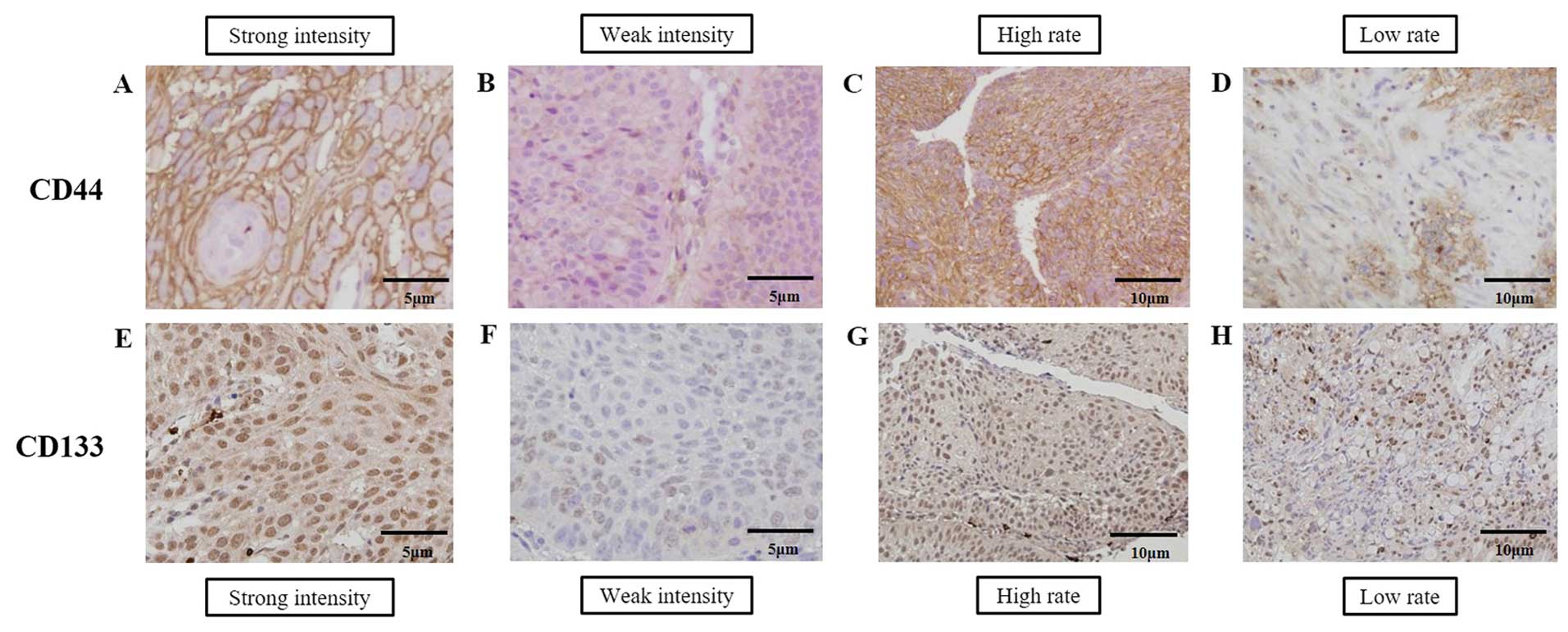
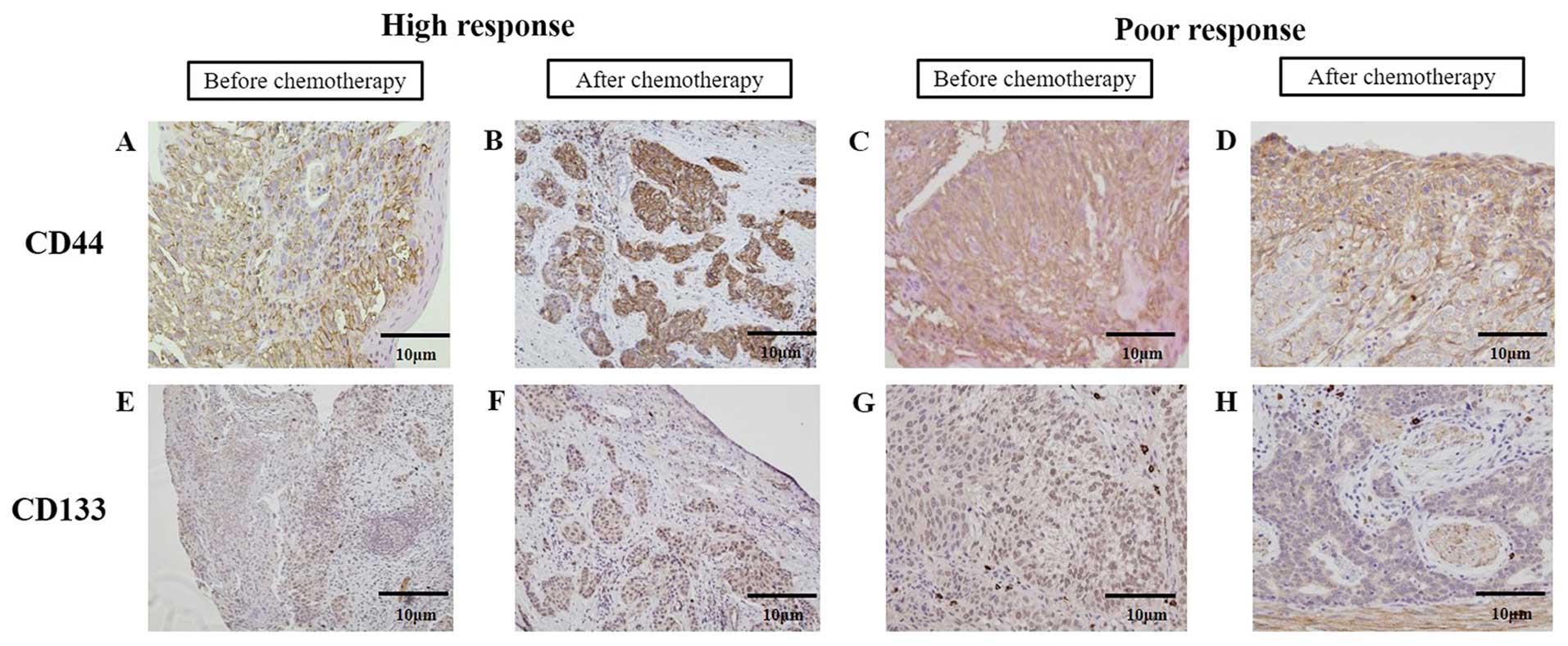
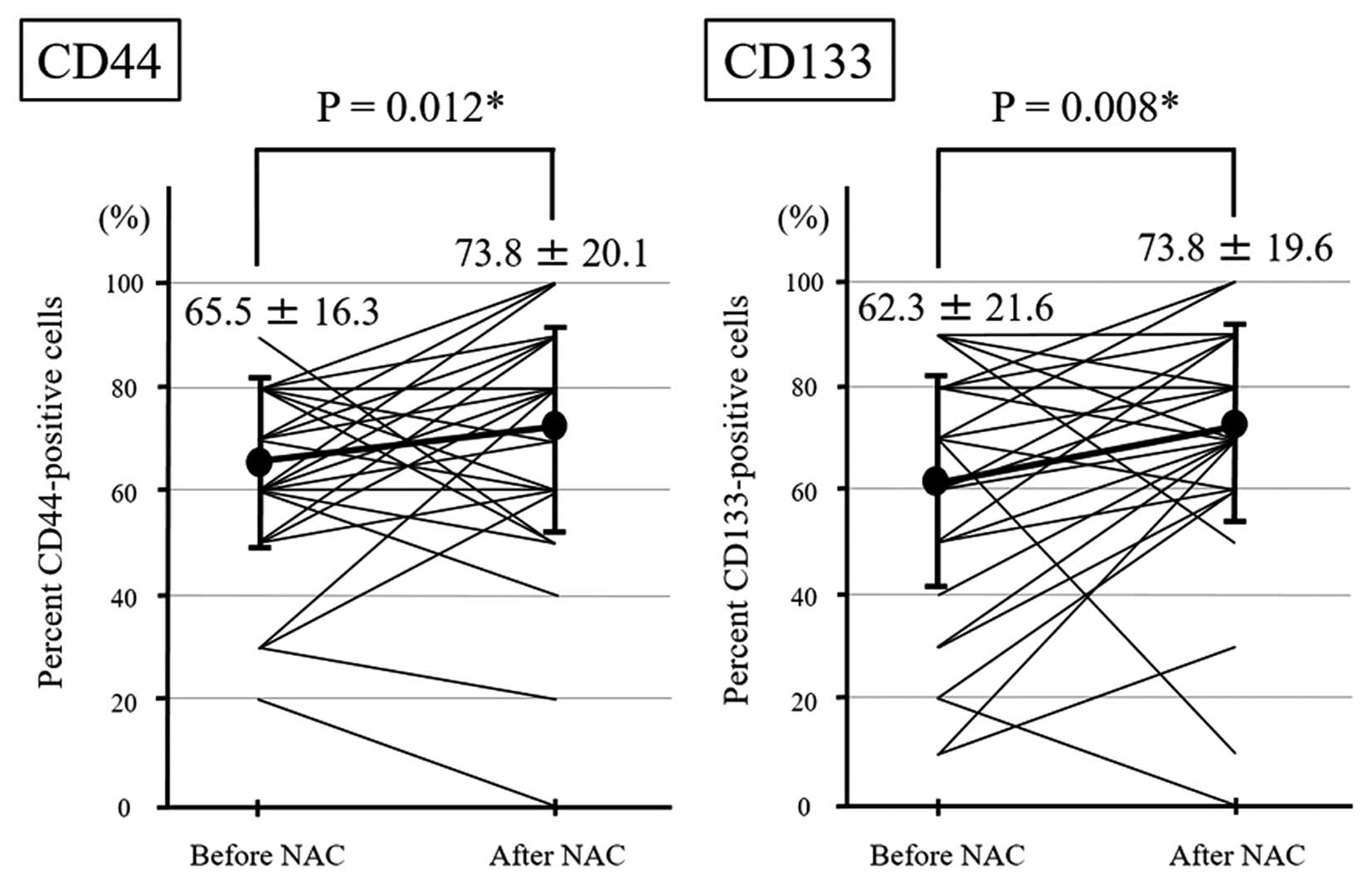
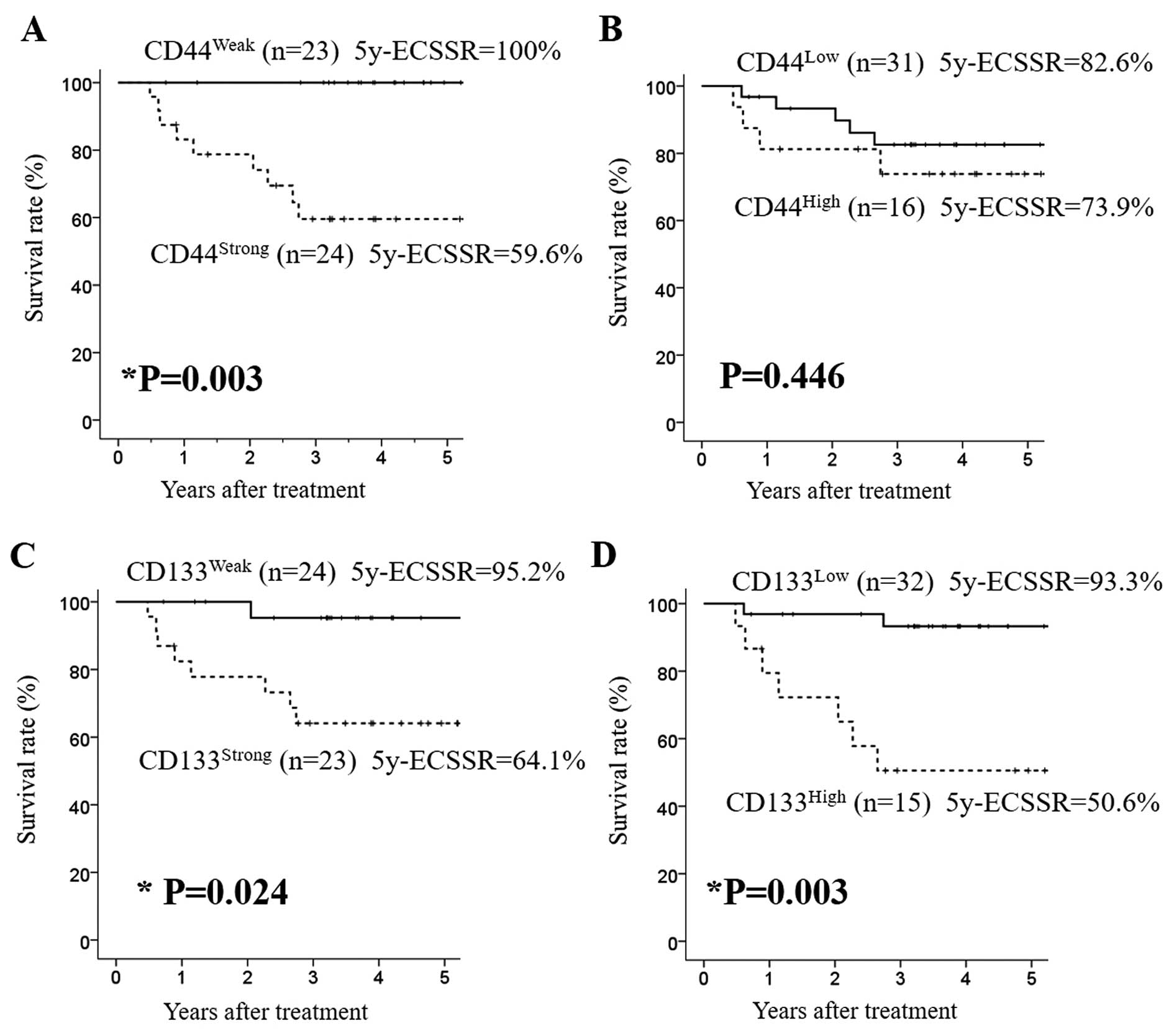
|
1
|
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa
S, Shimizu H, Nakamura T, Yabusaki H, Aoyama N, Kurita A, et al: A
randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with
cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for
localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic
esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 19:68–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kuwano H, Nishimura Y, Oyama T, Kato H,
Kitagawa Y, Kusano M, Shimada H, Takiuchi H, Toh Y, Doki Y, et al:
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Carcinoma of the
Esophagus April 2012 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society.
Esophagus. 12:1–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Xie J, Guo J, Manning HC, Gore JC
and Guo N: Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as cancer stem cell markers
for colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:1301–1308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Zhou J, Lu J, Xiong H, Shi X and
Gong L: Significance of CD44 expression in head and neck cancer: A
systemic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 14:152014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao S, He JL, Qiu ZX, Chen NY, Luo Z,
Chen BJ and Li WM: Prognostic value of CD44 variant exon 6
expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6761–6766. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nosrati A, Naghshvar F and Khanari S:
Cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD133 in primary gastric
adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Cell Med. 3:279–286. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mizukami T, Kamachi H, Mitsuhashi T,
Tsuruga Y, Hatanaka Y, Kamiyama T, Matsuno Y and Taketomi A:
Immunohistochemical analysis of cancer stem cell markers in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients after neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 14:6872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao JS, Li WJ, Ge D, Zhang PJ, Li JJ, Lu
CL, Ji XD, Guan DX, Gao H, Xu LY, et al: Tumor initiating cells in
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas express high levels of CD44.
PLoS One. 6:e214192011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horn PA, Tesch H, Staib P, Kube D, Diehl V
and Voliotis D: Expression of AC133, a novel hematopoietic
precursor antigen, on acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood.
93:1435–1437. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, Motohashi T,
Kunisada T and Moriwaki H: Characterization of CD133+
hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/progenitor cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:820–824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okamoto H, Fujishima F, Nakamura Y,
Zuguchi M, Ozawa Y, Takahashi Y, Miyata G, Kamei T, Nakano T,
Taniyama Y, et al: Significance of CD133 expression in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 11:512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sobin L, Gospodarowicz M and Wittekind C:
TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell;
Oxford: 2010
|
|
14
|
Fléjou JF: WHO Classification of digestive
tumors: the fourth edition. Ann Pathol. 31:(Suppl 5). S27–S31.
2011.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA,
Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van
Oosterom AT, Christian MC, et al: New guidelines to evaluate the
response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for
Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the
United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 92:205–216. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Japan Esophageal Society, . Japanese
Classification of Esophageal Cancer, tenth edition: part I.
Esophagus. 6:1–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meredith KL, Weber JM, Turaga KK, Siegel
EM, McLoughlin J, Hoffe S, Marcovalerio M, Shah N, Kelley S and
Karl R: Pathologic response after neoadjuvant therapy is the major
determinant of survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 17:1159–1167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aomatsu N, Yashiro M, Kashiwagi S,
Takashima T, Ishikawa T, Ohsawa M, Wakasa K and Hirakawa K: CD133
is a useful surrogate marker for predicting chemosensitivity to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. PLoS One. 7:e458652012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee HH, Seo KJ, An CH, Kim JS and Jeon HM:
CD133 expression is correlated with chemoresistance and early
recurrence of gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 106:999–1004. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piao LS, Hur W, Kim TK, Hong SW, Kim SW,
Choi JE, Sung PS, Song MJ, Lee BC, Hwang D, et al:
CD133+ liver cancer stem cells modulate radioresistance
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 315:129–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahlberg SH, Spiegelberg D, Glimelius B,
Stenerlöw B and Nestor M: Evaluation of cancer stem cell markers
CD133, CD44, CD24: Association with AKT isoforms and radiation
resistance in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e946212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pardal R, Clarke MF and Morrison SJ:
Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:895–902. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou F, Mu YD, Liang J, Liu ZX, Chen HS
and Zhang JF: Expression and prognostic value of tumor stem cell
markers ALDH1 and CD133 in colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
7:507–512. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Zhe H, Gao P, Zhang N, Li G and
Qin J: Cancer stem cell marker ALDH1 expression is associated with
lymph node metastasis and poor survival in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma: A study from high incidence area of northern China. Dis
Esophagus. 25:560–565. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hang D, Dong HC, Ning T, Dong B, Hou DL
and Xu WG: Prognostic value of the stem cell markers CD133 and
ABCG2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis
Esophagus. 25:638–644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shien K, Toyooka S, Ichimura K, Soh J,
Furukawa M, Maki Y, Muraoka T, Tanaka N, Ueno T, Asano H, et al:
Prognostic impact of cancer stem cell-related markers in non-small
cell lung cancer patients treated with induction chemoradiotherapy.
Lung Cancer. 77:162–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Biddle A, Liang X, Gammon L, Fazil B,
Harper LJ, Emich H, Costea DE and Mackenzie IC: Cancer stem cells
in squamous cell carcinoma switch between two distinct phenotypes
that are preferentially migratory or proliferative. Cancer Res.
71:5317–5326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geng S, Guo Y, Wang Q, Li L and Wang J:
Cancer stem-like cells enriched with CD29 and CD44 markers exhibit
molecular characteristics with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol Res. 305:35–47. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le Bras GF, Allison GL, Richards NF,
Ansari SS, Washington MK and Andl CD: CD44 upregulation in
E-cadherin-negative esophageal cancers results in cell invasion.
PLoS One. 6:e270632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen C, Zimmermann M, Tinhofer I, Kaufmann
AM and Albers AE: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer
stem(−like) cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 338:47–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED,
Almeida-Porada G, Ogawa M, Leary AG, Olweus J, Kearney J and Buck
DW: AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cells. Blood. 90:5002–5012. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Comparative genomics
on PROM1 gene encoding stem cell marker CD133. Int J Mol Med.
19:967–970. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jao SW, Chen SF, Lin YS, Chang YC, Lee TY,
Wu CC, Jin JS and Nieh S: Cytoplasmic CD133 expression is a
reliable prognostic indicator of tumor regression after neoadjuvant
concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 19:3432–3440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanei T, Morimoto K, Shimazu K, Kim SJ,
Tanji Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y and Noguchi S: Association of breast
cancer stem cells identified by aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression
with resistance to sequential Paclitaxel and epirubicin-based
chemotherapy for breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4234–4241.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|