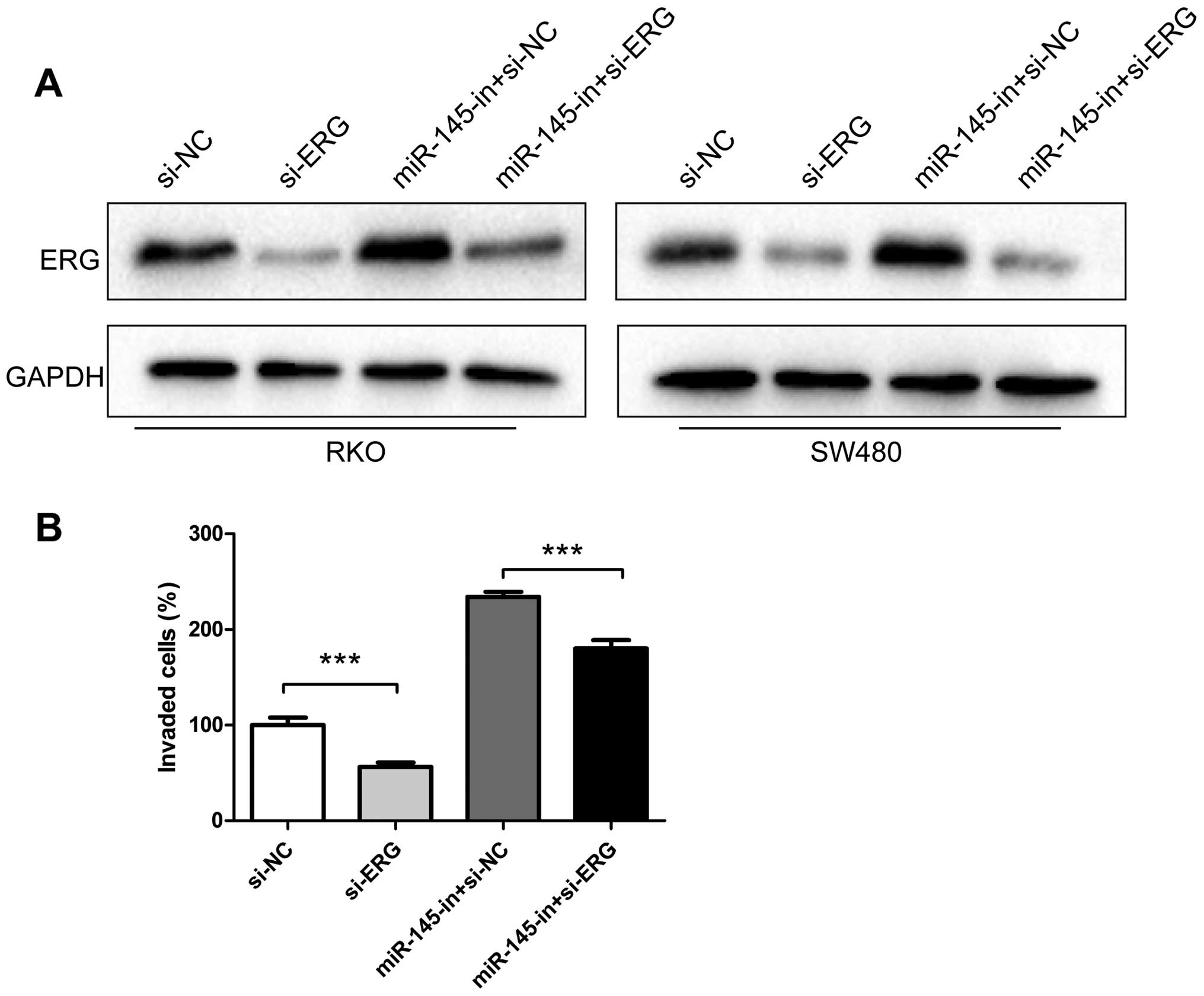
|
1
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loughran SJ, Kruse EA, Hacking DF, de
Graaf CA, Hyland CD, Willson TA, Henley KJ, Ellis S, Voss AK,
Metcalf D, et al: The transcription factor Erg is essential for
definitive hematopoiesis and the function of adult hematopoietic
stem cells. Nat Immunol. 9:810–819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Birdsey GM, Dryden NH, Amsellem V,
Gebhardt F, Sahnan K, Haskard DO, Dejana E, Mason JC and Randi AM:
Transcription factor Erg regulates angiogenesis and endothelial
apoptosis through VE-cadherin. Blood. 111:3498–3506. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iwamoto M, Tamamura Y, Koyama E, Komori T,
Takeshita N, Williams JA, Nakamura T, Enomoto-Iwamoto M and
Pacifici M: Transcription factor ERG and joint and articular
cartilage formation during mouse limb and spine skeletogenesis. Dev
Biol. 305:40–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao X, Li LY, Zhou FJ, Xie KJ, Shao CK, Su
ZL, Sun QP, Chen MK, Pang J, Zhou XF, et al: ERG rearrangement for
predicting subsequent cancer diagnosis in high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and lymph node metastasis. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:4163–4172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marcucci G, Maharry K, Whitman SP,
Vukosavljevic T, Paschka P, Langer C, Mrózek K, Baldus CD, Carroll
AJ, Powell BL, et al Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study: High
expression levels of the ETS-related gene, ERG, predict adverse
outcome and improve molecular risk-based classification of
cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: A Cancer and
Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol. 25:3337–3343. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Markert EK, Mizuno H, Vazquez A and Levine
AJ: Molecular classification of prostate cancer using curated
expression signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:21276–21281.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Becker-Santos DD, Guo Y, Ghaffari M,
Vickers ED, Lehman M, Altamirano-Dimas M, Oloumi A, Furukawa J,
Sharma M, Wang Y, et al: Integrin-linked kinase as a target for
ERG-mediated invasive properties in prostate cancer models.
Carcinogenesis. 33:2558–2567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Michael MZ, O' Connor SM, van Holst
Pellekaan NG, Young GP and James RJ: Reduced accumulation of
specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res.
1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O'Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs associated with
metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One. 6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang H, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Yang C, Li S,
Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth,
invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells
through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene.
33:387–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Panza A, Votino C, Gentile A, Valvano MR,
Colangelo T, Pancione M, Micale L, Merla G, Andriulli A, Sabatino
L, et al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-mediated
induction of microRNA-145 opposes tumor phenotype in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:1225–1236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arndt GM, Dossey L, Cullen LM, Lai A,
Druker R, Eisbacher M, Zhang C, Tran N, Fan H, Retzlaff K, et al:
Characterization of global microRNA expression reveals oncogenic
potential of miR-145 in metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer.
9:3742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benson AB III, Arnoletti JP, Bekaii-Saab
T, Chan E, Chen YJ, Choti MA, Cooper HS, Dilawari RA, Engstrom PF,
Enzinger PC, et al National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Anal
Carcinoma, version 2.2012: Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines.
J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 10:449–454. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schindelin J, Rueden CT, Hiner MC and
Eliceiri KW: The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical
image analysis. Mol Reprod Dev. 82:518–529. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sameer AS: Colorectal cancer: Molecular
mutations and polymorphisms. Front Oncol. 3:1142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo X, Burwinkel B, Tao S and Brenner H:
MicroRNA signatures: Novel biomarker for colorectal cancer? Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:1272–1286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Sempere LF, Galimberti F,
Freemantle SJ, Black C, Dragnev KH, Ma Y, Fiering S, Memoli V, Li
H, et al: Uncovering growth-suppressive MicroRNAs in lung cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:1177–1183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T,
Tanigawa N and Akao Y: Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and
-145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology. 77:12–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong R, Liu X, Zhang Q, Jiang Z, Li Y, Wei
Y, Li Y, Yang Q, Liu J, Wei JJ, et al: miR-145 inhibits tumor
growth and metastasis by targeting metadherin in high-grade serous
ovarian carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:10816–10829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qin J, Wang F, Jiang H, Xu J, Jiang Y and
Wang Z: MicroRNA-145 suppresses cell migration and invasion by
targeting paxillin in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:1328–1340. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shi B, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Prisco M, Linsley
P, de Angelis T and Baserga R: Micro RNA 145 targets the insulin
receptor substrate-1 and inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells.
J Biol Chem. 282:32582–32590. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu RL, Dong Y, Deng YZ, Wang WJ and Li
WD: Tumor suppressor miR-145 reverses drug resistance by directly
targeting DNA damage-related gene RAD18 in colorectal cancer.
Tumour Biol. 36:5011–5019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng W, Hu J, Zhu XD, Liu X, Wang CC, Li
WH and Chen ZY: Overexpression of miR-145 increases the sensitivity
of vemurafenib in drug-resistant colo205 cell line. Tumour Biol.
35:2983–2988. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pagliuca A, Valvo C, Fabrizi E, di Martino
S, Biffoni M, Runci D, Forte S, De Maria R and Ricci-Vitiani L:
Analysis of the combined action of miR-143 and miR-145 on oncogenic
pathways in colorectal cancer cells reveals a coordinate program of
gene repression. Oncogene. 32:4806–4813. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu XH, Wu XB, Wu SB, Liu HB and Chen Rand
Li Y: Identification of miRNAs differentially expressed in clinical
stages of human colorectal carcinoma-an investigation in Guangzhou,
China. PLoS One. 9:e940602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan W, Sui C, Liu Q, Tang W, An H and Ma
J: Up-regulation of microRNA-145 associates with lymph node
metastasis in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1020172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu H and Kohane IS: Tissue and process
specific microRNA-mRNA co-expression in mammalian development and
malignancy. PLoS One. 4:e54362009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chaudhuri K and Chatterjee R: MicroRNA
detection and target prediction: Integration of computational and
experimental approaches. DNA Cell Biol. 26:321–337. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu X, Xu X, Li S, Wu S, Chen R, Jiang Q,
Liu H, Sun Y, Li Y and Xu Y: Identification and validation of
potential biomarkers for the detection of dysregulated microRNA by
qPCR in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01200242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Seth A and Watson DK: ETS transcription
factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2462–2478. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dejana E, Taddei A and Randi AM: Foxs and
Ets in the transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell
differentiation and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1775:298–312. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mochmann LH, Neumann M, von der Heide EK,
Nowak V, Kühl AA, Ortiz-Tanchez J, Bock J, Hofmann WK and Baldus
CD: ERG induces a mesenchymal-like state associated with
chemoresistance in leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 5:351–362. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ito Y, Takeda T, Okada M and Matsuura N:
Expression of ets-1 and ets-2 in colonic neoplasms. Anticancer Res.
22:1581–1584. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Salek-Ardakani S, Smooha G, de Boer J,
Sebire NJ, Morrow M, Rainis L, Lee S, Williams O, Izraeli S and
Brady HJ: ERG is a megakaryocytic oncogene. Cancer Res.
69:4665–4673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peng C, Gao H, Niu Z, Wang B, Tan Z, Niu
W, Liu E, Wang J, Sun J, Shahbaz M, et al: Integrin αvβ6 and
transcriptional factor Ets-1 act as prognostic indicators in
colorectal cancer. Cell Biosci. 4:532014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Simpson S, Woodworth CD and DiPaolo JA:
Altered expression of Erg and Ets-2 transcription factors is
associated with genetic changes at 21q22.2–22.3 in immortal and
cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 14:2149–2157. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scheble VJ, Braun M, Beroukhim R, Mermel
CH, Ruiz C, Wilbertz T, Stiedl AC, Petersen K, Reischl M, Kuefer R,
et al: ERG rearrangement is specific to prostate cancer and does
not occur in any other common tumor. Mod Pathol. 23:1061–1067.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Coskun E, von der Heide EK, Schlee C,
Kühnl A, Gökbuget N, Hoelzer D, Hofmann WK, Thiel E and Baldus CD:
The role of microRNA-196a and microRNA-196b as ERG regulators in
acute myeloid leukemia and acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk
Res. 35:208–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hart M, Wach S, Nolte E, Szczyrba J, Menon
R, Taubert H, Hartmann A, Stoehr R, Wieland W, Grässer FA, et al:
The proto-oncogene ERG is a target of microRNA miR-145 in prostate
cancer. FEBS J. 280:2105–2116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zheng L, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Li D, Xiang X,
Huang K and Tong Q: miRNA-145 targets v-ets erythroblastosis virus
E26 oncogene homolog 1 to suppress the invasion, metastasis, and
angiogenesis of gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 11:182–193.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gu J, Chen Y, Huang H, Yin L, Xie Z and
Zhang MQ: Gene module based regulator inference identifying miR-139
as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Mol Biosyst.
10:3249–3254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang J, Guo H, Zhang H, Wang H, Qian G,
Fan X, Hoffman AR, Hu JF and Ge S: Putative tumor suppressor
miR-145 inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting oncogene
Friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene. Cancer. 117:86–95. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ban J, Jug G, Mestdagh P, Schwentner R,
Kauer M, Aryee DN, Schaefer KL, Nakatani F, Scotlandi K, Reiter M,
et al: Hsa-mir-145 is the top EWS-FLI1-repressed microRNA involved
in a positive feedback loop in Ewing's sarcoma. Oncogene.
30:2173–2180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|