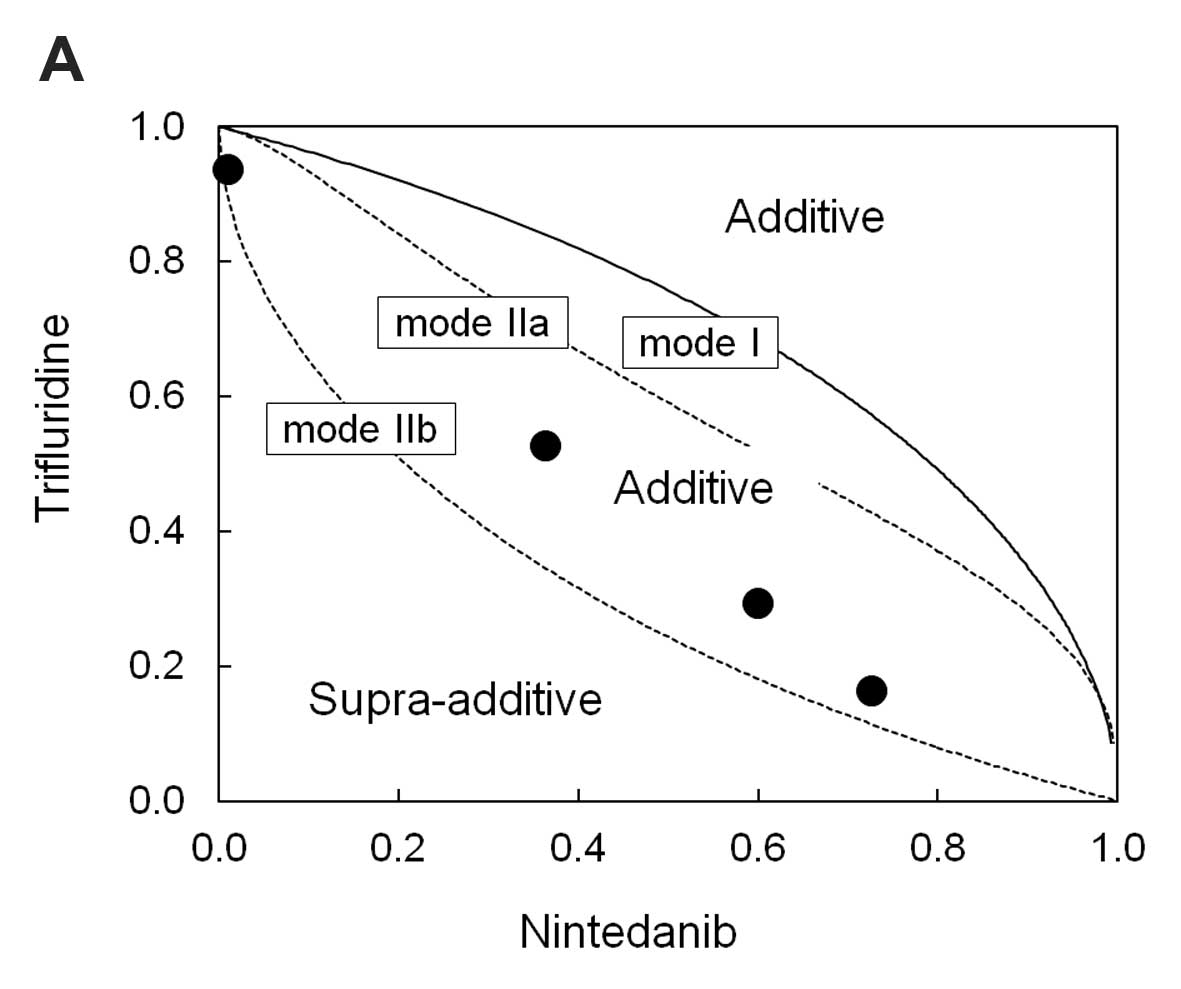
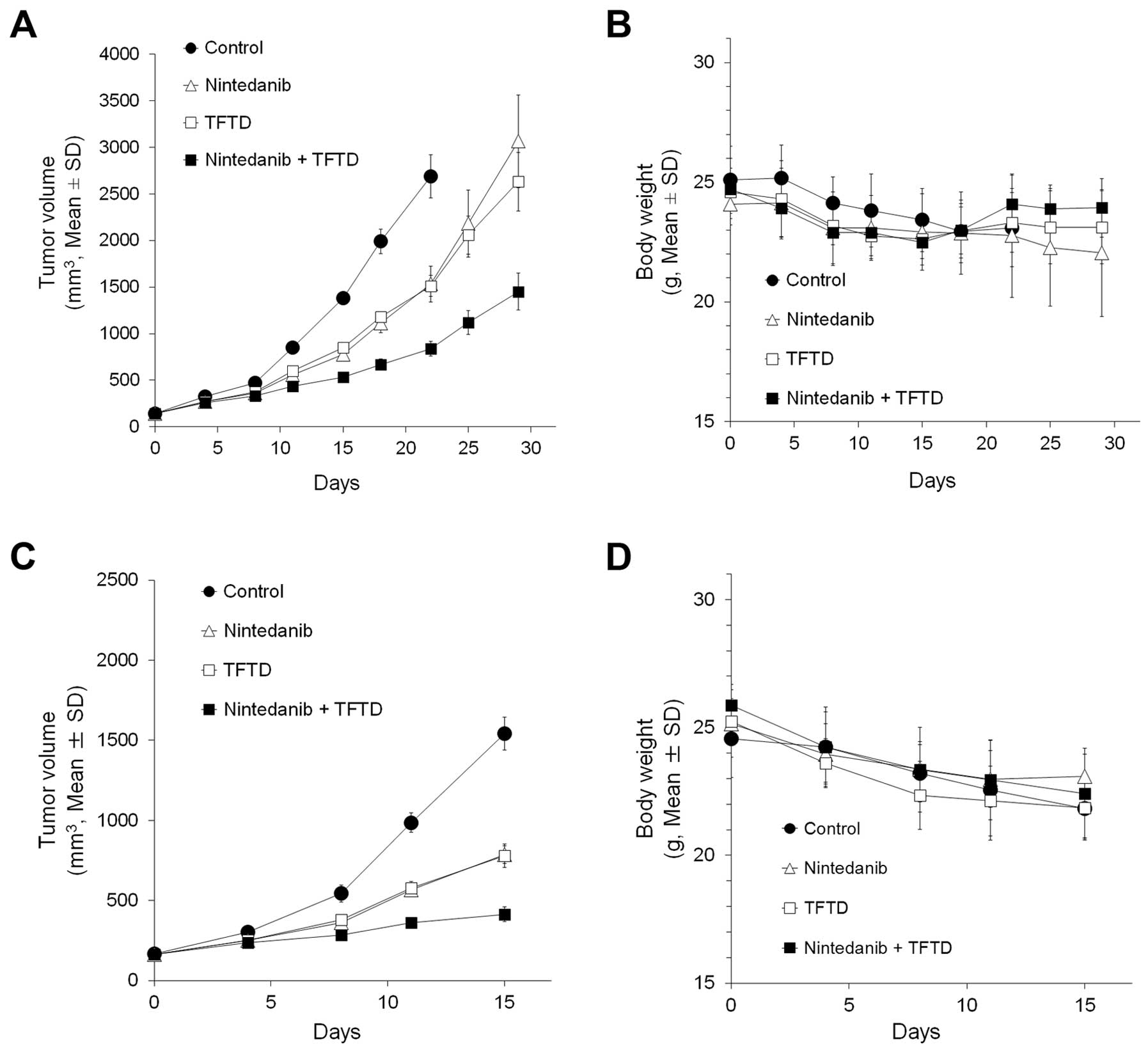
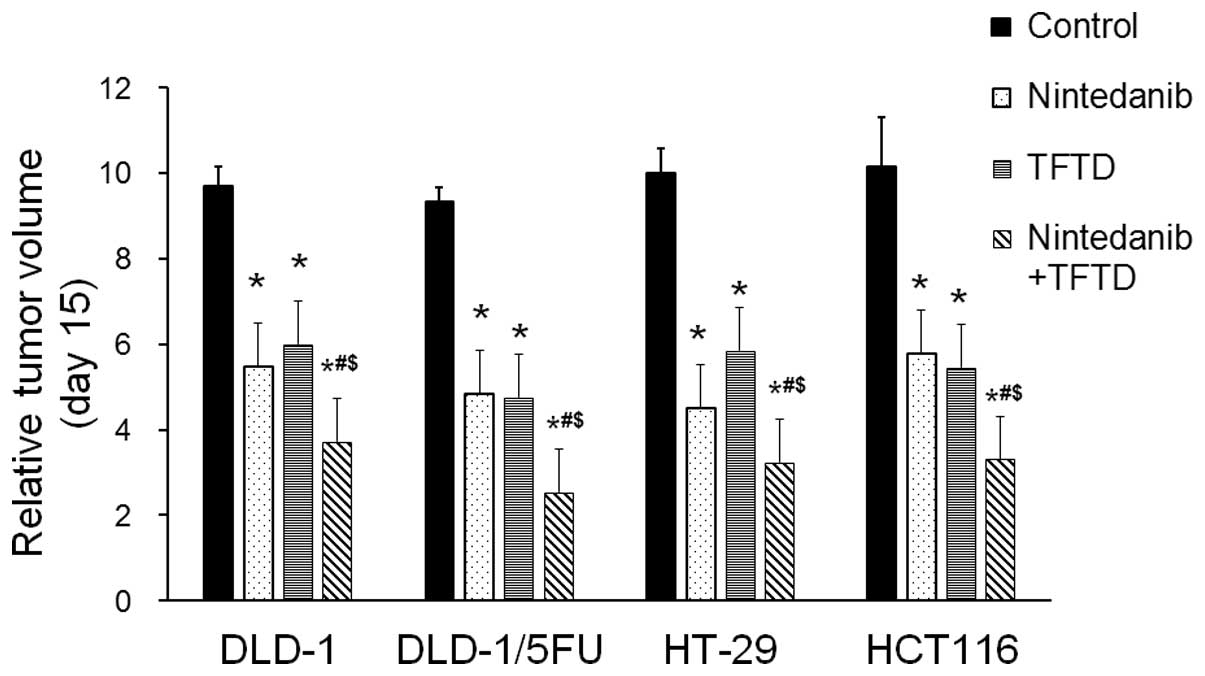
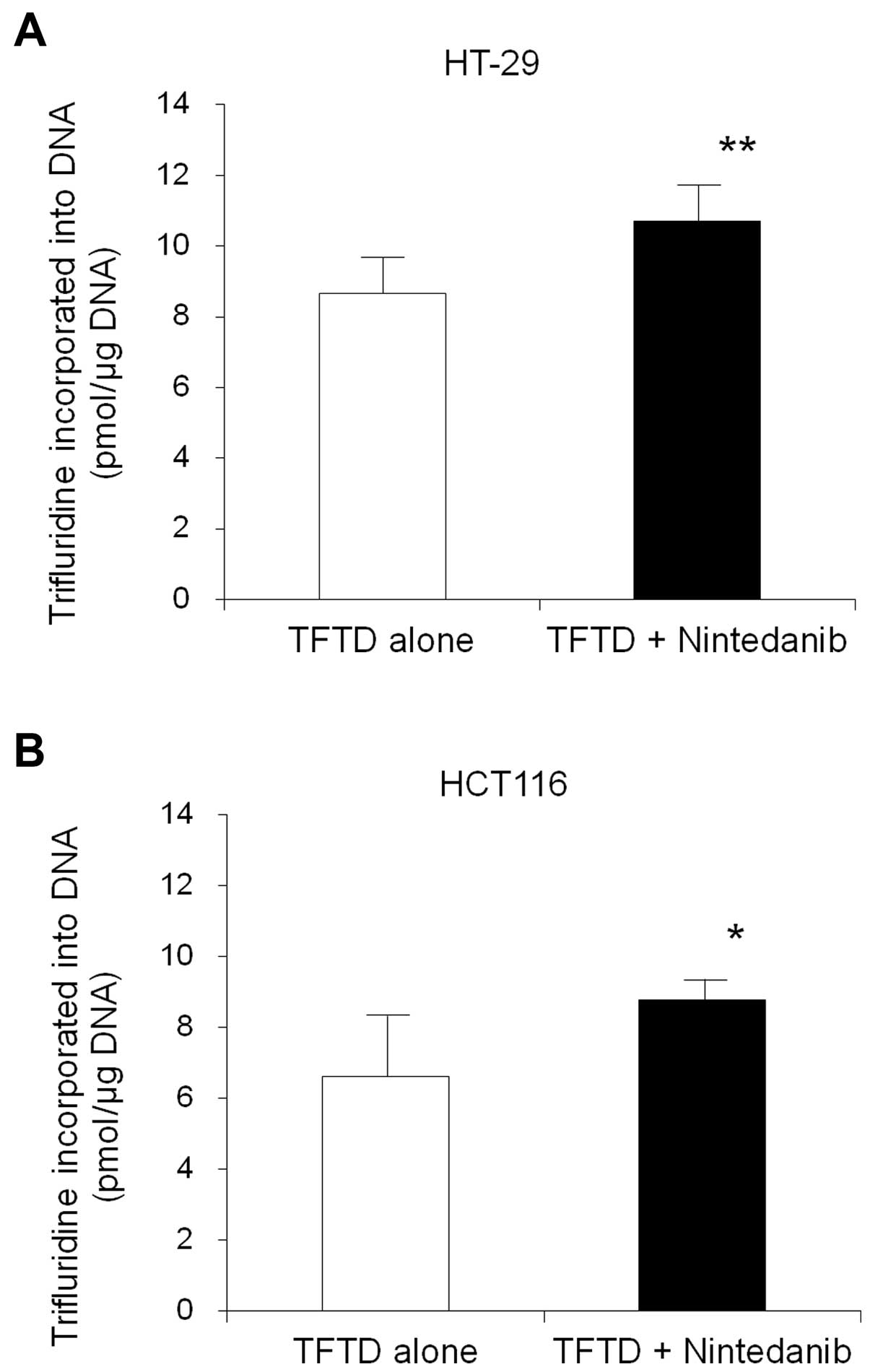
|
1
|
Heidelberger C, Birnie GD, Boohar J and
Wentland D: Fluorinated pyrimidines. XX. Inhibition of the
nucleoside phosphorylase cleavage of 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridine by
5-trifluoromethyl-2′-deoxyuridine. Biochim Biophys Acta.
76:315–318. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gottschling H and Heidelberger C:
Fluorinated pyrimidines. XIX some biological effects of
5-trifluoromthyluracil and 5-trifluoromethyl-2′-deoxyuridine of
Escherichia coli and bacteriophage T4G. J Mol Biol. 7:541–560.
1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reyes P and Heidelberger C: Fluorinated
pyrimidines. XXVI. Mammalian thymidylate synthetase: Its mechanism
of action and inhibition by fluorinated nucleotides. Mol Pharmacol.
1:14–30. 1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujiwara Y, Oki T and Heidelberger C:
Fluorinated pyrimidines. XXXVII. Effects of
5-trifluoromethyl-2′-deoxyuridine on the synthesis of
deoxyribonucleic acid of mammalian cells in culture. Mol Pharmacol.
6:273–280. 1970.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukushima M, Suzuki N, Emura T, Yano S,
Kazuno H, Tada Y, Yamada Y and Asao T: Structure and activity of
specific inhibitors of thymidine phosphorylase to potentiate the
function of antitumor 2′-deoxyribonucleosides. Biochem Pharmacol.
59:1227–1236. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Emura T, Suzuki N, Yamaguchi M, Ohshimo H
and Fukushima M: A novel combination antimetabolite, TAS-102,
exhibits antitumor activity in FU-resistant human cancer cells
through a mechanism involving FTD incorporation in DNA. Int J
Oncol. 25:571–578. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lenz HJ, Stintzing S and Loupakis F:
TAS-102, a novel antitumor agent: A review of the mechanism of
action. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:777–783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshino T, Mizunuma N, Yamazaki K, Nishina
T, Komatsu Y, Baba H, Tsuji A, Yamaguchi K, Muro K, Sugimoto N, et
al: TAS-102 monotherapy for pretreated metastatic colorectal
cancer: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2
trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:993–1001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mayer RJ, Van Cutsem E, Falcone A, Yoshino
T, Garcia-Carbonero R, Mizunuma N, Yamazaki K, Shimada Y, Tabernero
J, Komatsu Y, et al: RECOURSE Study Group: Randomized trial of
TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
372:1909–1919. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Al-Husein B, Abdalla M, Trepte M, Deremer
DL and Somanath PR: Antiangiogenic therapy for cancer: An update.
Pharmacotherapy. 32:1095–1111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moreira IS, Fernandes PA and Ramos MJ:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibition - a critical
review. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 7:223–245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rini BI, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg JE,
Bukowski RM, Sosman JA, Stadler WM, Hutson TE, Margolin K, Harmon
CS, DePrimo SE, et al: Antitumor activity and biomarker analysis of
sunitinib in patients with bevacizumab-refractory metastatic renal
cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 26:3743–3748. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason
GA, Christensen JG and Kerbel RS: Accelerated metastasis after
short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis.
Cancer Cell. 15:232–239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hilberg F, Roth GJ, Krssak M, Kautschitsch
S, Sommergruber W, Tontsch-Grunt U, Garin-Chesa P, Bader G, Zoephel
A, Quant J, et al: BIBF 1120: Triple angiokinase inhibitor with
sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer
Res. 68:4774–4782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bouche O, Maindrault-Goebel F, Ducreux M,
Lledo G, Andre T, Stopfer P, Amellal N, Merger M and De Gramont A:
Phase II trial of weekly alternating sequential BIBF 1120 and
afatinib for advanced colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:2271–2281. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Van Cutsem E, Prenen H, D'Haens G,
Bennouna J, Carrato A, Ducreux M, Bouché O, Sobrero A, Latini L,
Staines H, et al: A phase I/II, open-label, randomised study of
nintedanib plus mFOLFOX6 versus bevacizumab plus mFOLFOX6 in
first-line metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol.
26:2085–2091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Awasthi N and Schwarz RE: Profile of
nintedanib in the treatment of solid tumors: The evidence to date.
Onco Targets Ther. 8:3691–3701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nukatsuka M, Nakagawa F, Saito H, Sakata
M, Uchida J and Takechi T: Efficacy of combination chemotherapy
using a novel oral chemotherapeutic agent, TAS-102, with irinotecan
hydrochloride on human colorectal and gastric cancer xenografts.
Anticancer Res. 35:1437–1445. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nukatsuka M, Nakagawa F and Takechi T:
Efficacy of combination chemotherapy using a novel oral
chemotherapeutic agent, TAS-102, with oxaliplatin on human
colorectal and gastric cancer xenografts. Anticancer Res.
35:4605–4615. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsukihara H, Nakagawa F, Sakamoto K,
Ishida K, Tanaka N, Okabe H, Uchida J, Matsuo K and Takechi T:
Efficacy of combination chemotherapy using a novel oral
chemotherapeutic agent, TAS-102, together with bevacizumab,
cetuximab, or panitumumab on human colorectal cancer xenografts.
Oncol Rep. 33:2135–2142. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murakami Y, Kazuno H, Emura T, Tsujimoto
H, Suzuki N and Fukushima M: Different mechanisms of acquired
resistance to fluorinated pyrimidines in human colorectal cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 17:277–283. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saotome K, Morita H and Umeda M:
Cytotoxicity test with simplified crystal violet staining method
using microtitre plates and its application to injection drugs.
Toxicol In Vitro. 3:317–321. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Generalized
equations for the analysis of inhibitions of Michaelis-Menten and
higher-order kinetic systems with two or more mutually exclusive
and nonexclusive inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 115:207–216. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kudo K, Arao T, Tanaka K, Nagai T, Furuta
K, Sakai K, Kaneda H, Matsumoto K, Tamura D, Aomatsu K, et al:
Antitumor activity of BIBF 1120, a triple angiokinase inhibitor,
and use of VEGFR2+pTyr+ peripheral blood
leukocytes as a pharmacodynamic biomarker in vivo. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1373–1381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suzuki N, Nakagawa F, Nukatsuka M and
Fukushima M: Trifluorothymidine exhibits potent antitumor activity
via the induction of DNA double-strand breaks. Exp Ther Med.
2:393–397. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanaka N, Sakamoto K, Okabe H, Fujioka A,
Yamamura K, Nakagawa F, Nagase H, Yokogawa T, Oguchi K, Ishida K,
et al: Repeated oral dosing of TAS-102 confers high trifluridine
incorporation into DNA and sustained antitumor activity in mouse
models. Oncol Rep. 32:2319–2326. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bauer P, Röhmel J, Maurer W and Hothorn L:
Testing strategies in multi-dose experiments including active
control. Stat Med. 17:2133–2146. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suzuki N, Emura T and Fukushima M: Mode of
action of trifluorothymidine (TFT) against DNA replication and
repair enzymes. Int J Oncol. 39:263–270. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Markley JC, Chirakul P, Sologub D and
Sigurdsson ST: Incorporation of 2′-deoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)uridine
and 5-cyano-2′-deoxyuridine into DNA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
11:2453–2455. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor vasculature
with anti-angiogenic therapy: A new paradigm for combination
therapy. Nat Med. 7:987–989. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heldin CH, Rubin K, Pietras K and Ostman
A: High interstitial fluid pressure - an obstacle in cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:806–813. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mésange P, Poindessous V, Sabbah M,
Escargueil AE, de Gramont A and Larsen AK: Intrinsic bevacizumab
resistance is associated with prolonged activation of autocrine
VEGF signaling and hypoxia tolerance in colorectal cancer cells and
can be overcome by nintedanib, a small molecule angiokinase
inhibitor. Oncotarget. 5:4709–4721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ioannou M, Paraskeva E, Baxevanidou K,
Simos G, Papamichali R, Papacharalambous C, Samara M and Koukoulis
G: HIF-1α in colorectal carcinoma: Review of the literature. J
BUON. 20:680–689. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shimomura M, Hinoi T, Kuroda S, Adachi T,
Kawaguchi Y, Sasada T, Takakura Y, Egi H, Okajima M, Tashiro H, et
al: Overexpression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha is an
independent risk factor for recurrence after curative resection of
colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 20:(Suppl 3).
S527–S536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|