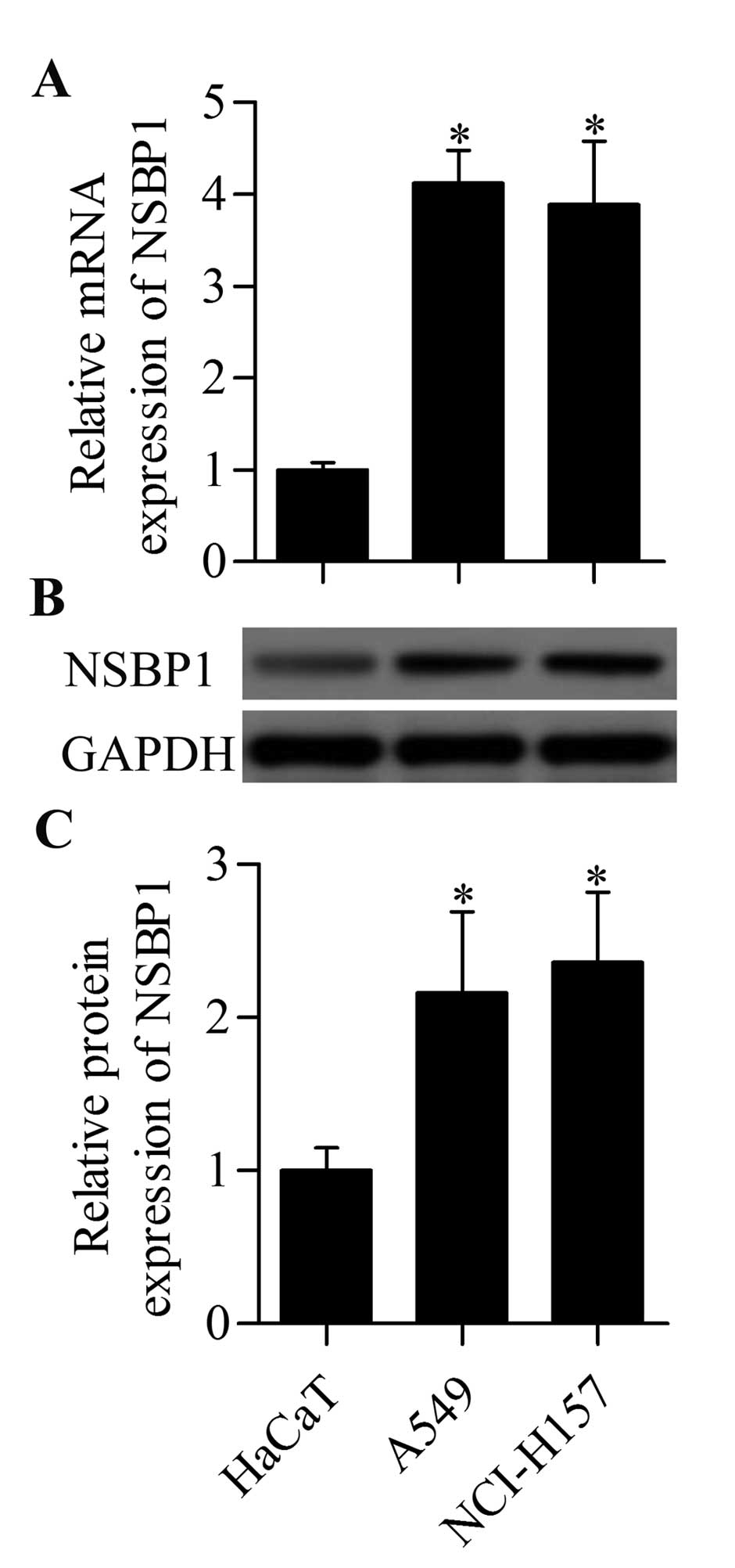
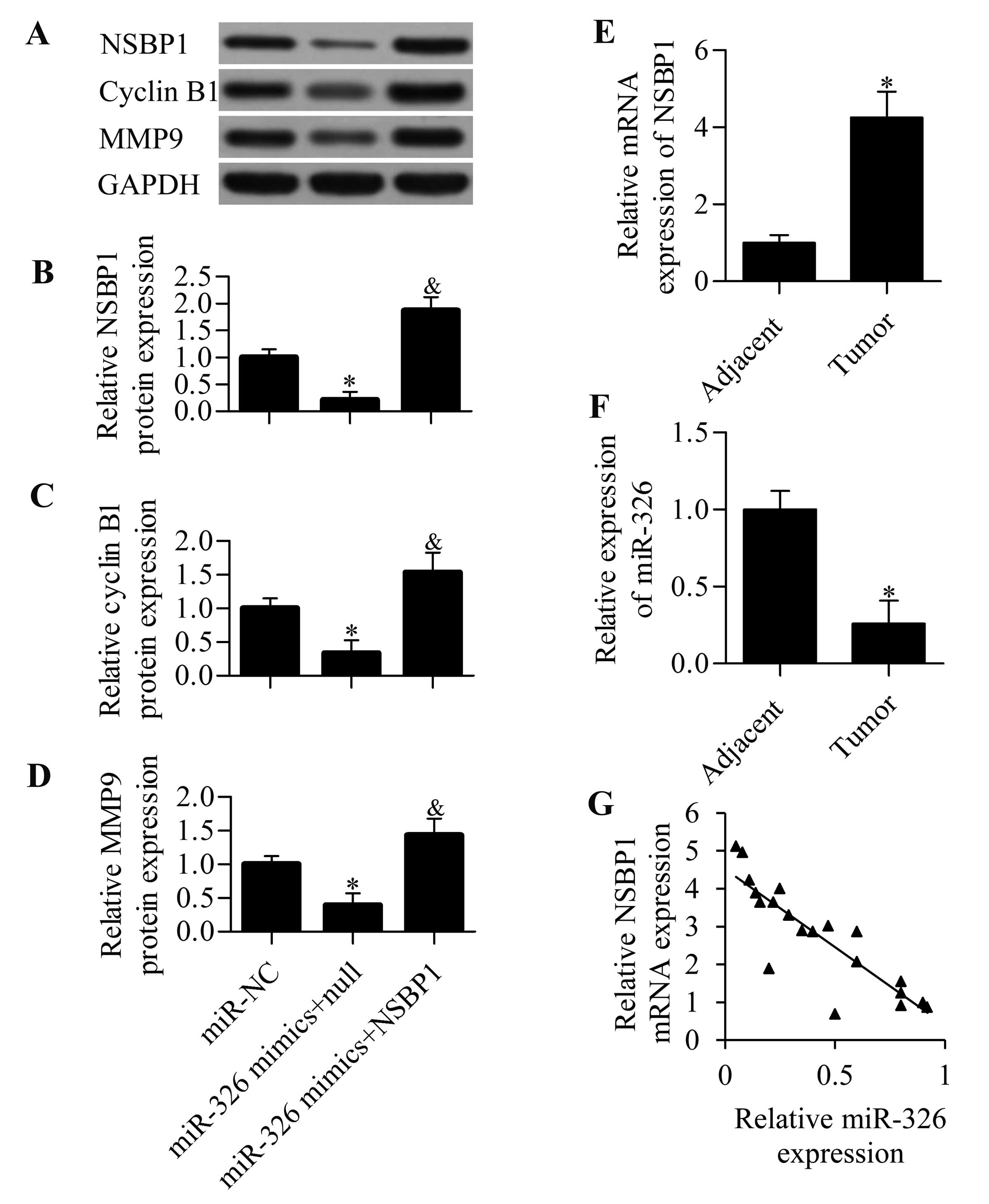
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger R, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, et al: International Association for the study of
lung cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society
International multidisciplinary classification of lung
adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Claassens L, van Meerbeeck J, Coens C,
Quinten C, Ghislain I, Sloan EK, Wang XS, Velikova G and Bottomley
A: Health-related quality of life in non-small cell lung cancer: An
update of a systematic review on methodologic issues in randomized
controlled trials. J Clin Oncol. 29:2104–2120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Tian T, Jin G, Shu
Y, Chen Y, Xu L, Zen K, Zhang C, et al: Serum microRNA signatures
identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling
predict survival of non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1721–1726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rottiers V, Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo
F, Gurumurthy S, Zhong L, Li Y, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE, Bardeesy N,
Mostoslavsky R, et al: MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic
diseases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 76:225–233. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aigner A: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer
invasion and metastasis: Therapeutic approaches based on
metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med Berl. 89:445–457. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hock R, Furusawa T, Ueda T and Bustin M:
HMG chromosomal proteins in development and disease. Trends Cell
Biol. 17:72–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shirakawa H, Landsman D, Postnikov YV and
Bustin M: NBP-45, a novel nucleosomal binding protein with a
tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression. J Biol
Chem. 275:6368–6374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
King LM and Francomano CA:
Characterization of a human gene encoding nucleosomal binding
protein NSBP1. Genomics. 71:163–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang N, Zhou LQ and Zhang XY:
Downregulation of the nucleosome-binding protein 1 (NSBP1) gene can
inhibit the in vitro and in vivo proliferation of prostate cancer
cells. Asian J Androl. 12:709–717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qu J, Yan R, Chen J, Xu T, Zhou J, Wang M,
Chen C, Yan Y and Lu Y: HMGN5: A potential oncogene in gliomas. J
Neurooncol. 104:729–736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wahafu W, He ZS, Zhang XY, Zhang CJ, Yao
K, Hao H, Song G, He Q, Li XS and Zhou LQ: The nucleosome binding
protein NSBP1 is highly expressed in human bladder cancer and
promotes the proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 32:931–939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weng M, Song F, Chen J, Wu J, Qin J, Jin T
and Xu J: The high-mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5 is
highly expressed in breast cancer and promotes the proliferation
and invasion of breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 36:959–966. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Yuan B, Yuan W, Wang C, Gao R and
Wang J: The expression and clinical significance of high mobility
group nucleosome binding domain 5 in human osteosarcoma. Tumour
Biol. 35:6539–6547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen P, Wang XL, Ma ZS, Xu Z, Jia B, Ren
J, Hu YX, Zhang QH, Ma TG, Yan BD, et al: Knockdown of HMGN5
expression by RNA interference induces cell cycle arrest in human
lung cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3223–3228. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barger JF and Nana-Sinkam SP: MicroRNA as
tools and therapeutics in lung cancer. Respir Med. 109:803–812.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang XY, Guo ZQ, Ji SQ, Zhang M, Jiang N,
Li XS and Zhou LQ: Small interfering RNA targeting HMGN5 induces
apoptosis via modulation of a mitochondrial pathway and Bcl-2
family proteins in prostate cancer cells. Asian J Androl.
14:487–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji SQ, Yao L, Zhang XY, Li XS and Zhou LQ:
Knockdown of the nucleosome binding protein 1 inhibits the growth
and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro and
in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang C, Gao R, Wang J, Yuan W, Wang C and
Zhou X: High-mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5 increases
drug resistance in osteosarcoma through upregulating autophagy.
Tumour Biol. 35:6357–6363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su B, Shi B, Tang Y, Guo Z, Yu X, He X, Li
X, Gao X and Zhou L: HMGN5 knockdown sensitizes prostate cancer
cells to ionizing radiation. Prostate. 75:33–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kefas B, Comeau L, Floyd DH, Seleverstov
O, Godlewski J, Schmittgen T, Jiang J, diPierro CG, Li Y, Chiocca
EA, et al: The neuronal microRNA miR-326 acts in a feedback loop
with notch and has therapeutic potential against brain tumors. J
Neurosci. 29:15161–15168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kefas B, Comeau L, Erdle N, Montgomery E,
Amos S and Purow B: Pyruvate kinase M2 is a target of the
tumor-suppressive microRNA-326 and regulates the survival of glioma
cells. Neuro-oncol. 12:1102–1112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Lu S, Geng S, Ma S, Liang Z and
Jiao B: Expression and clinical significance of microRNA-326 in
human glioma miR-326 expression in glioma. Med Oncol. 30:3732013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang ZL, Bai ZH, Wang XB, Bai L, Miao F
and Pei HH: miR-186 and 326 predict the prognosis of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma and affect the proliferation and migration of
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01188142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Xu T, Yan Y, Qin R, Wang H, Zhang
X, Huang Y, Wang Y, Lu Y, Fu D, et al: MicroRNA-326 functions as a
tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting the Nin one binding protein
(NOB1). PLoS One. 8:e684692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu L, Hui H, Wang LJ, Wang H, Liu QF and
Han SX: MicroRNA-326 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal
cancer by targeting the nin one binding protein. Oncol Rep.
33:2309–2318. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cai M, Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhou H, Jin L, Bai
R and Weng Y: Adam17, a target of miR-326, promotes EMT-induced
cells invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1175–1185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|