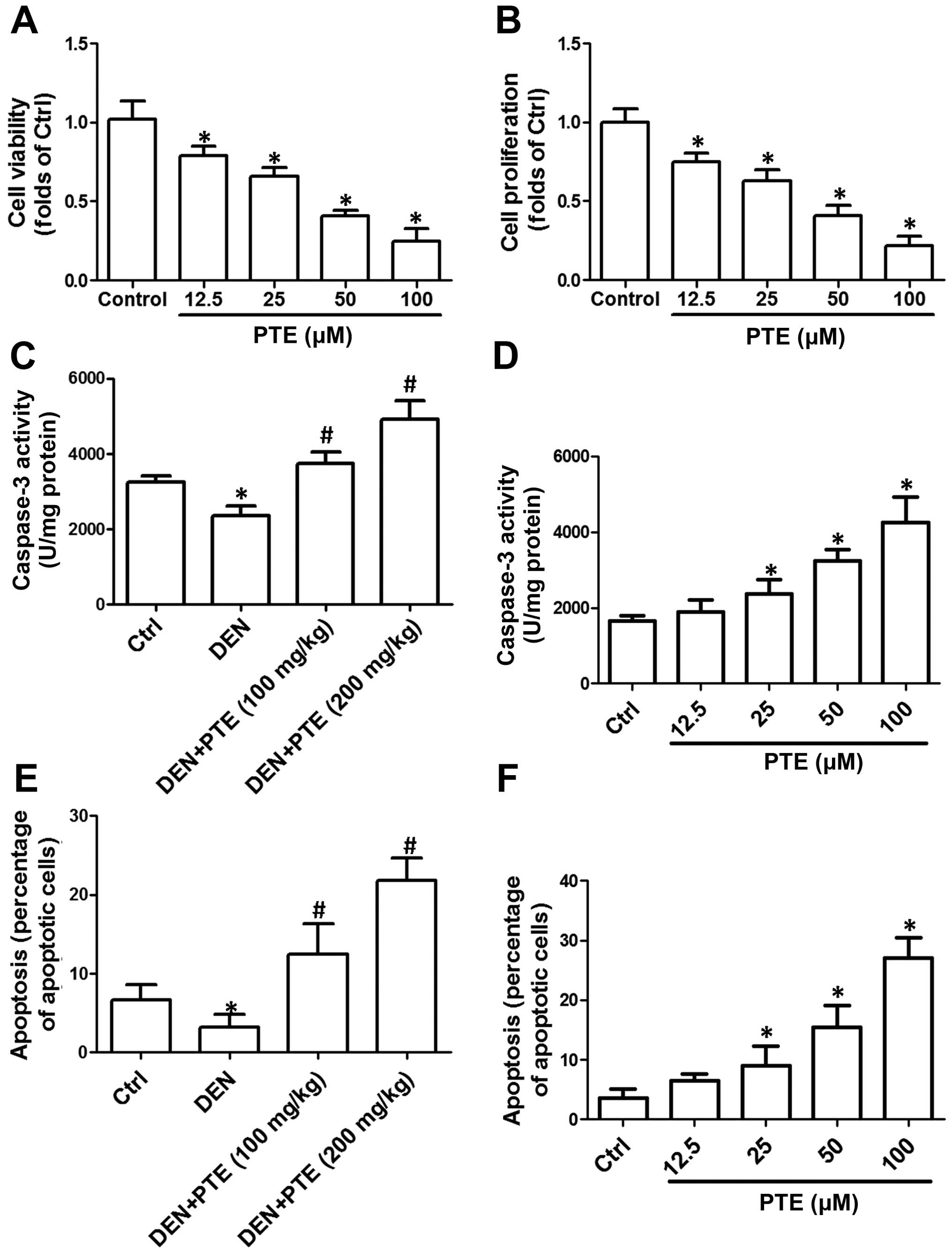
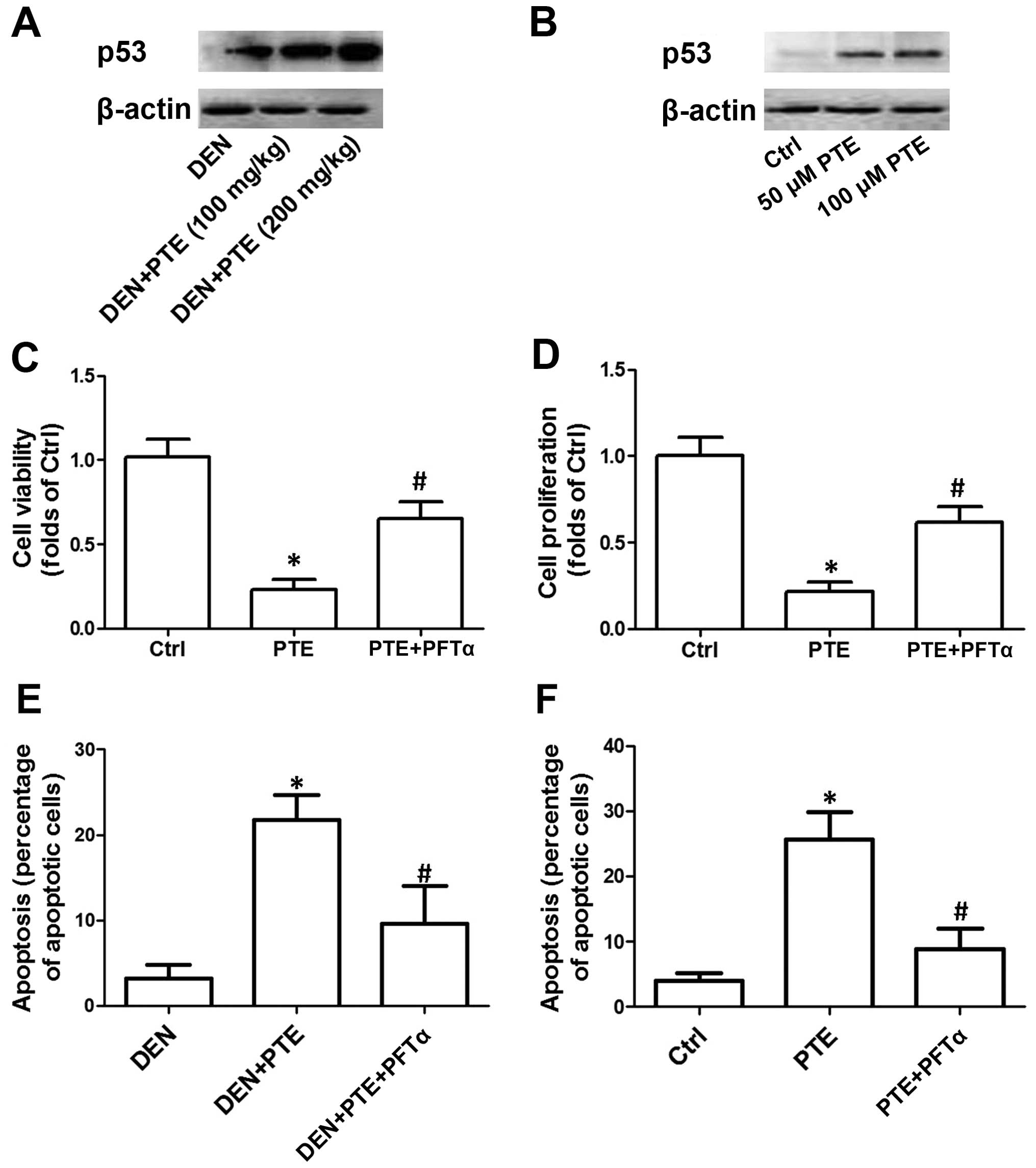
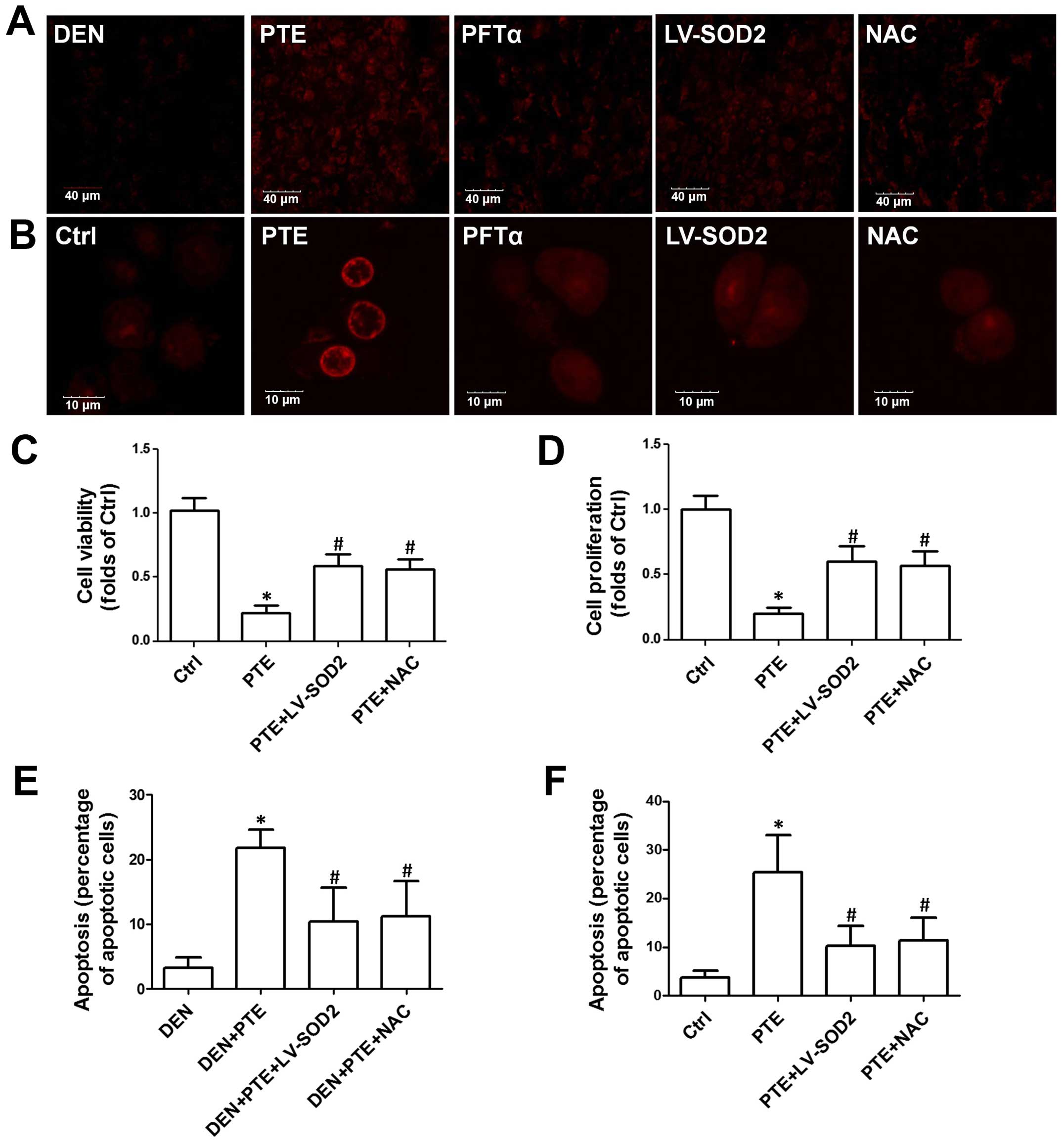
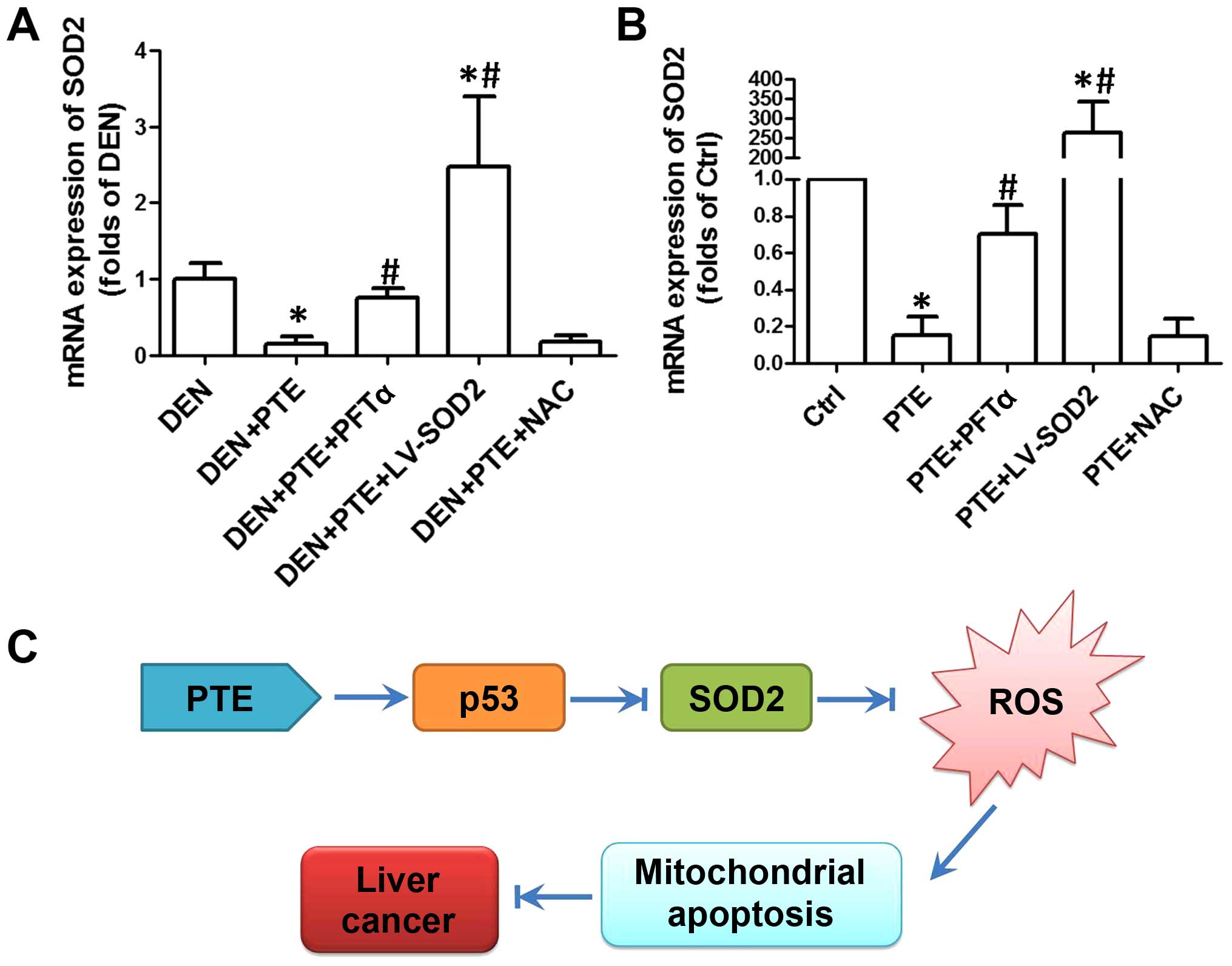
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yeh YP, Hu TH, Cho PY, Chen HH, Yen AM,
Chen SL, Chiu SY, Fann JC, Su WW, Fang YJ, et al: Changhua
Community-Based Abdominal Ultrasonography Screening Group:
Evaluation of abdominal ultrasonography mass screening for
hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. Hepatology. 59:1840–1849. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pascual S, Herrera I and Irurzun J: New
advances in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 8:421–438.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cabibbo G, Enea M, Attanasio M, Bruix J,
Craxì A and Cammà C: A meta-analysis of survival rates of untreated
patients in randomized clinical trials of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:1274–1283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmidt S, Follmann M, Malek N, Manns MP
and Greten TF: Critical appraisal of clinical practice guidelines
for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1779–1786. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roxburgh P and Evans TR: Systemic therapy
of hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we making progress? Adv Ther.
25:1089–1104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tejeda-Maldonado J, García-Juárez I,
Aguirre-Valadez J, González-Aguirre A, Vilatobá-Chapa M,
Armengol-Alonso A, Escobar-Penagos F, Torre A, Sánchez-Ávila JF and
Carrillo-Pérez DL: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma: An update. World J Hepatol. 7:362–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lombardi G, Vannini S, Blasi F,
Marcotullio MC, Dominici L, Villarini M, Cossignani L and Moretti
M: In vitro safety/protection assessment of resveratrol and
pterostilbene in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). Nat Prod
Commun. 10:1403–1408. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan MH, Chiou YS, Chen WJ, Wang JM,
Badmaev V and Ho CT: Pterostilbene inhibited tumor invasion via
suppressing multiple signal transduction pathways in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 30:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Remsberg CM, Yáñez JA, Ohgami Y,
Vega-Villa KR, Rimando AM and Davies NM: Pharmacometrics of
pterostilbene: Preclinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism,
anticancer, antiinflammatory, antioxidant and analgesic activity.
Phytother Res. 22:169–179. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng Y, Yang Y, Fan C, Di S, Hu W, Jiang
S, Li T, Ma Z, Chao D, Feng X, et al: Pterostilbene inhibits the
growth of human esophageal cancer cells by regulating endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1226–1244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dhar S, Kumar A, Zhang L, Rimando AM, Lage
JM, Lewin JR, Atfi A, Zhang X and Levenson AS: Dietary
pterostilbene is a novel MTA1-targeted chemopreventive and
therapeutic agent in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 7:18469–18484.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nikhil K, Sharan S and Roy P: A
pterostilbene derivative suppresses osteoclastogenesis by
regulating RANKL-mediated NFκB and MAPK signaling in RAW264.7
cells. Pharmacol Rep. 67:1264–1272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Wu X, Cai X, Song M, Zheng J, Pan
C, Qiu P, Zhang L, Zhou S, Tang Z, et al: Identification of
pinostilbene as a major colonic metabolite of pterostilbene and its
inhibitory effects on colon cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
60:1924–1932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang CS, Ho CT, Tu SH, Pan MH, Chuang CH,
Chang HW, Chang CH, Wu CH and Ho YS: Long-term ethanol
exposure-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and
invasion through lysyl oxidase activation are attenuated by
combined treatment with pterostilbene and curcumin analogues. J
Agric Food Chem. 61:4326–4335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hacker HJ, Mtiro H, Bannasch P and
Vesselinovitch SD: Histochemical profile of mouse hepatocellular
adenomas and carcinomas induced by a single dose of
diethylnitrosamine. Cancer Res. 51:1952–1958. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fausto N and Campbell JS: Mouse models of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 30:87–98. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao X, Fu J, Xu A, Yu L, Zhu J, Dai R, Su
B, Luo T, Li N, Qin W, et al: Gankyrin drives malignant
transformation of chronic liver damage-mediated fibrosis via the
Rac1/JNK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin XY, Tatsukawa H, Hitomi K, Shirakami
Y, Ishibashi N, Shimizu M, Moriwaki H and Kojima S: Metabolome
analyses uncovered a novel inhibitory effect of acyclic retinoid on
aberrant lipogenesis in a mouse diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic
tumorigenesis model. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 9:205–214. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shibata Y, Hara T, Nagano J, Nakamura N,
Ohno T, Ninomiya S, Ito H, Tanaka T, Saito K, Seishima M, et al:
The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in
diethylnitrosamine-induced liver carcinogenesis. PLoS One.
11:e01462792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kundu J, Chun KS, Aruoma OI and Kundu JK:
Mechanistic perspectives on cancer chemoprevention/chemotherapeutic
effects of thymoquinone. Mutat Res. 768:22–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang CF, Wen LZ, Yin C, Xu WP, Shi B,
Zhang X and Xie WF: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 mediates
the inhibitory effect of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:27408–27421.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Liang L, Liu Y, Luo Y, Liang X, Luo
D, Feng Z, Dang Y, Yang L and Chen G: Clinicopathological
significance of STAT4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effect on
cell growth and apoptosis. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1721–1734.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen X, Tan M, Xie Z, Feng B, Zhao Z, Yang
K, Hu C, Liao N, Wang T, Chen D, et al: Inhibiting
ROS-STAT3-dependent autophagy enhanced capsaicin-induced apoptosis
in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Free Radic Res.
50:744–755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang B, Wang XQ, Chen HY and Liu BH:
Involvement of the Nrf2 pathway in the regulation of
pterostilbene-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells via ER stress. J
Pharmacol Sci. 126:216–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsiao PC, Chou YE, Tan P, Lee WJ, Yang SF,
Chow JM, Chen HY, Lin CH, Lee LM and Chien MH: Pterostilbene
simultaneously induced G0/G1-phase arrest and MAPK-mediated
mitochondrial-derived apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukemia
cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e1053422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan C, Hu Y, Li J, Wang Z, Huang J, Zhang
S and Ding L: Estrogen receptor-α36 is involved in
pterostilbene-induced apoptosis and anti-proliferation in in vitro
and in vivo breast cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1044592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakano K and Vousden KH: PUMA, a novel
proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 7:683–694. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Zhang C, Hu W and Feng Z: Tumor
suppressor p53 and its mutants in cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett.
356:197–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chi SW: Structural insights into the
transcription-independent apoptotic pathway of p53. BMB Rep.
47:167–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maillet A and Pervaiz S: Redox regulation
of p53, redox effectors regulated by p53: a subtle balance.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1285–1294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Liu J, Jiang L, Wei X, Niu C, Wang
R, Zhang J, Meng D and Yao K: Bach1 induces endothelial cell
apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest through ROS generation. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016:62340432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Sun N, Li X, Li K, Tian J and Li
J: Diallyl trisulfide induces osteosarcoma cell apoptosis through
reactive oxygen species-mediated downregulation of the PI3K/Akt
pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:3648–3658. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jia J, Qin Y, Zhang L, Guo C, Wang Y, Yue
X and Qian J: Artemisinin inhibits gallbladder cancer cell lines
through triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.
13:4461–4468. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Sireesh D,
Sakthivadivel M, Sivasubramanian S, Gunasekaran P and Ramkumar KM:
Anti-hyperlipidemic and antiperoxidative role of pterostilbene via
Nrf2 signaling in experimental diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol. 777:9–16.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Elango B, Dornadula S, Paulmurugan R and
Ramkumar KM: Pterostilbene ameliorates streptozotocin-induced
diabetes through enhancing antioxidant signaling pathways mediated
by nrf2. Chem Res Toxicol. 29:47–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fridovich I: Superoxide radical and
superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem. 64:97–112. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang J, Qiu B, Li X, Zhang H and Liu W:
p53-p66shc/miR-21-Sod2 signaling is critical for the
inhibitory effect of betulinic acid on hepatocellular carcinoma.
Toxicol Lett. 238:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|