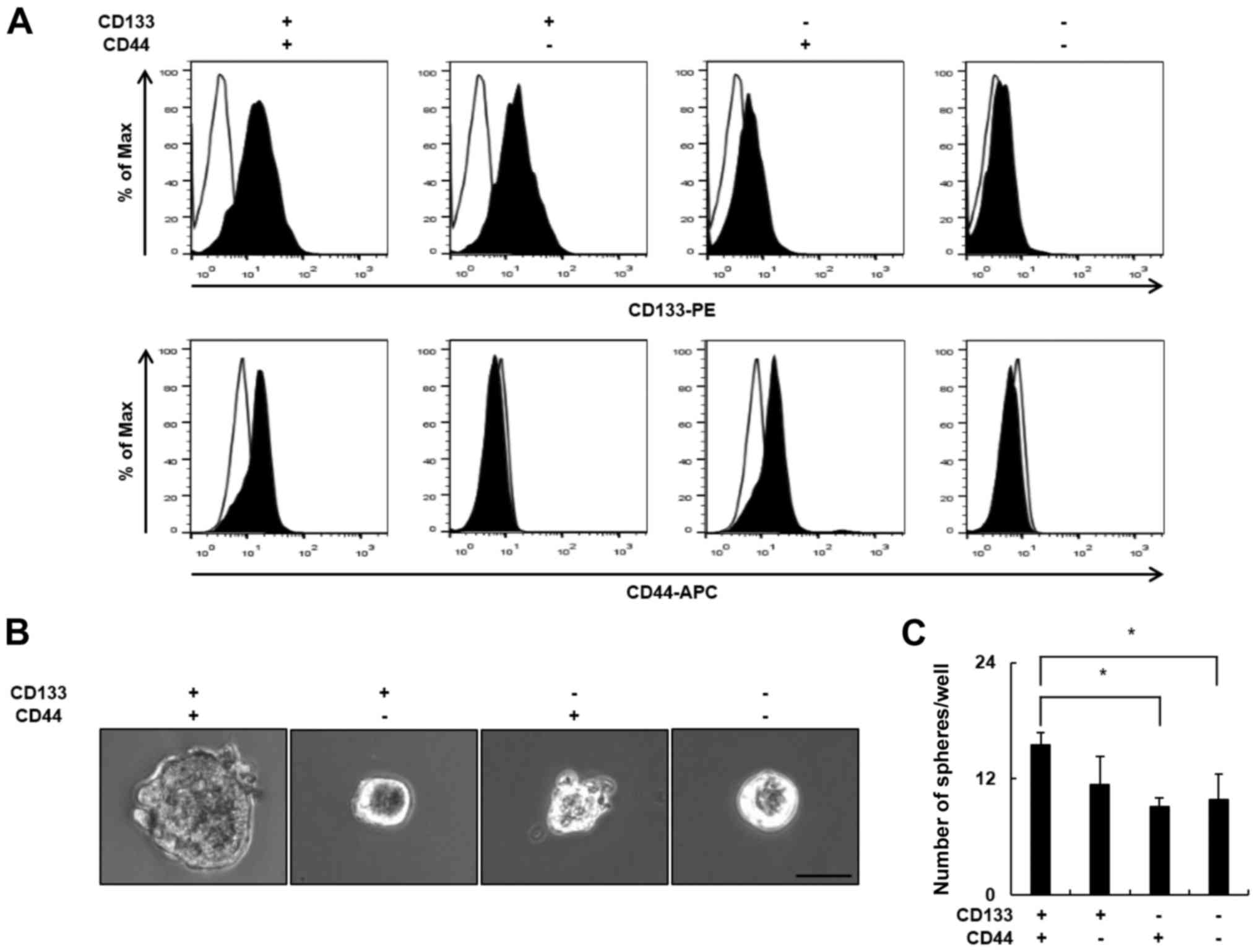
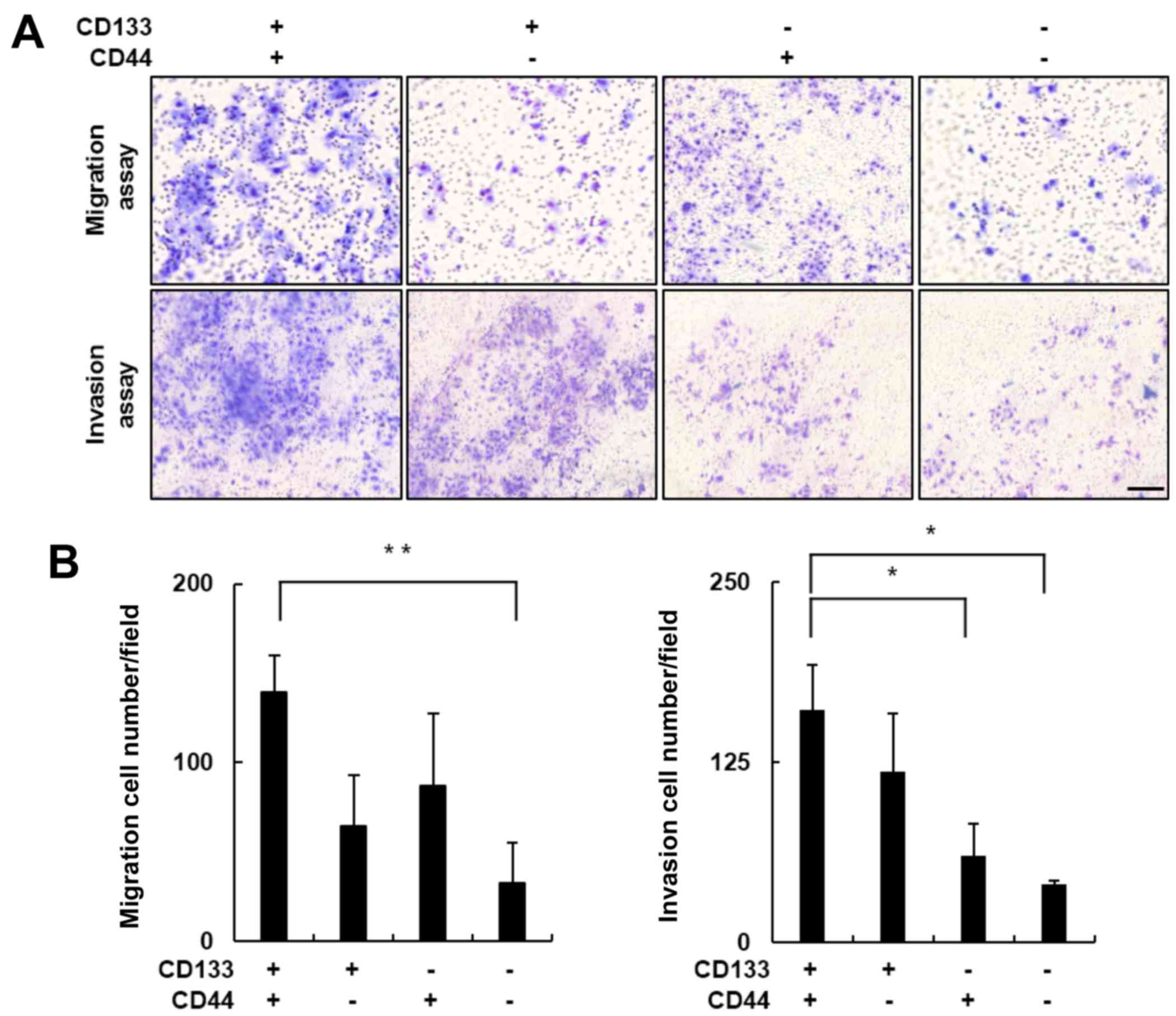
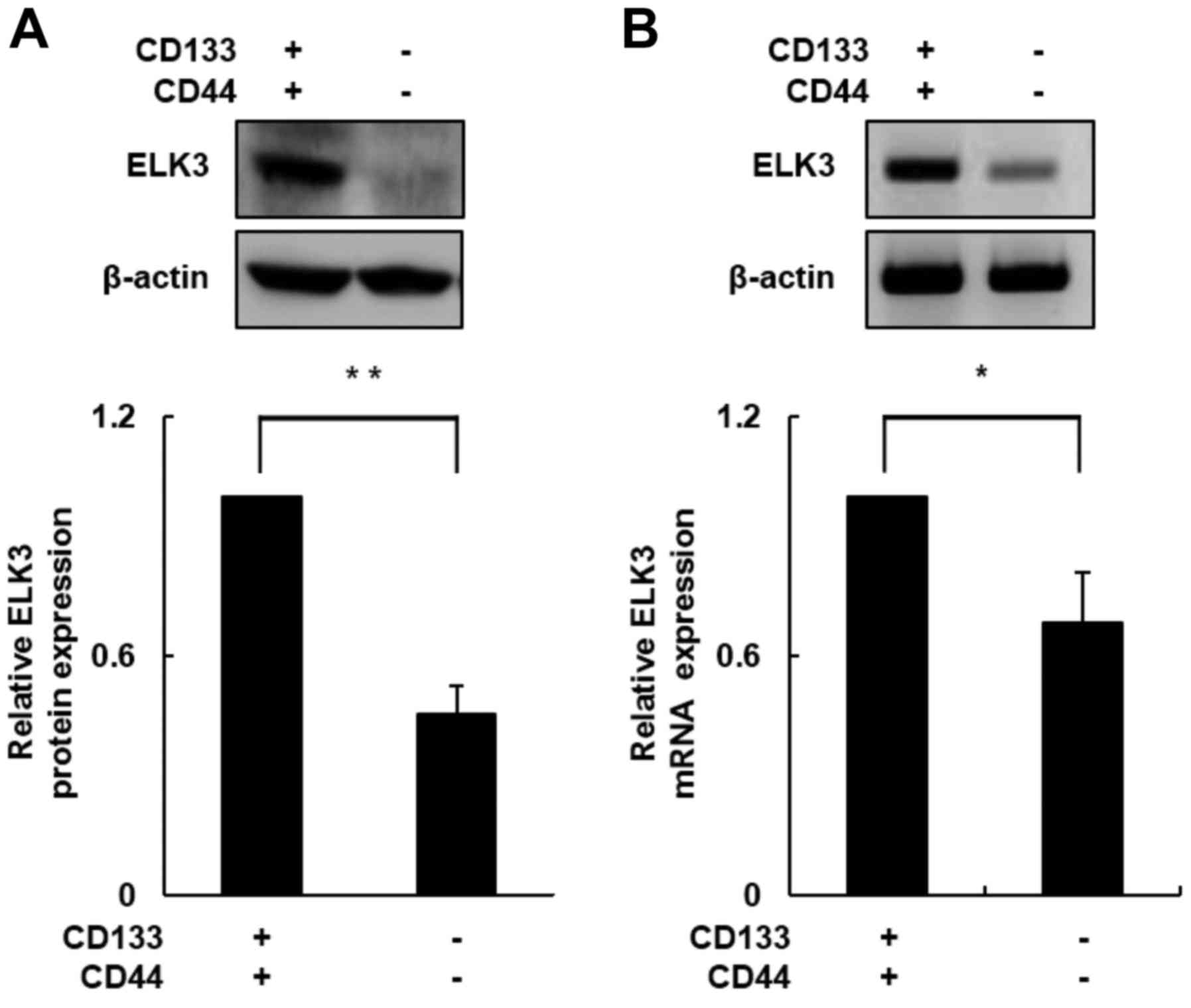
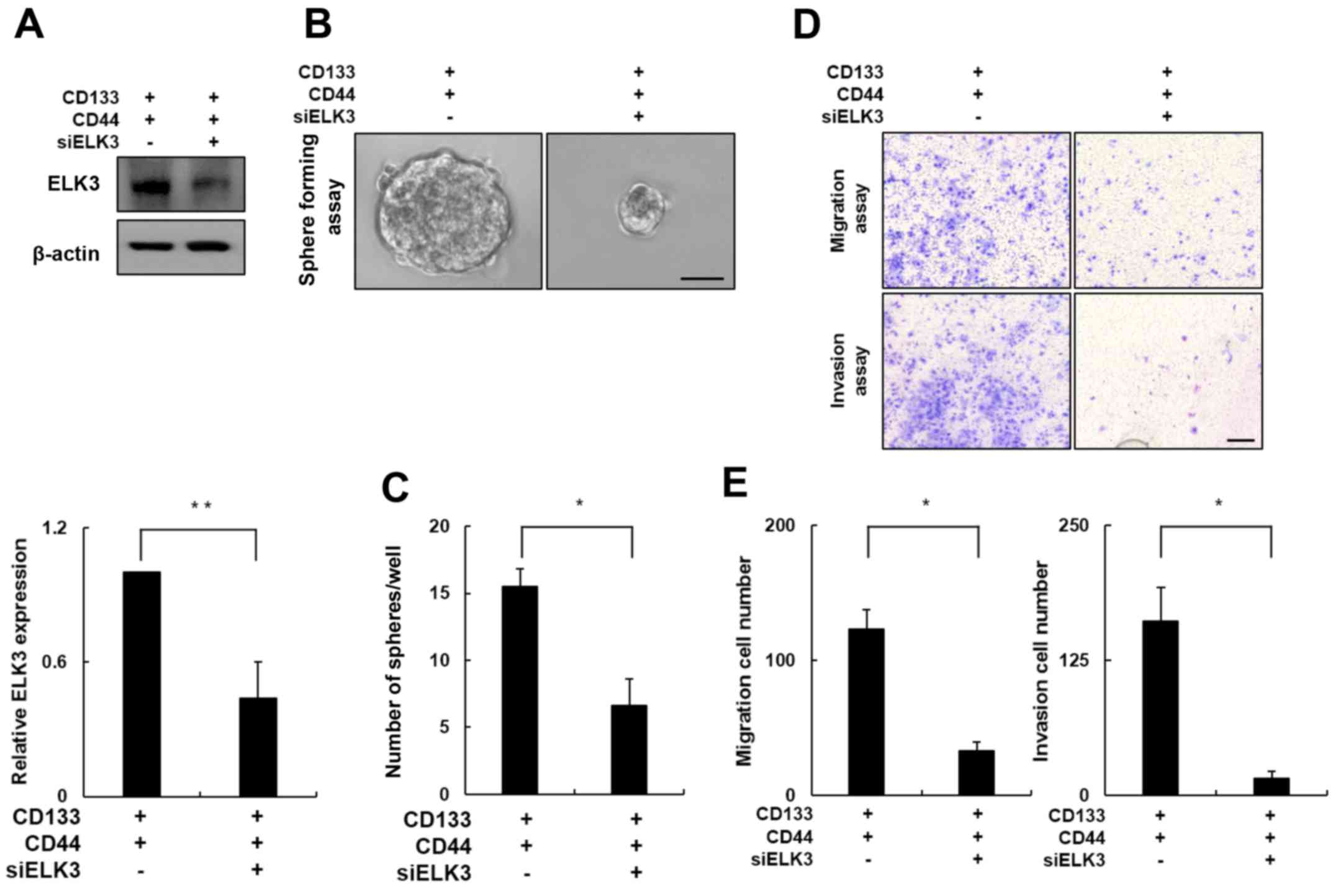
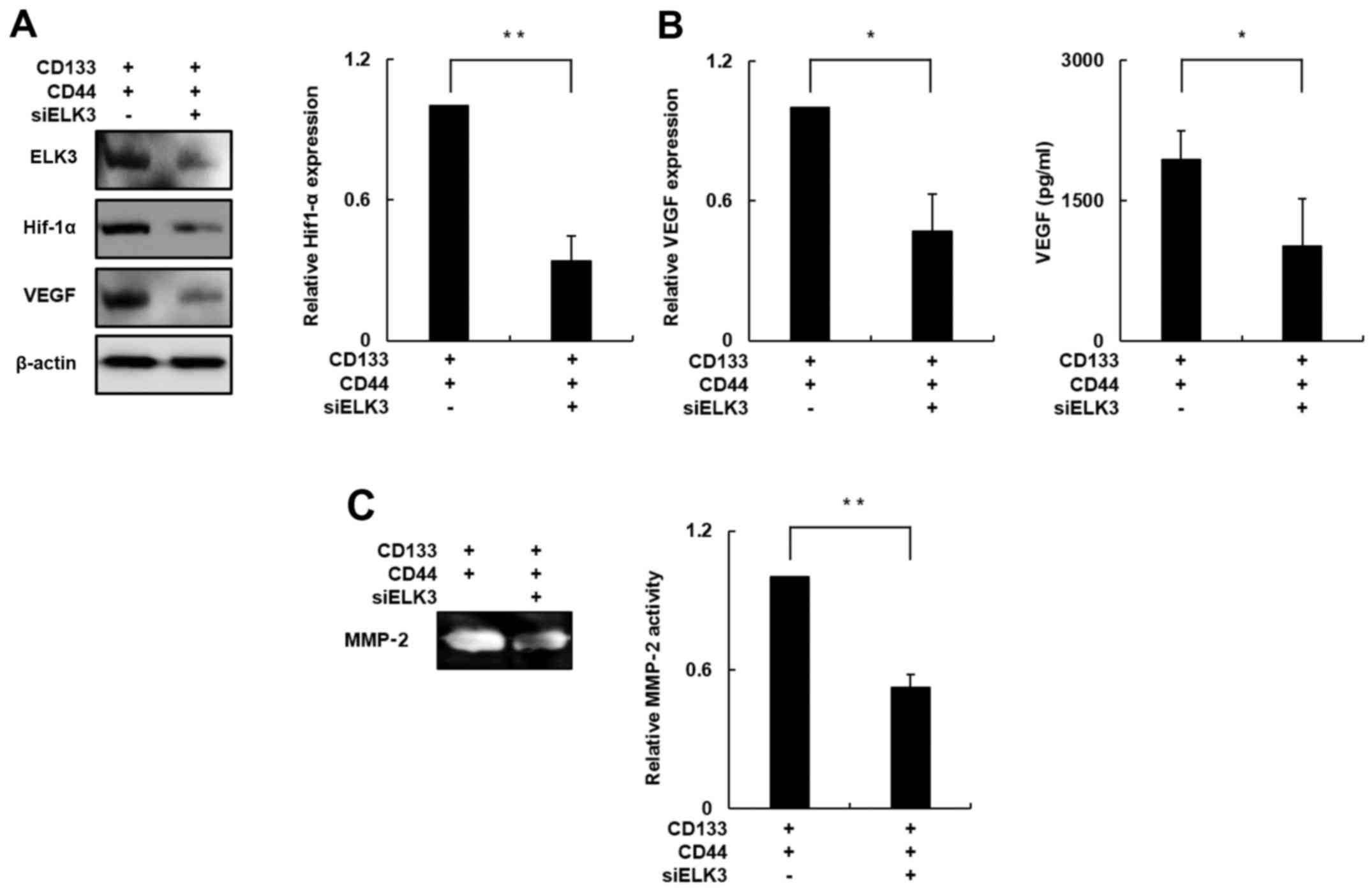
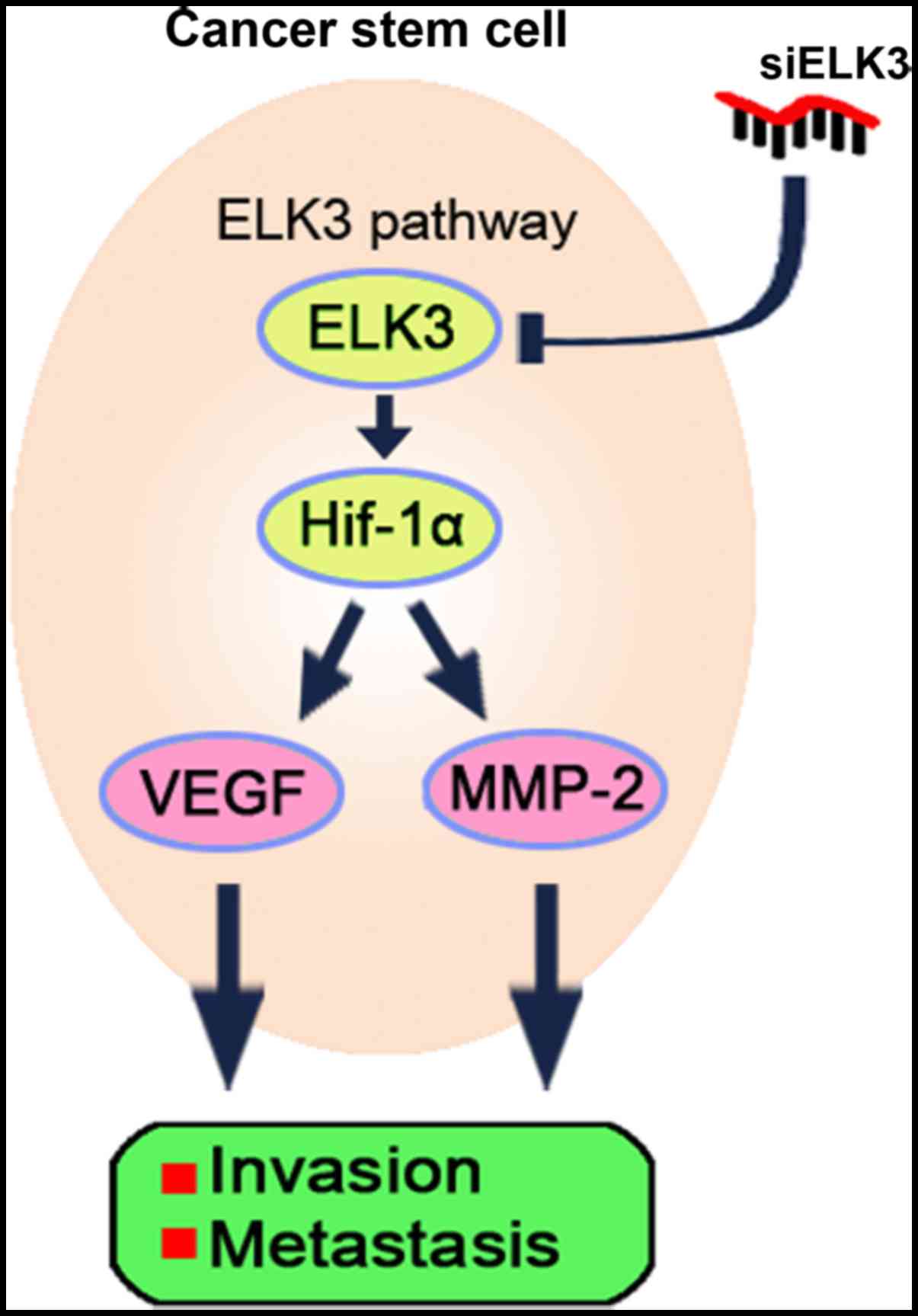
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo Z, Zhong JH, Jiang JH, Zhang J, Xiang
BD and Li LQ: Comparison of survival of patients with BCLC stage A
hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection or transarterial
chemoembolization: A propensity score-based analysis. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21:3069–3076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ueno M, Uchiyama K, Ozawa S, Hayami S,
Shigekawa Y, Tani M and Yamaue H: Adjuvant chemolipiodolization
reduces early recurrence derived from intrahepatic metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:3624–3631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells - perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR Workshop on Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamashita T and Wang XW: Cancer stem cells
in the development of liver cancer. J Clin Invest. 123:1911–1918.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee TK, Cheung VC and Ng IO: Liver
tumor-initiating cells as a therapeutic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 338:101–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grosse-Gehling P, Fargeas CA, Dittfeld C,
Garbe Y, Alison MR, Corbeil D and Kunz-Schughart LA: CD133 as a
biomarker for putative cancer stem cells in solid tumours:
Limitations, problems and challenges. J Pathol. 229:355–378. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kohga K, Tatsumi T, Takehara T, Tsunematsu
H, Shimizu S, Yamamoto M, Sasakawa A, Miyagi T and Hayashi N:
Expression of CD133 confers malignant potential by regulating
metalloproteinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
52:872–879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, Lee TK, Wo JY, Ng IO,
Zheng BJ and Guan XY: Identification and characterization of
tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology.
132:2542–2556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan M, Li H, Zhu M, Zhao F, Zhang L, Chen
T, Jiang G, Xie H, Cui Y, Yao M, et al: G protein-coupled receptor
87 (GPR87) promotes the growth and metastasis of CD133+
cancer stem-like cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e610562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hong SW, Hur W, Choi JE, Kim JH, Hwang D
and Yoon SK: Role of ADAM17 in invasion and migration of
CD133-expressing liver cancer stem cells after irradiation.
Oncotarget. 7:23482–23497. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie Z, Choong PF, Poon LF, Zhou J, Khng J,
Jasinghe VJ, Palaniyandi S and Chen CS: Inhibition of CD44
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells enhances apoptosis,
chemosensitivity, and reduces tumorigenesis and invasion. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 62:949–957. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hamilton SR, Fard SF, Paiwand FF, Tolg C,
Veiseh M, Wang C, McCarthy JB, Bissell MJ, Koropatnick J and Turley
EA: The hyaluronan receptors CD44 and Rhamm (CD168) form complexes
with ERK1,2 that sustain high basal motility in breast cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 282:16667–16680. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fillmore C and Kuperwasser C: Human breast
cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD24: Enriching for cells with
functional properties in mice or in man? Breast Cancer Res.
9:3032007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du L, Wang H, He L, Zhang J, Ni B, Wang X,
Jin H, Cahuzac N, Mehrpour M, Lu Y, et al: CD44 is of functional
importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6751–6760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buchwalter G, Gross C and Wasylyk B: Ets
ternary complex transcription factors. Gene. 324:1–14. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ducret C, Maira SM, Lutz Y and Wasylyk B:
The ternary complex factor Net contains two distinct elements that
mediate different responses to MAP kinase signalling cascades.
Oncogene. 19:5063–5072. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giovane A, Pintzas A, Maira SM,
Sobieszczuk P and Wasylyk B: Net, a new ets transcription factor
that is activated by Ras. Genes Dev. 8:1502–1513. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buchwalter G, Gross C and Wasylyk B: The
ternary complex factor Net regulates cell migration through
inhibition of PAI-1 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 25:10853–10862.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ayadi A, Zheng H, Sobieszczuk P,
Buchwalter G, Moerman P, Alitalo K and Wasylyk B: Net-targeted
mutant mice develop a vascular phenotype and up-regulate egr-1.
EMBO J. 20:5139–5152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wasylyk C, Zheng H, Castell C, Debussche
L, Multon MC and Wasylyk B: Inhibition of the Ras-Net (Elk-3)
pathway by a novel pyrazole that affects microtubules. Cancer Res.
68:1275–1283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng H, Wasylyk C, Ayadi A, Abecassis J,
Schalken JA, Rogatsch H, Wernert N, Maira SM, Multon MC and Wasylyk
B: The transcription factor Net regulates the angiogenic switch.
Genes Dev. 17:2283–2297. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ayadi A, Suelves M, Dollé P and Wasylyk B:
Net, an Ets ternary complex transcription factor, is expressed in
sites of vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and chondrogenesis during
mouse development. Mech Dev. 102:205–208. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li TZ, Kim SM, Hur W, Choi JE, Kim JH,
Hong SW, Lee EB, Lee JH and Yoon SK: Elk-3 contributes to the
progression of liver fibrosis by regulating the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Gut Liver. Aug 19–2016.(Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.5009/gnl15566.
|
|
27
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Książkiewicz M, Markiewicz A and Zaczek
AJ: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A hallmark in metastasis
formation linking circulating tumor cells and cancer stem cells.
Pathobiology. 79:195–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gross C, Dubois-Pot H and Wasylyk B: The
ternary complex factor Net/Elk-3 participates in the
transcriptional response to hypoxia and regulates HIF-1 alpha.
Oncogene. 27:1333–1341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gross C, Buchwalter G, Dubois-Pot H, Cler
E, Zheng H and Wasylyk B: The ternary complex factor net is
downregulated by hypoxia and regulates hypoxia-responsive genes.
Mol Cell Biol. 27:4133–4141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia L, Mo P, Huang W, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhu
H, Tian D, Liu J, Chen Z, Zhang Y, et al: The
TNF-α/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes
HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Carcinogenesis.
33:2250–2259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu Z, Liu E, Peng C, Li Y, He Z, Zhao C
and Niu J: Role of hypoxia-inducible-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells using a Tet-on inducible system to regulate its expression in
vitro. Oncol Rep. 27:573–578. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Denko NC: Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose
metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:705–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo D, Wang Z and Wu J, Jiang C and Wu J:
The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:4092722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, Zeng HY
and Gao DM: Gene expression profiling of fixed tissues identified
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, VEGF, and matrix metalloproteinase-2
as biomarkers of lymph node metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:5463–5472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin D and Wu J: Hypoxia inducible factor
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:12171–12178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Choi SH, Shin HW, Park JY, Yoo JY, Kim DY,
Ro WS, Yun CO and Han KH: Effects of the knockdown of hypoxia
inducible factor-1α expression by adenovirus-mediated shRNA on
angiogenesis and tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma cell
lines. Korean J Hepatol. 16:280–287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu Z, Hao X, Yan M, Yao M, Ge C, Gu J and
Li J: Cancer stem/progenitor cells are highly enriched in
CD133+CD44+ population in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:2067–2078. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pardal R, Clarke MF and Morrison SJ:
Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:895–902. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, Lau CK, Yu WC, Ngai
P, Chu PW, Lam CT, Poon RT and Fan ST: Significance of
CD90+ cancer stem cells in human liver cancer. Cancer
Cell. 13:153–166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Salnikov AV, Kusumawidjaja G, Rausch V,
Bruns H, Gross W, Khamidjanov A, Ryschich E, Gebhard MM,
Moldenhauer G, Büchler MW, et al: Cancer stem cell marker
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases is not
sufficient as single prognostic parameter. Cancer Lett.
275:185–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu LL, Fu D, Ma Y and Shen XZ: The power
and the promise of liver cancer stem cell markers. Stem Cells Dev.
20:2023–2030. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hou Y, Zou Q, Ge R, Shen F and Wang Y: The
critical role of CD133+CD44+/high tumor cells
in hematogenous metastasis of liver cancers. Cell Res. 22:259–272.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen KL, Pan F, Jiang H, Chen JF, Pei L,
Xie FW and Liang HJ: Highly enriched
CD133+CD44+ stem-like cells with
CD133+CD44high metastatic subset in HCT116
colon cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:751–763. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Piao LS, Hur W, Kim TK, Hong SW, Kim SW,
Choi JE, Sung PS, Song MJ, Lee BC, Hwang D, et al:
CD133+ liver cancer stem cells modulate radioresistance
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 315:129–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ding Q, Miyazaki Y, Tsukasa K, Matsubara
S, Yoshimitsu M and Takao S: CD133 facilitates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through interaction with the ERK
pathway in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer. 13:152014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|