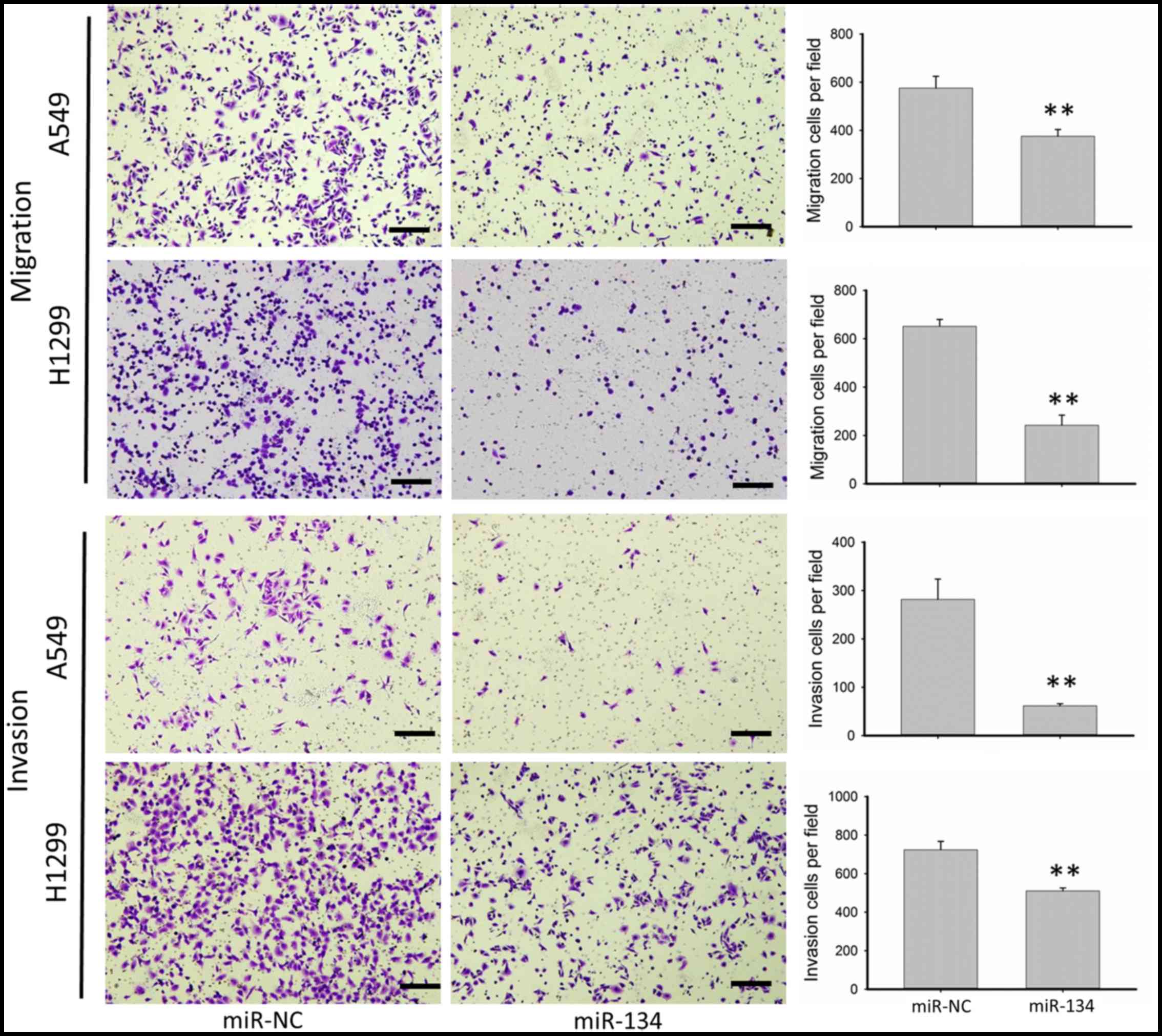
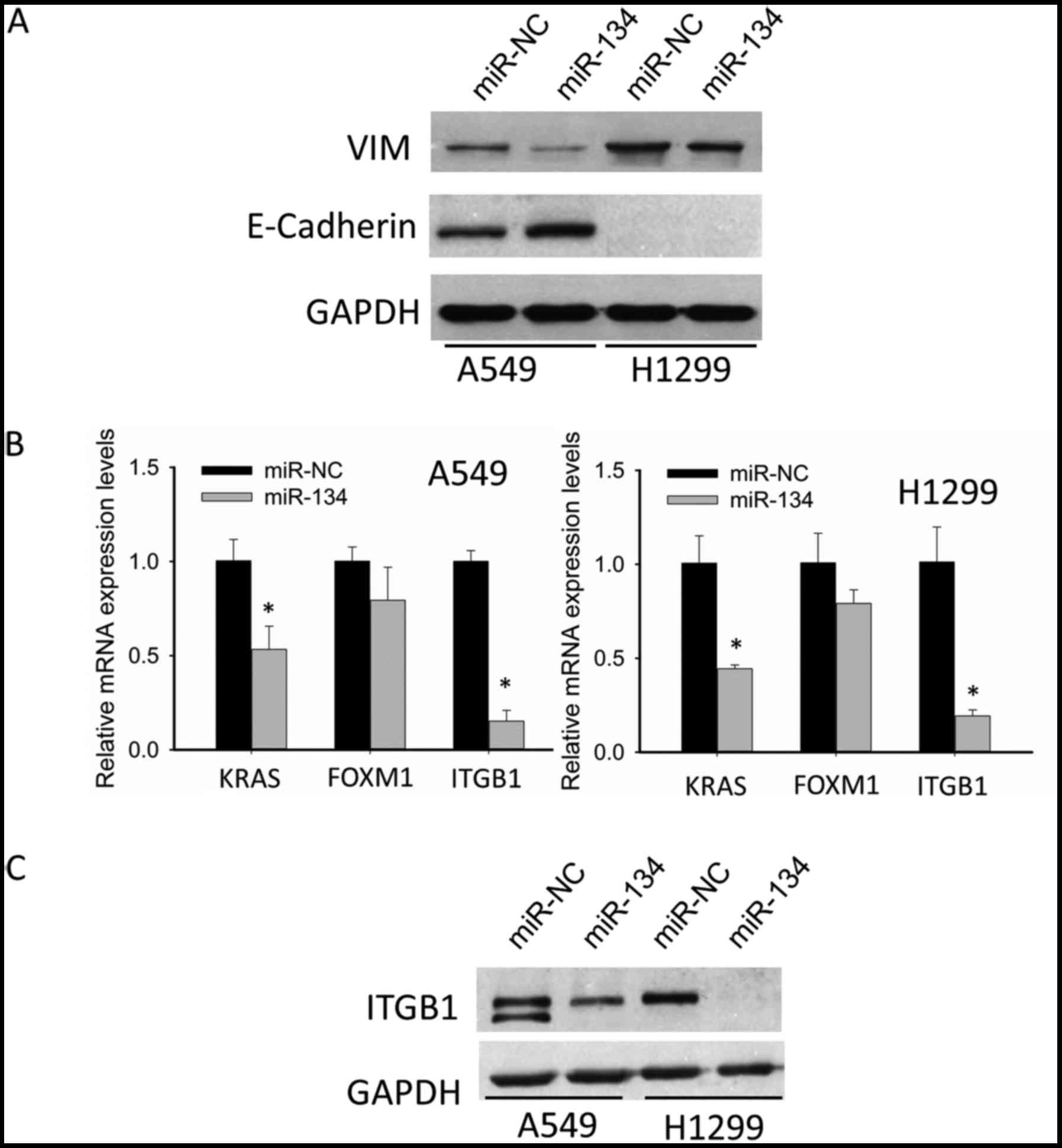
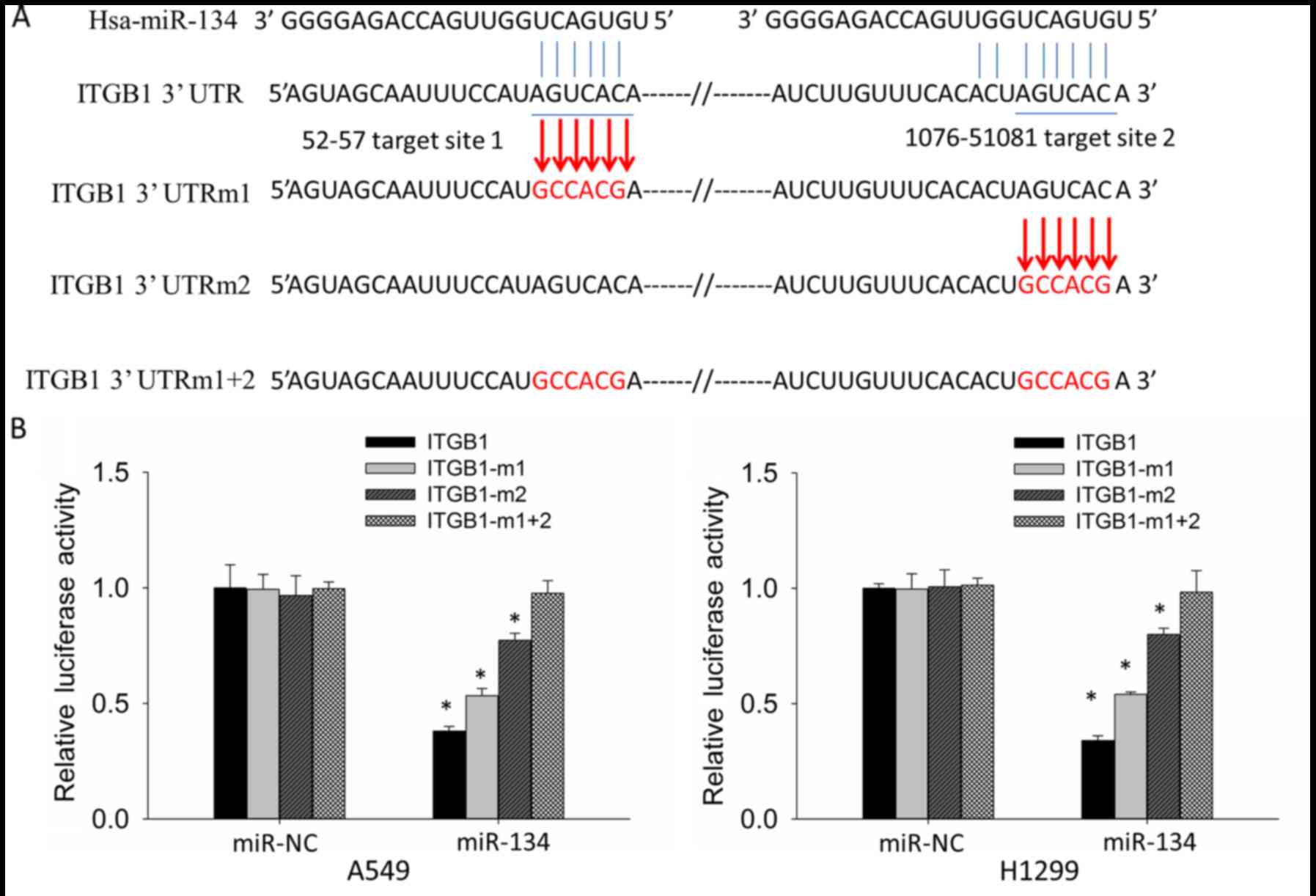
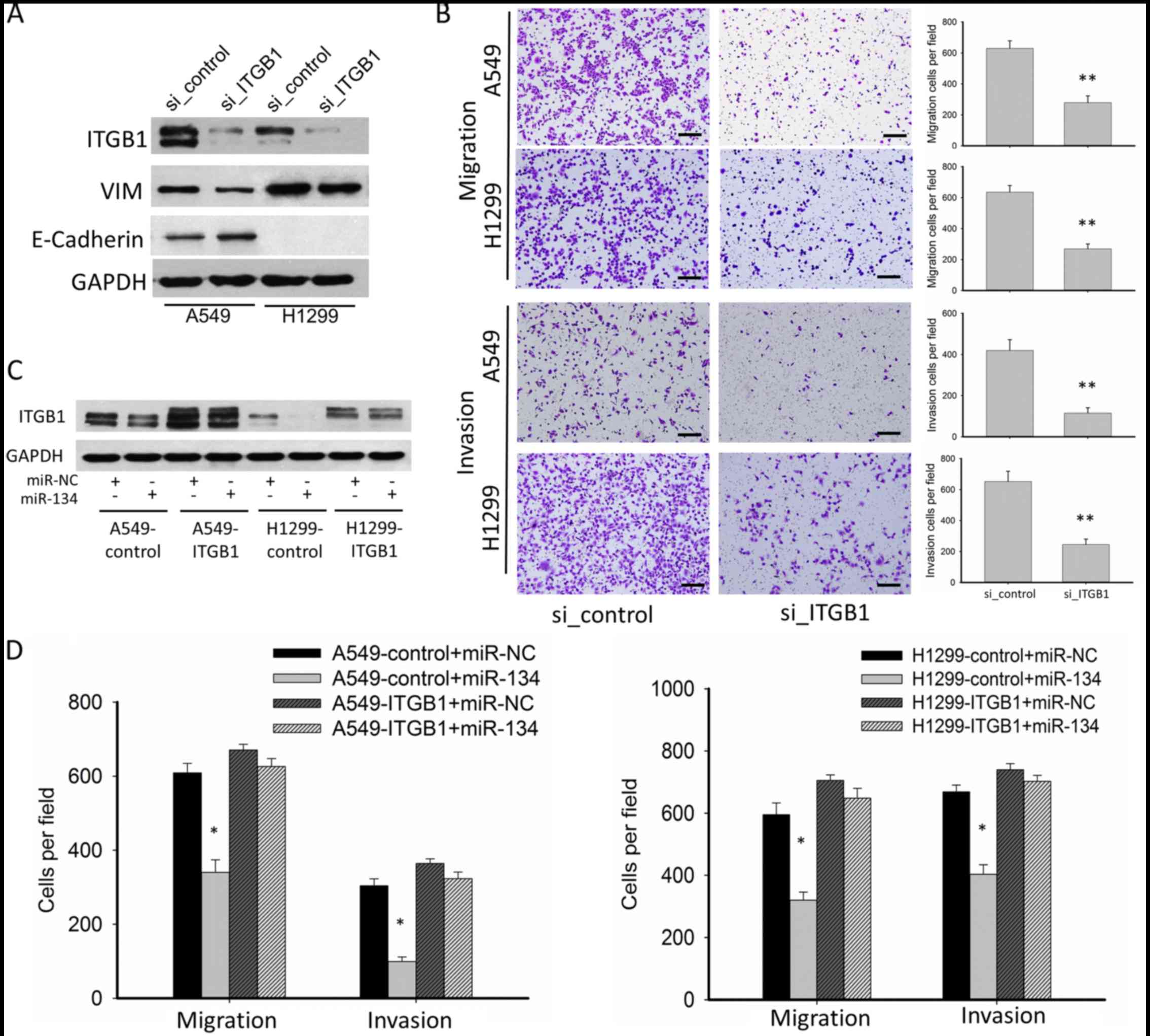
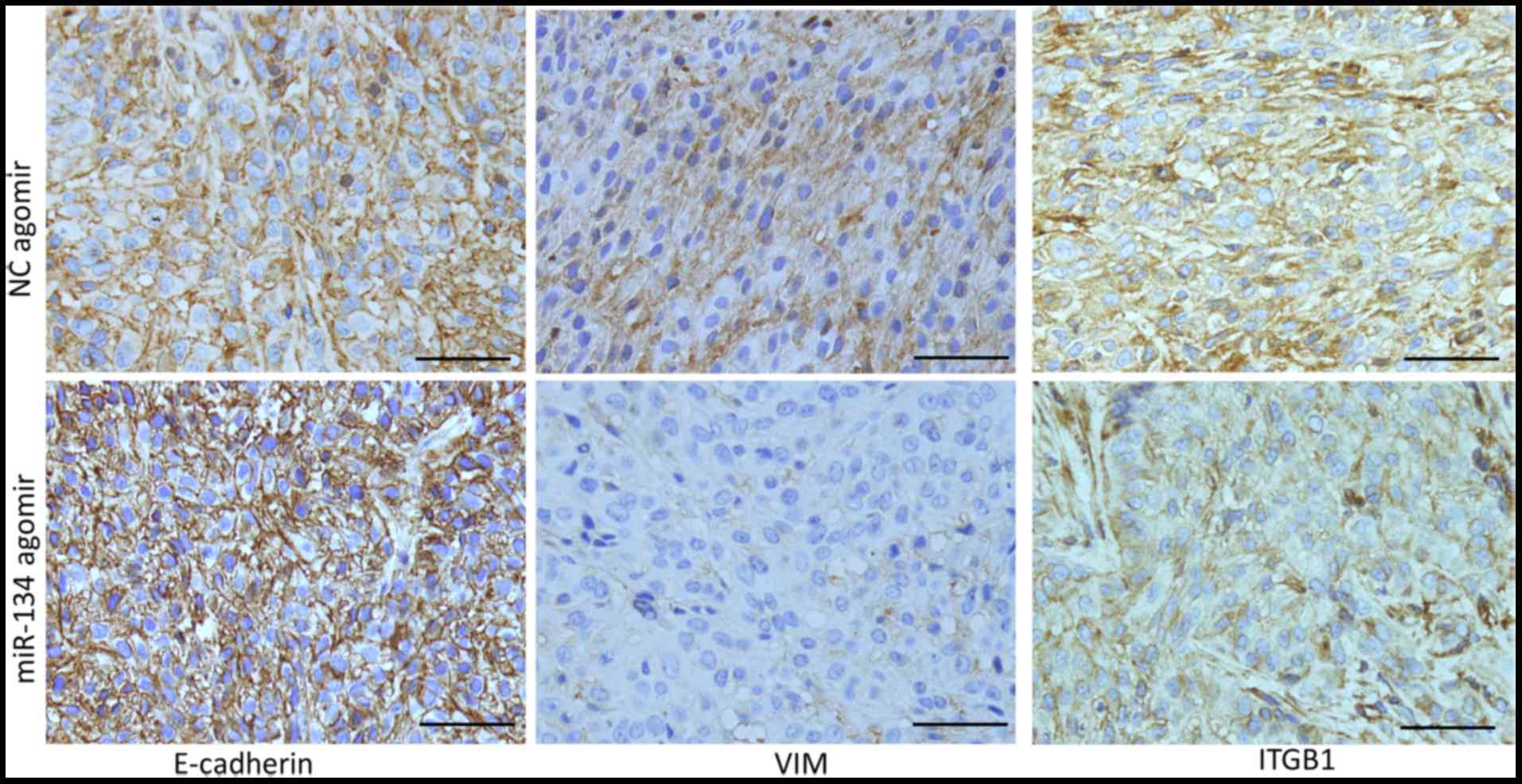
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: Epigenetics and
genetics. MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: Progress in validating
and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:849–864. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang H, Li Y and Lai M: The microRNA
network and tumor metastasis. Oncogene. 29:937–948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cui R, Meng W, Sun HL, Kim T, Ye Z, Fassan
M, Jeon YJ, Li B, Vicentini C, Peng Y, et al: MicroRNA-224 promotes
tumor progression in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:E4288–E4297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang RM, Xu JF, Fang F, Yang H and Yang
LY: MicroRNA-130b promotes proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis
via PTEN/p-AKT/HIF-1α signaling. Tumour Biol. 37:10609–10619. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG,
Sabatini ME, Kiebler M and Greenberg ME: A brain-specific microRNA
regulates dendritic spine development. Nature. 439:283–289. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Poitz DM, Stölzel F, Arabanian L,
Friedrichs J, Docheva D, Schieker M, Fierro FA, Platzbecker U,
Ordemann R, Werner C, et al: MiR-134-mediated β1 integrin
expression and function in mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1833:3396–3404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tay YM, Tam WL, Ang YS, Gaughwin PM, Yang
H, Wang W, Liu R, George J, Ng HH, Perera RJ, et al: MicroRNA-134
modulates the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells, where
it causes post-transcriptional attenuation of Nanog and LRH1. Stem
Cells. 26:17–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen T, Gao F, Feng S, Yang T and Chen M:
MicroRNA-134 regulates lung cancer cell H69 growth and apoptosis by
targeting WWOX gene and suppressing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:748–754. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kitamura K, Seike M, Okano T, Matsuda K,
Miyanaga A, Mizutani H, Noro R, Minegishi Y, Kubota K and Gemma A:
MiR-134/487b/655 cluster regulates TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance to gefitinib
by targeting MAGI2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:444–453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, Wang Y, Luo J, Fu Z, Ying J, Yu Y
and Yu W: miR-134 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by
targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
586:3761–3765. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu CJ, Shen WG, Peng SY, Cheng HW, Kao
SY, Lin SC and Chang KW: miR-134 induces oncogenicity and
metastasis in head and neck carcinoma through targeting WWOX gene.
Int J Cancer. 134:811–821. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Zhang M, Qian J, Bao M, Meng X,
Zhang S, Zhang L, Zhao R, Li S, Cao Q, et al: miR-134 functions as
a tumor suppressor in cell proliferation and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition by targeting KRAS in renal
cell carcinoma cells. DNA Cell Biol. 34:429–436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Niu CS, Yang Y and Cheng CD: MiR-134
regulates the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma cells by
reducing Nanog expression. Int J Oncol. 42:1533–1540.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yin C, Wang PQ, Xu WP, Yang Y, Zhang Q,
Ning BF, Zhang PP, Zhou WP, Xie WF, Chen WS, et al: Hepatocyte
nuclear factor-4α reverses malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma
through regulating miR-134 in the DLK1-DIO3 region. Hepatology.
58:1964–1976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zha R, Guo W, Zhang Z, Qiu Z, Wang Q, Ding
J, Huang S, Chen T, Gu J, Yao M, et al: Genome-wide screening
identified that miR-134 acts as a metastasis suppressor by
targeting integrin β1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e876652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Wang H, Zhang S, Song J, Zhang Y,
Wei X and Feng Z: MiR-134 functions as a regulator of cell
proliferation, apoptosis, and migration involving lung septation.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 48:131–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Kim J, Mueller AC, Dey B, Yang Y,
Lee DH, Hachmann J, Finderle S, Park DM, Christensen J, et al:
Multiple receptor tyrosine kinases converge on microRNA-134 to
control KRAS, STAT5B, and glioblastoma. Cell Death Differ.
21:720–734. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qin Q, Wei F, Zhang J, Wang X and Li B:
miR-134 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer growth by targeting the
epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1974–1983.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Y, Gao DY and Huang L: In vivo
delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:128–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oshita F, Kameda Y, Hamanaka N, Saito H,
Yamada K, Noda K and Mitsuda A: High expression of integrin beta1
and p53 is a greater poor prognostic factor than clinical stage in
small-cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 27:215–219. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Desgrosellier JS and Cheresh DA: Integrins
in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:9–22. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nikkola J, Vihinen P, Vlaykova T,
Hahka-Kemppinen M, Heino J and Pyrhönen S: Integrin chains beta1
and alphav as prognostic factors in human metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma Res. 14:29–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yao ES, Zhang H, Chen YY, Lee B, Chew K,
Moore D and Park C: Increased beta1 integrin is associated with
decreased survival in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res.
67:659–664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Damiano JS: Integrins as novel drug
targets for overcoming innate drug resistance. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 2:37–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cordes N, Seidler J, Durzok R, Geinitz H
and Brakebusch C: Beta1-integrin-mediated signaling essentially
contributes to cell survival after radiation-induced genotoxic
injury. Oncogene. 25:1378–1390. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park CC, Zhang HJ, Yao ES, Park CJ and
Bissell MJ: Beta1 integrin inhibition dramatically enhances
radiotherapy efficacy in human breast cancer xenografts. Cancer
Res. 68:4398–4405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang C, Park CC, Hilsenbeck SG, Ward R,
Rimawi MF, Wang YC, Shou J, Bissell MJ, Osborne CK and Schiff R: β1
integrin mediates an alternative survival pathway in breast cancer
cells resistant to lapatinib. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R842011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanda R, Kawahara A, Watari K, Murakami Y,
Sonoda K, Maeda M, Fujita H, Kage M, Uramoto H, Costa C, et al:
Erlotinib resistance in lung cancer cells mediated by integrin
β1/Src/Akt-driven bypass signaling. Cancer Res. 73:6243–6253. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jahangiri A, Aghi MK and Carbonell WS: β1
integrin: Critical path to antiangiogenic therapy resistance and
beyond. Cancer Res. 74:3–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park CC, Zhang H, Pallavicini M, Gray JW,
Baehner F, Park CJ and Bissell MJ: Beta1 integrin inhibitory
antibody induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells, inhibits growth,
and distinguishes malignant from normal phenotype in three
dimensional cultures and in vivo. Cancer Res. 66:1526–1535. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bhaskar V, Zhang D, Fox M, Seto P, Wong
MH, Wales PE, Powers D, Chao DT, Dubridge RB and Ramakrishnan V: A
function blocking anti-mouse integrin alpha5beta1 antibody inhibits
angiogenesis and impedes tumor growth in vivo. J Transl Med.
5:612007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eke I, Zscheppang K, Dickreuter E,
Hickmann L, Mazzeo E, Unger K, Krause M and Cordes N: Simultaneous
β1 integrin-EGFR targeting and radiosensitization of human head and
neck cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:dju4192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ricart AD, Tolcher AW, Liu G, Holen K,
Schwartz G, Albertini M, Weiss G, Yazji S, Ng C and Wilding G:
Volociximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody that specifically binds
α5β1 integrin: Α phase I, pharmacokinetic,
and biological correlative study. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7924–7929.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|