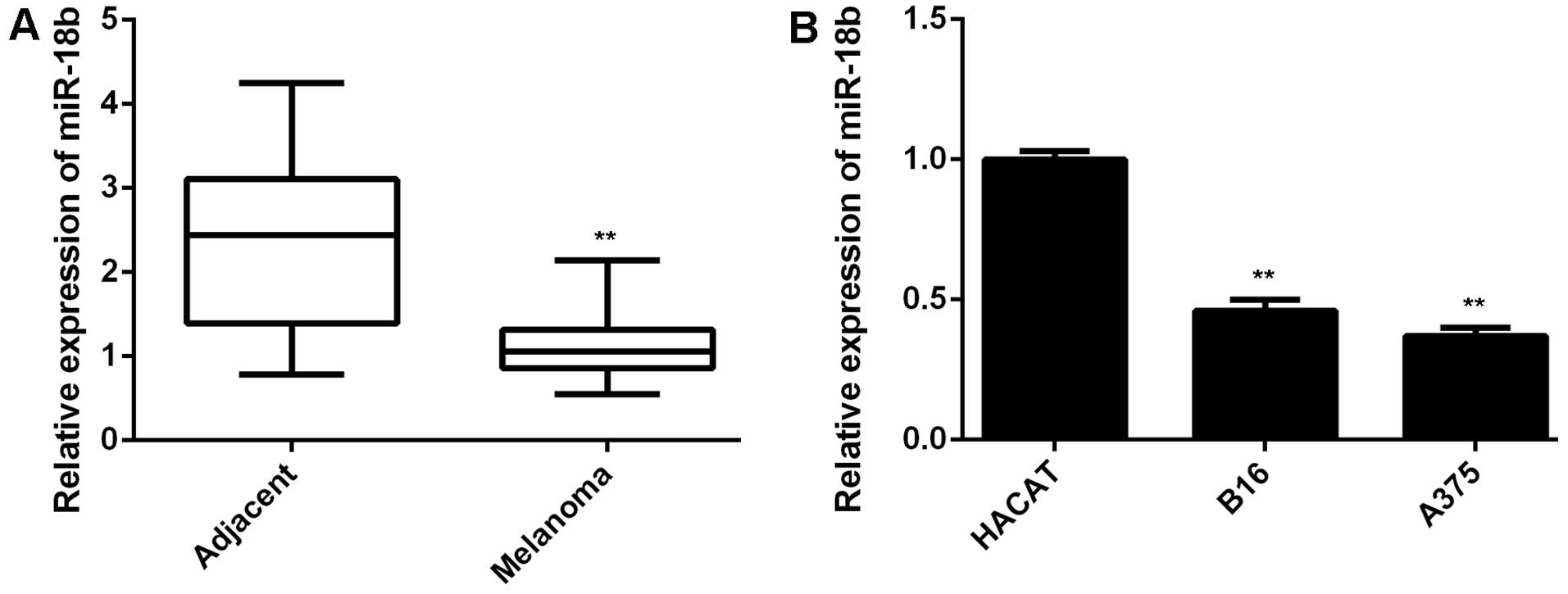
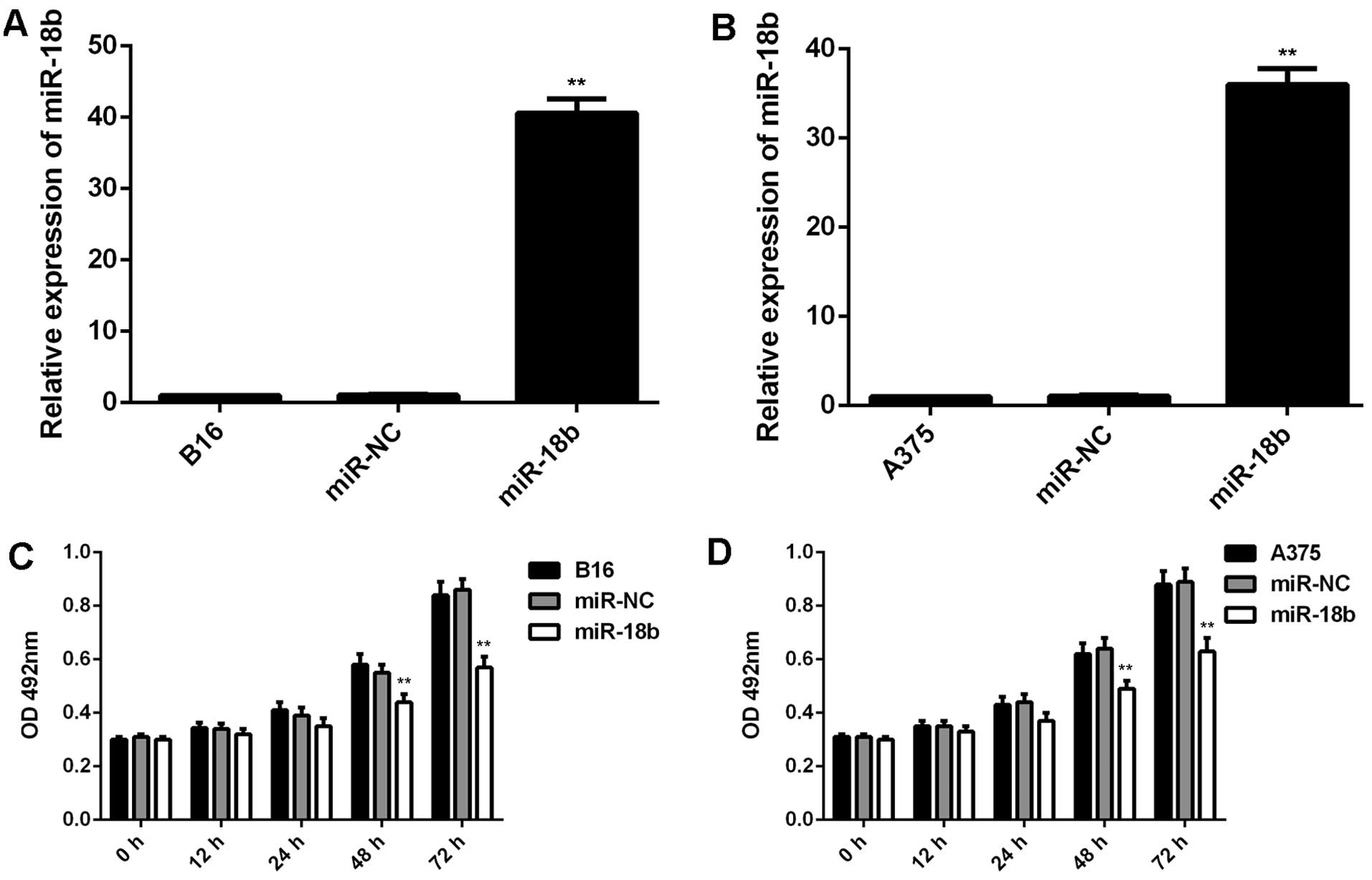
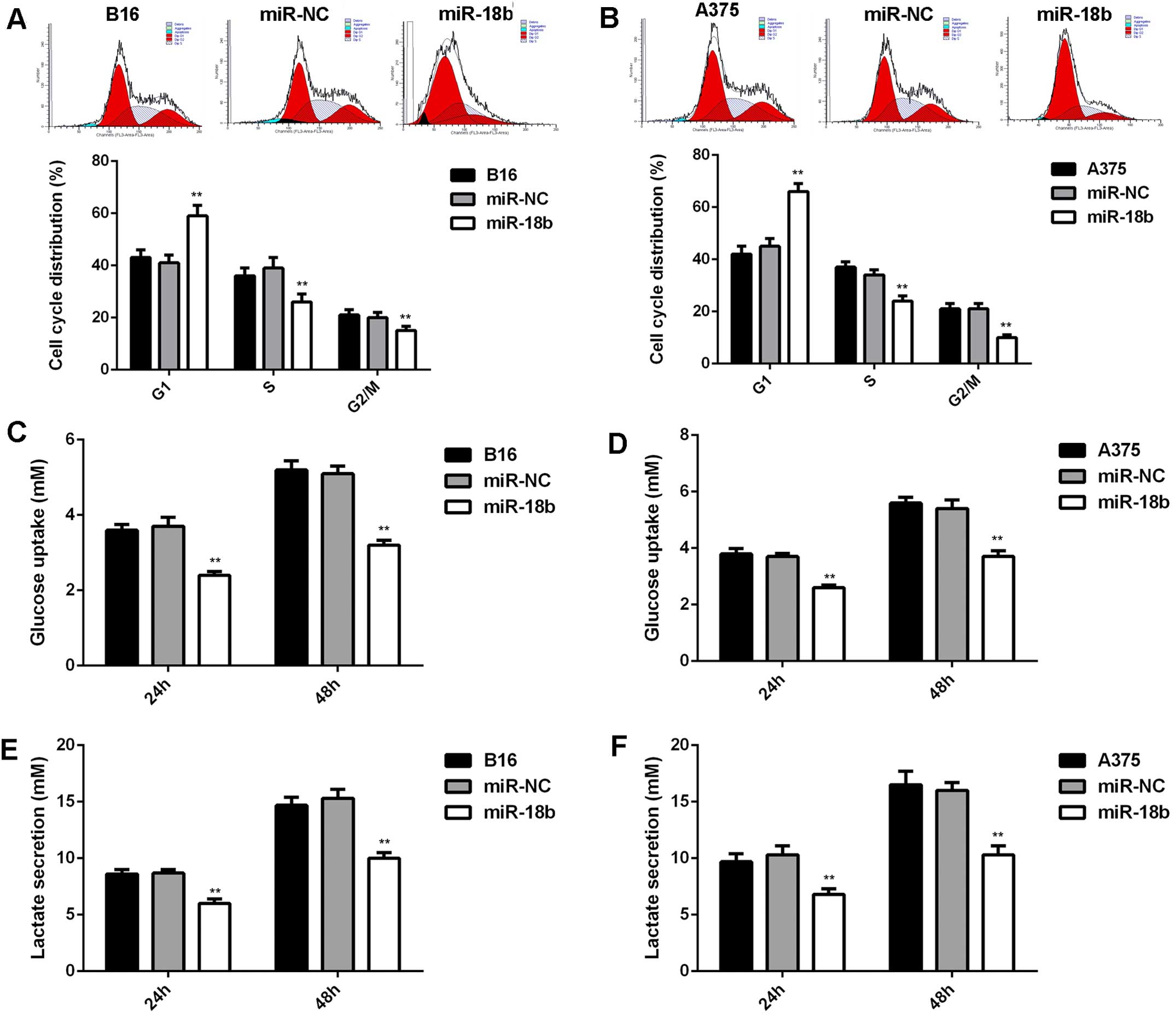
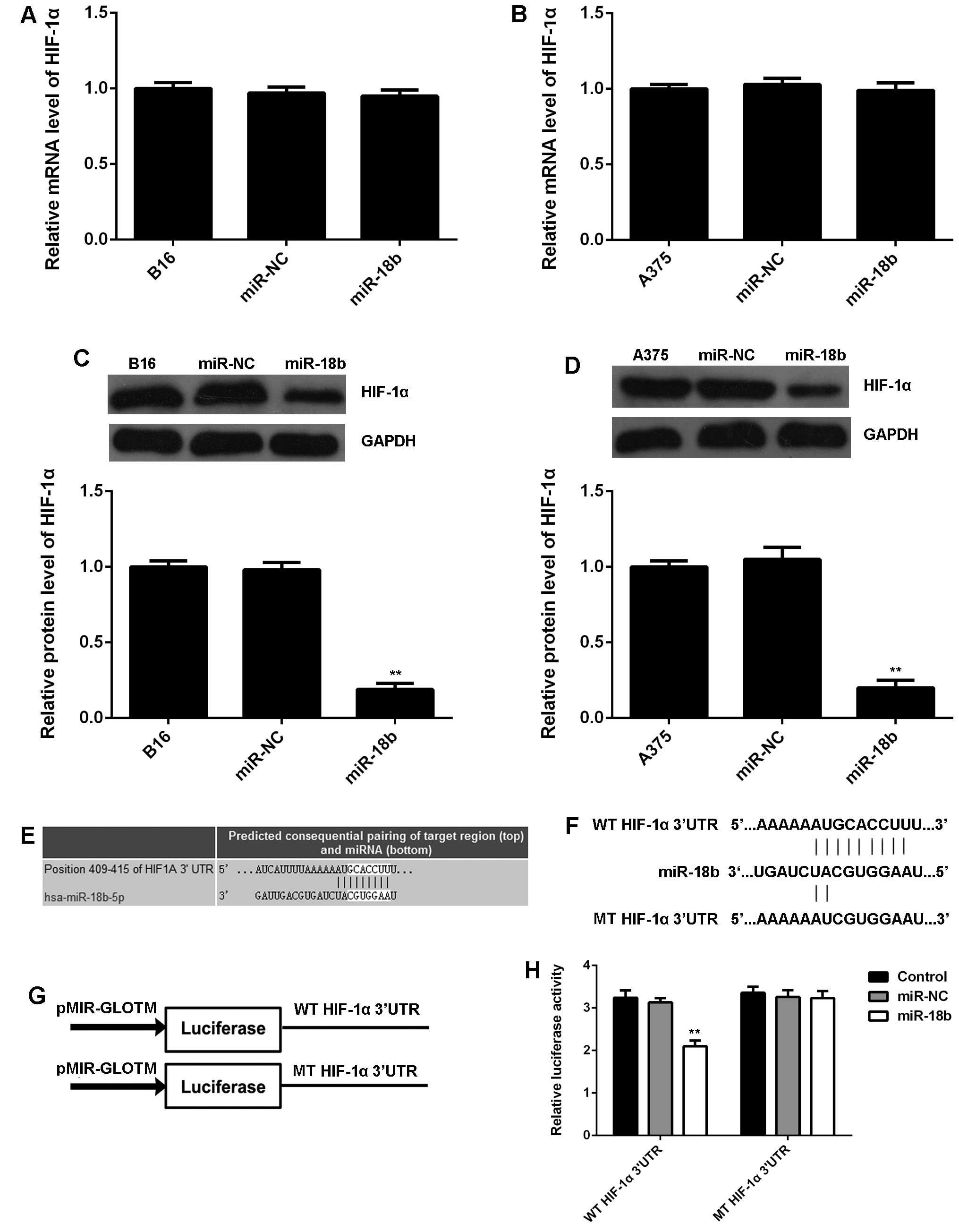
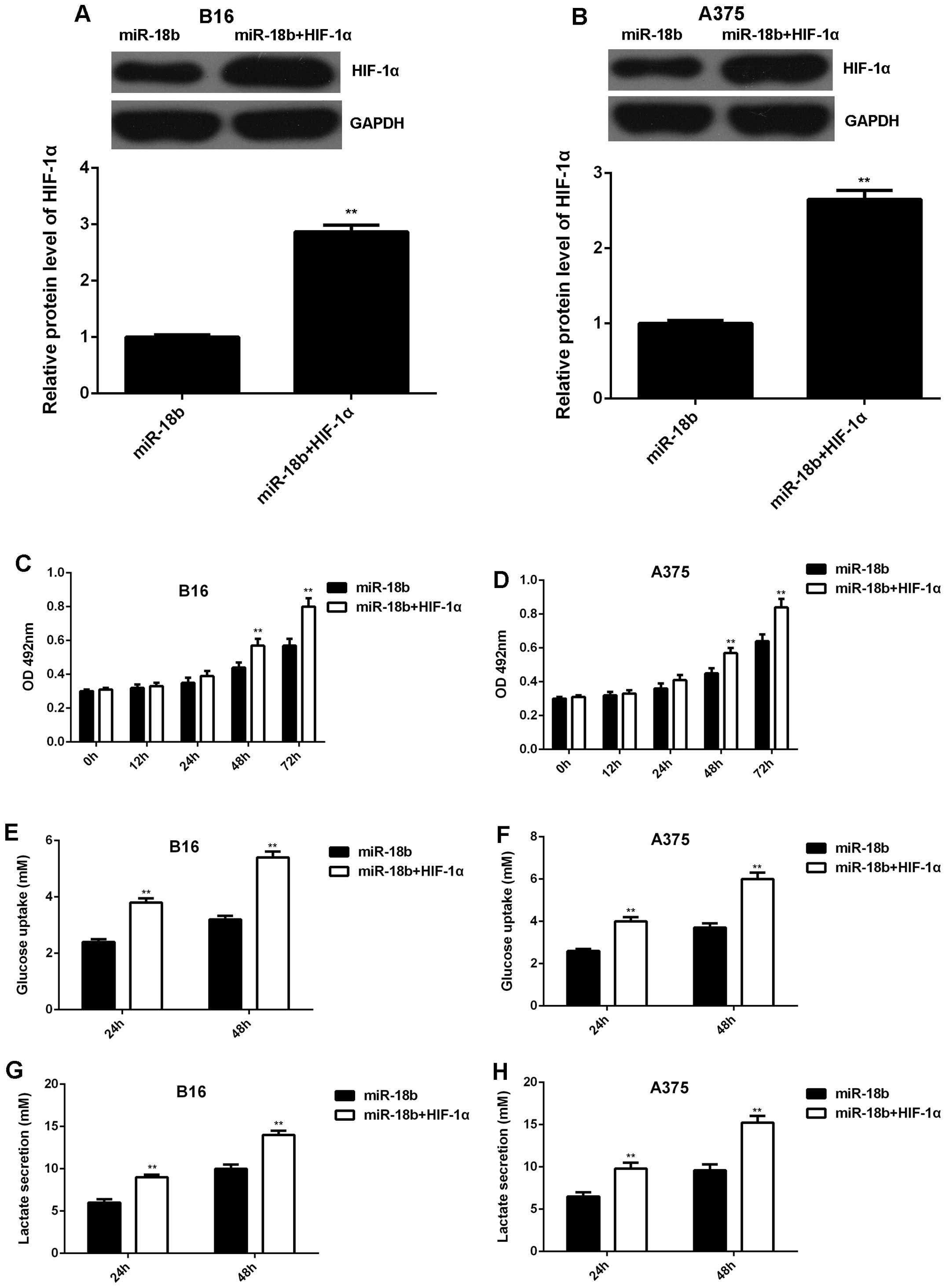
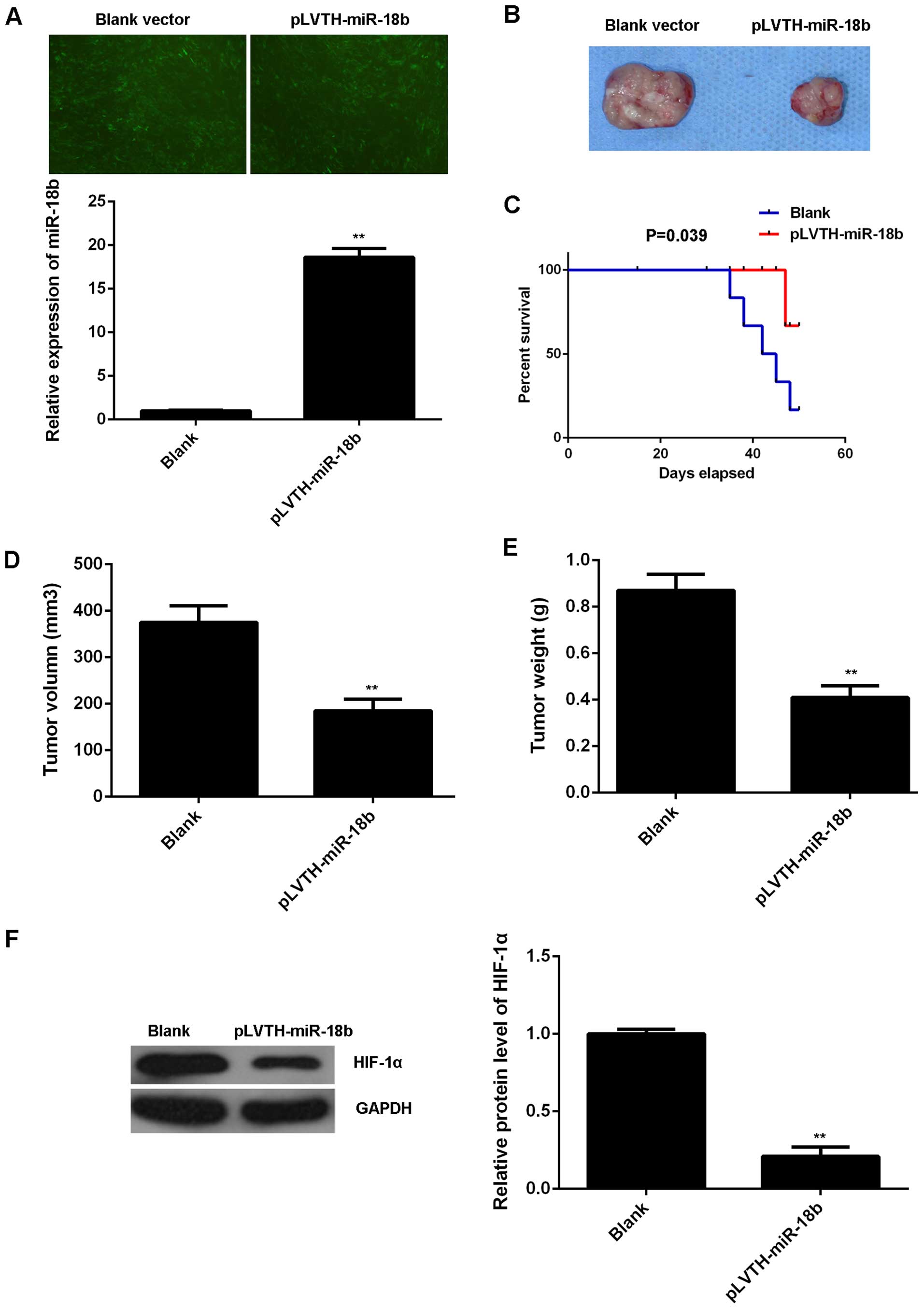
|
1
|
Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR and
Alaibac M: Melanoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis,
diagnosis and classification. In Vivo. 28:1005–1011.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Trotter SC, Sroa N, Winkelmann RR, Olencki
T and Bechtel M: A global review of melanoma follow-up guidelines.
J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 6:18–26. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Linos E, Swetter SM, Cockburn MG, Colditz
GA and Clarke CA: Increasing burden of melanoma in the United
States. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1666–1674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park WY, Hong BJ, Lee J, Choi C and Kim
MY: H3K27 Demethylase JMJD3 employs the NF-κB and BMP signaling
pathways to modulate the tumor microenvironment and promote
melanoma progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 76:161–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bang W, Jeon YJ, Cho JH, Lee RH, Park SM,
Shin JC, Choi NJ, Choi YH, Cho JJ, Seo JM, et al: β-lapachone
suppresses the proliferation of human malignant melanoma cells by
targeting specificity protein 1. Oncol Rep. 35:1109–1116.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee M and Yoon JH: Metabolic interplay
between glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidation: The reverse Warburg
effect and its therapeutic implication. World J Biol Chem.
6:148–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mikawa T, LLeonart ME, Takaori-Kondo A,
Inagaki N, Yokode M and Kondoh H: Dysregulated glycolysis as an
oncogenic event. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:1881–1892. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li XB, Gu JD and Zhou QH: Review of
aerobic glycolysis and its key enzymes - new targets for lung
cancer therapy. Thorac Cancer. 6:17–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Warmoes MO and Locasale JW: Heterogeneity
of glycolysis in cancers and therapeutic opportunities. Biochem
Pharmacol. 92:12–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 mediates metabolic
responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J Clin
Invest. 123:3664–3671. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Courtnay R, Ngo DC, Malik N, Ververis K,
Tortorella SM and Karagiannis TC: Cancer metabolism and the Warburg
effect: The role of HIF-1 and PI3K. Mol Biol Rep. 42:841–851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou J, Xu D, Xie H, Tang J, Liu R, Li J,
Wang S, Chen X, Su J, Zhou X, et al: miR-33a functions as a tumor
suppressor in melanoma by targeting HIF-1α. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:846–855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Moss EG: MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome.
Curr Biol. 12:R138–R140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aftab MN, Dinger ME and Perera RJ: The
role of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in the pathology,
diagnosis, and management of melanoma. Arch Biochem Biophys.
563:60–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu X, Zhen Y, Yang H, Wang H, Zhou Y, Wang
E, Marincola FM, Mai C, Chen Y, Wei H, et al: Loss of connective
tissue growth factor as an unfavorable prognosis factor activates
miR-18b by PI3K/AKT/C-Jun and C-Myc and promotes cell growth in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murakami Y, Tamori A, Itami S, Tanahashi
T, Toyoda H, Tanaka M, Wu W, Brojigin N, Kaneoka Y, Maeda A, et al:
The expression level of miR-18b in hepatocellular carcinoma is
associated with the grade of malignancy and prognosis. BMC Cancer.
13:992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dar AA, Majid S, Rittsteuer C, de Semir D,
Bezrookove V, Tong S, Nosrati M, Sagebiel R, Miller JR III and
Kashani-Sabet M: The role of miR-18b in MDM2-p53 pathway signaling
and melanoma progression. J Natl Cancer Inst. 105:433–442. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ribeiro J, Marinho-Dias J, Monteiro P,
Loureiro J, Baldaque I, Medeiros R and Sousa H: miR-34a and
miR-125b expression in HPV infection and cervical cancer
development. BioMed Res Int. 2015:3045842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tamura K: Development of cell-cycle
checkpoint therapy for solid tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
45:1097–1102. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schönenberger MJ and Kovacs WJ: Hypoxia
signaling pathways: Modulators of oxygen-related organelles. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 3:422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu N, Sun Q, Chen J, Li J, Zeng Y, Zhai
S, Li P, Wang B and Wang X: MicroRNA-9 suppresses uveal melanoma
cell migration and invasion through the NF-κB1 pathway. Oncol Rep.
28:961–968. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noguchi S, Kumazaki M, Yasui Y, Mori T,
Yamada N and Akao Y: MicroRNA-203 regulates melanosome transport
and tyrosinase expression in melanoma cells by targeting kinesin
superfamily protein 5b. J Invest Dermatol. 134:461–469. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bu P and Yang P: MicroRNA-203 inhibits
malignant melanoma cell migration by targeting versican. Exp Ther
Med. 8:309–315. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Feilotter HE, Paré GC, Zhang X,
Pemberton JG, Garady C, Lai D, Yang X and Tron VA: MicroRNA-193b
represses cell proliferation and regulates cyclin D1 in melanoma.
Am J Pathol. 176:2520–2529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan JY, Yang Y, Xie JY, Lu YL, Shi K and
Huang YQ: MicroRNA-144 mediates metabolic shift in ovarian cancer
cells by directly targeting Glut1. Tumour Biol. Dec 11–2015.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
29
|
Xu P, Li Y, Zhang H, Li M and Zhu H:
MicroRNA-340 mediates metabolic shift in oral squamous cell
carcinoma by targeting glucose transporter-1. J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 74:844–850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Serguienko A, Grad I, Wennerstrøm AB,
Meza-Zepeda LA, Thiede B, Stratford EW, Myklebost O and Munthe E:
Metabolic reprogramming of metastatic breast cancer and melanoma by
let-7a microRNA. Oncotarget. 6:2451–2465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cuninghame S, Jackson R and Zehbe I:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and its role in viral carcinogenesis.
Virology. 456–457:370–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Slominski A, Kim TK, Brożyna AA,
Janjetovic Z, Brooks DL, Schwab LP, Skobowiat C, Jóźwicki W and
Seagroves TN: The role of melanogenesis in regulation of melanoma
behavior: Melanogenesis leads to stimulation of HIF-1α expression
and HIF-dependent attendant pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys.
563:79–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Kouskoukis
C, Gatter KC, Harris AL and Koukourakis MI: Hypoxia-inducible
factors 1alpha and 2alpha are related to vascular endothelial
growth factor expression and a poorer prognosis in nodular
malignant melanomas of the skin. Melanoma Res. 13:493–501. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|