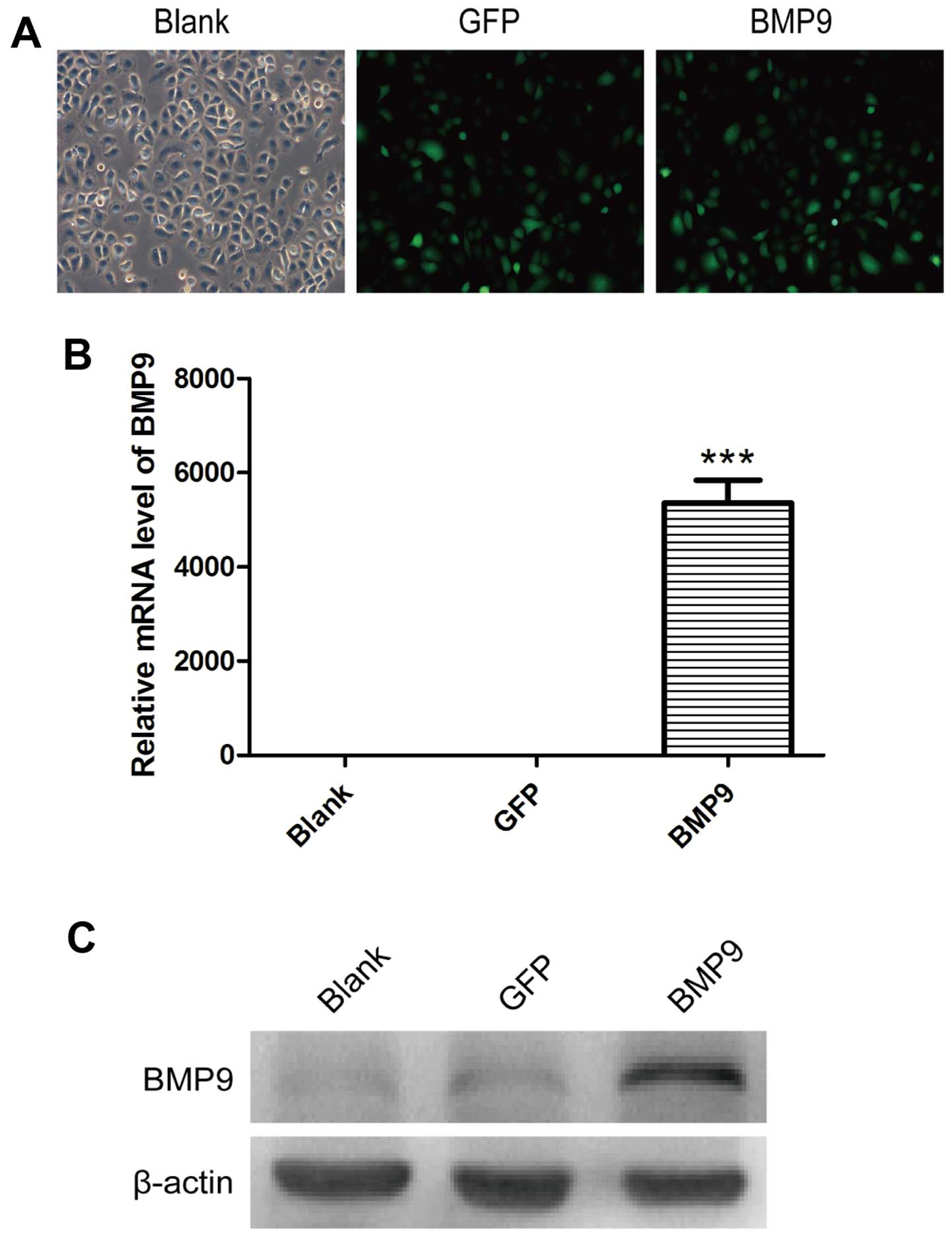
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
D'Addario G: Non-small-cell lung cancer:
ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 20(Suppl 4): 68–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siddiqui S, Ali MU, Ali MA, Shah N and
Nasreen S: Lung carcinoma: Its profile and changing trends. J Ayub
Med Coll Abbottabad. 22:116–119. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tamura T, Kurishima K, Nakazawa K,
Kagohashi K, Ishikawa H, Satoh H and Hizawa N: Specific organ
metastases and survival in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.
Mol Clin Oncol. 3:217–221. 2015.
|
|
5
|
Coleman RE: Metastatic bone disease:
Clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer
Treat Rev. 27:165–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tubiana-Hulin M: Incidence, prevalence and
distribution of bone metastases. Bone. 12(Suppl 1): S9–S10. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast. 1889.Cancer Metastasis Rev.
8:98–101. 1989.
|
|
8
|
Langley RR and Fidler IJ: Tumor cell-organ
microenvironment interactions in the pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis. Endocr Rev. 28:297–321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sivasubramaniyan K, Lehnen D, Ghazanfari
R, Sobiesiak M, Harichandan A, Mortha E, Petkova N, Grimm S,
Cerabona F, de Zwart P, et al: Phenotypic and functional
heterogeneity of human bone marrow- and amnion-derived MSC subsets.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1266:94–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baksh D, Song L and Tuan RS: Adult
mesenchymal stem cells: Characterization, differentiation, and
application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 8:301–316.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gomes CM: The dual role of mesenchymal
stem cells in tumor progression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sung SY, Hsieh CL, Law A, Zhau HE, Pathak
S, Multani AS, Lim S, Coleman IM, Wu LC, Figg WD, et al:
Coevolution of prostate cancer and bone stroma in three-dimensional
coculture: Implications for cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer
Res. 68:9996–10003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Windus LC, Glover TT and Avery VM:
Bone-stromal cells up-regulate tumourigenic markers in a
tumour-stromal 3D model of prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:1122013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goldstein RH, Reagan MR, Anderson K,
Kaplan DL and Rosenblatt M: Human bone marrow-derived MSCs can home
to orthotopic breast cancer tumors and promote bone metastasis.
Cancer Res. 70:10044–10050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hernanda PY, Pedroza-Gonzalez A, van der
Laan LJ, Bröker ME, Hoogduijn MJ, Ijzermans JN, Bruno MJ, Janssen
HL, Peppelenbosch MP and Pan Q: Tumor promotion through the
mesenchymal stem cell compartment in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:2330–2340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mizuguchi T, Hui T, Palm K, Sugiyama N,
Mitaka T, Demetriou AA and Rozga J: Enhanced proliferation and
differentiation of rat hepatocytes cultured with bone marrow
stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 189:106–119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song B, Kim B, Choi SH, Song KY, Chung YG,
Lee YS and Park G: Mesenchymal stromal cells promote tumor
progression in fibrosarcoma and gastric cancer cells. Korean J
Pathol. 48:217–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang MH, Hu YD, Xu Y, Xiao Y, Luo Y, Song
ZC and Zhou J: Human mesenchymal stem cells enhance autophagy of
lung carcinoma cells against apoptosis during serum deprivation.
Int J Oncol. 42:1390–1398. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian LL, Yue W, Zhu F, Li S and Li W:
Human mesenchymal stem cells play a dual role on tumor cell growth
in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 226:1860–1867. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seike T, Fujita K, Yamakawa Y, Kido MA,
Takiguchi S, Teramoto N, Iguchi H and Noda M: Interaction between
lung cancer cells and astrocytes via specific inflammatory
cytokines in the microenvironment of brain metastasis. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 28:13–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Sierra A, Price JE, García-Ramirez M,
Méndez O, López L and Fabra A: Astrocyte-derived cytokines
contribute to the metastatic brain specificity of breast cancer
cells. Lab Invest. 77:357–368. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kudo O, Sabokbar A, Pocock A, Itonaga I,
Fujikawa Y and Athanasou NA: Interleukin-6 and interleukin-11
support human osteoclast formation by a RANKL-independent
mechanism. Bone. 32:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M,
Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, et al: Bone
Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human
diseases. Genes Dis. 1:87–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ye L, Lewis-Russell JM, Kyanaston HG and
Jiang WG: Bone morphogenetic proteins and their receptor signaling
in prostate cancer. Histol Histopathol. 22:1129–1147.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J,
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC and He TC: Distinct roles
of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 25:665–677. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye L, Kynaston H and Jiang WG: Bone
morphogenetic protein-9 induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells,
the role of prostate apoptosis response-4. Mol Cancer Res.
6:1594–1606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang K, Feng H, Ren W, Sun X, Luo J, Tang
M, Zhou L, Weng Y, He TC and Zhang Y: BMP9 inhibits the
proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1687–1696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wan S, Liu Y, Weng Y, Wang W, Ren W, Fei
C, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Wang T, Wang J, et al: BMP9 regulates
cross-talk between breast cancer cells and bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 37:363–375. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Alam M, Wang JH, Coffey JC, Qadri SS,
O'Donnell A, Aherne T and Redmond HP: Characterization of the
effects of cyclooxy-genase-2 inhibition in the regulation of
apoptosis in human small and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
Ann Surg Oncol. 14:2678–2684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao J, Harper R, Barchowsky A and Di YP:
Identification of multiple MAPK-mediated transcription factors
regulated by tobacco smoke in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L480–L490. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kausar H, Jeyabalan J, Aqil F, Chabba D,
Sidana J, Singh IP and Gupta RC: Berry anthocyanidins
synergistically suppress growth and invasive potential of human
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 325:54–62. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lemmon CR, Woo JH, Tully E, Wilsbach K and
Gabrielson E: Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) mediates a
protective response in cancer cells treated with inhibitors of
fatty acid synthase. J Biol Chem. 286:31457–31465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bauml J, Mick R, Zhang Y, Watt CD, Vachani
A, Aggarwal C, Evans T and Langer C: Determinants of survival in
advanced non–small-cell lung cancer in the era of targeted
therapies. Clin Lung Cancer. 14:581–591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saad F, Lipton A, Cook R, Chen YM, Smith M
and Coleman R: Pathologic fractures correlate with reduced survival
in patients with malignant bone disease. Cancer. 110:1860–1867.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
El-Nikhely N, Larzabal L, Seeger W, Calvo
A and Savai R: Tumor-stromal interactions in lung cancer: Novel
candidate targets for therapeutic intervention. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 21:1107–1122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Peng X, Guo W, Ren T, Lou Z, Lu X, Zhang
S, Lu Q and Sun Y: Differential expression of the RANKL/RANK/OPG
system is associated with bone metastasis in human non-small cell
lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e583612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fei ZH, Yao CY, Yang XL, Huang XE and Ma
SL: Serum BMP-2 up-regulation as an indicator of poor survival in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:5293–5299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deng T, Lin D, Zhang M, Zhao Q, Li W,
Zhong B, Deng Y and Fu X: Differential expression of bone
morphogenetic protein 5 in human lung squamous cell carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:557–563.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Herrera B, van Dinther M, Ten Dijke P and
Inman GJ: Autocrine bone morphogenetic protein-9 signals through
activin receptor-like kinase-2/Smad1/Smad4 to promote ovarian
cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 69:9254–9262. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mu Y, Gudey SK and Landström M: Non-Smad
signaling pathways. Cell Tissue Res. 347:11–20. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|