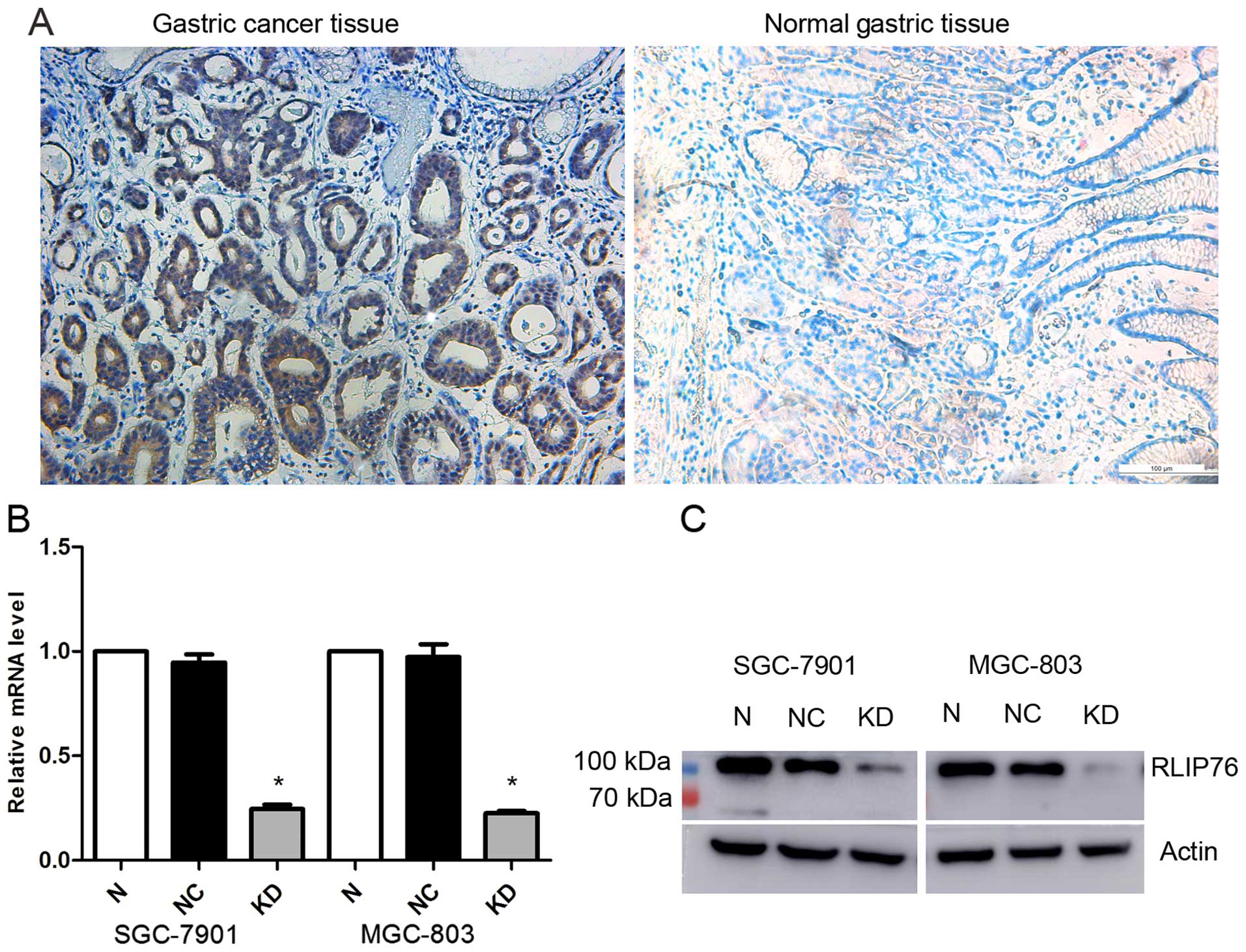
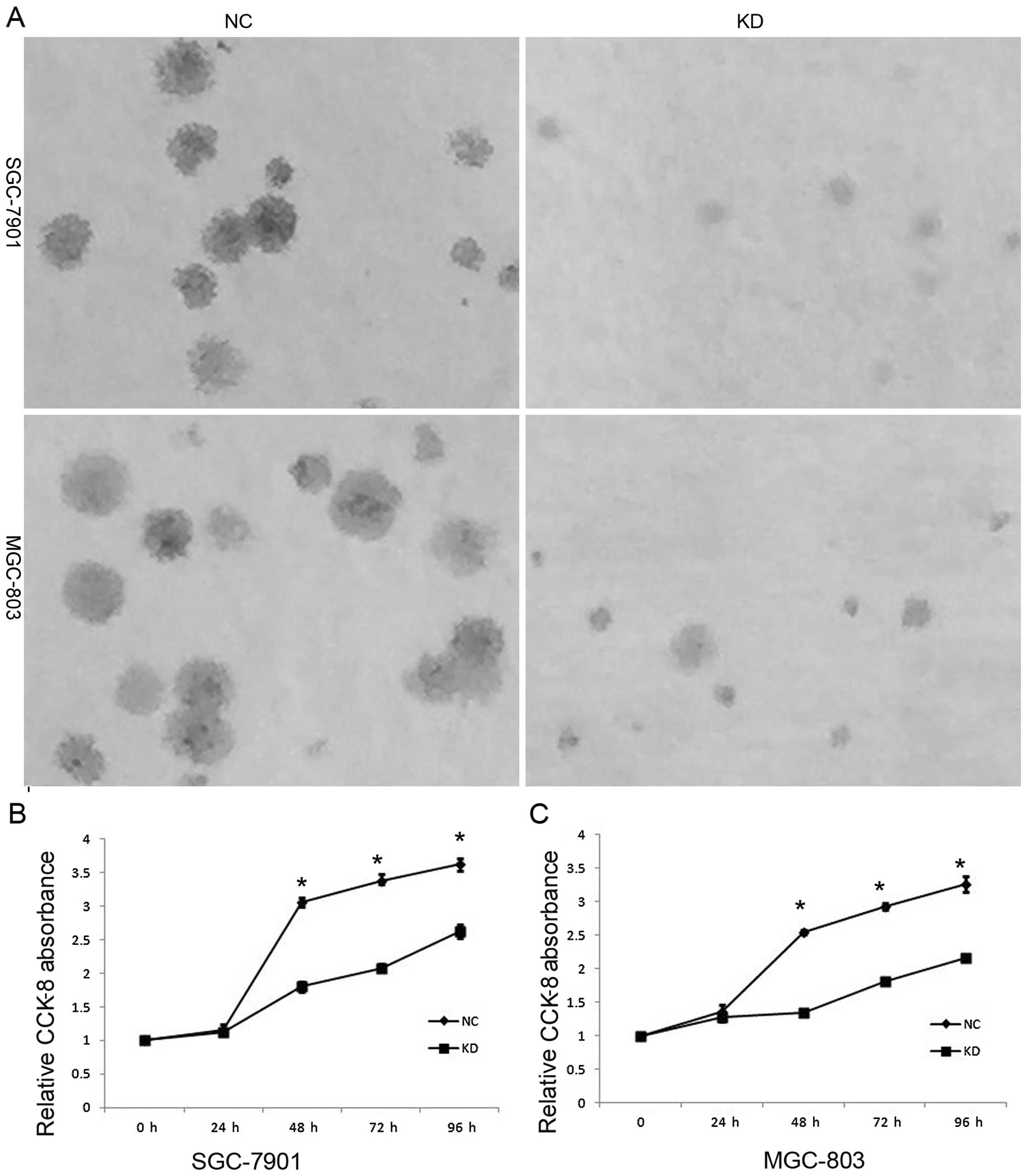
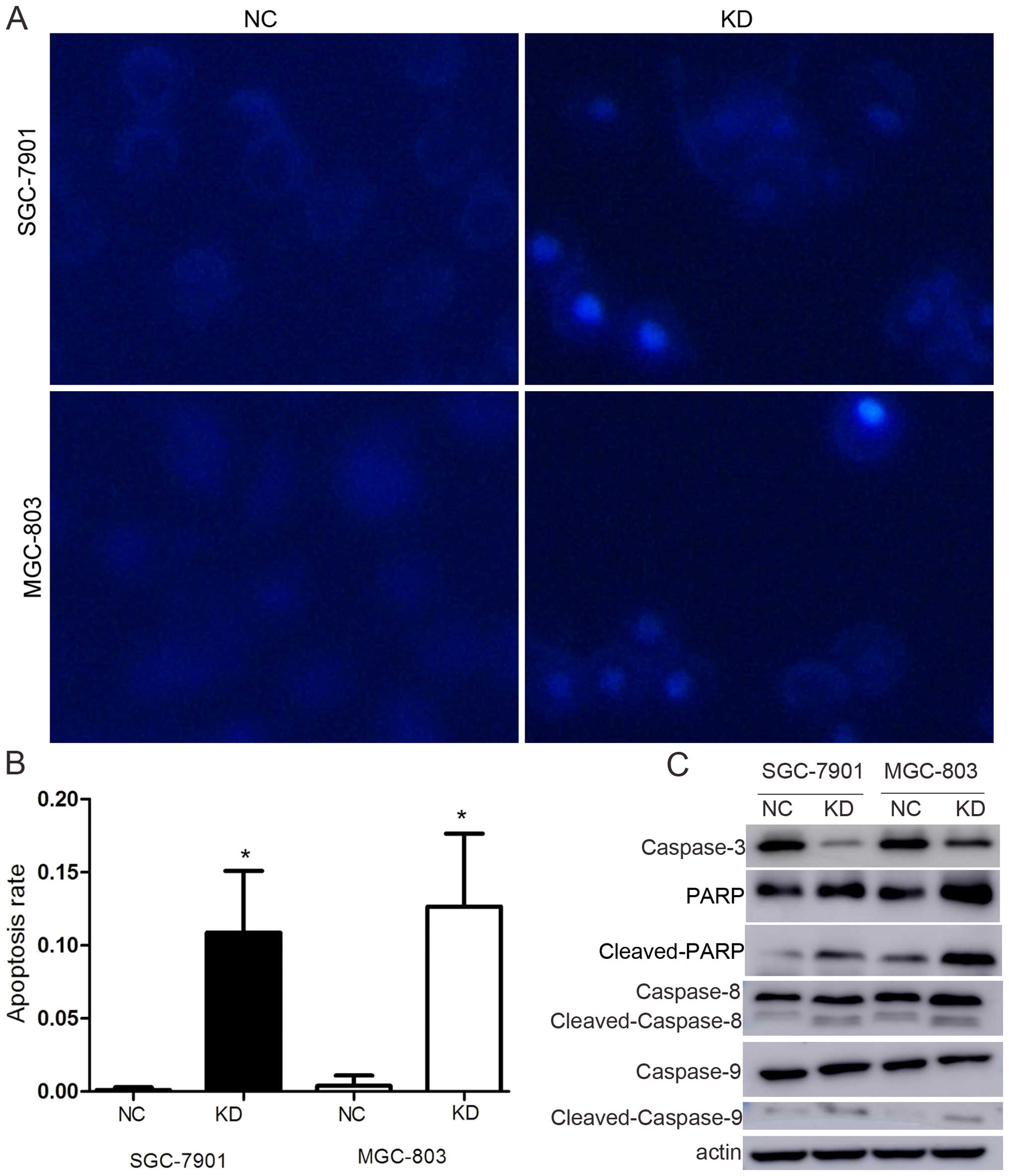
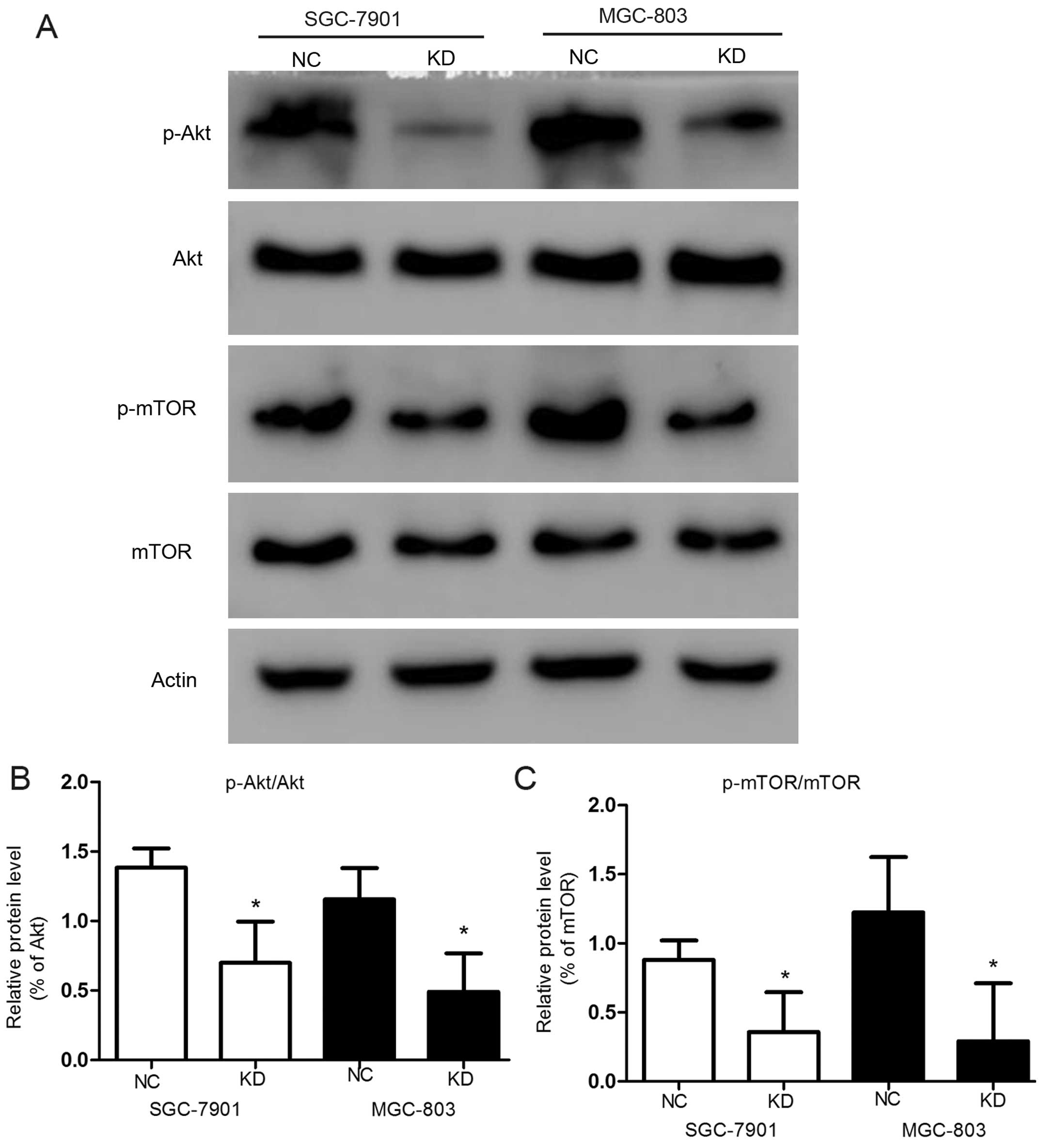
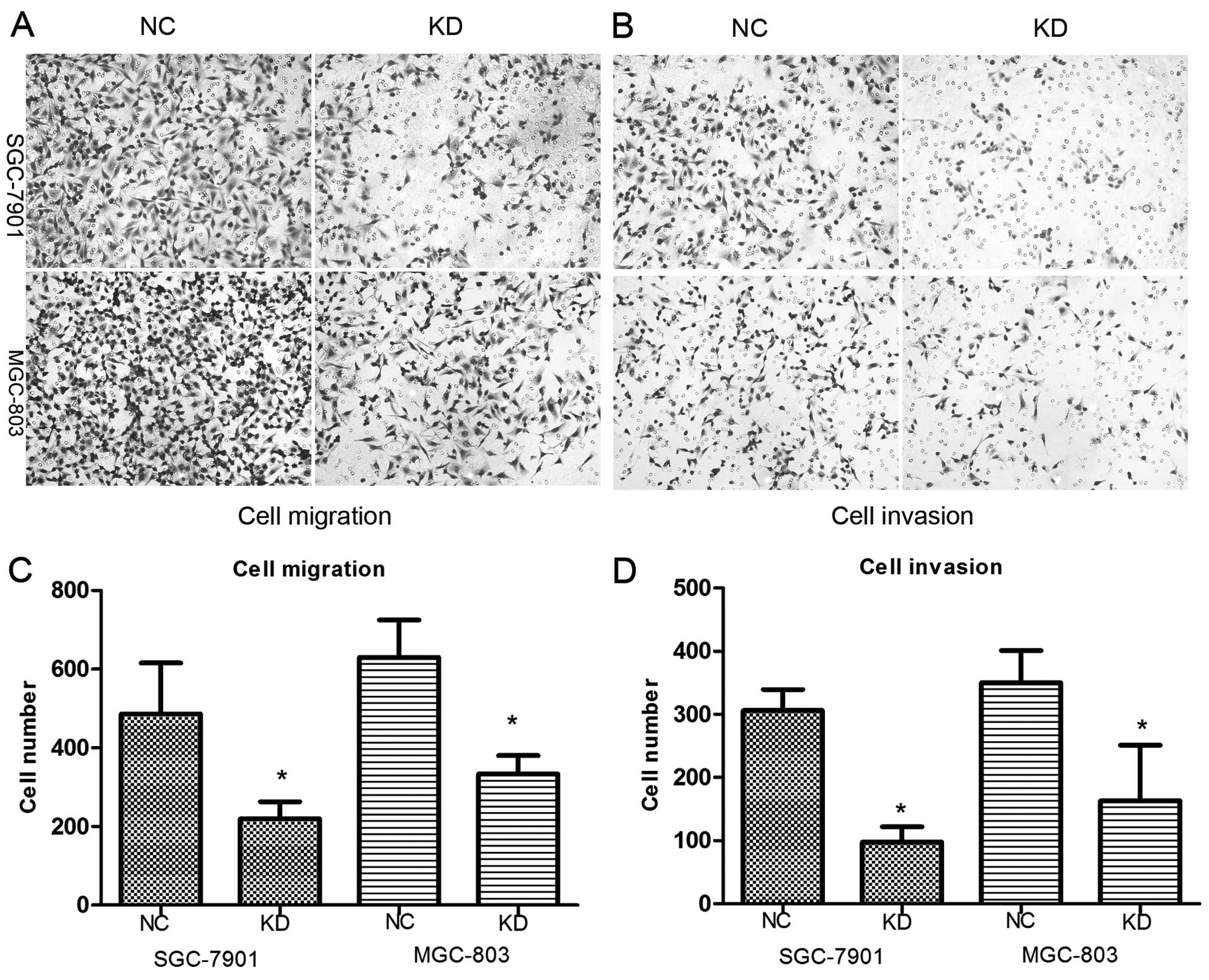
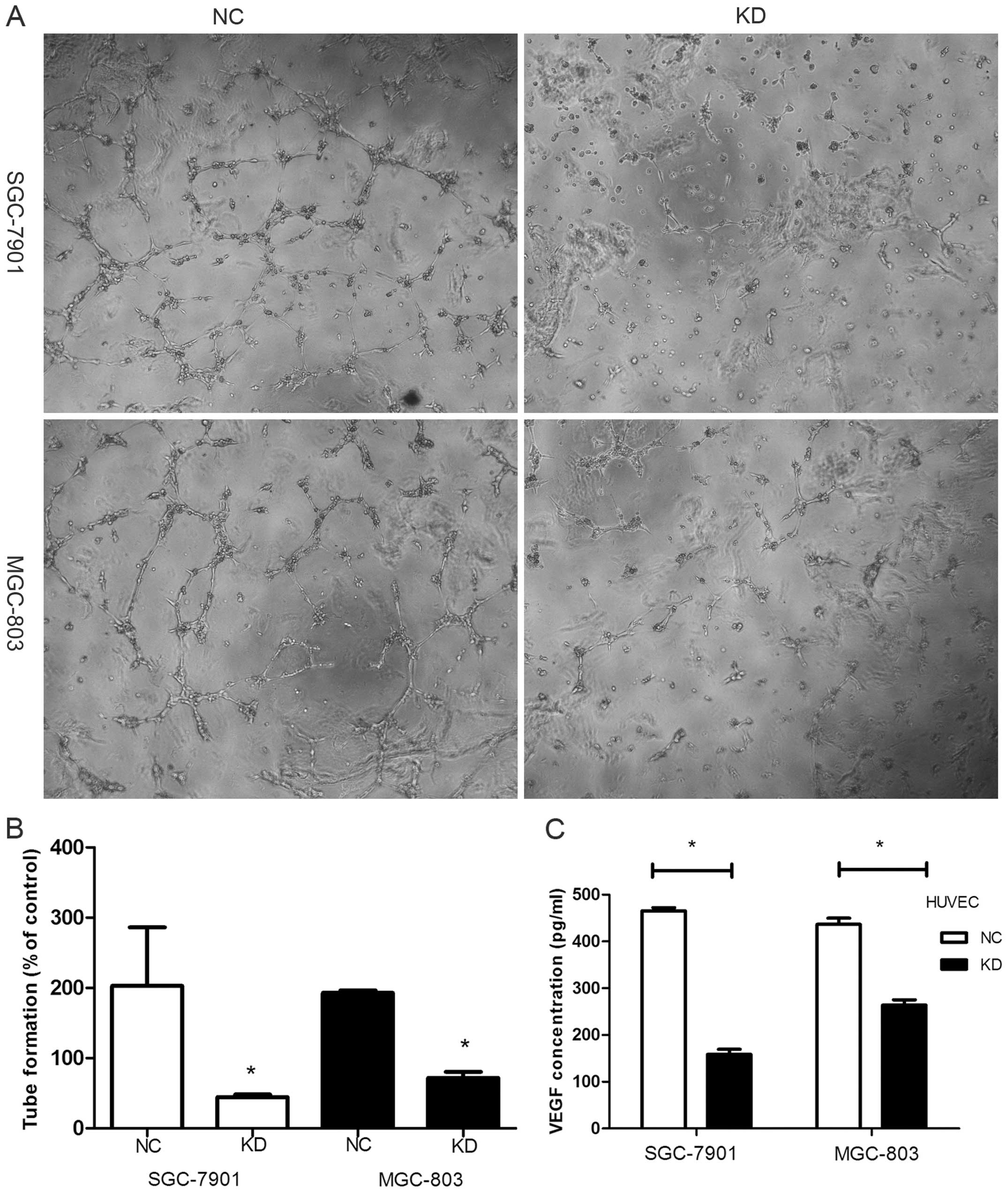
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quéro L, Guillerm S and Hennequin C:
Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for gastric cancer. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 7:102–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dassen AE, Lemmens VE, van de Poll-Franse
LV, Creemers GJ, Brenninkmeijer SJ, Lips DJ, Vd Wurff AA, Bosscha K
and Coebergh JW: Trends in incidence, treatment and survival of
gastric adenocarcinoma between 1990 and 2007: A population-based
study in the Netherlands. Eur J Cancer. 46:1101–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oba K, Paoletti X, Bang YJ, Bleiberg H,
Burzykowski T, Fuse N, Michiels S, Morita S, Ohashi Y, Pignon JP,
et al GASTRIC (Global Advanced/Adjuvant Stomach Tumor Research
International Collaboration) Group: Role of chemotherapy for
advanced/recurrent gastric cancer: An individual-patient-data
meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 49:1565–1577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buchner AM, Shahid MW, Heckman MG, Krishna
M, Ghabril M, Hasan M, Crook JE, Gomez V, Raimondo M, Woodward T,
et al: Comparison of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy with
virtual chromoendoscopy for classification of colon polyps.
Gastroenterology. 138:834–842. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li WB, Zuo XL, Li CQ, Zuo F, Gu XM, Yu T,
Chu CL, Zhang TG and Li YQ: Diagnostic value of confocal laser
endomicroscopy for gastric superficial cancerous lesions. Gut.
60:299–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanduleanu S, Driessen A, Gomez-Garcia E,
Hameeteman W, de Bruïne A and Masclee A: In vivo diagnosis and
classification of colorectal neoplasia by chromoendoscopy-guided
confocal laser endomicroscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
8:371–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wallace M, Lauwers GY, Chen Y, Dekker E,
Fockens P, Sharma P and Meining A: Miami classification for
probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Endoscopy. 43:882–891.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jullien-Flores V, Mahé Y, Mirey G,
Leprince C, Meunier-Bisceuil B, Sorkin A and Camonis JH, Gacon G
and Camonis JH: RLIP76, an effector of the GTPase Ral, interacts
with the AP2 complex: Involvement of the Ral pathway in receptor
endocytosis. J Cell Sci. 113:2837–2844. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakashima S, Morinaka K, Koyama S, Ikeda
M, Kishida M, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kishida S and Kikuchi A: Small G
protein Ral and its downstream molecules regulate endocytosis of
EGF and insulin receptors. EMBO J. 18:3629–3642. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kashatus DF, Lim KH, Brady DC, Pershing
NL, Cox AD and Counter CM: RALA and RALBP1 regulate mitochondrial
fission at mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1108–1115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goldfinger LE, Ptak C, Jeffery ED,
Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF and Ginsberg MH: RLIP76 (RalBP1) is an R-Ras
effector that mediates adhesion-dependent Rac activation and cell
migration. J Cell Biol. 174:877–888. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quaroni A and Paul EC: Cytocentrin is a
Ral-binding protein involved in the assembly and function of the
mitotic apparatus. J Cell Sci. 112:707–718. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Sharma R, Zimniak P
and Awasthi YC: Transport of glutathione conjugates and
chemotherapeutic drugs by RLIP76 (RALBP1): A novel link between
G-protein and tyrosine kinase signaling and drug resistance. Int J
Cancer. 106:635–646. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Awasthi YC, Martin
B, Woo JH, Cunningham CC and Frankel AE: RLIP76 and cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:4372–4377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Srivastava SK,
Zimniak P, Bajpai KK, Saxena M, Sharma R, Ziller SA III, Frenkel EP
and Singh SV: Adenosine triphosphate-dependent transport of
doxorubicin, daunomycin, and vinblastine in human tissues by a
mechanism distinct from the P-glycoprotein. J Clin Invest.
93:958–965. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Awasthi YC, Singhal SS, Gupta S, Ahmad H,
Zimniak P, Radominska A, Lester R and Sharma R: Purification and
characterization of an ATPase from human liver which catalyzes ATP
hydrolysis in the presence of the conjugates of bilirubin bile
acids and glutathione. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 175:1090–1096.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singhal SS, Roth C, Leake K, Singhal J,
Yadav S and Awasthi S: Regression of prostate cancer xenografts by
RLIP76 depletion. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1074–1083. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Singhal SS, Singhal J, Yadav S, Dwivedi S,
Boor PJ, Awasthi YC and Awasthi S: Regression of lung and colon
cancer xenografts by depleting or inhibiting RLIP76 (Ral-binding
protein 1). Cancer Res. 67:4382–4389. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singhal SS, Awasthi YC and Awasthi S:
Regression of melanoma in a murine model by RLIP76 depletion.
Cancer Res. 66:2354–2360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Singhal J, Cheng J,
Zimniak P and Awasthi YC: Role of RLIP76 in lung cancer doxorubicin
resistance: II. Doxorubicin transport in lung cancer by RLIP76. Int
J Oncol. 22:713–720. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Singhal J, Yang Y,
Zimniak P and Awasthi YC: Role of RLIP76 in lung cancer doxorubicin
resistance: III. Anti-RLIP76 antibodies trigger apoptosis in lung
cancer cells and synergistically increase doxorubicin cytotoxicity.
Int J Oncol. 22:721–732. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yadav S, Singhal SS, Singhal J,
Wickramarachchi D, Knutson E, Albrecht TB, Awasthi YC and Awasthi
S: Identification of membrane-anchoring domains of RLIP76 using
deletion mutant analyses. Biochemistry. 43:16243–16253. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stuckler D, Singhal J, Singhal SS, Yadav
S, Awasthi YC and Awasthi S: RLIP76 transports vinorelbine and
mediates drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
65:991–998. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singhal SS, Yadav S, Singhal J, Zajac E,
Awasthi YC and Awasthi S: Depletion of RLIP76 sensitizes lung
cancer cells to doxorubicin. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:481–488. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Awasthi S, Cheng J, Singhal SS, Saini MK,
Pandya U, Pikula S, Bandorowicz-Pikula J, Singh SV, Zimniak P and
Awasthi YC: Novel function of human RLIP76: ATP-dependent transport
of glutathione conjugates and doxorubicin. Biochemistry.
39:9327–9334. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Awasthi S, Cheng JZ, Singhal SS, Pandya U,
Sharma R, Singh SV, Zimniak P and Awasthi YC: Functional reassembly
of ATP-dependent xenobiotic transport by the N- and C-terminal
domains of RLIP76 and identification of ATP binding sequences.
Biochemistry. 40:4159–4168. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Akt1/Akt2 and
mammalian target of rapamycin/Bim play critical roles in osteoclast
differentiation and survival, respectively, whereas Akt is
dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J
Biol Chem. 280:3583–3589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Singhal SS, Singhal J, Figarola J, Horne D
and Awasthi S: RLIP76 targeted therapy for kidney cancer. Pharm
Res. 32:3123–3136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Sharma A, Sharma R, Patrick B,
Singhal SS, Zimniak P, Awasthi S and Awasthi YC: Cells
preconditioned with mild, transient UVA irradiation acquire
resistance to oxidative stress and UVA-induced apoptosis: Role of
4-hydroxynonenal in UVA-mediated signaling for apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 278:41380–41388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, He Q, Chan LL, Zhou F, El Naghy
M, Thompson EB and Ansari NH: Involvement of caspases in
4-hydroxy-alkenal-induced apoptosis in human leukemic cells. Free
Radic Biol Med. 30:699–706. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng JZ, Singhal SS, Saini M, Singhal J,
Piper JT, Van Kuijk FJ, Zimniak P, Awasthi YC and Awasthi S:
Effects of mGST A4 transfection on 4-hydroxynonenal-mediated
apoptosis and differentiation of K562 human erythroleukemia cells.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 372:29–36. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng JZ, Singhal SS, Sharma A, Saini M,
Yang Y, Awasthi S, Zimniak P and Awasthi YC: Transfection of mGSTA4
in HL-60 cells protects against 4-hydroxynonenal-induced apoptosis
by inhibiting JNK-mediated signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys.
392:197–207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sharma R, Brown D, Awasthi S, Yang Y,
Sharma A, Patrick B, Saini MK, Singh SP, Zimniak P, Singh SV, et
al: Transfection with 4-hydroxynonenal-metabolizing glutathione
S-transferase isozymes leads to phenotypic transformation and
immortalization of adherent cells. Eur J Biochem. 271:1690–1701.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Camandola S, Poli G and Mattson MP: The
lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal increases
AP-1-binding activity through caspase activation in neurons. J
Neurochem. 74:159–168. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Soh Y, Jeong KS, Lee IJ, Bae MA, Kim YC
and Song BJ: Selective activation of the c-Jun N-terminal protein
kinase pathway during 4-hydroxynonenal-induced apoptosis of PC12
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 58:535–541. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu W, Kato M, Akhand AA, Hayakawa A,
Suzuki H, Miyata T, Kurokawa K, Hotta Y, Ishikawa N and Nakashima
I: 4-hydroxynonenal induces a cellular redox status-related
activation of the caspase cascade for apoptotic cell death. J Cell
Sci. 113:635–641. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheng JZ, Sharma R, Yang Y, Singhal SS,
Sharma A, Saini MK, Singh SV, Zimniak P, Awasthi S and Awasthi YC:
Accelerated metabolism and exclusion of 4-hydroxynonenal through
induction of RLIP76 and hGST5.8 is an early adaptive response of
cells to heat and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 276:41213–41223.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Awasthi YC, Yang Y, Tiwari NK, Patrick B,
Sharma A, Li J and Awasthi S: Regulation of
4-hydroxynonenal-mediated signaling by glutathione S-transferases.
Free Radic Biol Med. 37:607–619. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su JL, Lin MT, Hong CC, Chang CC, Shiah
SG, Wu CW, Chen ST, Chau YP and Kuo ML: Resveratrol induces
FasL-related apoptosis through Cdc42 activation of
ASK1/JNK-dependent signaling pathway in human leukemia HL-60 cells.
Carcinogenesis. 26:1–10. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Oosterhoff JK, Penninkhof F, Brinkmann AO,
Anton Grootegoed J and Blok LJ: REPS2/POB1 is downregulated during
human prostate cancer progression and inhibits growth factor
signalling in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 22:2920–2925. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yadav S, Zajac E, Singhal SS, Singhal J,
Drake K, Awasthi YC and Awasthi S: POB1 over-expression inhibits
RLIP76-mediated transport of glutathione-conjugates, drugs and
promotes apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 328:1003–1009.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moriya R, Takahashi K, Kitahara A, Onuma
H, Handa K, Sumitani Y, Tanaka T, Katsuta H, Nishida S, Itagaki E,
et al: Possible involvement of PI3K-dependent pathways in the
increased VEGF120 release from osteoblastic cells preloaded with
palmitate in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 445:275–281. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao W, Guo W, Zhou Q, Ma SN, Wang R, Qiu
Y, Jin M, Duan HQ and Kong D: In vitro antimetastatic effect of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor ZSTK474 on prostate cancer
PC3 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:13577–13591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takahashi K, Miyokawa-Gorin K, Handa K,
Kitahara A, Moriya R, Onuma H, Sumitani Y, Tanaka T, Katsuta H,
Nishida S, et al: Endogenous oxidative stress, but not ER stress,
induces hypoxia-independent VEGF120 release through
PI3K-dependent pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesit. 21:1625–1634.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|