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Wilt LH, Jansen G, Assaraf YG, van
Meerloo J, Cloos J, Schimmer AD, Chan ET, Kirk CJ, Peters GJ and
Kruyt FA: Proteasome-based mechanisms of intrinsic and acquired
bortezomib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 83:207–217. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Leung HW, Yang WH, Lai MY, Lin CJ and Lee
HZ: Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase during baicalein-induced human
lung non-small carcinoma H460 cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:403–411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Silvestri GA and Rivera MP: Targeted
therapy for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a
review of the epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists. Chest.
128:3975–3984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen YL, Li JH, Yu CY, Lin CJ, Chiu PH,
Chen PW, Lin CC and Chen WJ: Novel cationic antimicrobial peptide
GW-H1 induced caspase-dependent apoptosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma cell lines. Peptides. 36:257–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schweizer F: Cationic amphiphilic peptides
with cancer-selective toxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 625:190–194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Y, Xia X, Xu L and Wang Y: Design of
hybrid β-hairpin peptides with enhanced cell specificity and potent
anti-inflammatory activity. Biomaterials. 34:237–250. 2013.
|