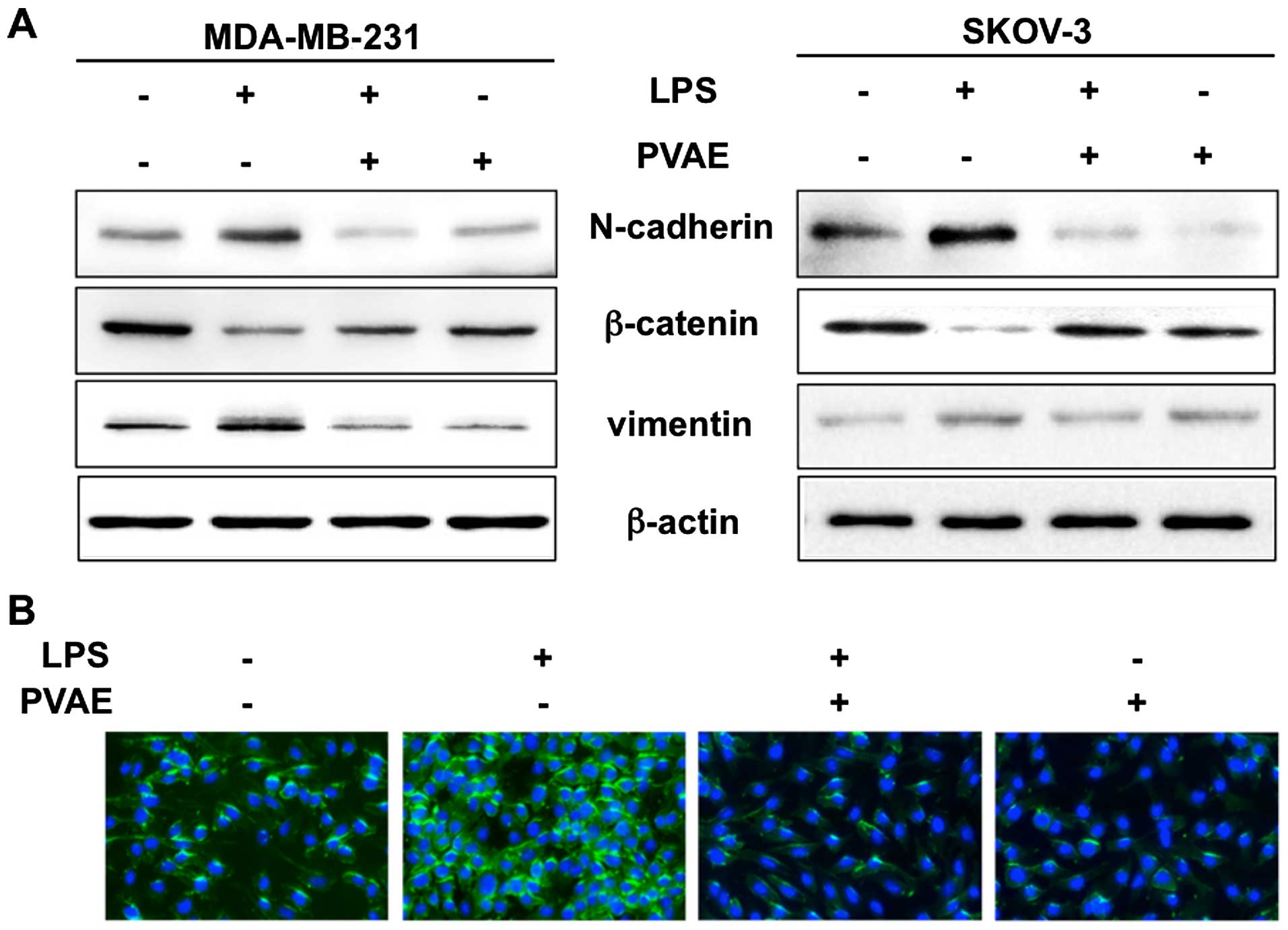
|
1
|
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z and Sarkar FH: Cancer
stem cells and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT)-phenotypic cells: Are They Cousins or Twins? Cancers (Basel).
3:716–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu HX, Lee SH, Lee SF, White RL and Blay
J: Isolation and characterization of an anti-HSV polysaccharide
from Prunella vulgaris. Antiviral Res. 44:43–54. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hwang YJ, Lee EJ, Kim HR and Hwang KA: In
vitro antioxidant and anticancer effects of solvent fractions from
Prunella vulgaris var. lilacina. BMC Complement Altern Med.
13:3102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park SH, Koo HJ, Sung YY and Kim HK: The
protective effect of Prunella vulgaris ethanol extract against
vascular inflammation in TNF-α-stimulated human aortic smooth
muscle cells. BMB Rep. 46:352–357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Psotová J, Kolár M, Sousek J, Svagera Z,
Vicar J and Ulrichová J: Biological activities of Prunella vulgaris
extract. Phytother Res. 17:1082–1087. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoon MY, Choi GJ, Choi YH, Jang KS, Park
MS, Cha B and Kim JC: Effect of polyacetylenic acids from Prunella
vulgaris on various plant pathogens. Lett Appl Microbiol.
51:511–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choi JH, Han EH, Hwang YP, Choi JM, Choi
CY, Chung YC, Seo JK and Jeong HG: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor
cell invasion and metastasis by aqueous extract isolated from
Prunella vulgaris via the inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9
expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:564–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim SH, Huang CY, Tsai CY, Lu SY, Chiu CC
and Fang K: The aqueous extract of Prunella vulgaris suppresses
cell invasion and migration in human liver cancer cells by
attenuating matrix metalloproteinases. Am J Chin Med. 40:643–656.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen MC, Chang WW, Kuan YD, Lin ST, Hsu HC
and Lee CH: Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in mouse melanoma model. Innate Immun. 18:685–693. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang T, Chen Z and Fang L: Curcumin
inhibits LPS-induced EMT through downregulation of NF-κB-Snail
signaling in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 29:117–124. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Herschkowitz JI, Zhao W, Zhang M, Usary J,
Murrow G, Edwards D, Knezevic J, Greene SB, Darr D, Troester MA, et
al: Comparative oncogenomics identifies breast tumors enriched in
functional tumor-initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:2778–2783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou
C, Hirsch HA, Tsichlis PN and Struhl K: Loss of miR-200 inhibition
of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the
formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell.
39:761–772. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li QQ, Xu JD, Wang WJ, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Tang F, Chen ZQ, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Twist1-mediated
adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to
multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2657–2665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim HI, Quan FS, Kim JE, Lee NR, Kim HJ,
Jo SJ, Lee CM, Jang DS and Inn KS: Inhibition of estrogen signaling
through depletion of estrogen receptor alpha by ursolic acid and
betulinic acid from Prunella vulgaris var. lilacina. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 451:282–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Blinman P, Alam M, Duric V, McLachlan SA
and Stockler MR: Patients' preferences for chemotherapy in
non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Lung Cancer.
69:141–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng L, Jia X, Zhu M, Chen Y and Shi F:
Chemoprevention by Prunella vulgaris L. extract of non-small cell
lung cancer via promoting apoptosis and regulating the cell cycle.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:1355–1358. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Feng L, Jia XB, Jiang J, Zhu MM, Chen Y,
Tan XB and Shi F: Combination of active components enhances the
efficacy of Prunella in prevention and treatment of lung cancer.
Molecules. 15:7893–7906. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu Y, Jiang Z, Ji G and Liu J: Inhibition
of bone metastasis from breast carcinoma by rosmarinic acid. Planta
Med. 76:956–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Y, Xu G, Liu L, Xu D and Liu J:
Anti-invasion effect of rosmarinic acid via the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase and oxidation-reduction pathway in Ls174-T
cells. J Cell Biochem. 111:370–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nguyen PT, Kudo Y, Yoshida M, Kamata N,
Ogawa I and Takata T: N-cadherin expression is involved in
malignant behavior of head and neck cancer in relation to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Histol Histopathol. 26:147–156.
2011.
|
|
26
|
Araki K, Shimura T, Suzuki H, Tsutsumi S,
Wada W, Yajima T, Kobayahi T, Kubo N and Kuwano H: E/N-cadherin
switch mediates cancer progression via TGF-β-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:1885–1893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang J, Xiao D, Li G, Ma J, Chen P, Yuan
W, Hou F, Ge J, Zhong M, Tang Y, et al: EphA2 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 33:2737–2747. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu Z, Chen L, Zhang X, Xu X, Xing H,
Zhang Y, Li W, Yu H, Zeng J and Jia J: RUNX3 regulates vimentin
expression via miR-30a during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:610–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ennen M, Klotz R, Touche N, Pinel S,
Barbieux C, Besancenot V, Brunner E, Thiebaut D, Jung AC,
Ledrappier S, et al: DDB2: A novel regulator of NF-κB and breast
tumor invasion. Cancer Res. 73:5040–5052. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu K, Zeng J, Li L, Fan J, Zhang D, Xue Y,
Zhu G, Yang L, Wang X and He D: Silibinin reverses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in metastatic prostate cancer
cells by targeting transcription factors. Oncol Rep. 23:1545–1552.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE,
Morimiya A, Badve S and Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin
expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2.
Oncogene. 26:711–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH and Sonenshein
GE: NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 104:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|