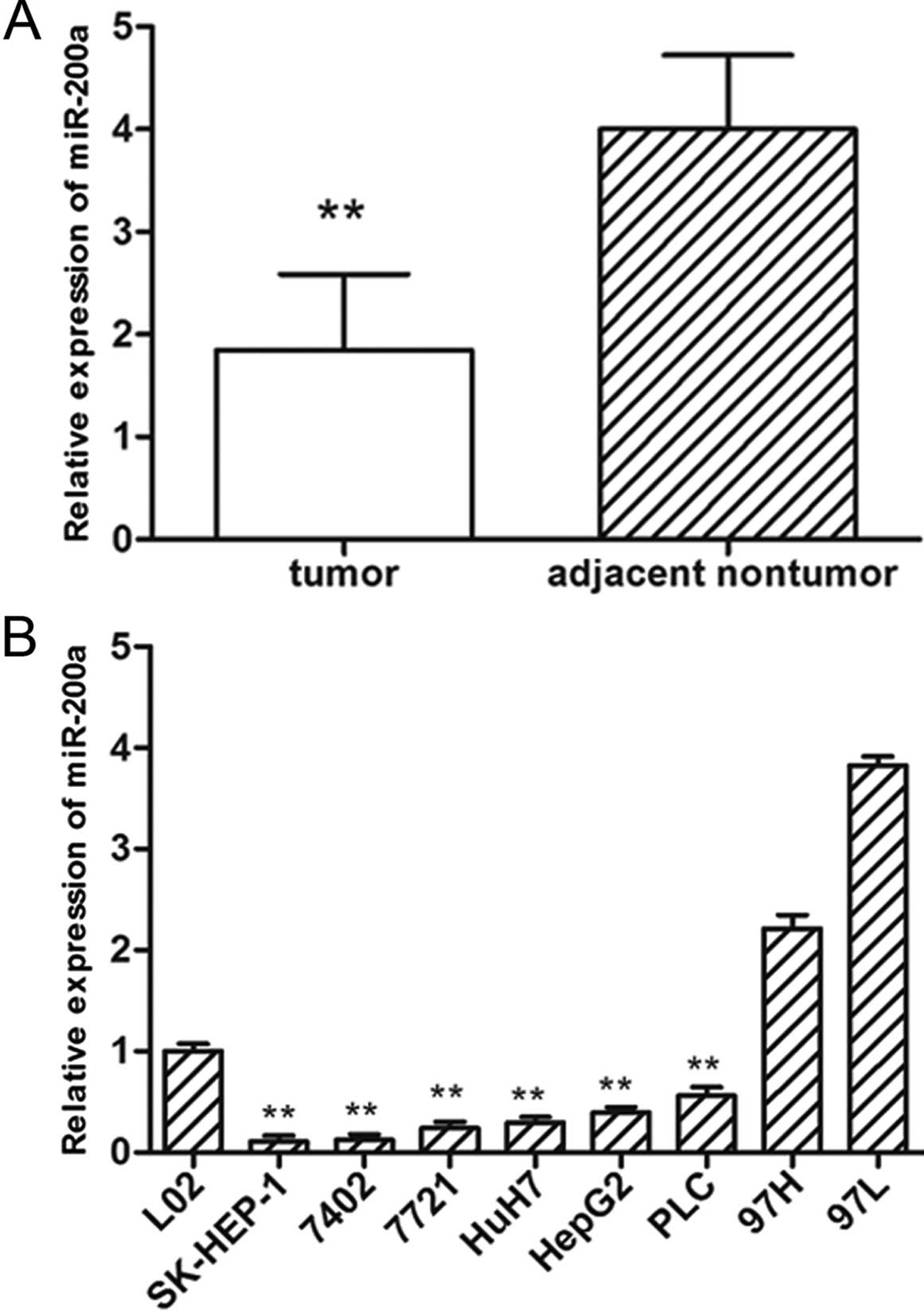
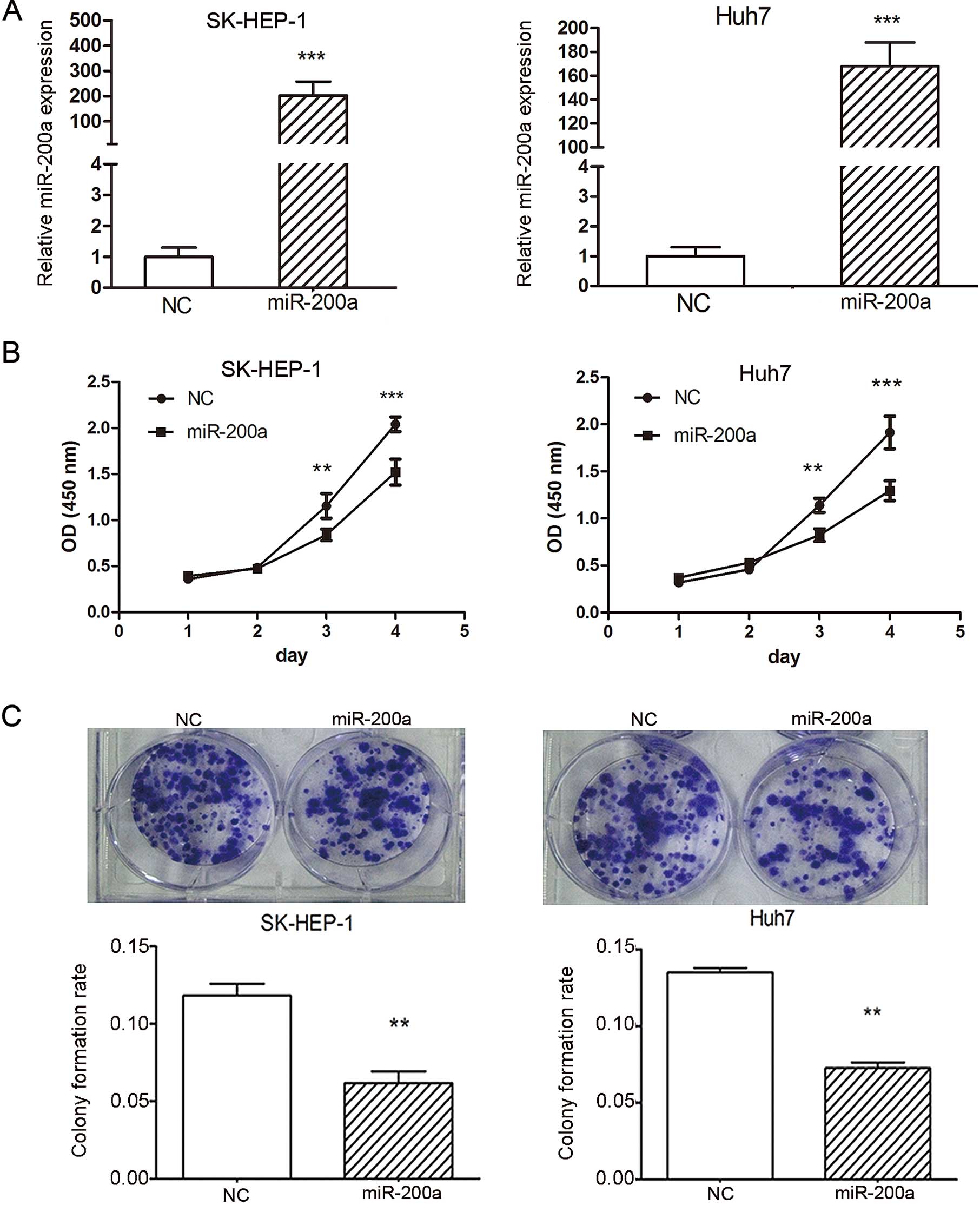
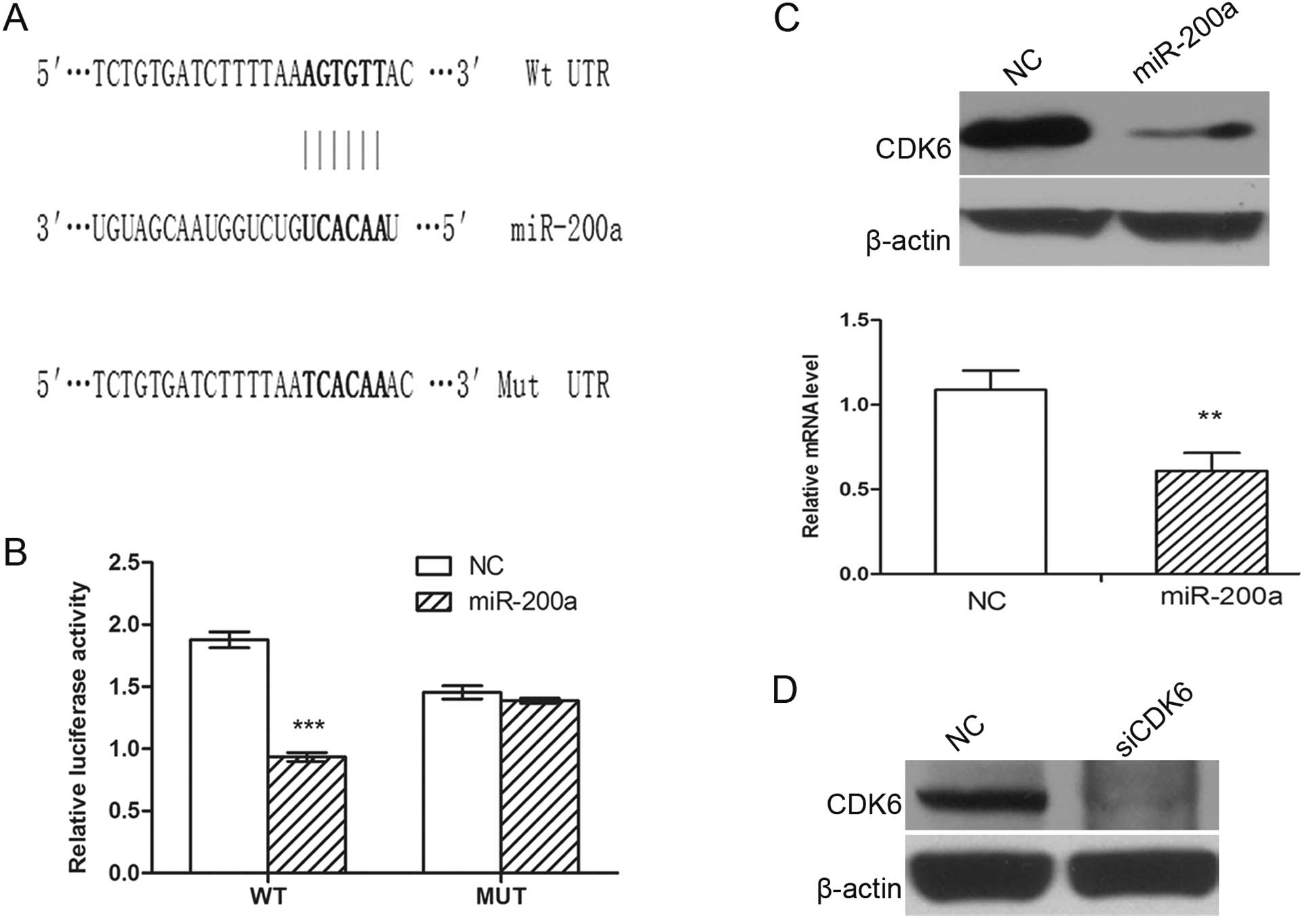
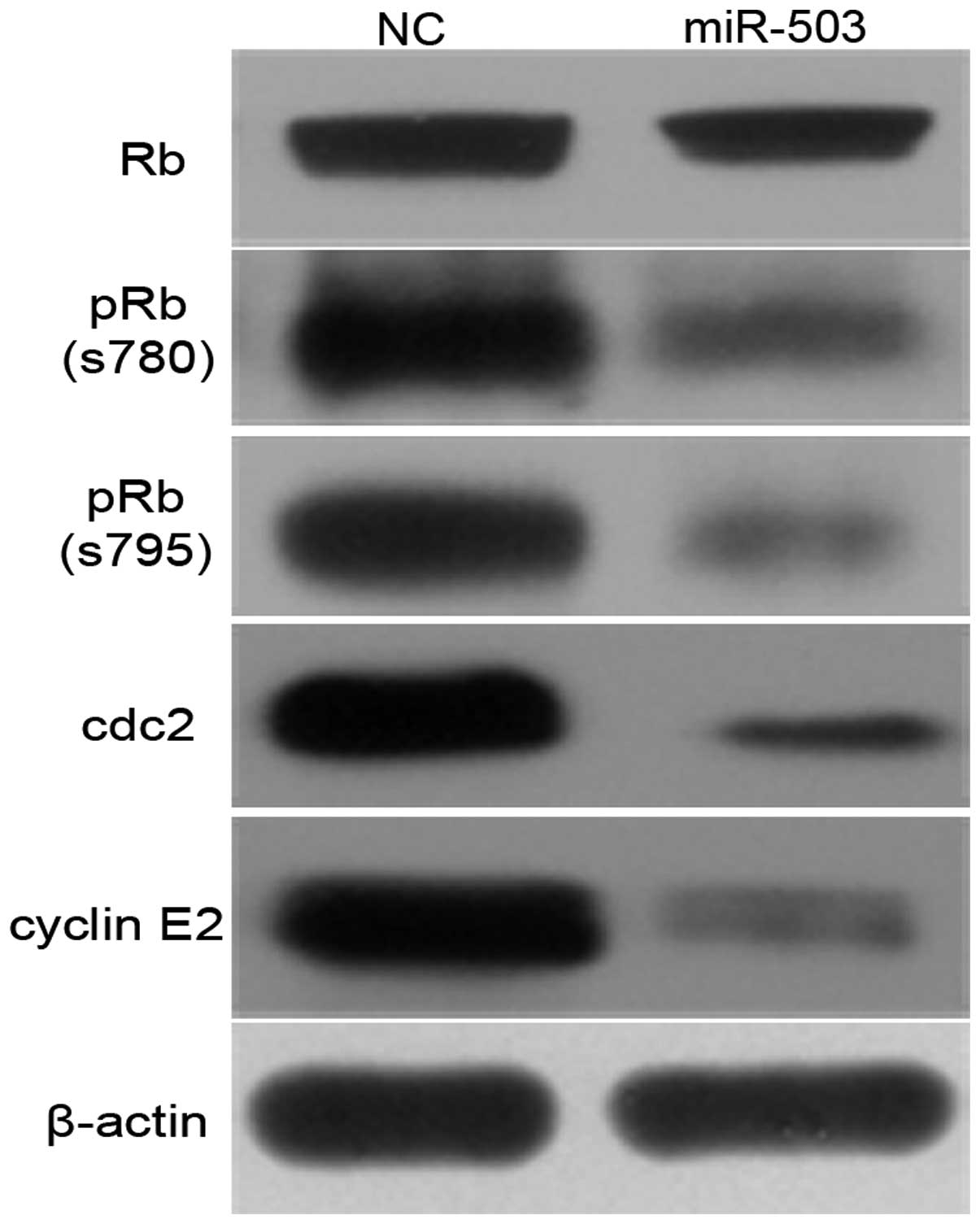
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, et al: A
brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development.
Nature. 439:283–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell
RB and Cohen SM: bantam encodes a developmentally regulated
microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the
proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 113:25–36. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, et al: MicroRNA-101,
down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and
suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, et al:
MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, et al:
Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in
hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene.
25:2537–2545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, et al:
Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 37:495–500.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Massagué J: G1 cell-cycle control and
cancer. Nature. 432:298–306. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Deshpande A, Sicinski P and Hinds PW:
Cyclins and cdks in development and cancer: a perspective.
Oncogene. 24:2909–2915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H and Qi ZT:
MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 33:1113–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP and
Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates
G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatology. 50:113–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers
identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol. 219:214–221. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ahn SM, Cha JY, Kim J, et al: Smad3
regulates E-cadherin via miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene. 31:3051–3059.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saydam O, Shen Y, Würdinger T, et al:
Downregulated microRNA-200a in meningiomas promotes tumor growth by
reducing E-cadherin and activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5923–5940. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, et al:
miR-200a-mediated downregulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially
inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and
invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:535–541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hung CS, Liu HH, Liu JJ, et al:
MicroRNA-200a and -200b mediated hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration through the epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers.
Ann Surg Oncol. Aug 7–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
28
|
Lee JW, Park YA, Choi JJ, et al: The
expression of the miRNA-200 family in endometrial endometrioid
carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 120:56–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grillo M, Bott MJ, Khandke N, et al:
Validation of cyclin D1/CDK4 as an anticancer drug target in MCF-7
breast cancer cells: effect of regulated overexpression of cyclin
D1 and siRNA-mediated inhibition of endogenous cyclin D1 and CDK4
expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 95:185–194. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bagchi A and Mills AA: The quest for the
1p36 tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 68:2551–2556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sato Y, Kobayashi H, Suto Y, et al:
Chromosomal instability in chromosome band 12p13: multiple breaks
leading to complex rearrangements including cytogenetically
undetectable sub-clones. Leukemia. 15:1193–1202. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|